Recombinant Human GDF-15 (E. coli-expressed) Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
Ala197-Ile308
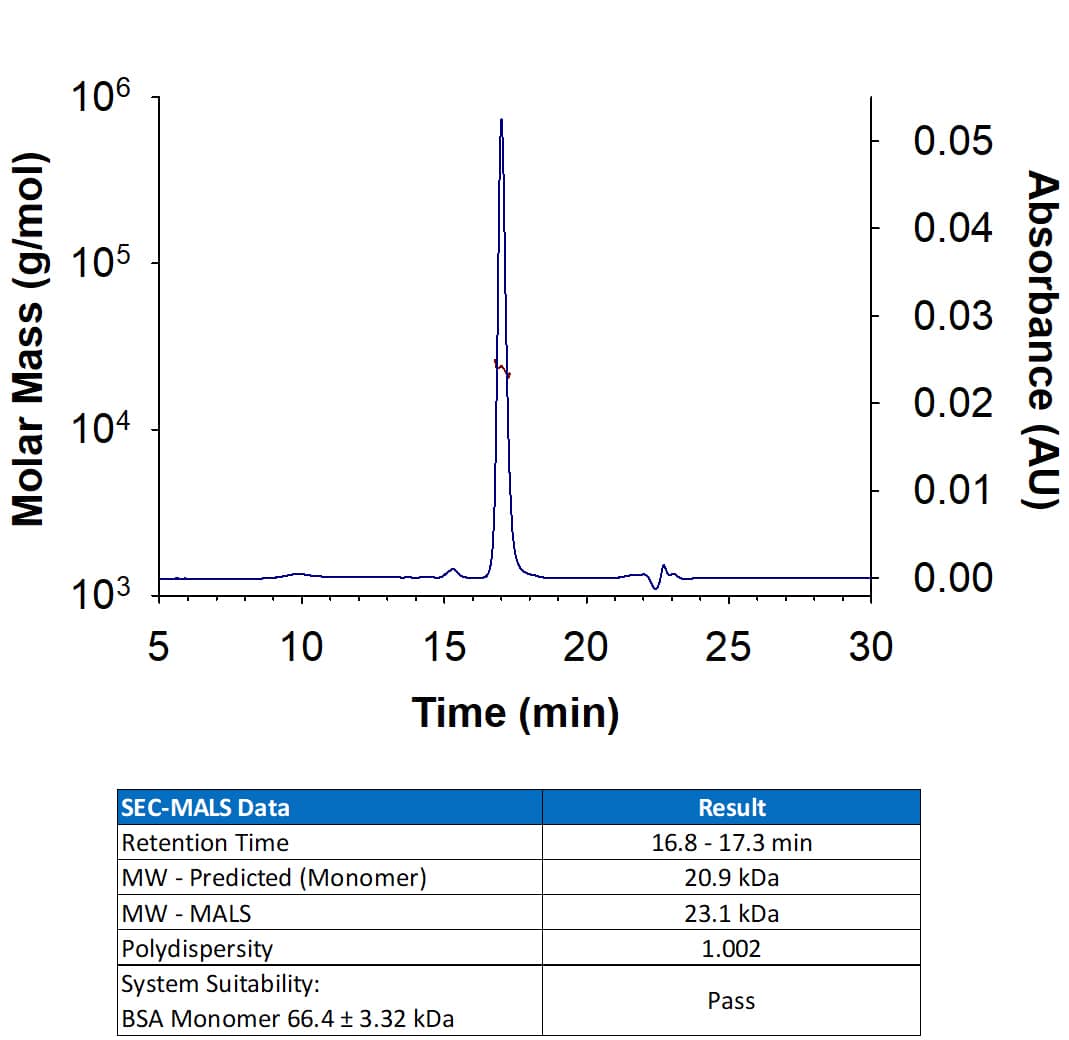
Analysis
Customers also Viewed
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
9279-GD
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in HCl. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 250 μg/mL in 4 mM HCl. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
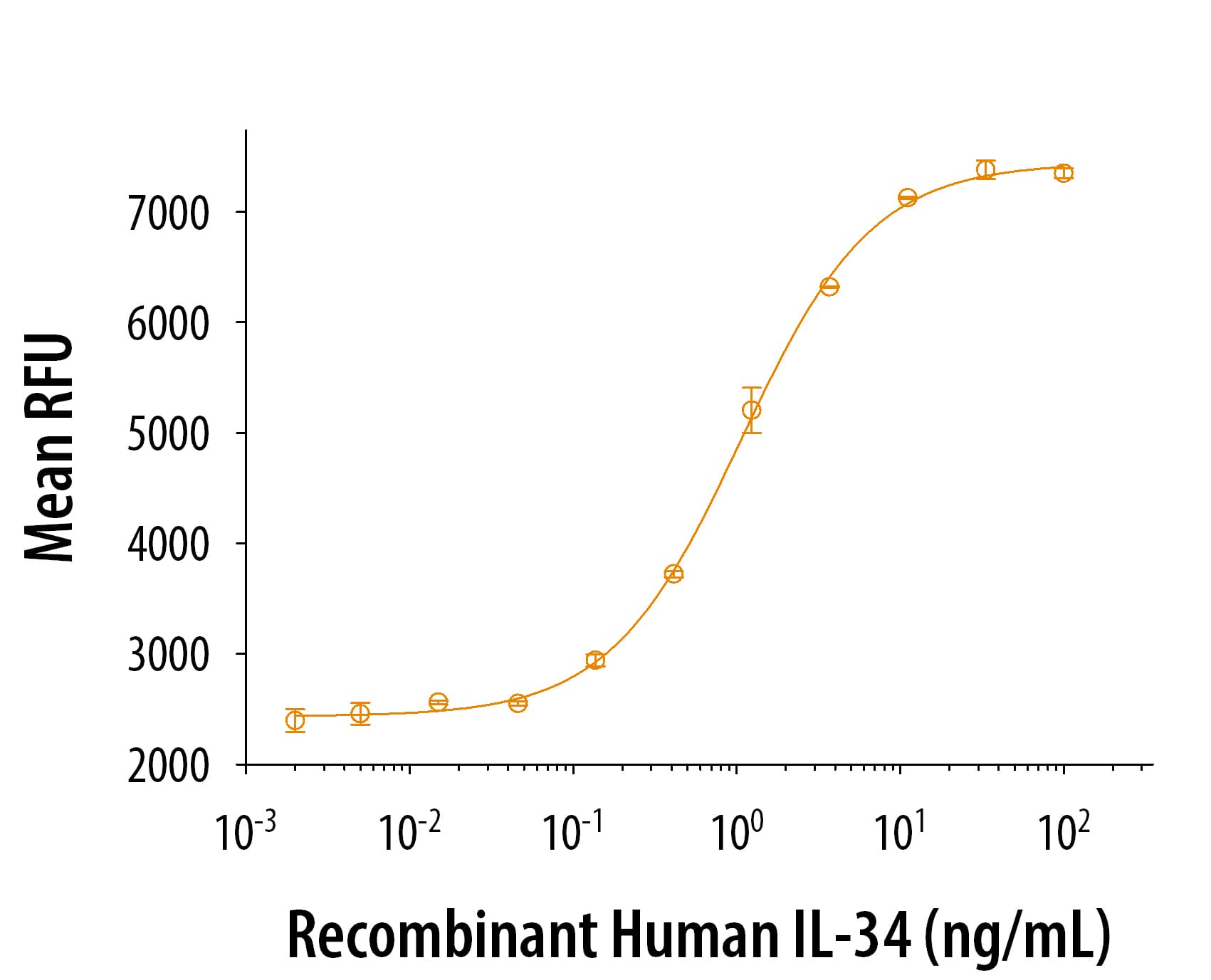
In a functional ELISA, Recombinant Human GDF-15 (Catalog # 9279-GD) binds to Recombinant Human GFR alpha -like Fc Chimera (9697-GR) with an ED50 of 0.0500-0.500 ng/mL.
 View Larger
View Larger
Recombinant Human GDF-15 (Catalog # 9270-GD) activates SRE-SEAP reporter in HEK293 human embryonic kidney cells transfected with human c-Ret and human GFRAL.
Background: GDF-15
Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF-15), also called Macrophage Inhibitory Cytokine 1 (MIC-1), Placental Transforming Growth Factor beta, Prostate-derived Factor, and Placental Bone Morphogenetic Protein, is a divergent member of the TGF-beta superfamily (1, 2). Human GDF-15 shares 66% and 68% amino acid sequence identity with the rat and mouse proteins, respectively (3). GDF-15 is highly expressed in placenta and brain, and it is expressed at lower levels in kidney, pancreas, prostate, and colon. Similar to other TGF-beta family proteins, the GDF-15 proprotein is cleaved at a dibasic cleavage site (RxxR) to release the mature protein (4). The C-terminal domain of GDF-15 contains seven characteristic conserved cysteine residues necessary for the formation of the cysteine knot and the single interchain disulfide bond (5). Biologically active GDF-15 is a disulfide-linked homodimer of the mature protein and signals through the heterodimeric receptor composed of TGF-beta RI/ALK-5 and TGF-beta RII (6). GDF-15 has been shown to have various functions, including inhibition of TNF-alpha production from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages and the induction of cartilage formation (1, 5). GDF-15 also promotes neuronal survival, and hypothalamic expression of GDF-15 causes appetite suppression via modulation of Neuropeptide Y and Pro-opiomelanocortin levels (7-9). GDF-15 is cardioprotective via inhibition of platelet activation, limiting atherosclerosis, inhibiting CXCL1-induced neutrophil adhesion, regulating angiogenesis, and inhibiting norepinephrine-induced mycardial hypertrophy (6, 10-15).
- Bootcov, M.R. et al. (1997) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:11514.
- Unsicker, K. et al. (2013) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 24:373.
- Bottner, M. et al. (1999) Gene 237:105.
- Fairlie, W.D. et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:16911.
- Paralkar, V.M. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273:13760.
- Artz, A. et al. (2016) Blood 128:529.
- Johnen, H. et al. (2007) Nat. Med. 13:1333.
- Strelau, J. et al. (2000) J. Neurosci. 20:8597.
- Strelau, J. et al. (2009) J. Neurosci. 29:13640.
- Whitson, R.J. et al. (2013) J. Cell. Biochem. 114:1424.
- Rossaint, J. et al. (2013) J. Thromb. Haemost. 11:335.
- Song, H. et al. (2012) Mol. Biol. Rep. 39:4017.
- Preusch, M.R. et al. (2013) Eur. J. Med. Res. 18:19.
- Kempf, T. et al. (2011) Nat. Med. 17:581.
- Xu, X.-Y. et al. (2014) J. Biol. Chem. 289:10084.
Citations for Recombinant Human GDF-15 (E. coli-expressed) Protein, CF
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
4
Citations: Showing 1 - 4
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Brainstem BDNF neurons are downstream of GFRAL/GLP1R signalling
Authors: Feetham, CH;Collabolletta, V;Worth, AA;Shoop, R;Groom, S;Harding, C;Boutagouga Boudjadja, M;Coskun, T;Emmerson, PJ;D'Agostino, G;Luckman, SM;
Nature communications
Species: Mouse, Transgenic Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In vivo assay -
GDF15 Promotes the Osteogenic Cell Fate of Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts, thus Affecting Their Mechanobiological Response
Authors: Lösch, L;Stemmler, A;Fischer, A;Steinmetz, J;Schuldt, L;Hennig, CL;Symmank, J;Jacobs, C;
International journal of molecular sciences
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Growth differentiation factor 15 induces cisplatin resistance through upregulation of xCT expression and glutathione synthesis in gastric cancer
Authors: Wang, SF;Chang, YL;Fang, WL;Li, AF;Chen, CF;Yeh, TS;Hung, GY;Huang, KH;Lee, HC;
Cancer science
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Targeting SLC7A11 improves efferocytosis by dendritic cells and wound healing in diabetes
Authors: S Maschalidi, P Mehrotra, BN Keçeli, HKL De Cleene, K Lecomte, R Van der Cr, P Janssen, J Pinney, G van Loo, D Elewaut, A Massie, E Hoste, KS Ravichandr
Nature, 2022-05-25;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In Vivo
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human GDF-15 (E. coli-expressed) Protein, CF
Average Rating: 4.5 (Based on 2 Reviews)
Have you used Recombinant Human GDF-15 (E. coli-expressed) Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: