Human Thrombospondin-2 Antibody Summary
Gly19-Ile1172
Accession # P35442
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
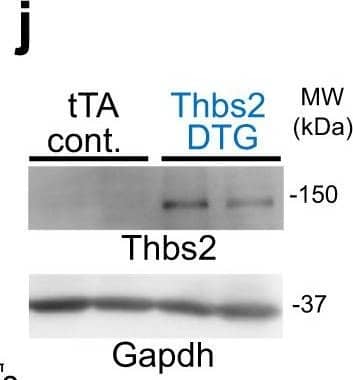
Detection of Mouse Thrombospondin-2 by Western Blot Endothelial cells and TGF beta are not affected by cardiac Thbs1 overexpression.a Quantification of capillary number per mm2 of tissue from histological sections of tTA cont. and Thbs1 DTG hearts stained with isolectin B4 at 6 weeks of age. b Quantification of endothelial cell proliferation as measured by EdU incorporation co-labeled with CD31 in tTA cont. and Thbs1 DTG hearts at 6 weeks of age. c Quantification of endothelial cell apoptosis detected by TUNEL staining co-labeled with isolectin B4 in tTA cont. and Thbs1 DTG hearts at 6 weeks of age. d ELISA-based quantification of total TGF beta and e active TGF beta in protein extracts from tTA cont. or Thbs1 DTG hearts at 6 weeks of age. f Schematic diagram of WT Thbs1 domain structure and the Thbs1 delta t1 mutant lacking the Thbs1 type-1 repeat domain region. g Representative western blot analysis for Thbs1 from total protein extracts (Total) and extracellular matrix (ECM) extracts from hearts of tTA cont., Thbs1 DTG, and Thbs1 DTG delta t1 mice at 4 weeks of age. Vinculin is presented as cytosolic control. Coomassie stained (Coom.) gel is shown as loading control. h VW/BW ratio at 4 weeks of age in the indicated groups of mice. *P < 0.0001 versus tTA cont.; statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons test. i Kaplan–Meier survival plot of tTA cont., Thbs1 DTG, and Thbs1 delta t1 DTG animals. *P < 0.0001 vs tTA cont. #P < 0.0001 vs Thbs1 DTG; both analyzed by two-tailed log-rank test. The same data from Fig. 2e are shown again here for tTA cont. and Thbs1 DTG mice (same strain and ages and sex ratio mix). j Representative western blots for Thbs2 and Gapdh as loading control, from heart protein extracts from tTA cont. and Thbs2 DTG mice at 8 weeks of age. k Heart weight (HW)/BW ratio, and l FS percentage at 8 weeks of age from tTA cont. and Thbs2 DTG mice. The number of biologically independent animals analyzed is indicated on each graph. Error bars are ±standard error of the mean. Source data are provided as a Source Data File. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34168130), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Thrombospondin-2
Thrombospondin-2 (TSP-2) is a 150 kDa calcium-binding protein that modulates cellular interactions with extracellular matrix. Thrombospondin-1 and -2 constitute subgroup A thrombospondin family members and form disulfide-linked homotrimers, whereas Thrombospondin-3, -4, and -5/COMP constitute subgroup B and form homopentamers (1-4). The human TSP-2 cDNA encodes a 1172 amino acid (aa) precursor that includes an 18 aa signal sequence followed by an N-terminal
heparin-binding domain, an oligomerization motif, one vWF-C domain, three TSP type-1 repeats, three EGF-like repeats, seven TSP type-3 repeats, and a lectin-like TSP C‑terminal domain (5). Human TSP-2 shares 88-90% aa sequence identity with bovine, mouse, and rat TSP-2. Within the TSP type-3 repeats and TSP C‑terminal domain, human TSP-2 shares 80% aa sequence identity with human TSP-1 and approximately 60% aa sequence identity with human TSP-3, -4, and -5/COMP. TSP-2 regulates collagen matrix formation by altering fibroblast behavior during development and in areas of tissue remodeling in the adult (6, 7). Trimerization of TSP-2 is required for the calcium-dependent cell attachment and spreading functions, while the heparin-binding domain is responsible for the destabilization of focal adhesion sites (8-10). The heparin-binding domain also mediates binding to Integrins alpha 3 beta 1 and alpha 6 beta 1 on microvascular endothelial cells (EC) and Integrin alpha 4 beta 1 on large blood vessel EC (11, 12). A fragment of TSP-2 (heparin-binding domain, oligomerization motif, and vWF-C domain) promotes EC survival, proliferation, and chemotaxis (11). Inclusion of the three TSP type-1 domains results in a molecule that inhibits VEGF-induced EC migration and vascular tube formation (13, 14). In vivo, full length TSP-2 blocks tumor angiogenesis and induces vascular EC apoptosis (13, 15). HPRG functions as an apparent decoy receptor by preventing interaction of TSP-2 with CD36 on macrophages and microvasculature EC (14). TSP-2 also binds MMP-2 and facilitates MMP-2 clearance by the scavenger receptor LRP (16).
- Elzie, C.A. and J.E. Murphy-Ullrich (2004) Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 36:1090.
- Armstrong, L.C. and P. Bornstein (2003) Matrix Biol. 22:63.
- Murphy-Ullrich, J.E. (2001) J. Clin. Invest. 107:785.
- Bornstein, P. and E.H. Sage (2002) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 14:608.
- LaBell, T.L. and P.H. Byers (1993) Genomics 17:225.
- Kyriakides, T.R. et al. (1998) J. Histochem. Cytochem. 46:1007.
- Kyriakides, T.R. et al. (1998) J. Cell Biol. 140:419.
- Anilkumar, N. et al. (2002) J. Cell Sci. 115:2357.
- Misenheimer, T.M. et al. (2003) Biochemistry 42:5125.
- Murphy-Ullrich, J.E. et al. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268:26784.
- Calzada, M.J. et al. (2004) Circ. Res. 94:462.
- Calzada, M.J. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:40679.
- Noh, Y-H. et al. (2003) J. Invest. Dermatol. 121:1536.
- Simantov, R. et al. (2005) Matrix Biol. 24:27.
- Streit, M. et al. (1999) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 96:14888.
- Yang, Z. et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:8403.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human Thrombospondin-2 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
3
Citations: Showing 1 - 3
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Thbs1 induces lethal cardiac atrophy through PERK-ATF4 regulated autophagy
Authors: D Vanhoutte, TG Schips, A Vo, KM Grimes, TA Baldwin, MJ Brody, F Accornero, MA Sargent, JD Molkentin
Nature Communications, 2021-06-24;12(1):3928.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Thrombospondin‑2 is upregulated in patients with aortic dissection and enhances angiotensin II‑induced smooth muscle cell apoptosis
Authors: Liping Qi, Kui Wu, Shutian Shi, Qingwei Ji, Huangtai Miao, Que Bin
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine
-
Thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) in primary myelofibrosis (PMF) — a megakaryocyte-derived biomarker which largely discriminates PMF from essential thrombocythemia
Authors: Michaela Muth, Bianca M. Engelhardt, Nicolaus Kröger, Kais Hussein, Jérôme Schlué, Guntram Büsche et al.
Annals of Hematology
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human Thrombospondin-2 Antibody
Average Rating: 4 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human Thrombospondin-2 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
Lanes in the WB are alternating between normal and diseased patients. Bands for thrombospondin-2 were resolved at the predicted MW; however, there was no difference between patients in this experiment. The results were clean, though, so I would consider using this for other applications in the future.



