AQUApure Di-Ub Chains (K63-linked) Protein, CF
AQUApure Di-Ub Chains (K63-linked) Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
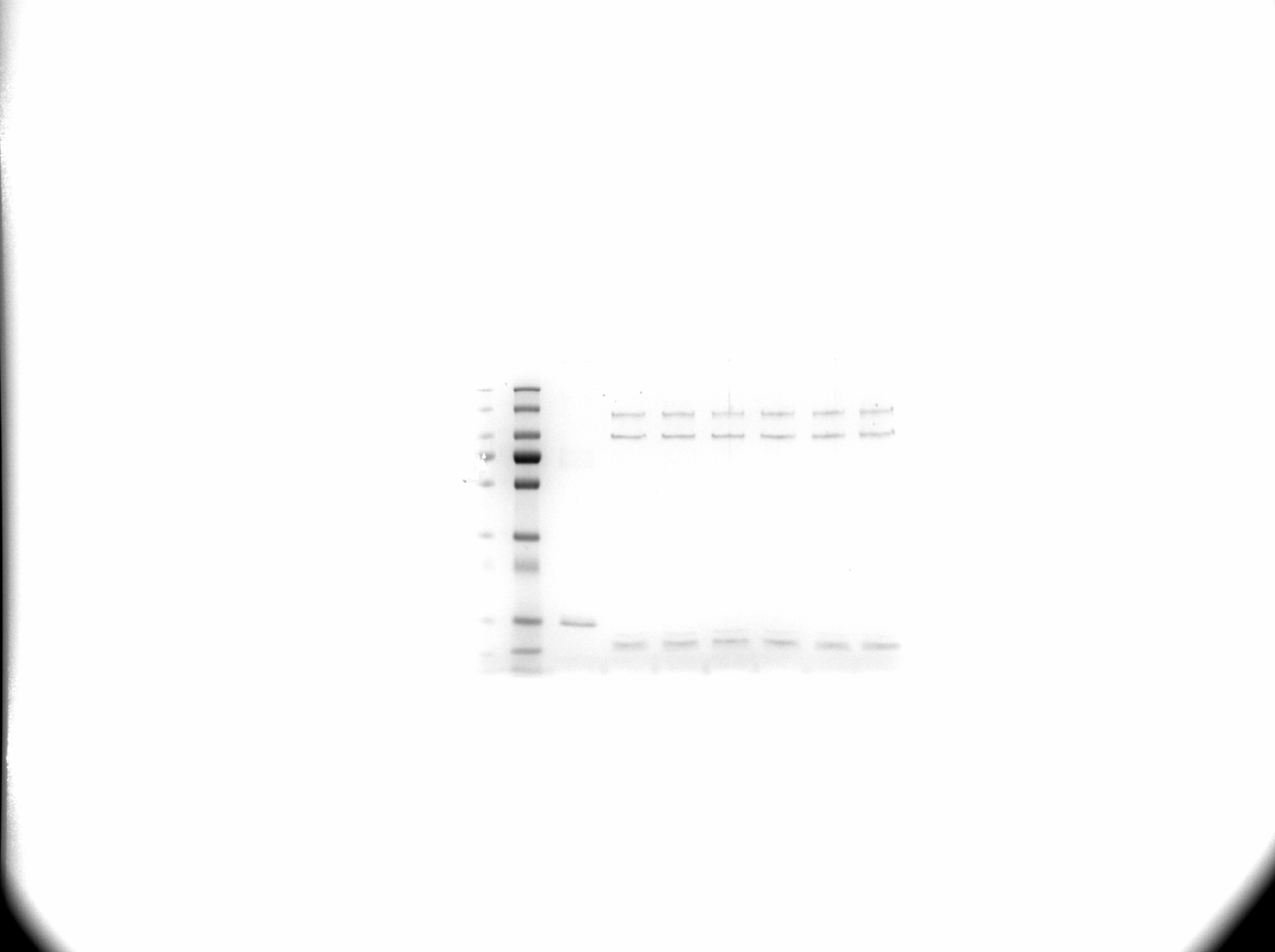
Ub-AQUA analysis:
K63: 99.04%
K11: 0.76%
K6 : 0.13%
All other linkages ≤ 0.04%
Ubiquitin chains vary in length, linkage, and function. K63-linked Di-Ubiquitin Chains (Ub2) are ideal for investigating Ubiquitin-binding proteins and as substrates for Ubiquitin-specific isopeptidases. Reaction conditions will need to be optimized for each specific application. IMPORTANT: Heating this product in SDS-PAGE buffer or terminating reactions containing this product with heated SDS-PAGE buffer could lead to unexpected, high apparent molecular weight banding or smearing on gels that is not representative of product purity. For optimal results, we recommend incubation in SDS-PAGE buffer + DTT at <40 °C for 20 minutes prior to gel electrophoresis.
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
UC-300B
| Formulation | 1 mg/ml (58 μM) in sterile, deionized water |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with dry ice or equivalent. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: Di-Ubiquitin
Linkage specific Poly-Ubiquitin chains may be used as a substrate for in vitro reactions with deubiquitinating enzymes ("DUB's") that cleave the peptide or isopeptide linkage between adjacent Ubiquitin molecules. Poly-Ubiquitin chains can also be used to investigate mechanisms of binding and recognition between the chains and other proteins that contain Ubiquitin-Associated domains (UBAs), Ubiquitin-interacting motifs (UIMs), ZnF's and/or other Ubiquitin-sensing elements.
K63-linked Di-Ubiquitin chains are manufactured using recombinant Ubiquitin and purely enzymatic techniques to avoid the potential for contaminating synthetic intermediates. The correctness of linkage and purity of each production lot is assessed using the Absolute Quantitation of Ubiquitin method (Ub-AQUA), an LCMS-based technique that provides extremely accurate information on the composition of Poly-Ubiquitin samples.
- Kirkpatrick D.S., et al. (2006) Nat Cell Biol. 8(7): 700-10
- Ordureau, A., et al. (2014) Mol. Cell 56(3): 360–375
- Ordureau, A., et al. (2015) Pro. Nat. Acad. of Sci. USA 112(21): 6637–6642
- Phu L., et al. (2011) Mol Cell Proteomics 10(5): M110.003756
Citations for AQUApure Di-Ub Chains (K63-linked) Protein, CF
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
14
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
A trio of ubiquitin ligases sequentially drives ubiquitylation and autophagic degradation of dysfunctional yeast proteasomes
Authors: RS Marshall, RD Vierstra
Cell Reports, 2022-03-15;38(11):110535.
Applications: Bioassay -
Structural insights into the mechanism and inhibition of transglutaminase-induced ubiquitination by the Legionella effector MavC
Authors: Y Mu, Y Wang, Y Huang, D Li, Y Han, M Chang, J Fu, Y Xie, J Ren, H Wang, Y Zhang, ZQ Luo, Y Feng
Nat Commun, 2020-04-14;11(1):1774.
Species: N/A
Sample Types: Recombinant Protein
Applications: Bioassay -
Post-translational Modification of OTULIN Regulates Ubiquitin Dynamics and Cell Death
Authors: T Douglas, M Saleh
Cell Rep, 2019-12-10;29(11):3652-3663.e5.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Protein
Applications: Bioassay -
ZUFSP Deubiquitylates K63-Linked Polyubiquitin Chains to Promote Genome Stability
Authors: P Haahr, N Borgermann, X Guo, D Typas, D Achuthanku, S Hoffmann, R Shearer, TK Sixma, N Mailand
Mol. Cell, 2018-03-22;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Bioassay -
Reactive-site-centric chemoproteomics identifies a distinct class of deubiquitinase enzymes
Authors: DS Hewings, J Heideker, TP Ma, AP AhYoung, F El Oualid, A Amore, GT Costakes, D Kirchhofer, B Brasher, T Pillow, N Popovych, T Maurer, C Schwerdtfe, WF Forrest, K Yu, J Flygare, M Bogyo, IE Wertz
Nat Commun, 2018-03-21;9(1):1162.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Protein
Applications: Bioassay -
PINK1 autophosphorylation is required for ubiquitin recognition
Authors: S Rasool, N Soya, L Truong, N Croteau, GL Lukacs, JF Trempe
EMBO Rep., 2018-02-23;0(0):.
Species: Insect - Tribolium castaneum
Sample Types: Recombinant Protein
Applications: Bioassay -
OTUD4 Is a Phospho-Activated K63 Deubiquitinase that Regulates MyD88-Dependent Signaling
Authors: Y Zhao, MC Mudge, JM Soll, RB Rodrigues, AK Byrum, EA Schwarzkop, TR Bradstreet, SP Gygi, BT Edelson, N Mosammapar
Mol. Cell, 2018-02-01;69(3):505-516.e5.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Recombinant Protein
Applications: Bioassay -
Characterization of the deubiquitination activity and substrate specificity of the chicken ubiquitin-specific protease 1/USP associated factor 1 complex
Authors: H Zheng, M Wang, C Zhao, S Wu, P Yu, Y Lü, T Wang, Y Ai
PLoS ONE, 2017-11-01;12(11):e0186535.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Recombinant Protein
Applications: Bioassay -
Cholesterol and fatty acids regulate cysteine ubiquitylation of ACAT2 through competitive oxidation
Authors: YJ Wang, Y Bian, J Luo, M Lu, Y Xiong, SY Guo, HY Yin, X Lin, Q Li, CCY Chang, TY Chang, BL Li, BL Song
Nat. Cell Biol., 2017-06-12;19(7):808-819.
Applications: Control -
In�Vivo Ubiquitin Linkage-type Analysis Reveals that the Cdc48-Rad23/Dsk2 Axis Contributes to K48-Linked Chain Specificity of the Proteasome
Authors: H Tsuchiya, F Ohtake, N Arai, A Kaiho, S Yasuda, K Tanaka, Y Saeki
Mol. Cell, 2017-05-18;66(4):488-502.e7.
Applications: Bioassay -
Deubiquitinase-based analysis of ubiquitin chain architecture using Ubiquitin Chain Restriction (UbiCRest).
Authors: Hospenthal, Manuela, Mevissen, Tycho E, Komander, David
Nat Protoc, 2015-01-29;10(2):349-61.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Protein
-
USP45 deubiquitylase controls ERCC1-XPF endonuclease-mediated DNA damage responses.
Authors: Perez-Oliva A, Lachaud C, Szyniarowski P, Munoz I, Macartney T, Hickson I, Rouse J, Alessi D
EMBO J, 2014-12-23;34(3):326-43.
-
The vOTU domain of highly-pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus displays a differential substrate preference.
Authors: Deaton M, Spear A, Faaberg K, Pegan S
Virology, 2014-03-15;454(0):247-53.
-
A selective USP1-UAF1 inhibitor links deubiquitination to DNA damage responses.
Authors: Liang, Qin, Dexheimer, Thomas S, Zhang, Ping, Rosenthal, Andrew S, Villamil, Mark A, You, Changjun, Zhang, Qiuting, Chen, Junjun, Ott, Christin, Sun, Hongmao, Luci, Diane K, Yuan, Bifeng, Simeonov, Anton, Jadhav, Ajit, Xiao, Hui, Wang, Yinsheng, Maloney, David J, Zhuang, Zhihao
Nat Chem Biol, 2014-02-16;10(4):298-304.
Applications: Inhibition
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for AQUApure Di-Ub Chains (K63-linked) Protein, CF
Average Rating: 4.5 (Based on 2 Reviews)
Have you used AQUApure Di-Ub Chains (K63-linked) Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
Reason for Rating: The faculty were pleased with the outcome.