Recombinant Human Dkk-2 Protein Summary
Product Specifications
Met1-Ile259
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
6628-DK
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS and EDTA with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
6628-DK/CF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS and EDTA. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Recombinant Human Wnt-3a (Catalog # 5036-WN) induces a dose responsive increase in Wnt reporter activity in HEK293 cells (green circles). Recombinant Human Dkk-2 (Catalog # 6628-DK) inhibits a constant dose of 500 ng/mL of Recombinant Human Wnt-3a. The ED50 for this effect is 50-300 ng/mL (orange circles).
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: Dkk-2
Dickkopf related protein 2 (Dkk-2) is a member of the Dickkopf family of secreted Wnt modulators (1-3). Dkk proteins contain a signal peptide and two conserved cysteine-rich domains that are separated by a linker region. The second cysteine-rich domain mediates Dkk-2 binding activities, and its interaction with beta -propeller domains of LRP‑5/6 has been mapped (2-4, 7). The 226 amino acid (aa), ~35 kDa mature human Dkk-2 shares 96%, 97%, 97%, 97%, 97% and 98% aa identity with mouse, rat, canine, equine, bovine and porcine Dkk-2, respectively. Mouse Dkk-2 can activate the canonical Wnt signaling pathway in Xenopus embryos, showing evolutionary conservation of function (5). Dkk proteins modify Wnt engagement of a receptor complex composed of a Frizzled protein and a low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein, either LRP‑5 or LRP‑6 (3). Also, Kremen-1 and Kremen-2 are high affinity receptors for Dkk-1 and Dkk-2 (9). When LRP‑6 is over-expressed, direct high‑affinity binding of Dkk-2 to LRP can enhance canonical Wnt signaling (6-8). However, when Dkk‑2 and LRP‑6 form a ternary complex with Kremen‑2, Wnt signaling is inhibited due to internalization of Dkk‑2/LRP6/Krm2 complexes (9, 10). Thus, depending on the cellular context, Dkk‑2 can either activate or inhibit canonical Wnt signaling (3). In contrast, binding of Dkk-1 or Dkk-4 to LRP is consistently antagonistic (3). Dkk proteins are expressed in mesenchymal tissues and control epithelial transformations. Dkk-2 expression has been studied most in bone and eye, although it is expressed as early as periimplantation in mice (11). Mouse Dkk-1 or Dkk-2 deficiencies have opposite effects on bone homeostasis, despite down‑regulating Wnt antagonism in both cases (12, 13). Dkk-2 expression is induced by Wnts in bone, and is thought to enhance bone density by promoting terminal differentiation of osteoblasts and mineral deposition (12). In contrast, Dkk-1 negatively regulates late osteoblast proliferation, which limits bone density (13). Dkk-2-deficient mice are blind, exhibiting faulty differentiation of corneal epithelium and ectopic blood vessels in the periocular mesenchyme (14, 15).
- Monaghan, A.P. et al. (1999) Mech. Dev. 87:45.
- Krupnik, V.E. et al. (1999) Gene 238:301.
- Niehrs, C. (2006) Oncogene 25:7469.
- Chen, L. et al. (2008) J. Biol. Chem. 283:23364.
- Wu, W. et al. (2000) Current Biol. 10:1611.
- Mao, B. et al. (2001) Nature 411:321.
- Li, L. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:5977.
- Brott, B. and S.Y. Sokol (2002) Mol. Cell. Biol. 22:6100.
- Mao, B. et al. (2002) Nature 417:664.
- Mao, B. and C. Niehrs (2003) Gene 302:179.
- Zhang, Y. et al. (2009) J. Reprod. Dev. 55:17.
- Li, X. et al. (2005) Nat. Genet. 37:945.
- van der Horst, G. et al. (2005) J. Bone Miner. Res. 20:1867.
- Mukhopadhyay, M. et al. (2006) Development 133:2149.
- Gage, P.J. et al. (2008) Dev. Biol. 317:310.
Citations for Recombinant Human Dkk-2 Protein
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
4
Citations: Showing 1 - 4
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Improvement of an Effective Protocol for Directed Differentiation of Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Adult Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Corneal Endothelial Cells
Authors: CM Marta, M Adrian, FD Jorge, AM Francisco, MP De Miguel
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021-11-05;22(21):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Pluripotent stem cell-derived corneal endothelial cells as an alternative to donor corneal endothelium in keratoplasty
Authors: M Ali, SY Khan, JD Gottsch, EK Hutchinson, A Khan, SA Riazuddin
Stem Cell Reports, 2021-08-05;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Generation and Proteome Profiling of PBMC-Originated, iPSC-Derived Corneal Endothelial Cells
Authors: M Ali, SY Khan, S Vasanth, MR Ahmed, R Chen, CH Na, JJ Thomson, C Qiu, JD Gottsch, SA Riazuddin
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 2018-05-01;59(6):2437-2444.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Widespread potential for growth-factor-driven resistance to anticancer kinase inhibitors.
Authors: Wilson TR, Fridlyand J, Yan Y, Penuel E, Burton L, Chan E, Peng J, Lin E, Wang Y, Sosman J, Ribas A, Li J, Moffat J, Sutherlin DP, Koeppen H, Merchant M, Neve R, Settleman J
Nature, 2012-07-26;487(7408):505-9.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human Dkk-2 Protein
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Recombinant Human Dkk-2 Protein?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
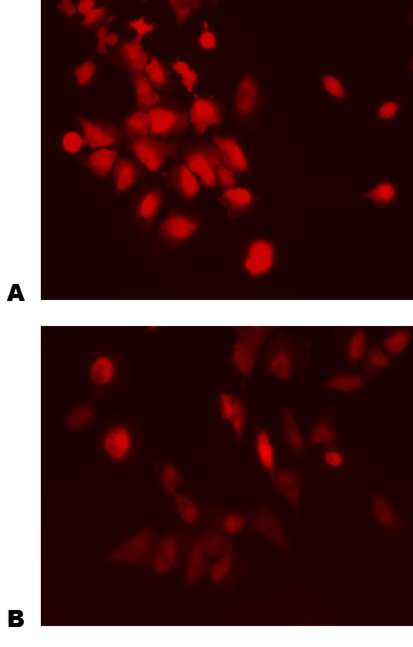
Immunofluorescent staining of MDA-MB-231 cells using Wnt5a antibody before (A) and after (B) treatment with Wnt-inhibitor DKK-2 protein (#6628-DK) for 72 hours. Primary antibody 1:50, secondary antibody 1:100.