Human Pref-1/DLK1/FA1 Antibody Summary
Ala24-Pro297 with Arg248Pro and Lys295Ser substitutions
Accession # AAA75364
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
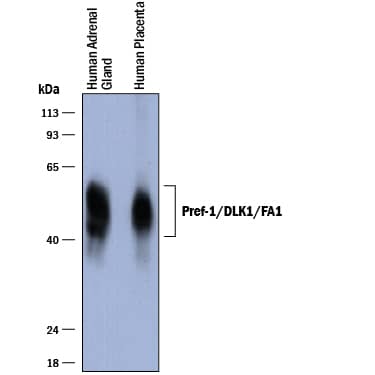
Detection of Human Pref‑1/DLK1/FA1 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of human adrenal gland tissue and human placenta tissue. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human Pref-1/DLK1/FA1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1144) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for Pref-1/DLK1/FA1 at approximately 45-60 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
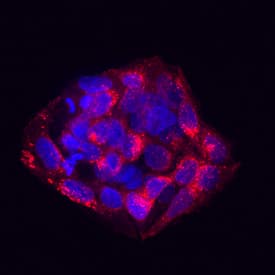
Pref‑1/DLK1/FA1 in HepG2 Human Cell Line. Pref-1/DLK1/FA1 was detected in immersion fixed HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line using Goat Anti-Human Pref-1/DLK1/FA1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1144) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
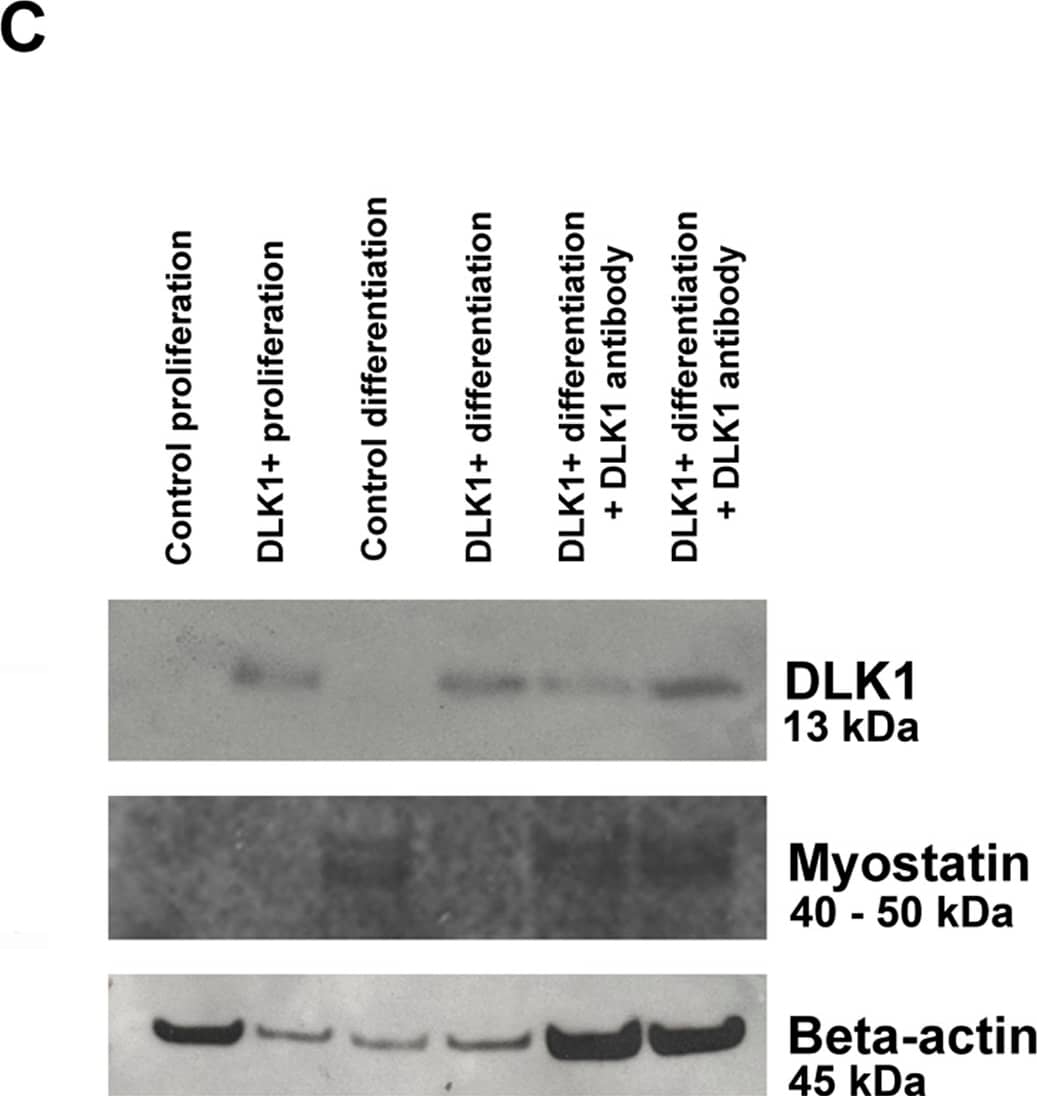
Detection of Mouse Pref-1/DLK1/FA1 by Western Blot Dlk1 inhibits myoblast differentiation in vitro.A: C2C12 cells were constructed to constitutively express full-length Dlk1 under control by the CMV promotor, DLK1-C2C12. Cell morphology and myogenic differentiation potential was analyzed by immunocytochemistry. Forced expression of Dlk1 resulted in inhibition of myogenic differentiation observed as no formation of myotubes, lack of myostatin expression and reduced Desmin staining compared to C2C12 parental control cells. Addition of Dlk1 antibody to the culture supernatant during differentiation reverted the effect of forced Dlk1 expression observed as a regained ability to form myotubes and express myogenin compared to control cells. Scalebars: 20 µm in all images. B: DLK1-C2C12 cells (DLK1) and C2C12 parental control cells were cultured under proliferating conditions for 3 days followed by differentiation for another 5 days. Cells were harvested and analyzed at 1, 3, 5, and 8 days in culture. The differentiation process was analyzed by qPCR of Dlk1, the myogenic markers Mef2a, Myf5, Myod, and Myogenin in addition to Myostatin, Follistatin, TGF beta 1, Smad7 and Decorin. All qPCR analyses were run in triplicates on duplicate analyses containing triplicate samples (n = 2 for each time point) and presented as relative expression levels with normalization to.Actb, Gusb, Pgk1, Gapdh and Tfrc as described in materials and methods. Black bars: DLK1+ cells; white bars: control cells. C: Dlk1 (13 kDa band) and myostatin (a double band corresponding to 40–50 kDa) protein level was analyzed with western blotting during proliferation and differentiation of DLK1-C2C12 and control cells. Dlk1 protein was only expressed by DLK1-C2C12 cells and not by control cells. Myostatin protein was expressed in control cells during differentiation but not during proliferation of either of the cells lines or during differentiation of DLK1-C2C12 cells. However, addition of Dlk1 antibody resulted in expression of myostatin by the DLK1-C2C12 cells during differentiation. Beta-actin (45 kDa) was used as control. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060692), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
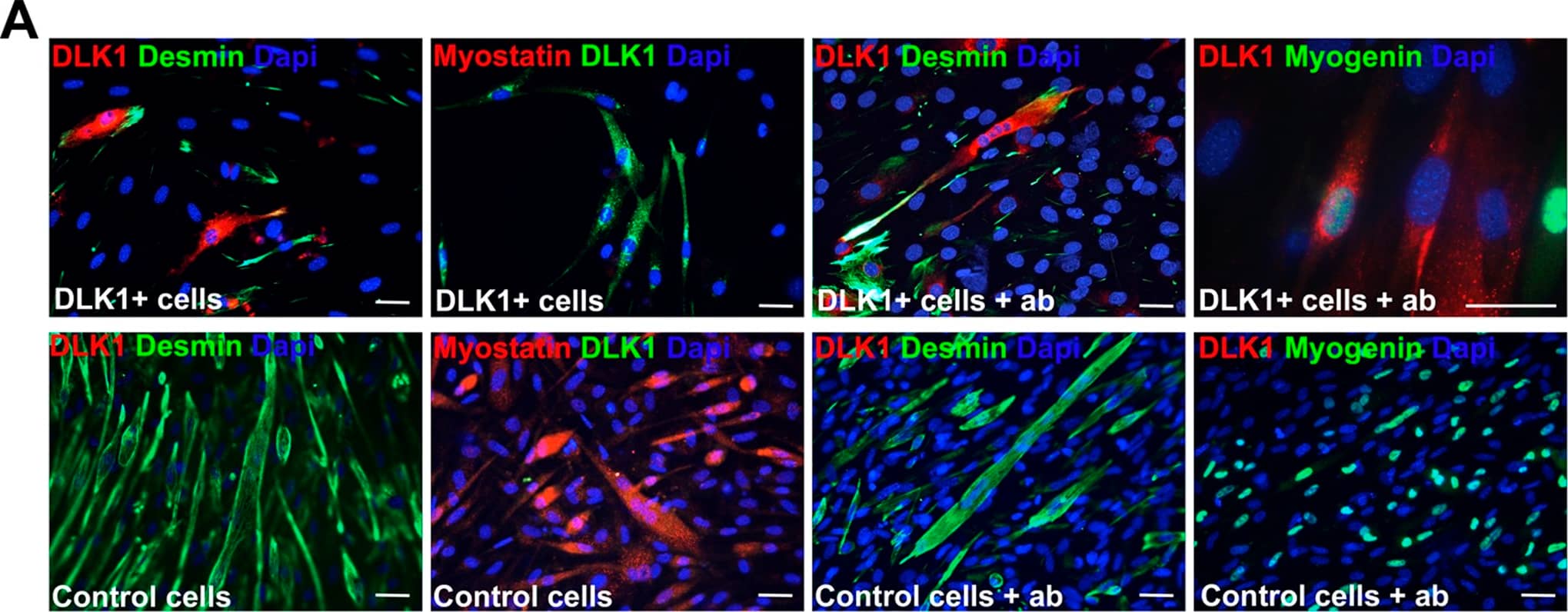
Detection of Mouse Pref-1/DLK1/FA1 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence Dlk1 inhibits myoblast differentiation in vitro.A: C2C12 cells were constructed to constitutively express full-length Dlk1 under control by the CMV promotor, DLK1-C2C12. Cell morphology and myogenic differentiation potential was analyzed by immunocytochemistry. Forced expression of Dlk1 resulted in inhibition of myogenic differentiation observed as no formation of myotubes, lack of myostatin expression and reduced Desmin staining compared to C2C12 parental control cells. Addition of Dlk1 antibody to the culture supernatant during differentiation reverted the effect of forced Dlk1 expression observed as a regained ability to form myotubes and express myogenin compared to control cells. Scalebars: 20 µm in all images. B: DLK1-C2C12 cells (DLK1) and C2C12 parental control cells were cultured under proliferating conditions for 3 days followed by differentiation for another 5 days. Cells were harvested and analyzed at 1, 3, 5, and 8 days in culture. The differentiation process was analyzed by qPCR of Dlk1, the myogenic markers Mef2a, Myf5, Myod, and Myogenin in addition to Myostatin, Follistatin, TGF beta 1, Smad7 and Decorin. All qPCR analyses were run in triplicates on duplicate analyses containing triplicate samples (n = 2 for each time point) and presented as relative expression levels with normalization to.Actb, Gusb, Pgk1, Gapdh and Tfrc as described in materials and methods. Black bars: DLK1+ cells; white bars: control cells. C: Dlk1 (13 kDa band) and myostatin (a double band corresponding to 40–50 kDa) protein level was analyzed with western blotting during proliferation and differentiation of DLK1-C2C12 and control cells. Dlk1 protein was only expressed by DLK1-C2C12 cells and not by control cells. Myostatin protein was expressed in control cells during differentiation but not during proliferation of either of the cells lines or during differentiation of DLK1-C2C12 cells. However, addition of Dlk1 antibody resulted in expression of myostatin by the DLK1-C2C12 cells during differentiation. Beta-actin (45 kDa) was used as control. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060692), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
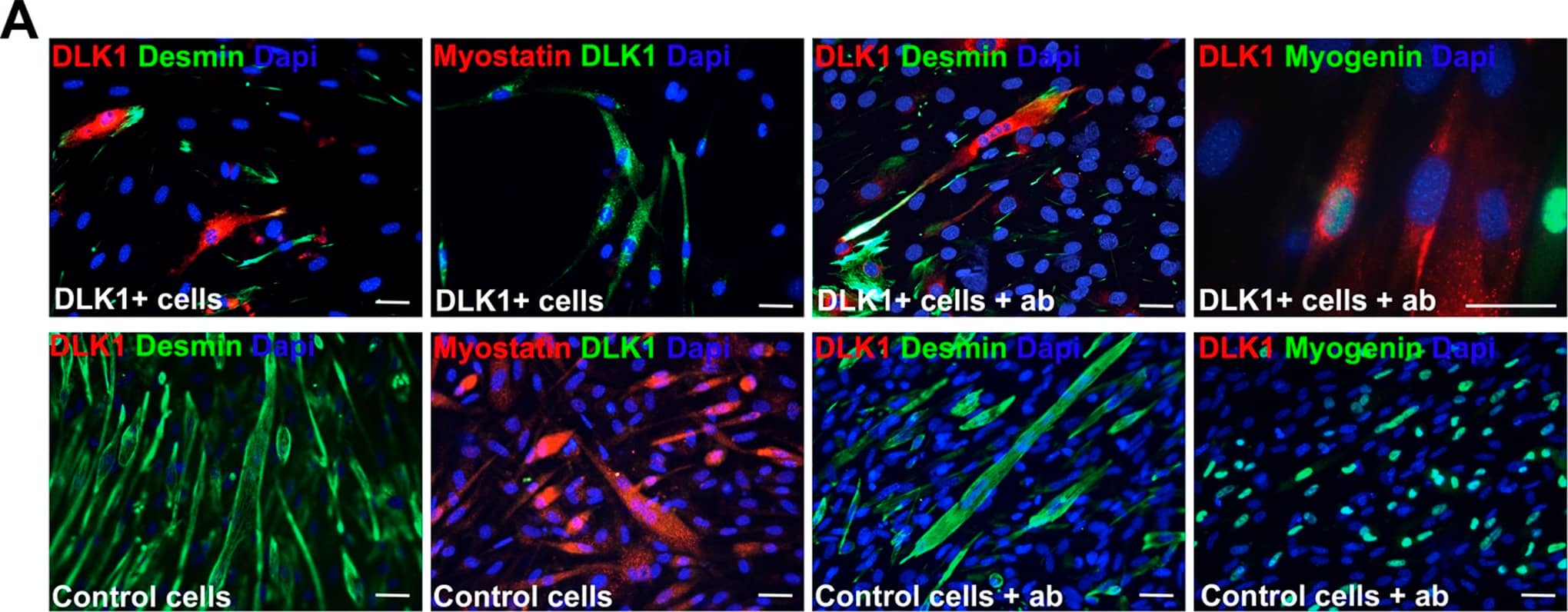
Detection of Mouse Pref-1/DLK1/FA1 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence Dlk1 inhibits myoblast differentiation in vitro.A: C2C12 cells were constructed to constitutively express full-length Dlk1 under control by the CMV promotor, DLK1-C2C12. Cell morphology and myogenic differentiation potential was analyzed by immunocytochemistry. Forced expression of Dlk1 resulted in inhibition of myogenic differentiation observed as no formation of myotubes, lack of myostatin expression and reduced Desmin staining compared to C2C12 parental control cells. Addition of Dlk1 antibody to the culture supernatant during differentiation reverted the effect of forced Dlk1 expression observed as a regained ability to form myotubes and express myogenin compared to control cells. Scalebars: 20 µm in all images. B: DLK1-C2C12 cells (DLK1) and C2C12 parental control cells were cultured under proliferating conditions for 3 days followed by differentiation for another 5 days. Cells were harvested and analyzed at 1, 3, 5, and 8 days in culture. The differentiation process was analyzed by qPCR of Dlk1, the myogenic markers Mef2a, Myf5, Myod, and Myogenin in addition to Myostatin, Follistatin, TGF beta 1, Smad7 and Decorin. All qPCR analyses were run in triplicates on duplicate analyses containing triplicate samples (n = 2 for each time point) and presented as relative expression levels with normalization to.Actb, Gusb, Pgk1, Gapdh and Tfrc as described in materials and methods. Black bars: DLK1+ cells; white bars: control cells. C: Dlk1 (13 kDa band) and myostatin (a double band corresponding to 40–50 kDa) protein level was analyzed with western blotting during proliferation and differentiation of DLK1-C2C12 and control cells. Dlk1 protein was only expressed by DLK1-C2C12 cells and not by control cells. Myostatin protein was expressed in control cells during differentiation but not during proliferation of either of the cells lines or during differentiation of DLK1-C2C12 cells. However, addition of Dlk1 antibody resulted in expression of myostatin by the DLK1-C2C12 cells during differentiation. Beta-actin (45 kDa) was used as control. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060692), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Pref-1/DLK1/FA1
Pref-1 (Preadipocyte factor 1; also DLK-1 and FA1) is a 58-65 kDa member of the Notch/Serrata/Delta family of proteins. It is expressed in prechondrocytes and preadipocytes and appears to block progenitor cell differentiation into mature cell lineages. Mature human Pref-1 is a 360 amino acid (aa) type I transmembrane N- and O-linked glycoprotein. It contains a 280 aa extracellular region (aa 24-303), a 24 aa transmembrane segment (aa 304-327), and a 56 aa cytoplasmic domain (aa 328-383). The extracellular region contains six EGF-like domains, and undergoes proteolytic cleavage to generate a bioactive 50 kDa fragment, plus three 25‑31 kDa fragments that show no activity. There are multiple potential splice variants. One shows a deletion of aa 229-301, a second possesses a six aa substitution for aa 1‑52, a third shows a deletion of aa 210-277, while a fourth contains a six aa substitution for aa # 207-383. Over aa 24-297, human Pref-1 shares 82% aa identity with mouse Pref-1.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human Pref-1/DLK1/FA1 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
3
Citations: Showing 1 - 3
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Dermal EZH2 orchestrates dermal differentiation and epidermal proliferation during murine skin development
Authors: Venkata Thulabandu, Timothy Nehila, James W. Ferguson, Radhika P. Atit
Developmental Biology
-
Distinct fibroblast lineages determine dermal architecture in skin development and repair.
Authors: Driskell R, Lichtenberger B, Hoste E, Kretzschmar K, Simons B, Charalambous M, Ferron S, Herault Y, Pavlovic G, Ferguson-Smith A, Watt F
Nature, 2013-12-12;504(7479):277-81.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr -
Delta-Like 1 Homolog (Dlk1): A Marker for Rhabdomyosarcomas Implicated in Skeletal Muscle Regeneration
Authors: Louise H. Jørgensen, Jeeva Sellathurai, Erica E. Davis, Tania Thedchanamoorthy, Rua W. A. Al-Bader, Charlotte H. Jensen et al.
PLoS ONE
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human Pref-1/DLK1/FA1 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human Pref-1/DLK1/FA1 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human Pref-1/DLK1/FA1 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image



