Human MICA APC-conjugated Antibody Summary
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of MICA in K562 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human MICA APC-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB1300A, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC0041A, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
 View Larger
View Larger
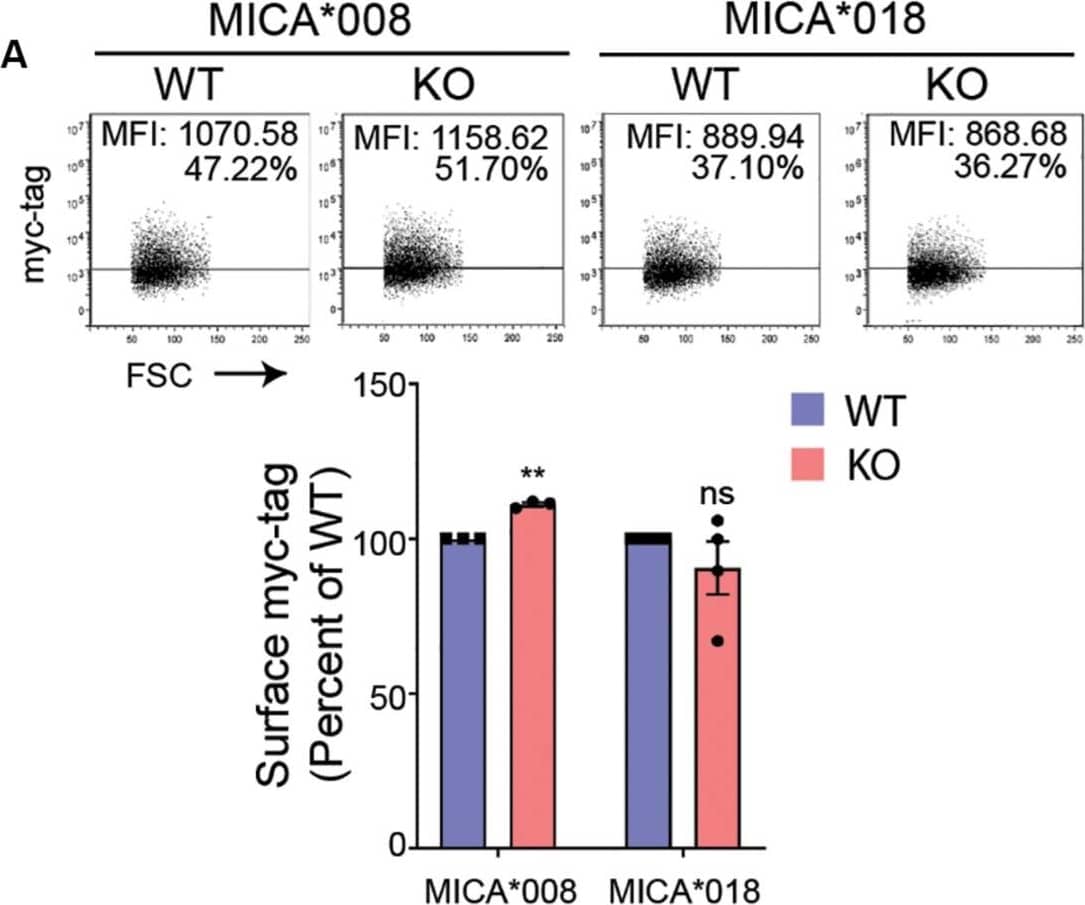
Detection of Mouse MICA by Flow Cytometry UDP-GlcNAc upregulates MICA expression. (A) HEK293 wildtype (WT) and HEK293 MGAT5 knockout (KO) cells were transfected with GFP-myc-tagged MICA*008 or MICA*018 under CMV promoter and detected on the surface the following day as surface myc-tag expression on GFP-positive cells. Data are displayed as isotype-corrected mean fluorescence intensity ( delta MFI) relative to WT from three-four independent experiments. Dot plots are representative of all experiments. Grid is set to 5% of corresponding isotype controls. (B) MICA mRNAs were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR in total RNA purified from WT and KO cells. MICA expression was normalized to housekeeping gene RPLP0 and shown as ratio relative to WT cells from six independent experiments. (C) UDP-GlcNAc/UDP-GalNAc measurements from LC-HRMS analysis of intracellular metabolites in WT and KO cells are presented as relative peak areas (a.u.) corresponding to UDP-GlcNAc or UDP-GalNAc. Log10-transformed values from three experiments are shown as individual dots. (D) MICA mRNA analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR in total RNA purified from WT and KO cells after 8 days cultivation with indicated concentrations of GlcNAc. MICA expression is normalized to housekeeping gene RPLP0 and displayed as ratio relative to untreated WT cells from two independent experiments. All data are displayed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using one-sample t-test in (A,B), and unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction in (C). **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001, p-value is presented in (C). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32849657), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse MICA by Flow Cytometry Hydroxycitrate reduces MICA expression in activated T cells and multiple cancer cells. (A) MICA mRNA analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR in total RNA purified from HEK293 cells after more than 30 passages in glucose (Glc) and galactose (Gal). MICA expression is normalized to housekeeping gene RPLP0 and displayed as mean ± SEM from six independent experiments. (B) MICA surface expression analyzed by flow cytometry of Glc and Gal cells at basal levels. Dot plots are representative of at least three independent experiments. Grid is set to ∼5% of corresponding isotype control stainings. (C) Mitochondrial stress test on HEK293 cultivated in Glc or Gal under same conditions as in Figure 4A. The graph is baselined to measuring point three and displays mean ± SEM from two independent experiments. (D) MICA/B surface expression of peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs) activated for 3 days in Glc or Gal growth medium prior to 18 h treatment with FR901228 (20 ng/mL). Grids in dot plots are set to ∼5% of corresponding isotype control staining and dot plots are representative of seven different donors. The bar graph displays mean ± SEM of isotype-corrected MICA/B MFI ( delta MFI) from seven donors. Left panel is zoomed in on the difference between untreated Glc and Gal PBLs. (E,F) HEK293 MGAT5 knockout (KO) cells were treated with (E) 2DG (20 mM) or (F) hydroxycitrate (HC) (15 mM) in addition to PBS (UT), citrate (10 mM), or GlcNAc (25 mM) for 22–24 h. Bar graphs display MICA surface expression as mean ± SEM of delta MFI values from three independent experiments. Data of UT samples share values with UT samples in Figure 3H. (G) MICA surface expression in several cancer cell lines after 18 or 42 h treatment with HC (10 mM). delta MFI values are normalized to UT control and shown as mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments. (H,I) MICA surface expression (H) and NKG2D-fc binding (I) in cancer cell lines after 2.5 h treatment with HC (10 mM) prior to 18 h stimulation with FR901228 (FR, 20 ng/mL) or sodium butyrate (But, 5 mM). Bar graphs display MICA surface expression as mean ± SEM of delta MFI values (H), or NKG2D-fc surface binding as ± SEM of delta MFI normalized to untreated (UT) control (I), from three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction in (A,E,F), ratio paired t-test in (D), one-sample t-test in (G), and two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test (H,I). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32849657), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse MICA by Flow Cytometry Hydroxycitrate reduces MICA expression in activated T cells and multiple cancer cells. (A) MICA mRNA analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR in total RNA purified from HEK293 cells after more than 30 passages in glucose (Glc) and galactose (Gal). MICA expression is normalized to housekeeping gene RPLP0 and displayed as mean ± SEM from six independent experiments. (B) MICA surface expression analyzed by flow cytometry of Glc and Gal cells at basal levels. Dot plots are representative of at least three independent experiments. Grid is set to ∼5% of corresponding isotype control stainings. (C) Mitochondrial stress test on HEK293 cultivated in Glc or Gal under same conditions as in Figure 4A. The graph is baselined to measuring point three and displays mean ± SEM from two independent experiments. (D) MICA/B surface expression of peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs) activated for 3 days in Glc or Gal growth medium prior to 18 h treatment with FR901228 (20 ng/mL). Grids in dot plots are set to ∼5% of corresponding isotype control staining and dot plots are representative of seven different donors. The bar graph displays mean ± SEM of isotype-corrected MICA/B MFI ( delta MFI) from seven donors. Left panel is zoomed in on the difference between untreated Glc and Gal PBLs. (E,F) HEK293 MGAT5 knockout (KO) cells were treated with (E) 2DG (20 mM) or (F) hydroxycitrate (HC) (15 mM) in addition to PBS (UT), citrate (10 mM), or GlcNAc (25 mM) for 22–24 h. Bar graphs display MICA surface expression as mean ± SEM of delta MFI values from three independent experiments. Data of UT samples share values with UT samples in Figure 3H. (G) MICA surface expression in several cancer cell lines after 18 or 42 h treatment with HC (10 mM). delta MFI values are normalized to UT control and shown as mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments. (H,I) MICA surface expression (H) and NKG2D-fc binding (I) in cancer cell lines after 2.5 h treatment with HC (10 mM) prior to 18 h stimulation with FR901228 (FR, 20 ng/mL) or sodium butyrate (But, 5 mM). Bar graphs display MICA surface expression as mean ± SEM of delta MFI values (H), or NKG2D-fc surface binding as ± SEM of delta MFI normalized to untreated (UT) control (I), from three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction in (A,E,F), ratio paired t-test in (D), one-sample t-test in (G), and two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test (H,I). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32849657), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human MICA by Flow Cytometry Histograms showing sample flow cytometry profiles for the ligands studied. Bars in each plot indicate the population expressing each aNKR, Gates were set using Unstained, single stained controls, fluorescence minus one, and secondary antibody alone controls. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/9/10/295), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Background: MICA
MICA (MHC class I chain-related gene A) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that functions as a ligand for human NKG2D. A closely related protein, MICB, shares 85% amino acid identity with MICA. These proteins are distantly related to the MHC class I proteins. They possess three extracellular Ig-like domains, but they have no capacity to bind peptide or interact with beta 2-microglobulin. The genes encoding these proteins are found within the Major Histocompatibility Complex on human chromosome 6. The MICA locus is highly polymorphic with more than 50 recognized human alleles. MICA is absent from most cells but is frequently expressed in epithelial tumors and can be induced by bacterial and viral infections. MICA is a ligand for human NKG2D, an activating receptor expressed on NK cells, NKT cells, gamma δ T cells, and CD8+ alpha beta T cells. Recognition of MICA by NKG2D results in the activation of cytolytic activity and/or cytokine production by these effector cells. MICA recognition is involved in tumor surveillance, viral infections, and autoimmune diseases.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human MICA APC-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
14
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
NKp30 and NKG2D contribute to natural killer recognition of HIV-infected cells
Authors: Zhao, NQ;Pi, R;Nguyen, DN;Ranganath, T;Seiler, C;Holmes, S;Marson, A;Blish, CA;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Functional MICA Variants Are Differentially Associated with Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases
Authors: Wang, CM;Tan, KP;Wu, YJ;Zheng, JW;Wu, J;Chen, JY;
International journal of molecular sciences
Species: Human
Sample Types: Transfected Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
NKG2A and HLA-E define an alternative immune checkpoint axis in bladder cancer
Authors: Bérengère Salomé, John P. Sfakianos, Daniel Ranti, Jorge Daza, Christine Bieber, Andrew Charap et al.
Cancer Cell
-
Immunomodulatory effect of NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibition in Multiple Myeloma: upregulation of NKG2D ligands and sensitization to Natural Killer cell recognition
Authors: S Petillo, C Capuano, R Molfetta, C Fionda, A Mekhloufi, C Pighi, F Antonangel, A Zingoni, A Soriani, MT Petrucci, R Galandrini, R Paolini, A Santoni, M Cippitelli
Cell Death & Disease, 2021-09-04;12(9):836.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Cytoplasmic Citrate Flux Modulates the Immune Stimulatory NKG2D Ligand MICA in Cancer Cells
Authors: Sofie H. Møller, Maiken Mellergaard, Mikkel Madsen, Amaia V. Bermejo, Stine D. Jepsen, Marie H. Hansen et al.
Frontiers in Immunology
-
Expression of ligands for activating natural killer cell receptors on cell lines commonly used to assess natural killer cell function
Authors: A Tremblay-M, S Coenraads, Z Kiani, FP Dupuy, NF Bernard
BMC Immunol., 2019-01-29;20(1):8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Complete Remission with Reduction of High-risk Clones following Haploidentical NK Cell Therapy against MDS and AML
Authors: AT Björklund, M Carlsten, E Sohlberg, LL Liu, T Clancy, M Karimi, S Cooley, JS Miller, M Klimkowska, M Schaffer, E Watz, KI Wikstrom, P Blomberg, BE Wahlin, M Palma, L Hansson, P Ljungman, E Hellström-, HG Ljunggren, KJ Malmberg
Clin. Cancer Res., 2018-02-14;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Expression Profiles of Ligands for Activating Natural Killer Cell Receptors on HIV Infected and Uninfected CD4? T Cells
Authors: A Tremblay-M, J Bruneau, B Lebouché, I Lisovsky, R Song, NF Bernard
Viruses, 2017-10-12;9(10):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
NZ28-induced inhibition of HSF1, SP1 and NF-kappa B triggers the loss of the natural killer cell-activating ligands MICA/B on human tumor cells
Authors: Daniela Schilling, Annett Kühnel, Fabian Tetzlaff, Sarah Konrad, Gabriele Multhoff
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy
-
Modulation of NKG2D ligand expression and metastasis in tumors by spironolactone via RXRgamma activation.
Authors: Leung W, Vong Q, Lin W, Janke L, Chen T, Leung W
J Exp Med, 2013-11-04;210(12):2675-92.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Biomarkers on melanoma patient T cells associated with ipilimumab treatment.
Authors: Wang W, Yu D, Sarnaik A, Yu B, Hall M, Morelli D, Zhang Y, Zhao X, Weber J
J Transl Med, 2012-07-12;10(0):146.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF54/dUTPase downregulates a ligand for the NK activating receptor NKp44.
Authors: Madrid, Alexis S, Ganem, Don
J Virol, 2012-06-06;86(16):8693-704.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
MHC class I-related chain A and B ligands are differentially expressed in human cervical cancer cell lines
Authors: Susana del Toro-Arreola, Naela Arreygue-Garcia, Adriana Aguilar-Lemarroy, Angel Cid-Arregui, Miriam Jimenez-Perez, Jesse Haramati et al.
Cancer Cell International
-
Expression of the ULBP ligands for NKG2D by B-NHL cells plays an important role in determining their susceptibility to rituximab-induced ADCC.
Authors: Inagaki A, Ishida T, Yano H, Ishii T, Kusumoto S, Ito A, Ri M, Mori F, Ding J, Komatsu H, Iida S, Ueda R
Int. J. Cancer, 2009-07-01;125(1):212-21.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human MICA APC-conjugated Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human MICA APC-conjugated Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human MICA APC-conjugated Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image

