Mouse IKK beta Antibody Summary
Val530-Asp757
Accession # O88351
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse IKK beta by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of BaF3 mouse pro-B cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.5 µg/mL of Rat Anti-Mouse IKK beta Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB7155) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Rat IgG Secondary Antibody. A specific band was detected for IKK beta at approximately 87 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
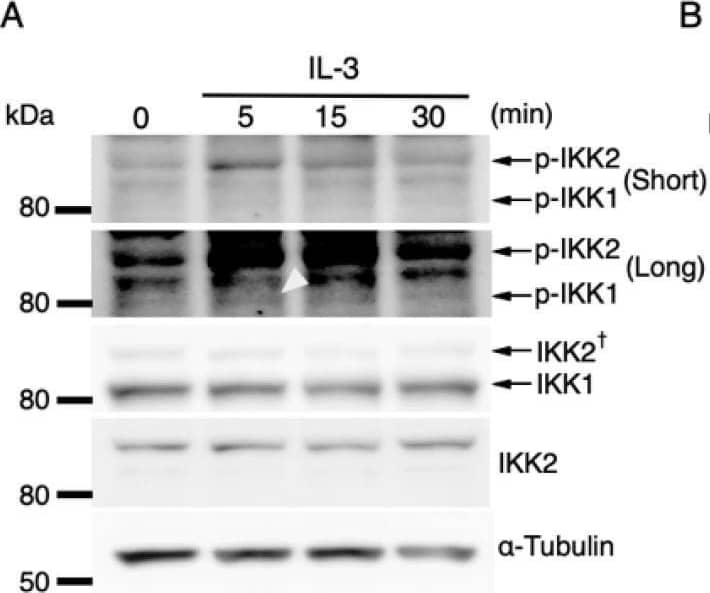
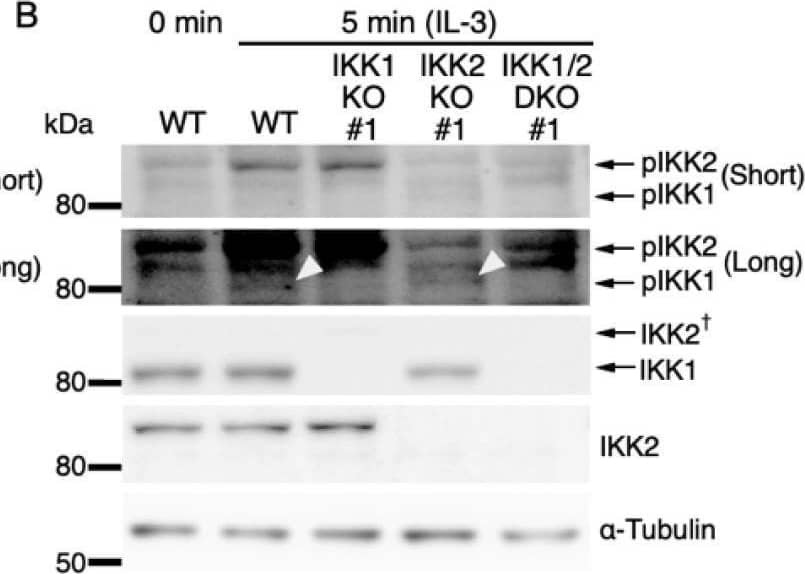
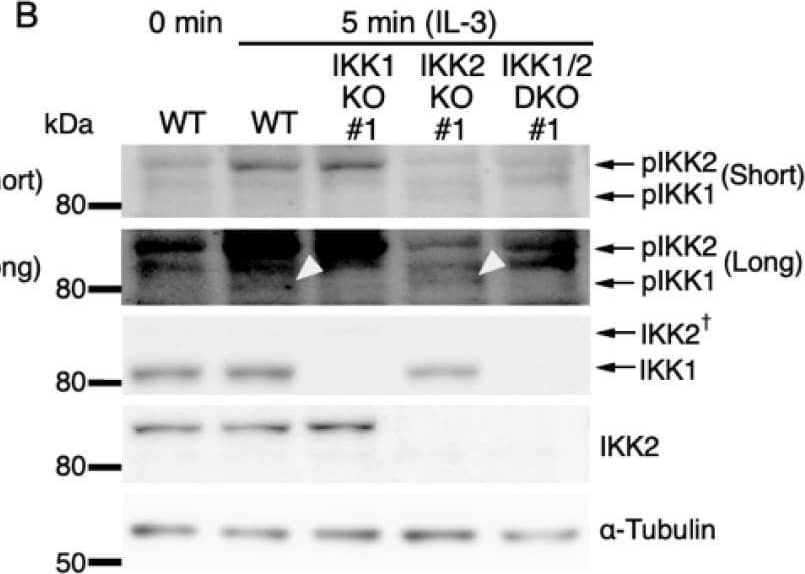
Detection of IKK beta by Western Blot IL-3-induced IKK activation was not associated with the degradation of I kappa B-alpha followed by nuclear translocation of p65. (A) Phosphorylation of IKKs after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 for the indicated times, and whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted using the indicated Abs. Long and short exposures to detect phosphorylated IKK1 and IKK2 are shown. An arrowhead indicates the band corresponding to phosphorylated IKK1 at 5 min after IL-3 stimulation. A dagger denotes the detection of IKK2 by potential cross-reactivity of the anti-IKK1 Ab. (B) Phosphorylation of IKKs in IKK KO cells after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 parental (WT), IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells were stimulated with IL-3 for 5 min. Immunoblot analysis was performed with whole-cell lysates using the indicated Abs. Arrowheads indicate the bands corresponding to phosphorylated IKK1. (C) Degradation of I kappa B-alpha by TNF-alpha but not by IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 or TNF-alpha for the indicated durations, and whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted using the indicated Abs. (D) Induction of nuclear translocation of p65 by TNF-alpha but not by IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 or TNF-alpha for the indicated times and immunoblotted with Abs to the cytosol marker alpha -tubulin and the nuclear marker fibrillarin. Long and short exposures to detect p65 are shown. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35563758), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of IKK beta by Western Blot IL-3-induced IKK activation was not associated with the degradation of I kappa B-alpha followed by nuclear translocation of p65. (A) Phosphorylation of IKKs after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 for the indicated times, and whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted using the indicated Abs. Long and short exposures to detect phosphorylated IKK1 and IKK2 are shown. An arrowhead indicates the band corresponding to phosphorylated IKK1 at 5 min after IL-3 stimulation. A dagger denotes the detection of IKK2 by potential cross-reactivity of the anti-IKK1 Ab. (B) Phosphorylation of IKKs in IKK KO cells after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 parental (WT), IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells were stimulated with IL-3 for 5 min. Immunoblot analysis was performed with whole-cell lysates using the indicated Abs. Arrowheads indicate the bands corresponding to phosphorylated IKK1. (C) Degradation of I kappa B-alpha by TNF-alpha but not by IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 or TNF-alpha for the indicated durations, and whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted using the indicated Abs. (D) Induction of nuclear translocation of p65 by TNF-alpha but not by IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 or TNF-alpha for the indicated times and immunoblotted with Abs to the cytosol marker alpha -tubulin and the nuclear marker fibrillarin. Long and short exposures to detect p65 are shown. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35563758), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
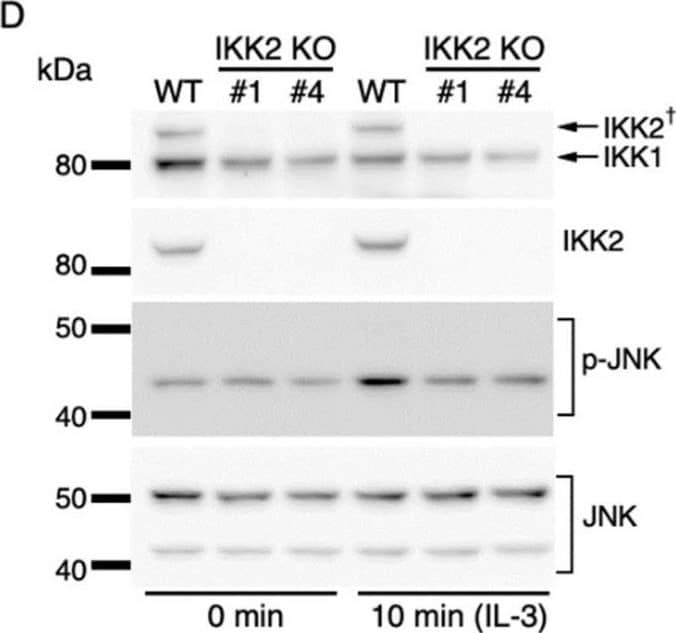
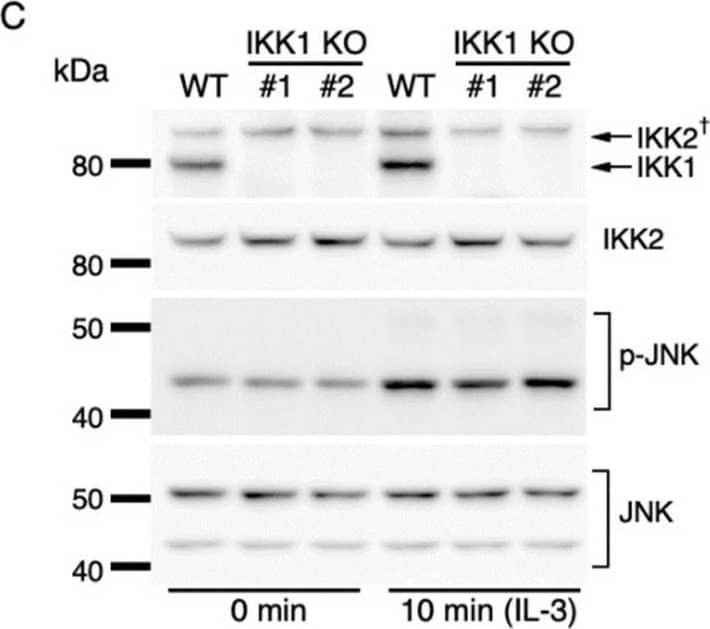
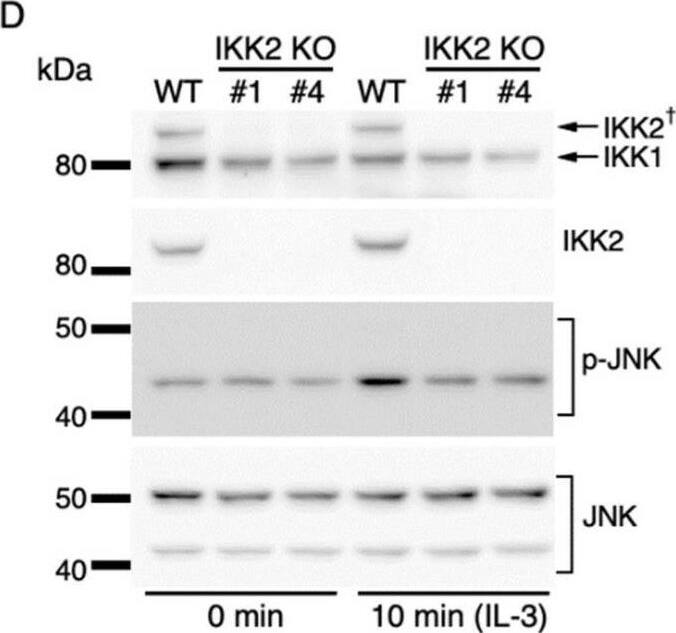
Detection of IKK beta by Western Blot IKK2-mediated activation of JNK regulates c-fos and c-jun expression. (A) Phosphorylation of JNK after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 for the indicated durations, and whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using the indicated Abs. (B–D) Phosphorylation of JNK in IKK KO cells after IL-3 stimulation. Ba/F3 parental (WT), IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells were stimulated with IL-3 after IL-3 deprivation for 6 h. Immunoblot analysis was performed with whole-cell lysates using the indicated Abs. (E) Expression levels of c-fos, c-jun, and c-myc mRNAs 20 and 40 min after IL-3 stimulation in the presence of JNK-IN-8 or DMSO. Ba/F3 cells were pre-incubated with 0.5 µM JNK-IN-8 or DMSO for 6 h and then stimulated with IL-3. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; n.s., not significant, as assessed by Mann-Whitney U-tests, for differences between JNK-IN-8-treated and control cells at each time point. Each dot represents the result from independent experiments (n = 5). Means are indicated by bars. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35563758), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of IKK beta by Western Blot IKK2-mediated activation of JNK regulates c-fos and c-jun expression. (A) Phosphorylation of JNK after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 for the indicated durations, and whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using the indicated Abs. (B–D) Phosphorylation of JNK in IKK KO cells after IL-3 stimulation. Ba/F3 parental (WT), IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells were stimulated with IL-3 after IL-3 deprivation for 6 h. Immunoblot analysis was performed with whole-cell lysates using the indicated Abs. (E) Expression levels of c-fos, c-jun, and c-myc mRNAs 20 and 40 min after IL-3 stimulation in the presence of JNK-IN-8 or DMSO. Ba/F3 cells were pre-incubated with 0.5 µM JNK-IN-8 or DMSO for 6 h and then stimulated with IL-3. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; n.s., not significant, as assessed by Mann-Whitney U-tests, for differences between JNK-IN-8-treated and control cells at each time point. Each dot represents the result from independent experiments (n = 5). Means are indicated by bars. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35563758), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of IKK beta by Western Blot IKK2-mediated activation of JNK regulates c-fos and c-jun expression. (A) Phosphorylation of JNK after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 for the indicated durations, and whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using the indicated Abs. (B–D) Phosphorylation of JNK in IKK KO cells after IL-3 stimulation. Ba/F3 parental (WT), IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells were stimulated with IL-3 after IL-3 deprivation for 6 h. Immunoblot analysis was performed with whole-cell lysates using the indicated Abs. (E) Expression levels of c-fos, c-jun, and c-myc mRNAs 20 and 40 min after IL-3 stimulation in the presence of JNK-IN-8 or DMSO. Ba/F3 cells were pre-incubated with 0.5 µM JNK-IN-8 or DMSO for 6 h and then stimulated with IL-3. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; n.s., not significant, as assessed by Mann-Whitney U-tests, for differences between JNK-IN-8-treated and control cells at each time point. Each dot represents the result from independent experiments (n = 5). Means are indicated by bars. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35563758), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
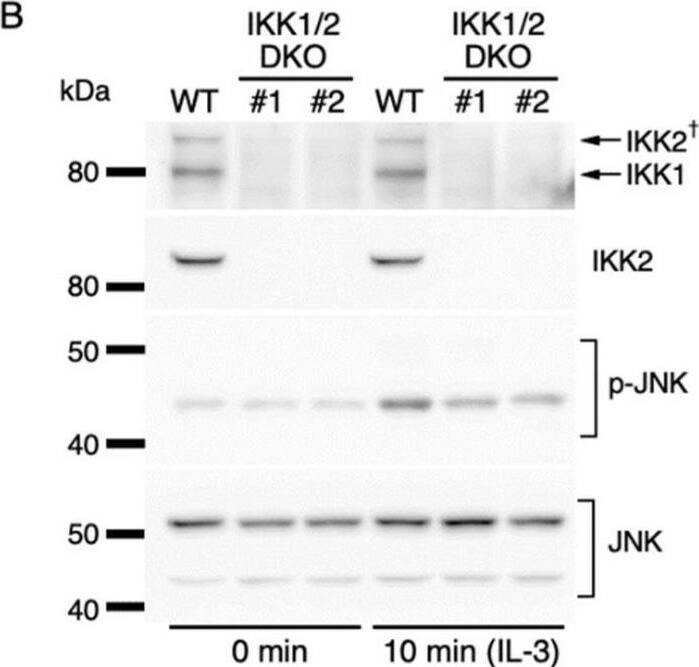
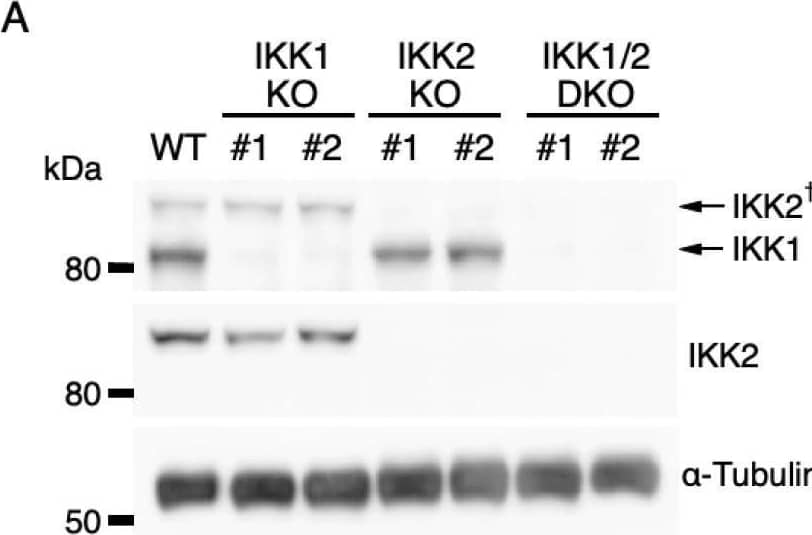
Detection of IKK beta by Western Blot Effects of IKK1 and/or IKK2 KO on IL-3-induced expression of IEGs. (A) IKK1 and IKK2 protein levels in Ba/F3 parental cells (WT) and CRISPR/Cas9-mediated IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells. Whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated Abs. A dagger denotes the detection of IKK2 by potential cross-reactivity of the anti-IKK1 Ab. (B–D) Relative levels of expression of c-fos (B), c-jun (C), and c-myc (D) mRNAs measured 20, 40, and 40 min, respectively, after IL-3 stimulation of Ba/F3 parental, IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells. * p < 0.05; n.s., not significant, as assessed by the Kruskal-Wallis test with the Steel-Dwass test. Each dot represents the result from independent experiments (n = 5). Means are indicated by bars. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35563758), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of IKK beta by Western Blot IKK2-mediated activation of JNK regulates c-fos and c-jun expression. (A) Phosphorylation of JNK after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 for the indicated durations, and whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using the indicated Abs. (B–D) Phosphorylation of JNK in IKK KO cells after IL-3 stimulation. Ba/F3 parental (WT), IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells were stimulated with IL-3 after IL-3 deprivation for 6 h. Immunoblot analysis was performed with whole-cell lysates using the indicated Abs. (E) Expression levels of c-fos, c-jun, and c-myc mRNAs 20 and 40 min after IL-3 stimulation in the presence of JNK-IN-8 or DMSO. Ba/F3 cells were pre-incubated with 0.5 µM JNK-IN-8 or DMSO for 6 h and then stimulated with IL-3. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; n.s., not significant, as assessed by Mann-Whitney U-tests, for differences between JNK-IN-8-treated and control cells at each time point. Each dot represents the result from independent experiments (n = 5). Means are indicated by bars. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35563758), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of IKK beta by Western Blot IL-3-induced IKK activation was not associated with the degradation of I kappa B-alpha followed by nuclear translocation of p65. (A) Phosphorylation of IKKs after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 for the indicated times, and whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted using the indicated Abs. Long and short exposures to detect phosphorylated IKK1 and IKK2 are shown. An arrowhead indicates the band corresponding to phosphorylated IKK1 at 5 min after IL-3 stimulation. A dagger denotes the detection of IKK2 by potential cross-reactivity of the anti-IKK1 Ab. (B) Phosphorylation of IKKs in IKK KO cells after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 parental (WT), IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells were stimulated with IL-3 for 5 min. Immunoblot analysis was performed with whole-cell lysates using the indicated Abs. Arrowheads indicate the bands corresponding to phosphorylated IKK1. (C) Degradation of I kappa B-alpha by TNF-alpha but not by IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 or TNF-alpha for the indicated durations, and whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted using the indicated Abs. (D) Induction of nuclear translocation of p65 by TNF-alpha but not by IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 or TNF-alpha for the indicated times and immunoblotted with Abs to the cytosol marker alpha -tubulin and the nuclear marker fibrillarin. Long and short exposures to detect p65 are shown. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35563758), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
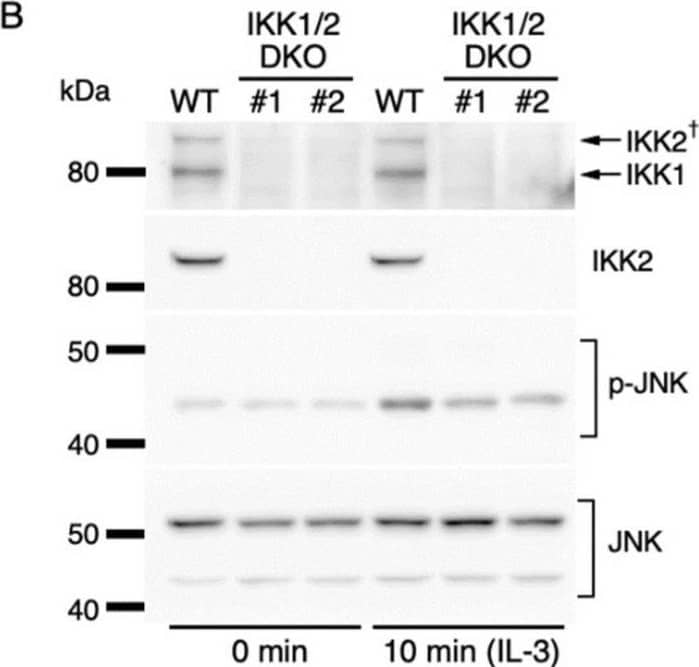
Detection of IKK beta by Western Blot IKK2-mediated activation of JNK regulates c-fos and c-jun expression. (A) Phosphorylation of JNK after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 for the indicated durations, and whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using the indicated Abs. (B–D) Phosphorylation of JNK in IKK KO cells after IL-3 stimulation. Ba/F3 parental (WT), IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells were stimulated with IL-3 after IL-3 deprivation for 6 h. Immunoblot analysis was performed with whole-cell lysates using the indicated Abs. (E) Expression levels of c-fos, c-jun, and c-myc mRNAs 20 and 40 min after IL-3 stimulation in the presence of JNK-IN-8 or DMSO. Ba/F3 cells were pre-incubated with 0.5 µM JNK-IN-8 or DMSO for 6 h and then stimulated with IL-3. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; n.s., not significant, as assessed by Mann-Whitney U-tests, for differences between JNK-IN-8-treated and control cells at each time point. Each dot represents the result from independent experiments (n = 5). Means are indicated by bars. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35563758), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
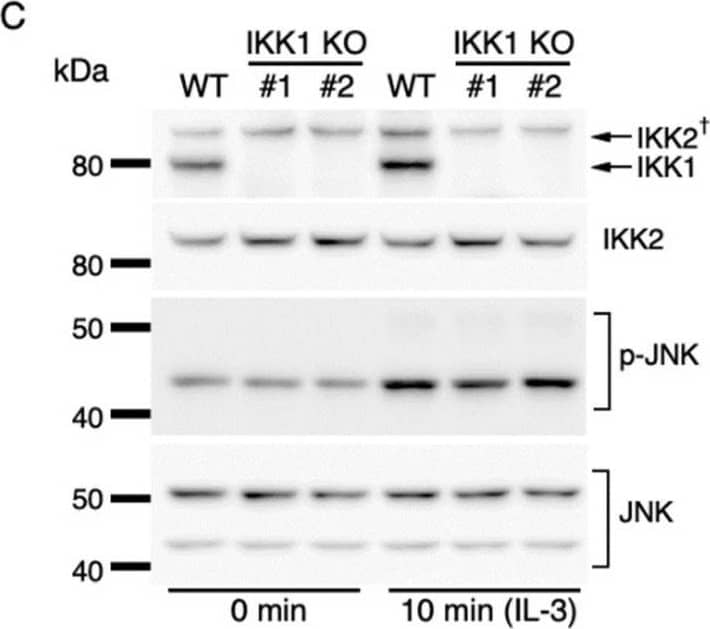
Detection of IKK beta by Western Blot IKK2-mediated activation of JNK regulates c-fos and c-jun expression. (A) Phosphorylation of JNK after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 for the indicated durations, and whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using the indicated Abs. (B–D) Phosphorylation of JNK in IKK KO cells after IL-3 stimulation. Ba/F3 parental (WT), IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells were stimulated with IL-3 after IL-3 deprivation for 6 h. Immunoblot analysis was performed with whole-cell lysates using the indicated Abs. (E) Expression levels of c-fos, c-jun, and c-myc mRNAs 20 and 40 min after IL-3 stimulation in the presence of JNK-IN-8 or DMSO. Ba/F3 cells were pre-incubated with 0.5 µM JNK-IN-8 or DMSO for 6 h and then stimulated with IL-3. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; n.s., not significant, as assessed by Mann-Whitney U-tests, for differences between JNK-IN-8-treated and control cells at each time point. Each dot represents the result from independent experiments (n = 5). Means are indicated by bars. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35563758), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
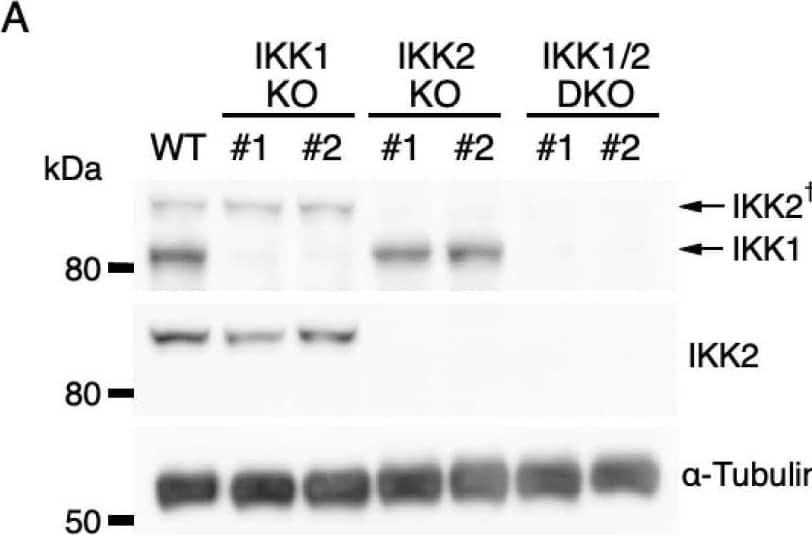
Detection of IKK beta by Western Blot Effects of IKK1 and/or IKK2 KO on IL-3-induced expression of IEGs. (A) IKK1 and IKK2 protein levels in Ba/F3 parental cells (WT) and CRISPR/Cas9-mediated IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells. Whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated Abs. A dagger denotes the detection of IKK2 by potential cross-reactivity of the anti-IKK1 Ab. (B–D) Relative levels of expression of c-fos (B), c-jun (C), and c-myc (D) mRNAs measured 20, 40, and 40 min, respectively, after IL-3 stimulation of Ba/F3 parental, IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells. * p < 0.05; n.s., not significant, as assessed by the Kruskal-Wallis test with the Steel-Dwass test. Each dot represents the result from independent experiments (n = 5). Means are indicated by bars. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35563758), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
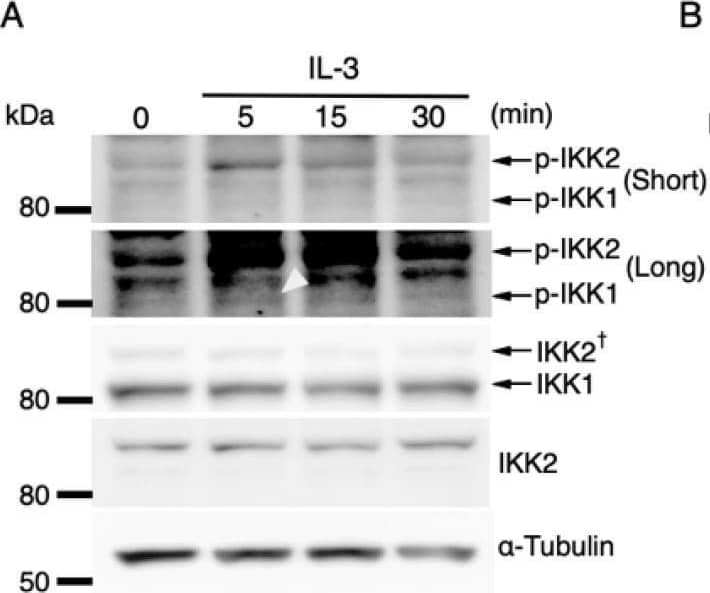
Detection of IKK beta by Western Blot IL-3-induced IKK activation was not associated with the degradation of I kappa B-alpha followed by nuclear translocation of p65. (A) Phosphorylation of IKKs after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 for the indicated times, and whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted using the indicated Abs. Long and short exposures to detect phosphorylated IKK1 and IKK2 are shown. An arrowhead indicates the band corresponding to phosphorylated IKK1 at 5 min after IL-3 stimulation. A dagger denotes the detection of IKK2 by potential cross-reactivity of the anti-IKK1 Ab. (B) Phosphorylation of IKKs in IKK KO cells after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 parental (WT), IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells were stimulated with IL-3 for 5 min. Immunoblot analysis was performed with whole-cell lysates using the indicated Abs. Arrowheads indicate the bands corresponding to phosphorylated IKK1. (C) Degradation of I kappa B-alpha by TNF-alpha but not by IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 or TNF-alpha for the indicated durations, and whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted using the indicated Abs. (D) Induction of nuclear translocation of p65 by TNF-alpha but not by IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 or TNF-alpha for the indicated times and immunoblotted with Abs to the cytosol marker alpha -tubulin and the nuclear marker fibrillarin. Long and short exposures to detect p65 are shown. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35563758), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: IKK beta
I kappa B kinase beta (IKK beta ) is also known as IKBKB and IKK2. The classical active IKK complex, composed of IKK alpha, IKK beta, and two forms of processed IKK gamma, phosphorylates and inactivates I kappa B, resulting in the release and nuclear translocation of active NF kappa B. Like IKK alpha, IKK beta contains kinase (aa 15-300), leucine zipper (aa 458‑479), and helix-loop-helix (aa 605-644) domains. NF kappa B-inducing kinase (NIK) phosphorylates and activates IKK alpha /IKK beta heterodimers. Within amino acids 530‑757, mouse IKKb shares 89% and 96% aa sequence identity with human and rat IKKb, respectively.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse IKK beta Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
6
Citations: Showing 1 - 6
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Mitochondrial permeabilization engages NF-kappa B-dependent anti-tumour activity under caspase deficiency
Authors: Evangelos Giampazolias, Barbara Zunino, Sandeep Dhayade, Florian Bock, Catherine Cloix, Kai Cao et al.
Nature Cell Biology
-
IL-3-Induced Immediate Expression of c-fos and c-jun Is Modulated by the IKK2-JNK Axis
Authors: H Fujita, T Fujita, H Fujii
Cells, 2022-04-25;11(9):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Uncaria tomentosa improves insulin sensitivity and inflammation in experimental NAFLD
Authors: LCC Araujo, KB Feitosa, GM Murata, IC Furigo, SA Teixeira, CF Lucena, LM Ribeiro, MN Muscará, SKP Costa, J Donato, S Bordin, R Curi, CRO Carvalho
Sci Rep, 2018-07-20;8(1):11013.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
IL6 mediated inflammatory loop reprograms normal to EMT(+) metastatic CSCs in pre-neoplastic liver of TGF? deficient ?2SP(+/-) mice
Authors: Abhisek Mitra
Hepatology, 2017-01-20;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Phosphorylation and linear ubiquitin direct A20 inhibition of inflammation.
Authors: Wertz I, Newton K, Seshasayee D, Kusam S, Lam C, Zhang J, Popovych N, Helgason E, Schoeffler A, Jeet S, Ramamoorthi N, Kategaya L, Newman R, Horikawa K, Dugger D, Sandoval W, Mukund S, Zindal A, Martin F, Quan C, Tom J, Fairbrother W, Townsend M, Warming S, DeVoss J, Liu J, Dueber E, Caplazi P, Lee W, Goodnow C, Balazs M, Yu K, Kolumam G, Dixit V
Nature, 2015-12-09;528(7582):370-5.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Epigenetic Roles of MLL Oncoproteins Are Dependent on NF-kappa B
Authors: Hsu-Ping Kuo, Zhong Wang, Dung-Fang Lee, Masayuki Iwasaki, Jesus Duque-Afonso, Stephen H.K. Wong et al.
Cancer Cell
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse IKK beta Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Mouse IKK beta Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Mouse IKK beta Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image









