VEGF - VEGF R2 Signaling Pathways
Click on one of the biological effects of VEGF-VEGF R2 signaling shown in the Explore Pathways box below to see the specific molecules involved in promoting each effect and the phosphorylation sites on VEGF R2 that are necessary for recruitment of key downstream adaptor proteins or kinases.
alphaV beta3
alphaV beta3
Oxidase
Oxidase
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Permeability
Permeability
and Cell Migration
and Cell Migration
and Cell Migration
and Cell Migration
and Cell Migration
and Cell Migration
Permeability
Permeability
and Proliferation
and Proliferation
Permeability
Permeability
Phosphorylation Site
is required for downstream
kinase activity.
Phosphorylation Site
is required for downstream kinase
activity.
VEGF-induced Cell Proliferation
Required for VEGF-induced
Cell Survival
VEGF-induced Vascular Permeability
Required for VEGF-induced
Cell Migration
Required for VEGF-induced
Cell Adhesion
NRP-2
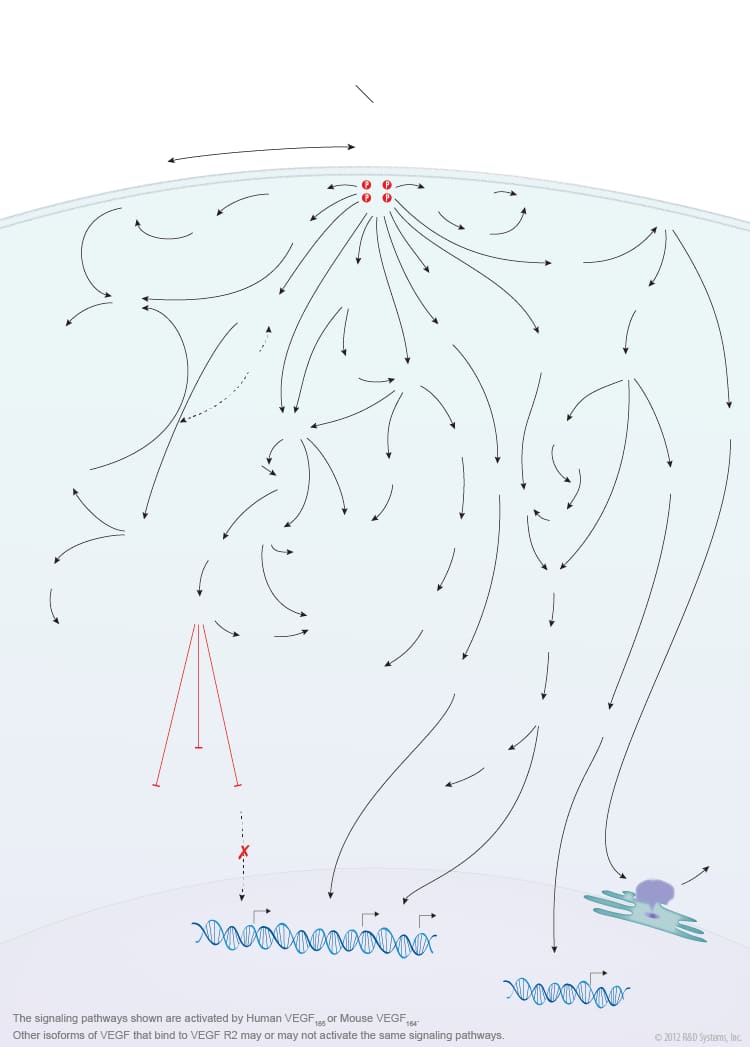
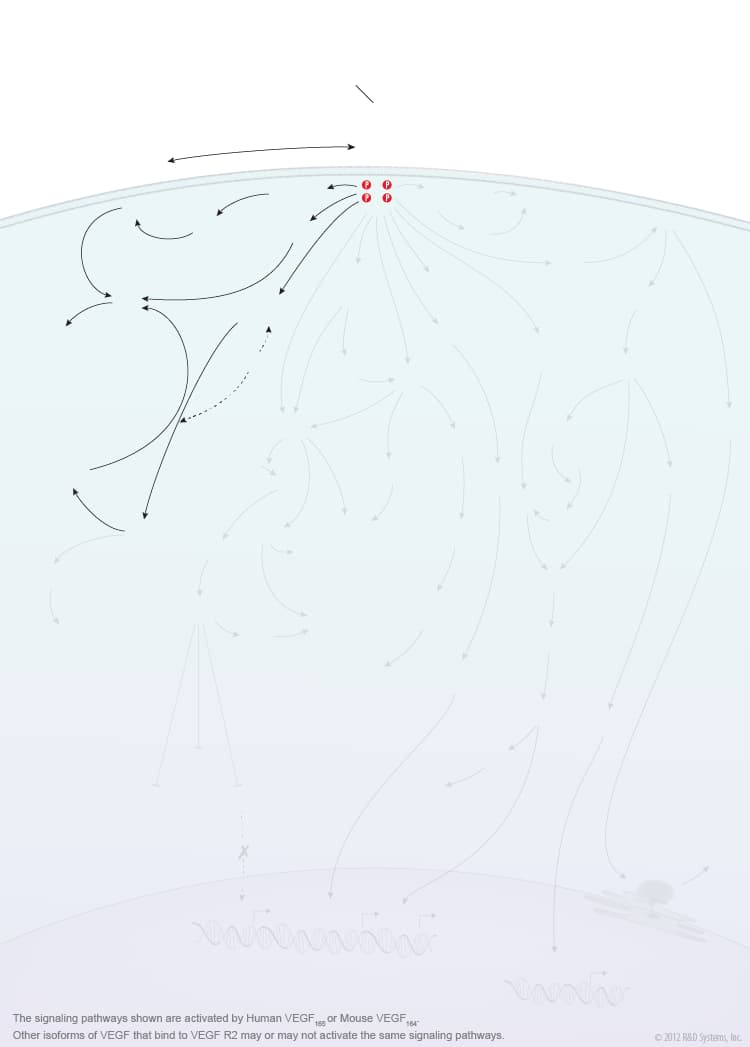
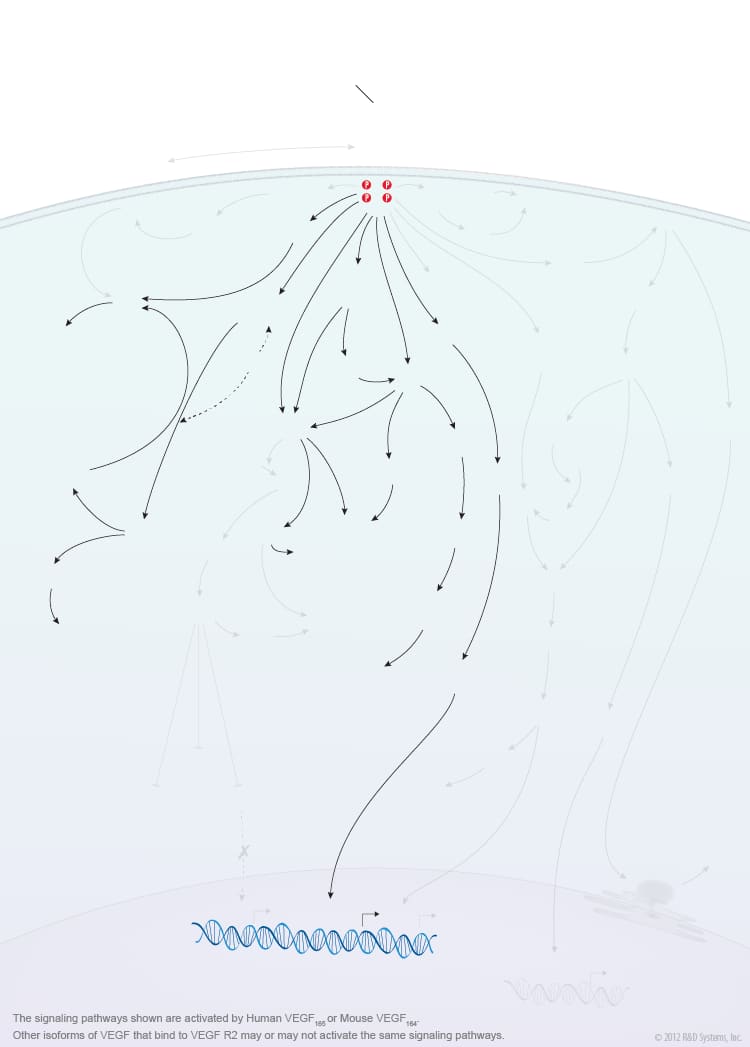
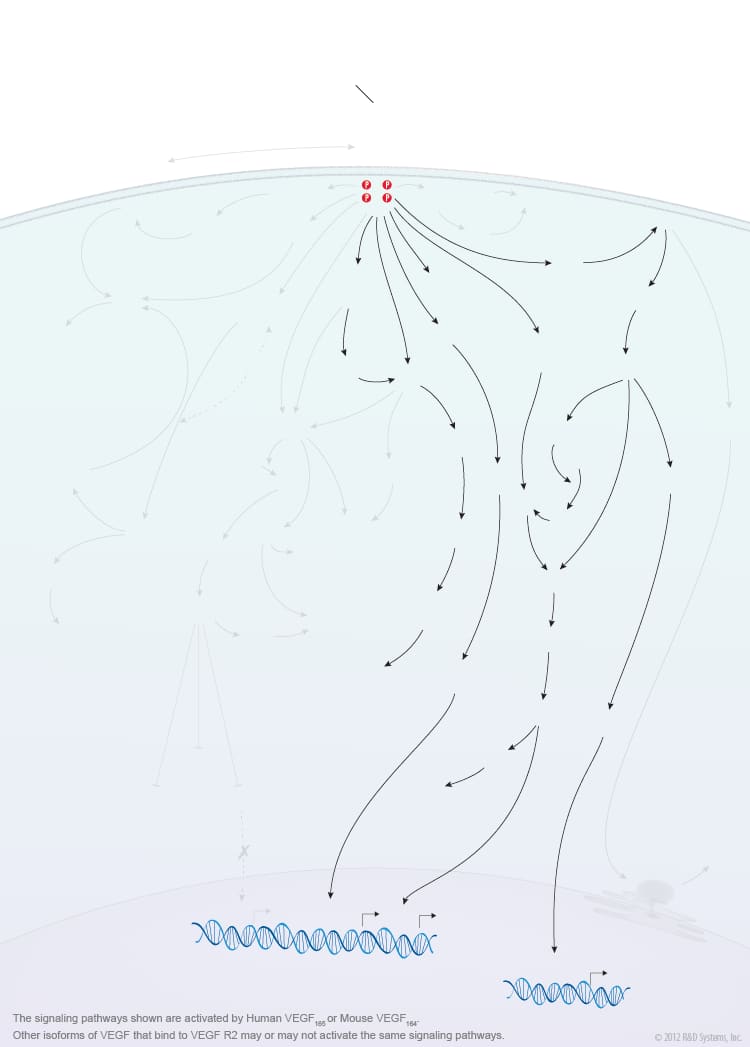
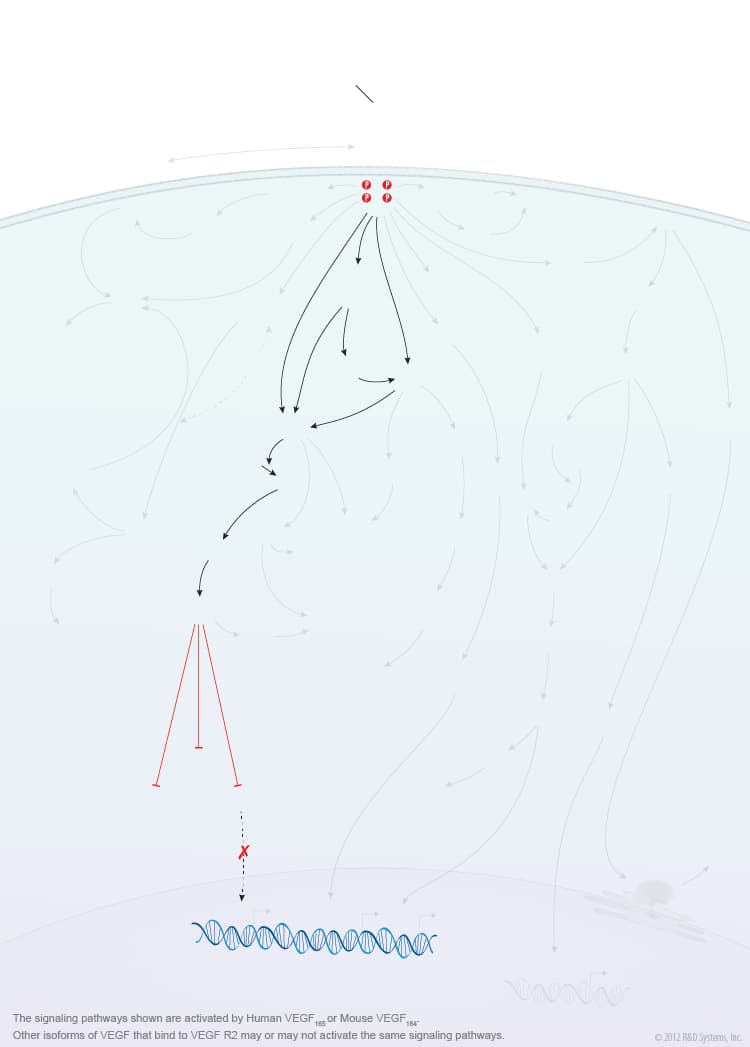
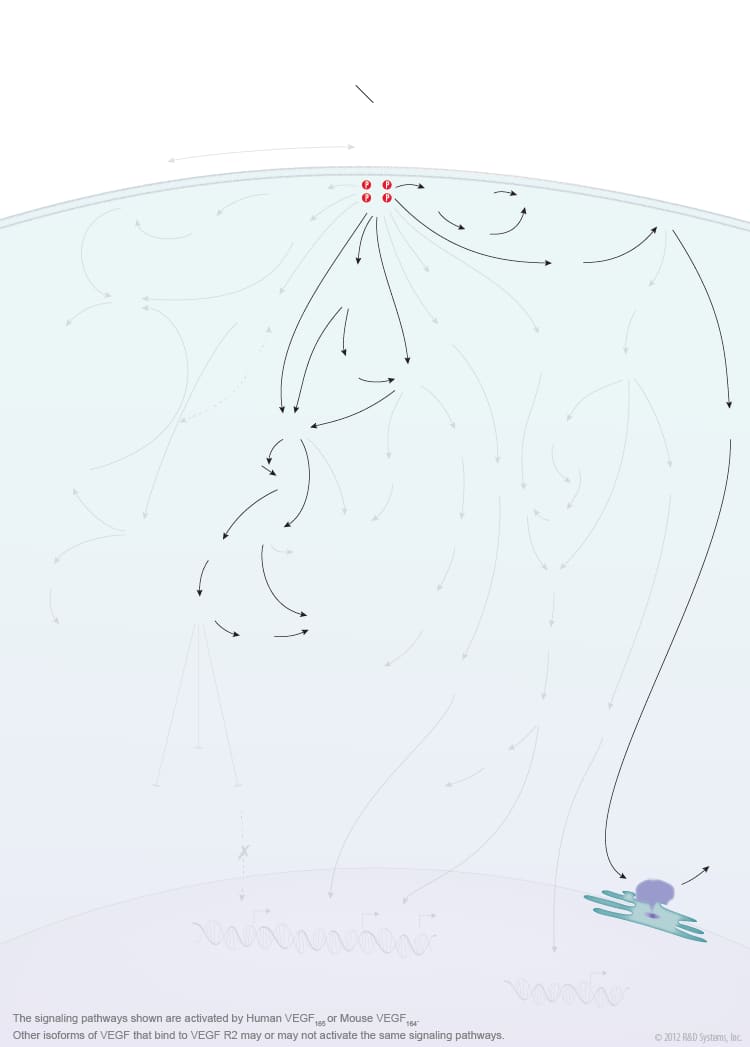
Overview of VEGF-VEGF R2 Signaling
Members of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family are master regulators of physiological and pathological vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and lymphangiogenesis. The VEGF family consists of six members VEGF-A (VEGF), VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, viral VEGF-E, and placental growth factor (PlGF). Human VEGF is composed of eight exons and can exist as multiple alternatively spliced isoforms including VEGF110, VEGF121, VEGF145, VEGF148, VEGF162, VEGF165, VEGF165b, VEGF183, VEGF189, and VEGF206, each with differing biological properties. The biological activities of the different VEGF isoforms are mediated via binding and activation of membrane-localized VEGF receptor tyrosine kinases (VEGF R). While three VEGF Rs have been identified (VEGF R1, VEGF R2, and VEGF R3), signaling through VEGF R2 is strongly associated with the initiation of angiogenesis. VEGF R2 is highly expressed by vascular endothelial cells and their embryonic precursors. It is also expressed by multiple non-endothelial cell types and is upregulated in some cancer cells. Multiple VEGF family members and isoforms bind and activate VEGF R2 in an isoform-specific manner including human VEGF110, VEGF121, VEGF145, VEGF148, VEGF162, VEGF165, VEGF165b, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, and VEGF-E. Similarly, mouse VEGF R2 binds mouse VEGF isoforms that correspond to the human isoform orthologs. VEGF binding and activation of VEGF R2 is further modulated by co-receptors such as neuropilins and heparin sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs).
VEGF binding to the extracellular portion of VEGF R2 leads to receptor dimerization, activation of its intracellular tyrosine kinase domains, and autophosphorylation. Major sites of human VEGF R2 phosphorylation have been characterized and include Tyr801, Tyr951, Tyr1054, Tyr1059, Tyr1175, and Tyr1214. Additional phosphorylation sites on VEGF R2 include Tyr1223, Tyr1305, Tyr1309, and Tyr1319, however the function of phosphorylation at these sites is not well-defined. Autophosphorylation of VEGF R2 on Tyr1054 and Tyr1059 upon receptor dimerization is critical for downstream kinase activity and may be preceded by autophosphorylation on Tyr801. The other major phosphorylation sites on VEGF R2 are necessary for the recruitment of downstream signaling molecules such as Src, SHB, PI 3-K, NCK/Fyn, CDC42, PLC-gamma, GRB2/SOS/Shc, and SH2D2A. Interaction sites on VEGF R2 for the recruitment of GRB2/GAB1, C3G/Crk, and Jak have not been identified. Common downstream signaling cascades initiated by VEGF R2 recruitment of these signaling molecules include the ERK1/2 MAP Kinase, FAK, p38 MAP Kinase, Akt, and Jak-STAT pathways, which result in the activation of a full range of biological responses that regulate angiogenesis including endothelial cell proliferation, survival, adhesion, and migration, as well as vascular permeability.
To learn more, please visit our VEGF Family Research Area.
Get Print Copy of this Pathway