Human MICB Antibody Summary
Ala23-Gly298
Accession # CAI18747
Applications
Human MICB Sandwich Immunoassay
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
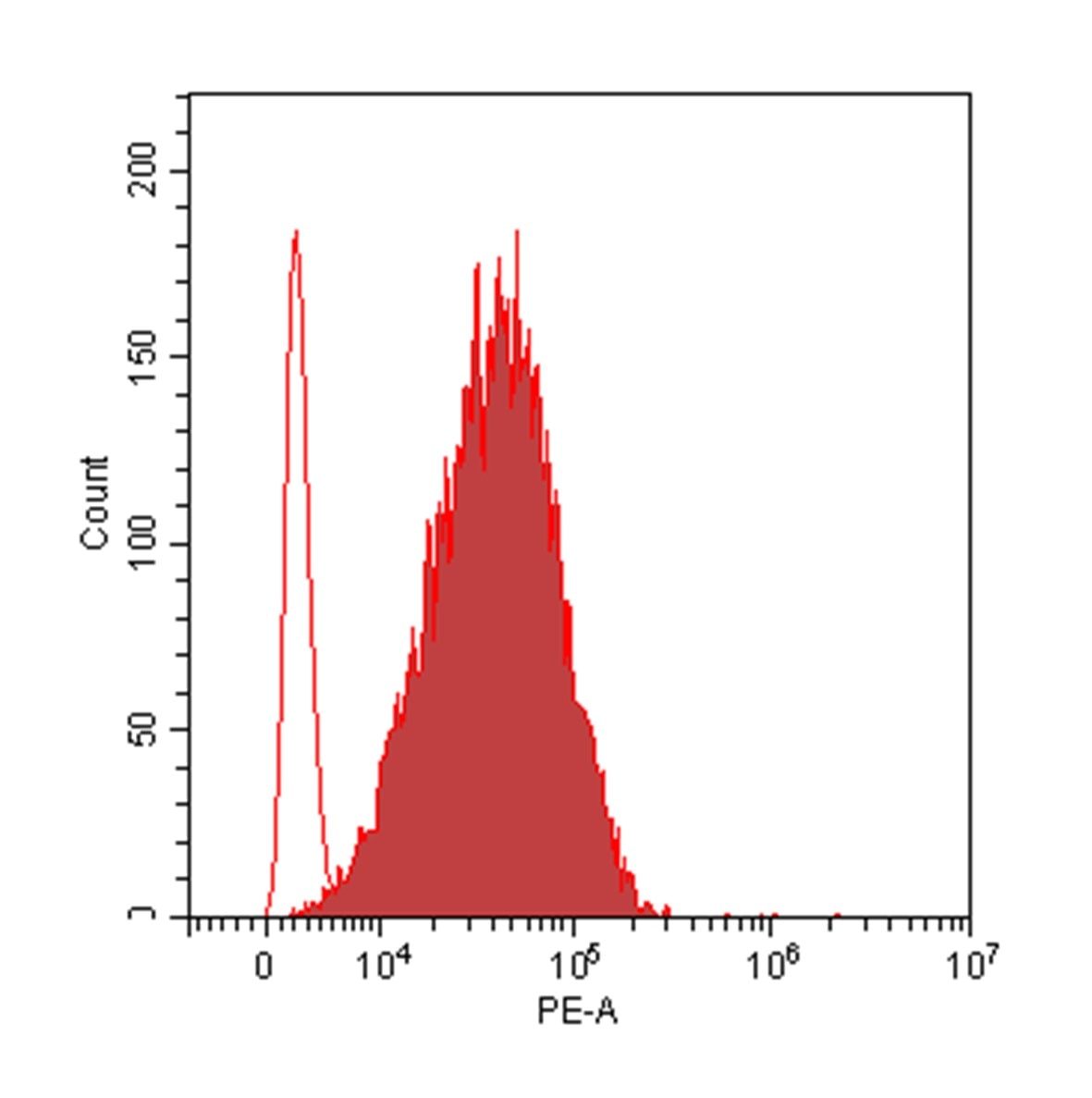
Detection of MICB in K562 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human MICB Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB1599, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB0041, open histogram), followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0102B).
 View Larger
View Larger
MICB Specificity is Shown by Flow Cytometry in Knockout Cell Line. MICB knockout K562 human myelogenous leukemia cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human MICB Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB1599, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB0041, open histogram) followed by anti-Mouse IgG PE-conjugated secondary antibody (Catalog # F0102B). No staining in the MICB knockout K562 cell line was observed. View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human MICB by Flow Cytometry Multiple receptors and ligands are involved in NK cell-mediated lysis of activated CD4+ T cells.Role of (A) activating and (B) inhibitory NK receptors in NK cell degranulation. Left column: representative histograms (of n≥3) for surface expression of ligands on activated (thick black line) and resting CD4+ T cells (thin black line). Isotype-matched control Ig are represented by dashed line (activated CD4+ T) and filled histogram (resting CD4+ T). Middle- and right column: NK and CD4+ T cells were activated for 4 days in vitro as described, and co-cultured for 4 hours with 10 ug/mL mAb (or relevant isotype-matched control Ig). Degranulation is shown for CD56dim (middle column) and CD56bright (right column) NK cells. Representative histograms of surface expression of receptors on activated (thick black line) and resting NK cells (thin black line). Isotype-matched control Ig are represented by dashed line (activated NK) and filled histogram (resting NK). * P<0.05, ** P<0.005, *** P<0.001. (C) Sorted IL-2-activated CD56dim and CD56bright NK cells were co-cultured with 51Cr-labeled activated CD4+ T cells in a 51Cr-release assay with human IgG4 isotype control (•) or anti-NKG2A mAb (○). Data represents n = 3 experiments. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22384114), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse MICB by Flow Cytometry Hydroxycitrate reduces MICA expression in activated T cells and multiple cancer cells. (A) MICA mRNA analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR in total RNA purified from HEK293 cells after more than 30 passages in glucose (Glc) and galactose (Gal). MICA expression is normalized to housekeeping gene RPLP0 and displayed as mean ± SEM from six independent experiments. (B) MICA surface expression analyzed by flow cytometry of Glc and Gal cells at basal levels. Dot plots are representative of at least three independent experiments. Grid is set to ∼5% of corresponding isotype control stainings. (C) Mitochondrial stress test on HEK293 cultivated in Glc or Gal under same conditions as in Figure 4A. The graph is baselined to measuring point three and displays mean ± SEM from two independent experiments. (D) MICA/B surface expression of peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs) activated for 3 days in Glc or Gal growth medium prior to 18 h treatment with FR901228 (20 ng/mL). Grids in dot plots are set to ∼5% of corresponding isotype control staining and dot plots are representative of seven different donors. The bar graph displays mean ± SEM of isotype-corrected MICA/B MFI ( delta MFI) from seven donors. Left panel is zoomed in on the difference between untreated Glc and Gal PBLs. (E,F) HEK293 MGAT5 knockout (KO) cells were treated with (E) 2DG (20 mM) or (F) hydroxycitrate (HC) (15 mM) in addition to PBS (UT), citrate (10 mM), or GlcNAc (25 mM) for 22–24 h. Bar graphs display MICA surface expression as mean ± SEM of delta MFI values from three independent experiments. Data of UT samples share values with UT samples in Figure 3H. (G) MICA surface expression in several cancer cell lines after 18 or 42 h treatment with HC (10 mM). delta MFI values are normalized to UT control and shown as mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments. (H,I) MICA surface expression (H) and NKG2D-fc binding (I) in cancer cell lines after 2.5 h treatment with HC (10 mM) prior to 18 h stimulation with FR901228 (FR, 20 ng/mL) or sodium butyrate (But, 5 mM). Bar graphs display MICA surface expression as mean ± SEM of delta MFI values (H), or NKG2D-fc surface binding as ± SEM of delta MFI normalized to untreated (UT) control (I), from three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction in (A,E,F), ratio paired t-test in (D), one-sample t-test in (G), and two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test (H,I). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32849657), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: MICB
MICB (MHC class I chain-related gene B) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that functions as a ligand for NKG2D. A closely related protein, MICA, shares 85% amino acid identity with MICB. These 2 proteins are distantly related to the MHC class I proteins. MICA and MICB (MICA/B) possess three extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains, but have no capacity to bind peptide or interact with beta 2-microglobulin. The genes encoding MICA/B are found within the major histocompatibility complex on human chromosome 6. The MICB locus is polymorphic with more than 15 recognized human alleles. MICA/B are minimally expressed on normal cells, but are frequently expressed on epithelial tumors and can be induced by bacterial and viral infections. MICA/B are ligands for NKG2D, an activating receptor expressed on NK cells, NKT cells, gamma δ T cells, and CD8+ alpha beta T cells. Recognition of MICA/B by NKG2D results in the activation of cytolytic activity and/or cytokine production by these effector cells. MICA/B recognition is involved in tumor surveillance, viral infections, and autoimmune diseases. The release of soluble forms of MICA/B from tumors down-regulates NKG2D surface expression on effector cells resulting in the impairment of anti-tumor immune response (1-7).
- Groh, V. et al. (2001) Nature Immunol. 2:255.
- Stephens, H. (2001) Trends Immunol. 22:378.
- Bauer, S. et al. (1999) Science 285:727.
- Groh, V. et al. (2002) Nature 419:734.
- Steinle, A. et al. (2001) Immunogenetics 53:279.
- Pende, D. et al. (2002) Cancer Res. 62:6178.
- Salih, H. et al. (2003) Blood 102:1389.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human MICB Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
47
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Cytoplasmic Citrate Flux Modulates the Immune Stimulatory NKG2D Ligand MICA in Cancer Cells
Authors: Sofie H. Møller, Maiken Mellergaard, Mikkel Madsen, Amaia V. Bermejo, Stine D. Jepsen, Marie H. Hansen et al.
Frontiers in Immunology
-
Combinations of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors with Distinct Latency Reversing Agents Variably Affect HIV Reactivation and Susceptibility to NK Cell-Mediated Killing of T Cells That Exit Viral Latency
Authors: Daniela A. Covino, Maria G. Desimio, Margherita Doria
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
-
Natural Killer Group 2D Ligand Depletion Reconstitutes Natural Killer Cell Immunosurveillance of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Authors: S Weil, S Memmer, A Lechner, V Huppert, A Giannattas, T Becker, A Müller-Run, K Lampe, D Beutner, A Quaas, R Schubert, E Herrmann, A Steinle, U Koehl, L Walter, MS von Bergwe, J Koch
Front Immunol, 2017-04-10;8(0):387.
-
Hexamethylene bisacetamide impairs NK cell-mediated clearance of acute T lymphoblastic leukemia cells and HIV-1-infected T cells that exit viral latency
Authors: Erica Giuliani, Maria Giovanna Desimio, Margherita Doria
Scientific Reports
-
Antitumor effects of NK cells expanded by activation pre?processing of autologous feeder cells before irradiation in colorectal cancer
Authors: Koh, EK;Lee, HR;Son, WC;Park, GY;Bae, J;Park, YS;
Oncology letters
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Combinatorial immunotherapy with gemcitabine and ex vivo-expanded NK cells induces anti-tumor effects in pancreatic cancer
Authors: Koh, EK;Lee, HR;Son, WC;Park, GY;Kim, J;Bae, JH;Park, YS;
Scientific reports
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
CRISPR activation screen identifies BCL-2 proteins and B3GNT2 as drivers of cancer resistance to T cell-mediated cytotoxicity
Authors: J Joung, PC Kirchgatte, A Singh, JH Cho, SP Nety, RC Larson, RK Macrae, R Deasy, YY Tseng, MV Maus, F Zhang
Nature Communications, 2022-03-25;13(1):1606.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Immunomodulatory effect of NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibition in Multiple Myeloma: upregulation of NKG2D ligands and sensitization to Natural Killer cell recognition
Authors: S Petillo, C Capuano, R Molfetta, C Fionda, A Mekhloufi, C Pighi, F Antonangel, A Zingoni, A Soriani, MT Petrucci, R Galandrini, R Paolini, A Santoni, M Cippitelli
Cell Death & Disease, 2021-09-04;12(9):836.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Rac1/ROCK-driven membrane dynamics promote natural killer cell cytotoxicity via granzyme-induced necroptosis
Authors: Y Zhu, J Xie, J Shi
Bmc Biology, 2021-07-30;19(1):140.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
The human cytomegalovirus protein UL147A downregulates the most prevalent MICA allele: MICA*008, to evade NK cell-mediated killing
Authors: E Seidel, L Dassa, C Schuler, E Oiknine-Dj, DG Wolf, VTK Le-Trillin, O Mandelboim
PloS Pathogens, 2021-05-03;17(5):e1008807.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
A slowly cleaved viral signal peptide acts as a protein-integral immune evasion domain
Authors: E Seidel, L Dassa, S Kahlon, B Tirosh, A Halenius, T Seidel Mal, O Mandelboim
Nature Communications, 2021-04-06;12(1):2061.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Human Metapneumovirus Escapes NK Cell Recognition through the Downregulation of Stress-Induced Ligands for NKG2D
Authors: M Diab, D Schmiedel, E Seidel, E Bacharach, O Mandelboim
Viruses, 2020-07-20;12(7):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Allogeneic ADSCs Induce the Production of Alloreactive Memory-CD8 T Cells through HLA-ABC Antigens
Authors: SH Chang, HJ Kim, CG Park
Cells, 2020-05-18;9(5):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
NK cell detachment from target cells is regulated by successful cytotoxicity and influences cytokine production
Authors: M Anft, P Netter, D Urlaub, I Prager, S Schaffner, C Watzl
Cell. Mol. Immunol., 2019-08-30;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Targetable mechanisms driving immunoevasion of persistent senescent cells link chemotherapy-resistant cancer to aging
Authors: DP Muñoz, SM Yannone, A Daemen, Y Sun, F Vakar-Lope, M Kawahara, AM Freund, F Rodier, JD Wu, PY Desprez, DH Raulet, PS Nelson, LJ van 't Vee, J Campisi, JP Coppé
JCI Insight, 2019-06-11;5(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: IHC -
The combination of ionizing radiation and proteasomal inhibition by bortezomib enhances the expression of NKG2D ligands in multiple myeloma cells
Authors: YS Lee, W Heo, J Nam, YH Jeung, J Bae
J. Radiat. Res., 2018-05-01;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Purine nucleotide metabolism regulates expression of the human immune ligand MICA
Authors: MT McCarthy, G Moncayo, TK Hiron, NA Jakobsen, A Valli, T Soga, J Adam, CA O'Callagha
J. Biol. Chem., 2017-12-26;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Human cytomegalovirus escapes immune recognition by NK cells through the downregulation of B7-H6 by the viral genes US18 and US20
Authors: Y Charpak-Am, T Kubsch, E Seidel, E Oiknine-Dj, N Cavaletto, R Yamin, D Schmiedel, D Wolf, G Gribaudo, M Messerle, L Cicin-Sain, O Mandelboim
Sci Rep, 2017-08-17;7(1):8661.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
MicroRNA-519a-3p mediates apoptosis resistance in breast cancer cells and their escape from recognition by natural killer cells
Authors: C Breunig, J Pahl, M Küblbeck, M Miller, D Antonelli, N Erdem, C Wirth, R Will, A Bott, A Cerwenka, S Wiemann
Cell Death Dis, 2017-08-03;8(8):e2973.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Increasing TIMP3 expression by hypomethylating agents diminishes soluble MICA, MICB and ULBP2 shedding in acute myeloid leukemia, facilitating NK cell-mediated immune recognition
Authors: AB Raneros, AM Puras, RM Rodriguez, E Colado, T Bernal, E Anguita, AV Mogorron, AC Gil, JR Vidal-Cast, L Márquez-Ki, PD Bulnes, AM Marin, MCG Garay, B Suarez-Alv, C Lopez-Larr
Oncotarget, 2017-05-09;8(19):31959-31976.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Vigilin Regulates the Expression of the Stress-Induced Ligand MICB by Interacting with Its 5' Untranslated Region
Authors: O Berhani, D Nachmani, R Yamin, D Schmiedel, Y Bar-On, O Mandelboim
J. Immunol., 2017-03-29;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Combination treatment with decitabine and ionizing radiation enhances tumor cells susceptibility of T cells
Sci Rep, 2016-09-27;6(0):32470.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Microchip-Based Single-Cell Imaging Reveals That CD56dimCD57-KIR-NKG2A+ NK Cells Have More Dynamic Migration Associated with Increased Target Cell Conjugation and Probability of Killing Compared to CD56dimCD57-KIR-NKG2A- NK Cells.
Authors: Forslund E, Sohlberg E, Enqvist M, Olofsson P, Malmberg K, Onfelt B
J Immunol, 2015-08-28;195(7):3374-81.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Genotoxic Stress Induces Senescence-Associated ADAM10-Dependent Release of NKG2D MIC Ligands in Multiple Myeloma Cells.
Authors: Zingoni A, Cecere F, Vulpis E, Fionda C, Molfetta R, Soriani A, Petrucci M, Ricciardi M, Fuerst D, Amendola M, Mytilineos J, Cerboni C, Paolini R, Cippitelli M, Santoni A
J Immunol, 2015-06-12;195(2):736-48.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Cytotoxicity and infiltration of human NK cells in in vivo-like tumor spheroids.
Authors: Giannattasio A, Weil S, Kloess S, Ansari N, Stelzer E, Cerwenka A, Steinle A, Koehl U, Koch J
BMC Cancer, 2015-05-03;15(0):351.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
NKG2D-dependent activation of dendritic epidermal T cells in contact hypersensitivity.
Authors: Nielsen M, Dyring-Andersen B, Schmidt J, Witherden D, Lovato P, Woetmann A, Odum N, Poulsen S, Havran W, Geisler C, Bonefeld C
J Invest Dermatol, 2015-01-29;135(5):1311-9.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: FACS -
Altered microRNA expression after infection with human cytomegalovirus leads to TIMP3 downregulation and increased shedding of metalloprotease substrates, including MICA.
Authors: Esteso G, Luzon E, Sarmiento E, Gomez-Caro R, Steinle A, Murphy G, Carbone J, Vales-Gomez M, Reyburn H
J Immunol, 2014-06-27;193(3):1344-52.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
Applications: ELISA Development -
RNA-binding proteins regulate the expression of the immune activating ligand MICB.
Authors: Nachmani, Daphna, Gutschner, Tony, Reches, Adi, Diederichs, Sven, Mandelboim, Ofer
Nat Commun, 2014-06-13;5(0):4186.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Two novel human cytomegalovirus NK cell evasion functions target MICA for lysosomal degradation.
Authors: Fielding C, Aicheler R, Stanton R, Wang E, Han S, Seirafian S, Davies J, McSharry B, Weekes M, Antrobus P, Prod'homme V, Blanchet F, Sugrue D, Cuff S, Roberts D, Davison A, Lehner P, Wilkinson G, Tomasec P
PLoS Pathog, 2014-05-01;10(5):e1004058.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
MicroRNA editing facilitates immune elimination of HCMV infected cells.
Authors: Nachmani D, Zimmermann A, Oiknine Djian E, Weisblum Y, Livneh Y, Khanh Le V, Galun E, Horejsi V, Isakov O, Shomron N, Wolf D, Hengel H, Mandelboim O
PLoS Pathog, 2014-02-27;10(2):e1003963.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
MiR-10b Downregulates the Stress-Induced Cell Surface Molecule MICB, a Critical Ligand for Cancer Cell Recognition by Natural Killer Cells.
Authors: Tsukerman P, Stern-Ginossar N, Gur C, Glasner A, Nachmani D, Bauman Y, Yamin R, Vitenshtein A, Stanietsky N, Bar-Mag T, Lankry D, Mandelboim O
Cancer Res, 2012-08-21;72(21):5463-72.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Cytotoxicity of CD56(bright) NK cells towards autologous activated CD4+ T cells is mediated through NKG2D, LFA-1 and TRAIL and dampened via CD94/NKG2A.
Authors: Nielsen N, Odum N, Urso B, Lanier LL, Spee P
PLoS ONE, 2012-02-22;7(2):e31959.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
DNAM-1 ligand expression on Ag-stimulated T lymphocytes is mediated by ROS-dependent activation of DNA-damage response: relevance for NK-T cell interaction.
Authors: Ardolino M, Zingoni A, Cerboni C, Cecere F, Soriani A, Iannitto ML, Santoni A
Blood, 2011-03-15;117(18):4778-86.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, Neutralization -
Thermal- and Oxidative Stress Causes Enhanced Release of NKG2D Ligand-Bearing Immunosuppressive Exosomes in Leukemia/Lymphoma T and B Cells.
Authors: Hedlund M, Nagaeva O, Kargl D, Baranov V, Mincheva-Nilsson L
PLoS ONE, 2011-02-25;6(2):e16899.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, Western Blot -
Rapid expansion and long-term persistence of elevated NK cell numbers in humans infected with hantavirus.
Authors: Bjorkstrom NK, Lindgren T, Stoltz M, Fauriat C, Braun M, Evander M, Michaelsson J, Malmberg KJ, Klingstrom J, Ahlm C, Ljunggren HG
J. Exp. Med., 2010-12-20;208(1):13-21.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Inhibition of NKG2D expression in NK cells by cytokines secreted in response to human cytomegalovirus infection.
Authors: Muntasell A, Magri G, Pende D, Angulo A, Lopez-Botet M
Blood, 2010-04-14;115(25):5170-9.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Post-translational modification of the NKG2D ligand RAET1G leads to cell surface expression of a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked isoform.
Authors: Ohashi M, Eagle RA, Trowsdale J
J. Biol. Chem., 2010-03-19;285(22):16408-15.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Obstructing shedding of the immunostimulatory MHC class I chain-related gene B prevents tumor formation.
Authors: Wu JD, Atteridge CL, Wang X, Seya T, Plymate SR
Clin. Cancer Res., 2009-01-15;15(2):632-40.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Detuning CD8+ T lymphocytes by down-regulation of the activating receptor NKG2D: role of NKG2D ligands released by activated T cells.
Authors: Cerboni C, Ardolino M, Santoni A, Zingoni A
Blood, 2009-01-05;113(13):2955-64.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Cutting edge: the metalloproteinase ADAM17/TNF-alpha-converting enzyme regulates proteolytic shedding of the MHC class I-related chain B protein.
Authors: Boutet P, Aguera-Gonzalez S, Atkinson S, Pennington CJ, Edwards DR, Murphy G, Reyburn HT, Vales-Gomez M
J. Immunol., 2009-01-01;182(1):49-53.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
Applications: ELISA Development -
NK cells recognize and lyse Ewing sarcoma cells through NKG2D and DNAM-1 receptor dependent pathways.
Authors: Verhoeven DH, de Hooge AS, Mooiman EC, Santos SJ, ten Dam MM, Gelderblom H, Melief CJ, Hogendoorn PC, Egeler RM, van Tol MJ, Schilham MW, Lankester AC
Mol. Immunol., 2008-07-26;45(15):3917-25.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Induction of MHC class I-related chain B (MICB) by 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine.
Authors: Tang KF, He CX, Zeng GL, Wu J, Song GB, Shi YS, Zhang WG, Huang AL, Steinle A, Ren H
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2008-04-04;370(4):578-83.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Cancer cells become susceptible to natural killer cell killing after exposure to histone deacetylase inhibitors due to glycogen synthase kinase-3-dependent expression of MHC class I-related chain A and B.
Authors: Skov S, Pedersen MT, Andresen L, Straten PT, Woetmann A, Odum N
Cancer Res., 2005-12-01;65(23):11136-45.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Reassessment of the Role of TSC, mTORC1 and MicroRNAs in Amino Acids-Meditated Translational Control of TOP mRNAs
Authors: Ilona Patursky-Polischuk, Judith Kasir, Rachel Miloslavski, Zvi Hayouka, Mirit Hausner-Hanochi, Miri Stolovich-Rain et al.
PLoS ONE
-
The HHV-6A Proteins U20 and U21 Target NKG2D Ligands to Escape Immune Recognition
Authors: Abigael Eva Chaouat, Barbara Seliger, Ofer Mandelboim, Dominik Schmiedel
Frontiers in Immunology
-
Anti-NKG2D single domain-based antibodies for the modulation of anti-tumor immune response
Authors: Adeline Raynaud, Klervi Desrumeaux, Laurent Vidard, Elise Termine, Daniel Baty, Patrick Chames et al.
OncoImmunology
-
Inosine pranobex enhances human NK cell cytotoxicity by inducing metabolic activation and NKG2D ligand expression
Authors: Michael T. McCarthy, Da Lin, Tomoyoshi Soga, Julie Adam, Christopher A. O'Callaghan
European Journal of Immunology
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human MICB Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human MICB Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: