Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Antibody Summary
Ser2-Glu466
Accession # P08670
*Small pack size (-SP) is supplied either lyophilized or as a 0.2 µm filtered solution in PBS.
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
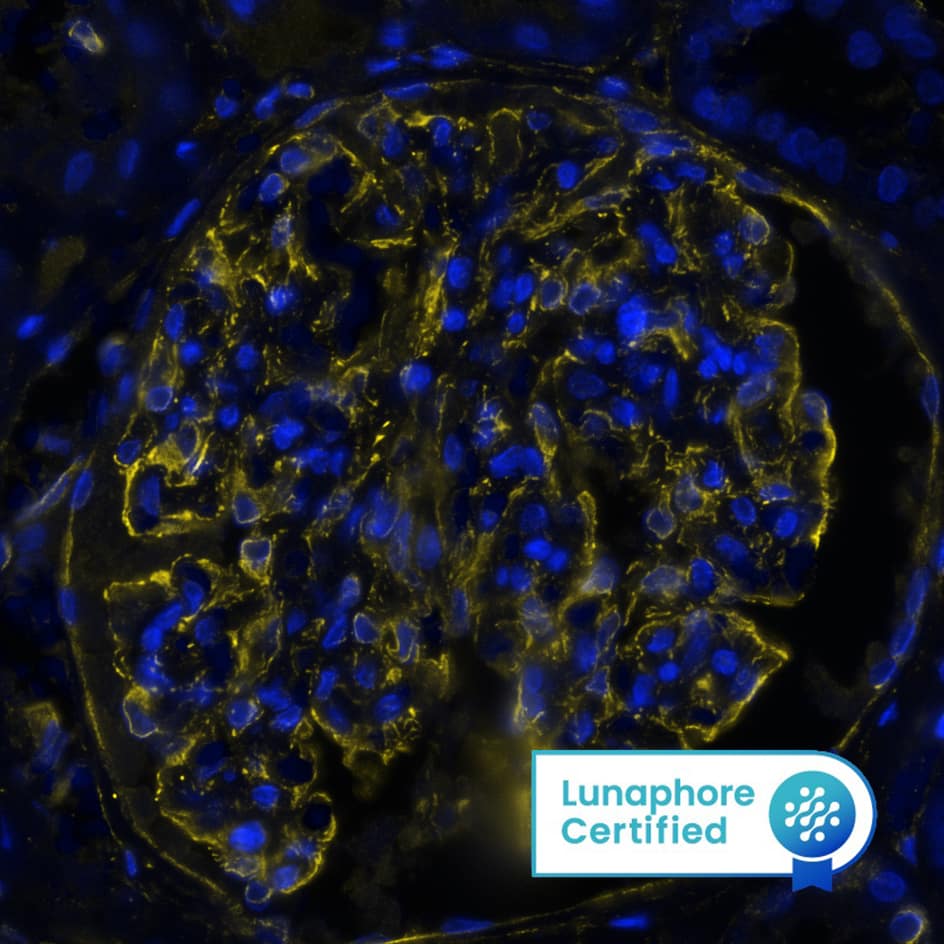 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Vimentin in Human Kidney via seqIF™ staining on COMET™ Vimentin was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human kidney using Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB21052) at 0.05 µg/mL at 37 ° Celsius for 4 minutes. Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue underwent an all-in-one dewaxing and antigen retrieval preprocessing using PreTreatment Module (PT Module) and Dewax and HIER Buffer H (pH 9; Epredia Catalog # TA-999-DHBH).Tissue was stained using the Alexa Fluor™ 647 Goat anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody at 1:200 at 37 ° Celsius for 2 minutes. (Yellow; Lunaphore Catalog # DR647MS) and counterstained with DAPI (blue; Lunaphore Catalog # DR100). Specific staining was localized to the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. Protocol available in COMET™ Panel Builder.
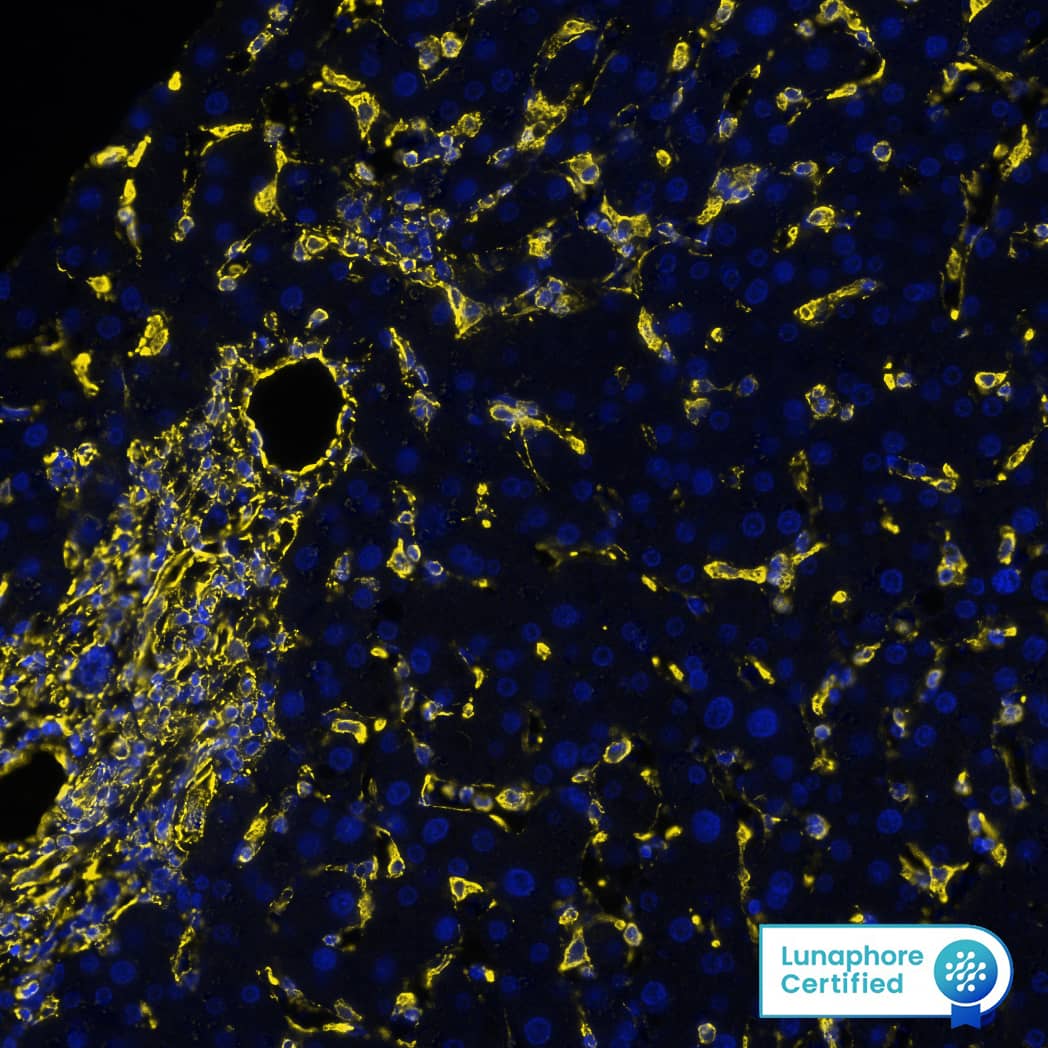 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Vimentin in Human Liver via seqIF™ staining on COMET™ Vimentin was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human liver using Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB21052) at 0.05 µg/mL at 37 ° Celsius for 4 minutes. Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue underwent an all-in-one dewaxing and antigen retrieval preprocessing using PreTreatment Module (PT Module) and Dewax and HIER Buffer H (pH 9; Epredia Catalog # TA-999-DHBH).Tissue was stained using the Alexa Fluor™ 647 Goat anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody at 1:200 at 37 ° Celsius for 2 minutes. (Yellow; Lunaphore Catalog # DR647MS) and counterstained with DAPI (blue; Lunaphore Catalog # DR100). Specific staining was localized to the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. Protocol available in COMET™ Panel Builder.
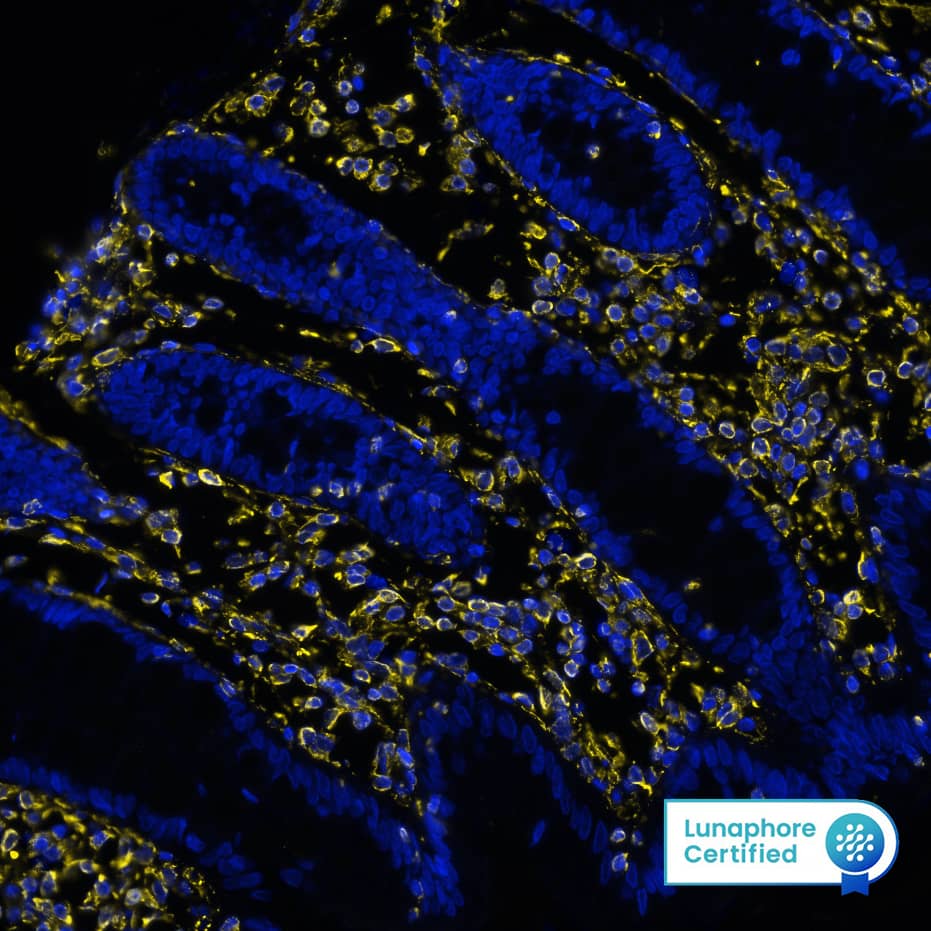 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Vimentin in Human Colon via seqIF™ staining on COMET™ Vimentin was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon using Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB21052) at 0.05 µg/mL at 37 ° Celsius for 4 minutes. Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue underwent an all-in-one dewaxing and antigen retrieval preprocessing using PreTreatment Module (PT Module) and Dewax and HIER Buffer H (pH 9; Epredia Catalog # TA-999-DHBH).Tissue was stained using the Alexa Fluor™ 647 Goat anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody at 1:200 at 37 ° Celsius for 2 minutes. (Yellow; Lunaphore Catalog # DR647MS) and counterstained with DAPI (blue; Lunaphore Catalog # DR100). Specific staining was localized to the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. Protocol available in COMET™ Panel Builder.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human, Mouse, and Rat Vimentin by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of Jurkat human acute T cell leukemia cell line, MEF mouse embryonic feeder cells, and NR8383 rat alveolar macrophage cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB21052) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF018). A specific band was detected for Vimentin at approximately 55 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 3.
 View Larger
View Larger
Vimentin in HeLa Human Cell Line. Vimentin was detected in immersion fixed HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cell line using Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB21052) at 8 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL007) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
Vimentin in Human Lymph Node. Vimentin was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human lymph node using Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB21052) at 5 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC001). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm in lymphocytes. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
 View Larger
View Larger
Vimentin Specificity is Shown by Immunocytochemistry in Knockout Cell Line. Vimentin was detected in immersion fixed K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line but is not detected in Vimentin knockout (KO) K562 Human Cell Line cell line using Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB21052) at 5 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 493-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (green; Catalog # NL009) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.
 View Larger
View Larger
Vimentin in Human Tonsil Using Dual RNAscope®ISH and IHC. Vimentin mRNA (red) and protein (green) was detected in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections of human tonsil probed with ACD RNAScope®Probe (Catalog # 310441) followed by immunohistochemistry using R&D Systems Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog# MAB21052) at 5ug/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte HRP Polymer Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # VC001). Tissue was stained using ACD RNAscope®2.5 HD Duplex Detection Reagents (Catalog # 322500).
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Vimentin
Vimentin is a 57 kDa class III intermediate filament (IF) protein that belongs to the intermediate filament family. It is the predominant IF in cells of mesenchymal origin such as vascular endothelium and blood cells (1-3). The human Vimentin cDNA encodes a 466 amino acid (aa) protein that contains head and tail regions with multiple regulatory Ser/Thr phosphorylation sites, and a central rod domain with three coiled-coil regions separated by linkers (1, 2). Human Vimentin shares 97-98% aa identity with mouse, rat, ovine, bovine, and canine Vimentin. Sixteen Vimentin coiled-coil dimers self-assemble to form intermediate (10-12 nm wide) filaments (4). These filaments then anneal longitudinally to form non-polarized fibers that support cell structure and withstand stress (4). IF fibers are highly dynamic, and half-life depends on the balance between kinase and phosphatase activity. For example, phosphorylation followed by dephosphorylation drives IF disintegration, followed by reorganization during mitosis (1, 5, 6). Interactions of head and tail domains link IFs with other structures such as actin and microtubule cytoskeletons (7). Vimentin is involved in positioning autophagosomes, lysosomes and the Golgi complex within the cell (8). It facilitates cell migration and motility by recycling internalized trailing edge integrins back to the cell surface at the leading edge (9-11). Vimentin helps maintain the lipid composition of cellular membranes, and caspase cleavage of Vimentin is a key event in apoptosis (8, 12). Phosphorylation promotes secretion of Vimentin by TNF-alpha -stimulated macrophages (13). Extracellular Vimentin has been shown to associate with several microbes, and appears to promote an antimicrobial oxidative burst (13, 14). Cell-associated Vimentin can also interact with NKp46 to recruit NK cells to tuberculosis-infected monocytes (15).
- Omary, M.B. et al. (2006) Trends Biochem. Sci. 31:383.
- Ivaska, J. et al. (2007) Exp. Cell Res. 313:2050.
- Ferrari, S. et al. (1986) Mol. Cell. Biol. 6:3614.
- Sokolova, A.V. et al. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:16206.
- Eriksson, J.E. et al. (2004) J. Cell Sci. 117:919.
- Li, Q-F. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:34716.
- Esue, O. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:30393.
- Styers, M.L. et al. (2005) Traffic 6:359.
- McInroy, L. and A. Maata (2007) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 360:109.
- Nieminen, M. et al. (2006) Nat. Cell Biol. 8:156.
- Ivaska, J. et al. (2005) EMBO J. 24:3834.
- Byun, Y. et al. (2001) Cell Death Differ. 8:443.
- Mor-Vaknin, N. et al. (2003) Nat. Cell Biol. 5:59.
- Zou, Y. et al. (2006) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 351:625.
- Garg, A. et al. (2006) J. Immunol. 177:6192.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
3
Citations: Showing 1 - 3
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Effects of Nitric Oxide on Bladder Detrusor Overactivity through the NRF2 and HIF-1? Pathways: A Rat Model Induced by Metabolic Syndrome and Ovarian Hormone Deficiency
Authors: Lin, HY;Lu, JH;Lin, RJ;Chueh, KS;Juan, TJ;Mao, JW;Lee, YC;Chuang, SM;Shen, MC;Sun, TW;Juan, YS;
International journal of molecular sciences
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Ameliorates Detrusor Hyperactivity with Impaired Contractility via Transient Potential Vanilloid Channels: A Rat Model for Ovarian Hormone Deficiency
Authors: Chueh, KS;Juan, TJ;Lu, JH;Wu, BN;Lin, RJ;Mao, JW;Lin, HY;Chuang, SM;Chang, CY;Shen, MC;Sun, TW;Juan, YS;
International journal of molecular sciences
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Nuclear soluble cGAS senses double-stranded DNA virus infection
Authors: Yakun Wu, Kun Song, Wenzhuo Hao, Jack Li, Lingyan Wang, Shitao Li
Communications Biology
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Antibody
Average Rating: 4.8 (Based on 4 Reviews)
Have you used Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:





