Human IL-15 Antibody Summary
Asn49-Ser162
Accession # P40933.1
Customers also Viewed
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
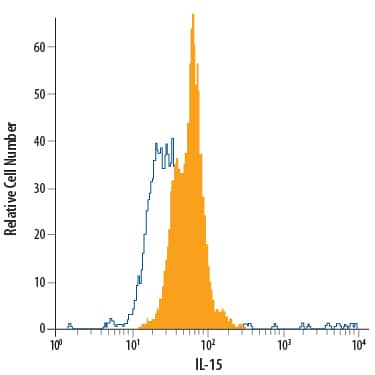
 View Larger
View Larger
IL‑15 in Human Placenta. IL‑15 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human placenta using Mouse Anti-Human IL‑15 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB2472) at 5 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC001). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using VisUCyte Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # VCTS021). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm and nuclei in decidual cells. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
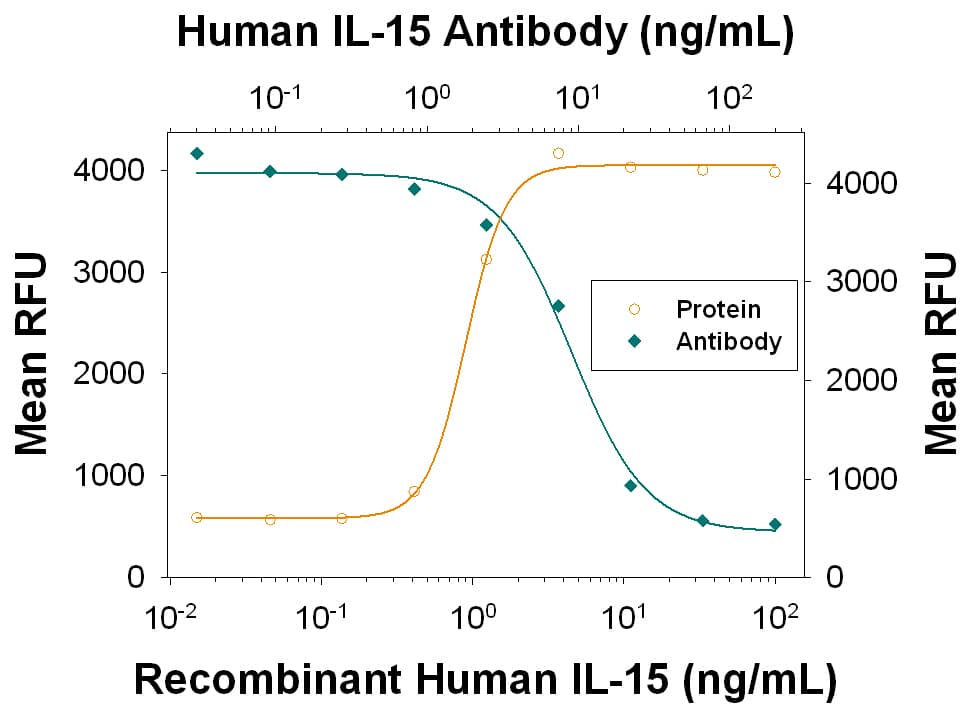
 View Larger
View Larger
IL‑15 in HeLa Cells (Human). IL‑15 was detected in immersion fixed HeLa cells (human) using Mouse Anti-Human IL‑15 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB2472) at 8 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL007) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
IL‑15 in RAW264.7 cells. IL‑15 was detected in immersion fixed using Mouse Anti-Human IL‑15 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB2472) at 8 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL007) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: IL-15
Interleukin 15 (IL-15) is a widely expressed 14 kDa cytokine that is structurally and functionally related to IL-2 and plays an important role in many immunological diseases (1, 2). Mature human IL-15 protein shares 70% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat IL-15. Alternative splicing generates isoforms of Interleukin 15 with either a long or short signal peptide (LSP or SSP), and the SSP isoform is retained intracellularly (3). The IL-15 protein binds with high affinity to IL-15 R alpha (4). It binds with lower affinity to a complex of IL-2 R beta and the common gamma chain ( gamma c) which are also subunits of the IL-2 receptor complex (5). IL-15 associates with IL-15 R alpha in the endoplasmic reticulum, and this complex is expressed on the cell surface (6). The dominant mechanism of IL-15 action is known as transpresentation in which IL-15 and IL-15 R alpha are coordinately expressed on the surface of one cell and interact with complexes of IL-2 R beta / gamma c on adjacent cells (7). This enables cells to respond to Interleukin 15 even if they do not express IL-15 R alpha (6). In human and mouse, soluble IL-15-binding forms of IL-15 R alpha can be generated by proteolytic shedding and bind up nearly all the IL-15 protein in circulation (8-10). Soluble IL-15 R alpha functions as an inhibitor that limits IL-15 action (4, 9). Ligation of membrane-associated IL-15/IL-15 R alpha complexes also induces reverse signaling that promotes activation of the IL-15/IL-15 R alpha expressing cells (11). IL-15 induces or enhances the differentiation, maintenance, or activation of multiple T cell subsets including NK, NKT, Th17, Treg, and CD8+ memory cells (12-16). An important component of these functions is the ability of IL-15 to induce dendritic cell differentiation and inflammatory activation (11, 14). IL-15 exhibits anti-tumor activity independent of its actions on NK cells or CD8+ T cells (17). It also inhibits the deposition of lipid in adipocytes, and its circulating levels are decreased in obesity (18).
- De Sabatino, A. et al. (2011) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22:19.
- Grabstein, K. et al. (1994) Science 264:965.
- Tagaya, Y. et al. (1997) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:14444.
- Giri, J.G. et al. (1995) EMBO J. 14:3654.
- Giri, J. et al. (1994) EMBO J. 13:2822.
- Dubois, S. et al. (2002) Immunity 17:537.
- Castillo, E.F. and K.S. Schluns (2012) Cytokine 59:479.
- Budagian, V. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279:40368.
- Mortier, E. et al. (2004) J. Immunol. 173:1681.
- Bergamaschi, C. et al. (2012) Blood 120:e1.
- Budagian, V. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279:42192.
- Mortier, E. et al. (2003) J. Exp. Med. 205:1213.
- Gordy, L.E. et al. (2011) J. Immunol. 187:6335.
- Harris, K.M. (2011) J. Leukoc. Biol. 90:727.
- Xia, J. et al. (2010) Clin. Immunol. 134:130.
- Schluns, K.S. et al. (2002) J. Immunol. 168:4827.
- Davies, E. et al. (2010) J. Leukoc. Biol. 88:529.
- Barra, N.G. et al. (2010) Obesity 18:1601.
Product Datasheets
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human IL-15 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human IL-15 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human IL-15 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image