Recombinant Human IDO Protein, CF
Recombinant Human IDO Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
| M | HHHHHH | Human IDO (Ala2-Gly403) Accession # P14902 |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | |
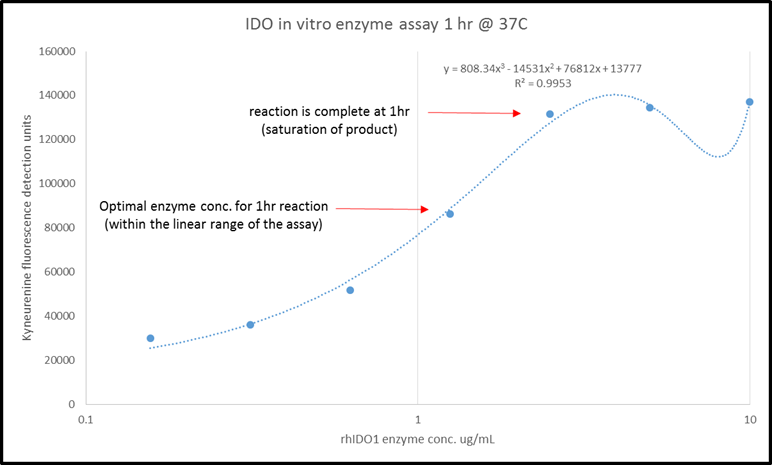
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
6030-AO
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Sodium Acetate, NaCl and Glycerol. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with dry ice or equivalent. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Assay Procedure
- Assay Buffer: 50 mM MES, pH 6.5
- 0.405 M Tris, pH 8.0
- Recombinant Human Indoleamine 2,3‑dioxygenase/IDO (rhIDO) (Catalog # 6030-AO)
- Ascorbic Acid (Sigma, Catalog # 255564), 500 mM stock in deionized water
- L-Tryptophan (Sigma, Catalog # T0254), 10 mM stock in deionized water
- Catalase (Sigma, Catalog # C30), 100,000 units/mL stock in Assay Buffer
- Methylene Blue (Sigma, Catalog # 28514), 10 mM stock in deionized water
- 96-well Clear Plate (Costar, Catalog # 92592)
- Plate Reader (Model: SpectraMax Plus by Molecular Devices) or equivalent
- Prepare the Substrate Mixture.
- Dilute Ascorbic Acid to 80 mM in 0.405 M Tris, pH 8.0.
- Prepare a mixture of 800 μM L-Tryptophan, 9000 units/mL catalase, and 40 μM Methyene Blue in Assay Buffer.
- Mix equal volumes of 1a and 1b for final concentrations of 40 mM Ascorbic Acid, 400 μM L-Tryptophan, 4500 units/mL Catalase, and 20 μM Methylene Blue.
- Dilute rhIDO to 16 ng/μL in Assay Buffer.
- Load into a plate 50 μL of 16 ng/μL rhIDO, and start the reaction by adding 50 μL of Substrate Mixture.
- Include a Substrate Blank containing 50 μL of Assay Buffer and 50 μL of Substrate Mixture.
- Read at 321 nm in kinetic mode for 5 minutes.
|
Specific Activity (pmol/min/µg) = |
Adjusted Vmax* (OD/min) x well volume (L) x 1012 pmol/mol |
| ext. coeff** (M-1cm-1) x path corr.*** (cm) x amount of enzyme (µg) |
*Adjusted for Substrate Blank
**Using the extinction coefficient 3750 M-1cm-1
***Using the path correction 0.32 cm
Note: the output of many spectrophotometers is in mOD. Per Well:
- rhIDO: 0.800 µg
- Ascorbic Acid: 20 mM
- L-Tryptophan: 200 μM
- Catalase: 225 units
- Methylene Blue: 10 µM
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase/IDO
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is a heme-containing intracellular dioxygenase catalyzing the degradation of the essential amino acid L-tryptophan to N‑formyl‑kynurenine (1). This degradation is the first and rate-limiting step of the L-kynurenine pathway (2). IDO is widely expressed in dendritic cells, macrophages, microglia, eosinophils, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and most tumor cells. In immune cells, its expression is mainly induced by cytokines such as IFN‑ gamma, IFN‑ alpha, IFN‑ beta, and IL‑10. IDO has an antimicrobial function due to its decreasing the availability of the essential amino acid tryptophan in inflammatory environments (3). Recent studies have demonstrated that IDO induces immunosuppression during infection, pregnancy, transplantation, autoimmunity, and neoplasia (3‑5).
- Lewis-Ballester, A. et al. (2009) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 106:17371.
- Costantino, G. (2009) Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 13:247.
- Xu, H. et al. (2008) Immunol. Lett. 121:1.
- Lob, S. et al. (2009) Nat. Rev. Cancer 9:445.
- Curti, A. et al. (2009) Blood 113:2394.
Citations for Recombinant Human IDO Protein, CF
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
3
Citations: Showing 1 - 3
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Iron activates microglia and directly stimulates indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase activity in the N171-82Q mouse model of Huntington's disease
Authors: DW Donley, M Realing, JP Gigley, JH Fox
PLoS ONE, 2021-05-14;16(5):e0250606.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Recombinant Protein
Applications: Bioassay -
Influence of Indoleamine-2,3-Dioxygenase and Its Metabolite Kynurenine on gammadelta T Cell Cytotoxicity against Ductal Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Cells
Authors: H Jonescheit, HH Oberg, D Gonnermann, M Hermes, V Sulaj, C Peters, D Kabelitz, D Wesch
Cells, 2020-05-06;9(5):.
Species: N/A
Sample Types:
-
Dendritic Cells Treated with Exogenous Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Maintain an Immature Phenotype and Suppress Antigen-specific T cell Proliferation
Authors: E Bracho-San, A Hassanzade, MA Brusko, MA Wallet, BG Keselowsky
J Immunol Regen Med, 2019-02-10;5(0):.
Species: Human, Mouse
Sample Types: Small Molecule, Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human IDO Protein, CF
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Recombinant Human IDO Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: