Human TIM-1/KIM-1/HAVCR DuoSet ELISA Summary
* Provided that the recommended microplates, buffers, diluents, substrates and solutions are used, and the assay is run as summarized in the Assay Procedure provided.
This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human T cell Immunoglobulin Mucin-1 (TIM-1). The suggested diluent is suitable for the analysis of most cell culture supernate, serum, plasma, and urine samples. Diluents for complex matrices, such as serum, plasma, and urine, should be evaluated prior to use in this DuoSet.
Product Features
- Optimized capture and detection antibody pairings with recommended concentrations save lengthy development time
- Development protocols are provided to guide further assay optimization
- Assay can be customized to your specific needs
- Economical alternative to complete kits
Kit Content
- Capture Antibody
- Detection Antibody
- Recombinant Standard
- Streptavidin conjugated to horseradish-peroxidase (Streptavidin-HRP)
Other Reagents Required
DuoSet Ancillary Reagent Kit 2 (5 plates): (Catalog # DY008) containing 96 well microplates, plate sealers, substrate solution, stop solution, plate coating buffer (PBS), wash buffer, and Reagent Diluent Concentrate 2.
The components listed above may be purchased separately:
PBS: (Catalog # DY006), or 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 8.1 mM Na2HPO4, 1.5 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.2 - 7.4, 0.2 µm filtered
Wash Buffer: (Catalog # WA126), or 0.05% Tween® 20 in PBS, pH 7.2-7.4
Reagent Diluent: (Catalog # DY995), or 1% BSA in PBS, pH 7.2-7.4, 0.2 µm filtered
Substrate Solution: 1:1 mixture of Color Reagent A (H2O2) and Color Reagent B (Tetramethylbenzidine) (Catalog # DY999)
Stop Solution: 2 N H2SO4 (Catalog # DY994)
Microplates: R&D Systems (Catalog # DY990)
Plate Sealers: ELISA Plate Sealers (Catalog # DY992)
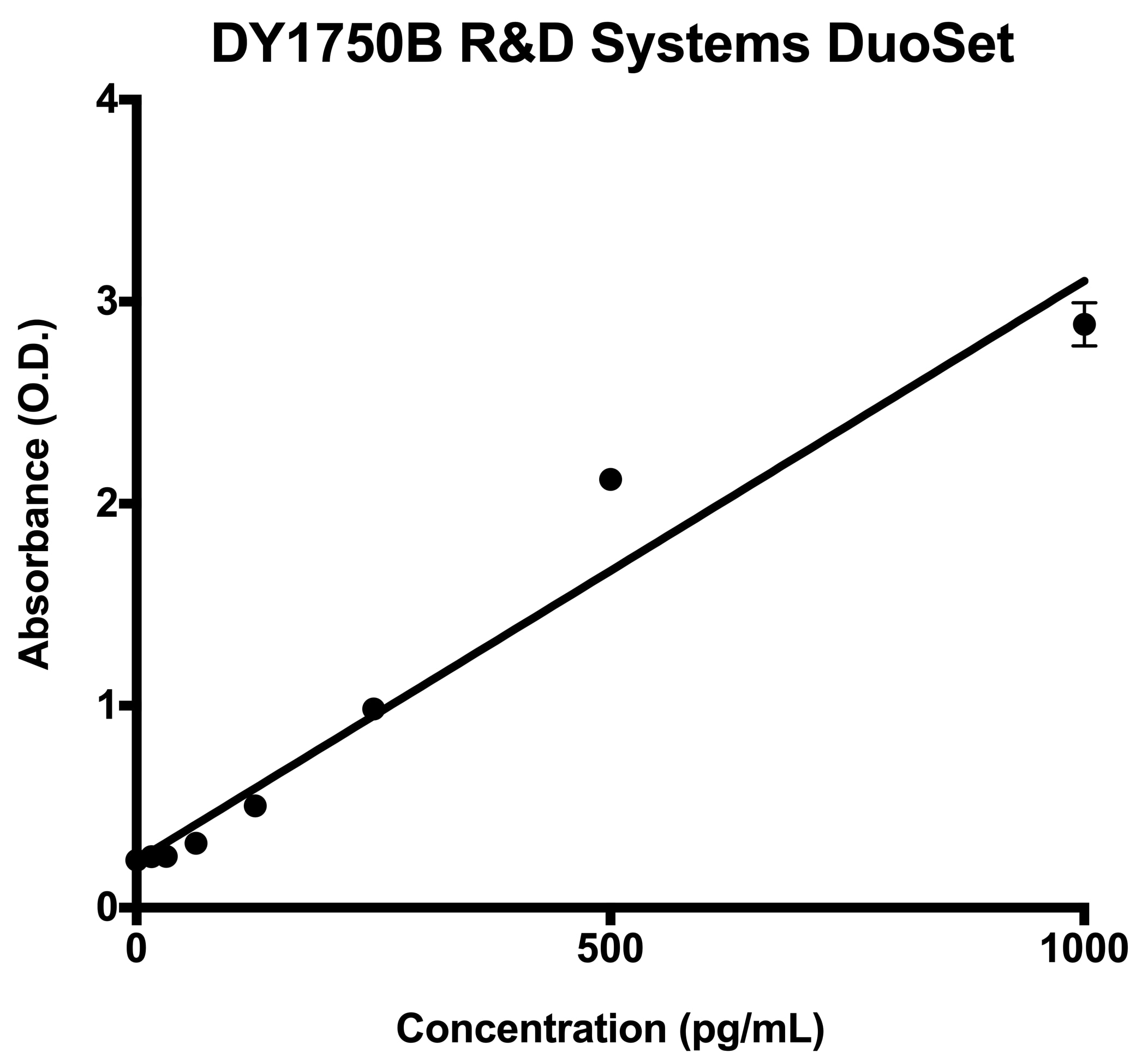
Scientific Data
Product Datasheets
Preparation and Storage
Background: TIM-1/KIM-1/HAVCR
T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 1 (TIM-1), also known as Kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1) and Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 1 (HAVcr1), is a member of the TIM family which is involved in the regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses (1, 2). TIM-1 is a type I transmembrane protein that contains an N-terminal immunoglobulin-like domain, a mucin domain with O- and N-linked glycosylations, a transmembrane segment, and a cytoplasmic signaling domain (3, 4). Multiple TIM-1 variants can be produced due to polymorphisms or alternative splicing resulting in deletions in the mucin domain (3). Some of these polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to atopy, autoimmunity, and severe hepatitis A virus infection in humans (5). Within the extracellular domain, human TIM-1 shares 41% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat TIM-1.
Assay Procedure
GENERAL ELISA PROTOCOL
Plate Preparation
- Dilute the Capture Antibody to the working concentration in PBS without carrier protein. Immediately coat a 96-well microplate with 100 μL per well of the diluted Capture Antibody. Seal the plate and incubate overnight at room temperature.
- Aspirate each well and wash with Wash Buffer, repeating the process two times for a total of three washes. Wash by filling each well with Wash Buffer (400 μL) using a squirt bottle, manifold dispenser, or autowasher. Complete removal of liquid at each step is essential for good performance. After the last wash, remove any remaining Wash Buffer by aspirating or by inverting the plate and blotting it against clean paper towels.
- Block plates by adding 300 μL Reagent Diluent to each well. Incubate at room temperature for a minimum of 1 hour.
- Repeat the aspiration/wash as in step 2. The plates are now ready for sample addition.
Assay Procedure
- Add 100 μL of sample or standards in Reagent Diluent, or an appropriate diluent, per well. Cover with an adhesive strip and incubate 2 hours at room temperature.
- Repeat the aspiration/wash as in step 2 of Plate Preparation.
- Add 100 μL of the Detection Antibody, diluted in Reagent Diluent, to each well. Cover with a new adhesive strip and incubate 2 hours at room temperature.
- Repeat the aspiration/wash as in step 2 of Plate Preparation.
- Add 100 μL of the working dilution of Streptavidin-HRP to each well. Cover the plate and incubate for 20 minutes at room temperature. Avoid placing the plate in direct light.
- Repeat the aspiration/wash as in step 2.
- Add 100 μL of Substrate Solution to each well. Incubate for 20 minutes at room temperature. Avoid placing the plate in direct light.
- Add 50 μL of Stop Solution to each well. Gently tap the plate to ensure thorough mixing.
- Determine the optical density of each well immediately, using a microplate reader set to 450 nm. If wavelength correction is available, set to 540 nm or 570 nm. If wavelength correction is not available, subtract readings at 540 nm or 570 nm from the readings at 450 nm. This subtraction will correct for optical imperfections in the plate. Readings made directly at 450 nm without correction may be higher and less accurate.
Citations for Human TIM-1/KIM-1/HAVCR DuoSet ELISA
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
19
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
The Human Phospholipase B-II Precursor (HPLBII-P) in Urine as a Novel Biomarker of Glomerular Activity in COVID-19 and Diabetes Mellitus
Authors: Xu, S;Hultström, M;Larsson, A;Lipcsey, M;Lindskog, C;Bülow, S;Frithiof, R;Venge, P;
Journal of clinical medicine
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Potential Utility of Urinary Follistatin as a Non-Invasive Indicator of Acute Tubular Damage in Patients with Acute Kidney Injury
Authors: Nagayama, I;Takayanagi, K;Nagata, D;Hasegawa, H;Maeshima, A;
Cells
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Impact of microgravity on a three-dimensional microphysiologic culture of the human kidney proximal tubule epithelium: cell response to serum and vitamin D
Authors: Kelly, E;Lindberg, K;Jones-Isaac, K;Yang, J;Bain, J;Wang, L;MacDonald, J;Bammler, T;Calamia, J;Thummel, K;Yeung, C;Countryman, S;Koenig, P;Himmelfarb, J;
Research square
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
No impact of a high-fat meal coupled with intermittent hypoxemia on acute kidney injury biomarkers in adults with and without obstructive sleep apnea
Authors: Goulet, N;Tetzlaff, EJ;Morin, R;Mauger, JF;Amaratunga, R;Kenny, GP;Imbeault, P;
Physiological reports
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Combining renal cell arrest and damage biomarkers to predict progressive AKI in patient with sepsis
Authors: X Tao, C Chen, W Luo, J Zhou, J Tian, X Yang, FF Hou
Bmc Nephrology, 2021-12-15;22(1):415.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Serum and urinary biomarkers for early detection of acute kidney injury following Hypnale spp. envenoming
Authors: ES Wijewickra, F Mohamed, IB Gawaramman, ZH Endre, NA Buckley, GK Isbister
PloS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2021-12-06;15(12):e0010011.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Urinary cytokines correlate with acute kidney injury in critically ill COVID-19 patients
Authors: A Gradin, H Andersson, T Luther, SB Anderberg, S Rubertsson, M Lipcsey, M Åberg, A Larsson, R Frithiof, M Hultström
Cytokine, 2021-05-24;146(0):155589.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Successful Urine Multiplex Bead Assay to Measure Lupus Nephritis Activity
Authors: EM Cody, MR Bennett, G Gulati, Q Ma, M Altaye, P Devarajan, HI Brunner
Kidney international reports, 2021-04-28;6(7):1949-1960.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Antisense oligonucleotide development for the selective modulation of CYP3A5 in renal disease
Authors: KA Lidberg, AJ Annalora, M Jozic, DJ Elson, L Wang, TK Bammler, S Ramm, MB Monteiro, J Himmelfarb, CB Marcus, PL Iversen, EJ Kelly
Scientific Reports, 2021-02-25;11(1):4722.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Early identification of acute kidney injury in Russell's viper (Daboia russelii) envenoming using renal biomarkers
Authors: I Ratnayake, F Mohamed, NA Buckley, IB Gawaramman, DM Dissanayak, U Chathurang, M Munasinghe, K Maduwage, S Jayamanne, ZH Endre, GK Isbister
PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2019-07-01;13(7):e0007486.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Acute Kidney Injury Biomarkers Predict an Increase in Serum Milrinone Concentration Earlier Than Serum Creatinine-Defined Acute Kidney Injury in Infants After Cardiac Surgery
Authors: KM Gist, DS Cooper, J Wrona, S Faubel, C Altmann, Z Gao, BS Marino, J Alten, KM Hock, T Mizuno, AA Vinks, MS Joy, MF Wempe, MR Bennett, SL Goldstein
Ther Drug Monit, 2018-04-01;40(2):186-194.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Propofol-based anaesthesia versus sevoflurane-based anaesthesia for living donor kidney transplantation: results of the VAPOR-1 randomized controlled trial
Authors: GJ Nieuwenhui, VB Nieuwenhui, MAJ Seelen, SP Berger, MC van den He, JGM Burgerhof, PJ Ottens, RJ Ploeg, HGD Leuvenink, MMRF Struys
Br J Anaesth, 2017-05-01;118(5):720-732.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Dexamethasone Modifies Cystatin C-Based Diagnosis of Acute Kidney Injury During Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy
Authors: TJ Pianta, JW Pickering, L Succar, M Chin, T Davidson, NA Buckley, F Mohamed, ZH Endre
Kidney Blood Press. Res, 2017-03-17;42(1):62-75.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Expression of Tim-1 in primary CNS lymphoma
Cancer Med, 2016-10-05;5(11):3235-3245.
Species: Human
Sample Types: CSF
-
Urinary adiponectin is an independent predictor of progression to end-stage renal disease in patients with type 1 diabetes and diabetic nephropathy.
Authors: Panduru N, Saraheimo M, Forsblom C, Thorn L, Gordin D, Waden J, Tolonen N, Bierhaus A, Humpert P, Groop P
Diabetes Care, 2015-02-26;38(5):883-90.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Assessment of Worldwide Acute Kidney Injury, Renal Angina and Epidemiology in critically ill children (AWARE): study protocol for a prospective observational study.
Authors: Basu R, Kaddourah A, Terrell T, Mottes T, Arnold P, Jacobs J, Andringa J, Goldstein S
BMC Nephrol, 2015-02-26;16(0):24.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Soluble TNF receptors and kidney dysfunction in the elderly.
Authors: Carlsson A, Larsson T, Helmersson-Karlqvist J, Larsson A, Lind L, Arnlov J
J Am Soc Nephrol, 2014-02-07;25(6):1313-20.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Urinary L-FABP and anaemia: distinct roles of urinary markers in type 2 diabetes.
Authors: von Eynatten M, Baumann M, Heemann U
Eur. J. Clin. Invest., 2009-11-11;40(2):95-102.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Assay validation for KIM-1: human urinary renal dysfunction biomarker.
Authors: Chaturvedi S, Farmer T, Kapke GF
Int. J. Biol. Sci., 2009-01-19;5(2):128-34.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all ELISA FAQsReviews for Human TIM-1/KIM-1/HAVCR DuoSet ELISA
Average Rating: 3.5 (Based on 2 Reviews)
Have you used Human TIM-1/KIM-1/HAVCR DuoSet ELISA?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
The only reason I didn't give the kit 5 stars is because we had a few technical issues with it that took some troubleshooting time to work out, but RnD Systems was very prompt in helping us resolve it and even sent a new kit after we found the problem.