Human/Mouse Angiopoietin-2 Antibody Summary
Asp68-Phe496
Accession # O15123
Applications
Human Angiopoietin-2 Sandwich Immunoassay
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Angiopoietin‑2 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tissue. Angiopoietin-2 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human hepatocellular carcinoma tissue (right panel; positive stain) using Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse Angiopoietin-2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB098) at 5 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC001). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to secreted and plasma membrane. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
 View Larger
View Larger
Angiopoietin-2 in Mouse Lymph Node Tissue. Angiopoietin-2 was detected in perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse lymph node tissue using Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse Angiopoietin-2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB098) at 1 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (brown; Catalog # VC001) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell membrane. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
 View Larger
View Larger
Angiopoietin-2 in Mouse Colon Tissue. Angiopoietin-2 was detected in perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse colon tissue using Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse Angiopoietin-2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB098) at 1 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (brown; Catalog # VC001) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to lymphocytes in colon mucosa. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Angiopoietin-2
Angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2; also ANGPT2) is a secreted glycoprotein that plays a complex role in angiogenesis and inflammation (1, 2). Mature Ang-2 is 478 amino acids (aa) in length. It contains one coiled-coil domain (aa 166 - 248) that mediates multimerization, and a C-terminal fibrinogen-like domain (aa 275 - 495) that mediates receptor binding. Under reducing conditions, secreted monomeric Ang-2 is 65 - 66 kDa in size. Under nonreducing conditions, both natural and recombinant Ang-2 form 140 kDa dimers, 200 kDa trimers, and 250 - 300 kDa tetramers and pentamers (3 - 6). Alternate splicing generates a short isoform that lacks 52 amino acids (aa) preceding the coiled-coil domain (4). Mature human Ang-2 shares 86% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat Ang-2. Ang-2 is widely expressed during development, but it is restricted postnatally to highly angiogenic tissues such as the placenta, ovaries, and uterus (3). It is particularly abundant in vascular endothelial cells (EC) where it is stored in intracellular Weibel-Palade bodies (1, 3, 7). Both Ang-2 and the related Angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1) are ligands for the receptor tyrosine kinase Tie-2 (2). While Ang-1 is a potent Tie-2 agonist, Ang-2 may act as either a Tie-2 antagonist or agonist, depending upon its state of multimerization. The higher the order of oligomer, the more effective Ang-2 becomes as a Tie-2 agonist (3, 8 - 11). The short isoform appears to block the binding of either Ang-1 or full-length Ang-2 to Tie-2 (4). Ang-2 functions as a pro-angiogenic factor, although it can also induce EC death and vessel regression (12, 13). Upon its release from quiescent EC, it regulates vascular remodeling by promoting EC survival, proliferation, and migration and destabilizing the interaction between EC and perivascular cells (8, 13, 14). Ang-2 is required for postnatal vascular remodeling, and it cooperates with Ang-1 during lymphatic vessel development (7, 15). It mediates the upregulation of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 on EC, which facilitates the adhesion of leukocytes during inflammation (16). Ang-2 is upregulated in both the endothelium and tumor cells of several cancers as well as in ischemic tissue (17 - 20). Its direct interaction with Integrins promotes tumor cell invasion (21, 22). Ang-2 also promotes the neuronal differentiation and migration of subventricular zone progenitor cells (20).
- Augustin, H.G. et al. (2009) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10:165.
- Murdoch, C. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 178:7405.
- Maisonpierre, P.C. et al. (1997) Science 27:55.
- Kim, I. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:18550.
- Procopio, W.N. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:30196.
- Kim, K-T. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:20126.
- Gale, N.W. et al. (2002) Dev. Cell 3:411.
- Yuan, H.T. et al. (2009) Mol. Cell. Biol. 29:2011.
- Falcon, B.L. et al. (2009) Am. J. Pathol. 175:2159.
- Kim, H-Z. et al. (2009) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1793:772.
- Kim, I. et al. (2001) Cardiovasc. Res. 49:872.
- Lobov, I.B. et al. (2002) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99:11205.
- Cao, Y. et al. (2007) Cancer Res. 67:3835.
- Nasarre, P. et al. (2009) Cancer Res. 69:1324.
- Dellinger, M. et al. (2008) Dev. Biol. 319:309.
- Fiedler, U. et al. (2006) Nat. Med. 12:235.
- Koga, K. et al. (2001) Cancer Res. 61:6248.
- Etoh, T. et al. (2001) Cancer Res. 61:2145.
- Tressel, S.L. et al. (2008) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28:1989.
- Liu, X.S. et al. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284:22680.
- Hu, B. et al. (2006) Cancer Res. 66:775.
- Imanishi, Y. et al. (2007) Cancer Res. 67:4254.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human/Mouse Angiopoietin-2 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
6
Citations: Showing 1 - 6
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Sirt3 deficiency promotes endothelial dysfunction and aggravates renal injury
Authors: Pezzotta, A;Perico, L;Corna, D;Morigi, M;Remuzzi, G;Benigni, A;Imberti, B;
PloS one
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Caveolae-mediated Tie2 signaling contributes to CCM pathogenesis in a brain endothelial cell-specific Pdcd10-deficient mouse model
Authors: HJ Zhou, L Qin, Q Jiang, KN Murray, H Zhang, B Li, Q Lin, M Graham, X Liu, J Grutzendle, W Min
Nature Communications, 2021-01-25;12(1):504.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
Applications: ELISA Capture -
Predictive Value of Clinical Findings and Plasma Biomarkers after Fourteen Days of Prednisone Treatment for Acute Graft-versus-host Disease.
Authors: McDonald G, Tabellini L, Storer B, Martin P, Lawler R, Rosinski S, Schoch H, Hansen J
Biol Blood Marrow Transplant, 2017-05-03;23(8):1257-1263.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Endothelial exocytosis of angiopoietin-2 resulting from CCM3 deficiency contributes to cerebral cavernous malformation.
Authors: Jenny Zhou H, Qin L, Zhang H, Tang W, Ji W, He Y, Liang X, Wang Z, Yuan Q, Vortmeyer A, Toomre D, Fuh G, Yan M, Kluger M, Wu D, Min W
Nat Med, 2016-08-22;22(9):1033-1042.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded interleukin-6 and G-protein-coupled receptor regulate angiopoietin-2 expression in lymphatic endothelial cells.
Authors: Vart RJ, Nikitenko LL, Lagos D, Trotter MW, Cannon M, Bourboulia D, Gratrix F, Takeuchi Y, Boshoff C
Cancer Res., 2007-05-01;67(9):4042-51.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: ICC, IHC-P -
Hyperoxia causes angiopoietin 2-mediated acute lung injury and necrotic cell death.
Authors: Bhandari V, Choo-Wing R, Lee CG, Zhu Z, Nedrelow JH, Chupp GL, Zhang X, Matthay MA, Ware LB, Homer RJ, Lee PJ, Geick A, de Fougerolles AR, Elias JA
Nat. Med., 2006-11-05;12(11):1286-93.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human/Mouse Angiopoietin-2 Antibody
Average Rating: 4.3 (Based on 6 Reviews)
Have you used Human/Mouse Angiopoietin-2 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
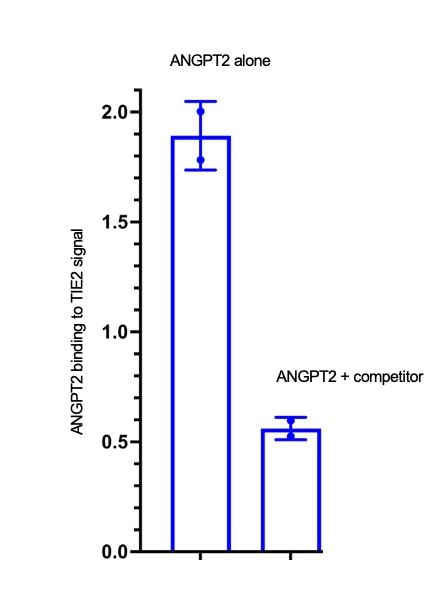
I used the antibody to do ELISA,by checking how my compound competes with 623-AN binding to TIE2. It works well, though I prefer AF623.
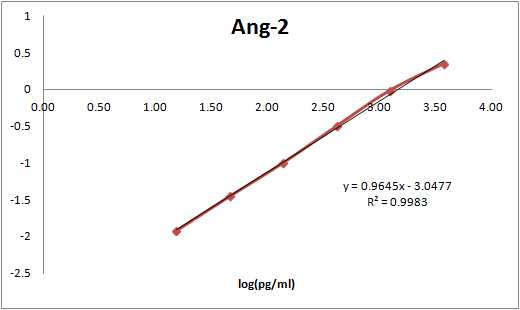
After biotinylation, used as a capture reagent according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Meso Scale Diagnostics LLC). Paired with SulfoTag-modified MAB0984 as a detection antibody. Calibration curve with Recombinant Human Angiopoietin (623-AN-025/CF) is shown (dynamic range 16-250,000 pg/ml).