FGF Family Signaling Pathways
Click on one of the FGF subfamilies shown in the Explore Pathways box below to see additional information about the FGF ligands belonging to each subfamily. Refer to the table below the pathway to see the reported receptor binding specificities for the different FGF ligands, their physiological functions, and the pathologies associated with mutations or amplification of different FGFs.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Degradation
Degradation
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Phosphatase
Phosphatase
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Differentiation
Differentiation
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Factor
Factor
Factor
Factor
Factor
Factor
Inhibitors
Inhibitors
| • FGF-1 subfamily members: FGF-1 and FGF-2. |
| • Both lack a classical secretory signal peptide and are secreted independently of the traditional ER-Golgi secretory pathway. |
| • Utilize heparin/HS as a co-factor to bind to FGF receptors. |
| • FGF-1 and FGF-2 are found in the nucleus of some cells. |
| • See the table below the pathway for additional information on the FGF-1 subfamily members including their suggested physiological functions and reported receptor binding specificities. |
| • FGF-4 subfamily members: FGF-4, FGF-5, and FGF-6. |
| • Have a cleavable N-terminal signal peptide. |
| • Utilize heparin/HS as a co-factor to bind to FGF receptors. |
| • See the table below the pathway for additional information on the FGF-4 subfamily members including their suggested physiological functions and reported receptor binding specificities. |
| • FGF-7 subfamily members: FGF-3, FGF-7, FGF-10, and FGF-22. |
| • Utilize heparin/HS as a co-factor to bind to FGF receptors. |
| • See the table below the pathway for additional information on the FGF-7 subfamily members including their suggested physiological functions and reported receptor binding specificities. |
| • FGF-8 subfamily members: FGF-8, FGF-17, and FGF-18. |
| • Have a cleavable N-terminal signal peptide. |
| • Utilize heparin/HS as a co-factor to bind to FGF receptors. |
| • Alternative splicing of FGF8 gives rise to four potential isoforms in human (FGF-8a, FGF-8b, FGF-8e, FGF-8f) and eight in mouse (FGF-8a-h). |
| • See the table below the pathway for additional information on the FGF-8 subfamily members including their suggested physiological functions and reported receptor binding specificities. |
| • FGF-9 subfamily members: FGF-9, FGF-16, and FGF-20. |
| • Lack a classical N-terminal signal peptide, but have an internal hydrophobic sequence that functions as a signal for their transport into the ER and secretion. |
| • Utilize heparin/HS as a co-factor to bind to FGF receptors. |
| • See the table below the pathway for additional information on the FGF-9 subfamily members including their suggested physiological functions and reported receptor binding specificities. |
| • FGF-11 subfamily members: FGF-11, FGF-12, FGF-13, and FGF-14. |
| • Also known as FGF homologous factors (FHFs), FGF-11 subfamily members have high sequence identity and structural homology with the FGF family, but are not secreted and do not activate FGF receptors. |
| • As intracellular FGFs, FGF-11 subfamily members interact with the cytosolic carboxy-terminal tail of voltage-gated sodium channels. |
| • See the table below the pathway for additional information on the FGF-11 subfamily members including their suggested physiological functions and reported receptor binding specificities. |
| • FGF-19 subfamily members: FGF-19 (human)/FGF-15 (mouse), FGF-21, and FGF-23. |
| • Bind to heparin/HS with very low affinity, facilitating their release from the ECM and their function as endocrine factors. |
| • Require Klotho proteins as co-factors to bind to FGF receptors. |
| • FGF-15 is the mouse orthologue of human FGF-19. |
| • See the table below the pathway for additional information on the FGF-19 subfamily members including their suggested physiological functions and reported receptor binding specificities. |
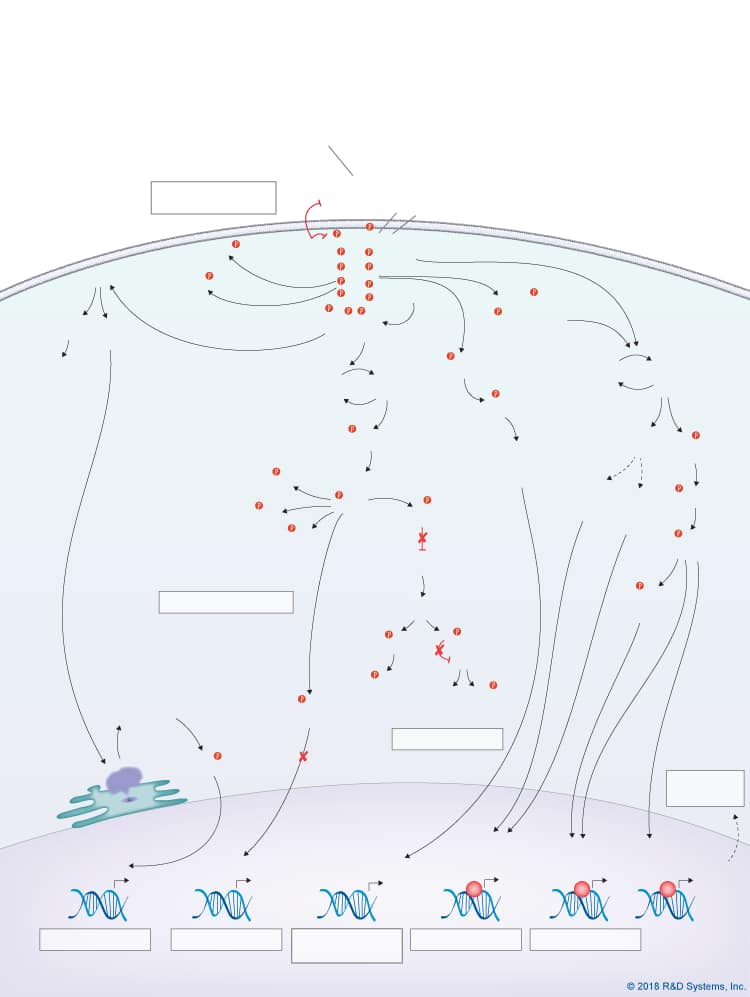
Overview of Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) Family Signaling Pathways
Overview of Chemokine Superfamily: Human/Mouse Ligand-Receptor Interactions
Chemokines are small cell surface-localized or secreted chemotactic cytokines that bind to and activate specific G protein-coupled chemokine receptors. Most chemokines have at least four conserved N-terminal cysteine residues that form two intramolecular disulfide bonds. Four chemokine subfamilies (CXC, CC, C, and CX3C) have been defined based upon the placement of the first two cysteine residues. The CXC chemokine subfamily is characterized by two cysteine residues separated by one amino acid. Within this subfamily, two CXC classes are further defined by the presence or absence of an ELR motif sequence. ELR- CXC chemokines act as chemoattractants for lymphocytes, while ELR+ CXC chemokines are chemoattractants for neutrophils. Additionally, CXC chemokines can mediate angiogenesis. The CC chemokine subfamily is defined by two adjacent cysteine residues. CC chemokines induce inflammatory responses via regulation of monocyte, macrophage, mast cell, and T cell migration. C chemokines are characterized by a single cysteine residue and are constitutively expressed in the thymus where they regulate T cell differentiation. The CX3C chemokine subfamily is defined by two cysteine residues separated by three amino acids. Cell surface-localized CX3CL1/Fractalkine mediates leukocyte adhesion, while soluble CX3CL1/Fractalkine is chemotactic for leukocytes. CX3CL1/Fractalkine is also a critical regulator of microglia-neuron communication during neural development.
While chemokine receptors generally bind only one subfamily of chemokines, within those subfamilies, most chemokines display promiscuous receptor binding patterns. The redundancy of chemokine ligand-receptor binding may ensure robust signaling. In addition, promiscuous binding and non-signaling chemokine receptors offer mechanisms by which chemokine signaling can be regulated by either subtle differences in receptor signaling or differences in ligand-receptor expression patterns. Select chemokine ligands and receptors are implicated in HIV infection and persistence, while aberrant chemokine expression and signaling is associated with pathological conditions including inflammatory diseases and cancer.
To learn more, please visit our Chemokines and Receptors Research Area.

