Recombinant Human IL-21R His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF
Recombinant Human IL-21R His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF Summary
Learn more about Avi-tag Biotinylated ProteinsProduct Specifications
| Human IL-21R (Cys20-Pro236) Accession # Q9HBE5.1 | 6-His tag | Avi-tag |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | |
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
AVI9249
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
When Recombinant Human IL-21 Protein (8879-IL) is immobilized at 1.0 μg/mL (100 μL/well), the concentration of Biotinylated Recombinant Human IL-21R His-tag Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI9249) that produces 50% of the optimal binding response is 40.0-240 ng/mL.
 View Larger
View Larger
2 μg/lane of Biotinylated Recombinant Human IL-21R His-tag Avi-tag Protein (Catalog # AVI9249) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 51-59 kDa.
Background: IL-21R
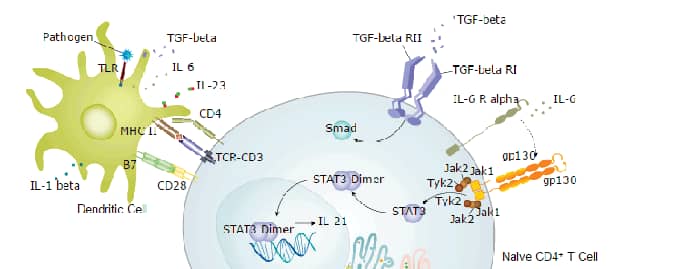
Interleukin-21 Receptor (IL-21 R )is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein within the class I cytokine receptor family (1). IL-21 R associates with the common gamma chain ( gamma c) which is also a component of the receptors for IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, and IL-15 (2, 3). Mature human IL-21 R consists of a 213 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ECD) with 4 conserved cysteine residues, a fibronectin type III domain, and a WSxWS motif, followed by a 21 aa transmembrane domain and a 285 aa cytoplasmic domain with a Box 1 motif, a kinase domain, and several sites for tyrosine phosphorylation (4, 5). Within the ECD, human IL-21 R shares 69% aa identity with mouse and rat IL-21 R, respectively. IL-21 R is expressed mainly on B cells (highest on mature, activated, follicular and germinal center B cells), NK cells, and activated T cells, but is also found on dendritic cells, alternatively activated macrophages, intestinal lamina propria fibroblasts and epithelial cells, and keratinocytes (1, 4, 5). Both IL-21 and IL-4 are necessary for efficient B cell IgG1 production and normal germinal center architecture (6). B cell IL-21 R engagement induces Blimp-1 (which mediates plasma cell differentiation) and is important for memory responses (7, 8). IL-21 R engagement enhances NK cell mediated cytotoxic activity and IFN-gamma production (4, 9), control of viral infection and tumor growth by CD8+ T cells (10), development of regulatory T cells (11), IL-23 responsiveness of encephalitogenic Th17 cells (12), but suppresses the accumulation of IL-17 secreting gamma δ T cells in the airway (13). IL-21 R expression is often upregulated in allergic skin inflammation, systemic lupus erythematosus and diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) (14, 15). Our Avi-tag Biotinylated human IL-21R features biotinylation at a single site contained within the Avi-tag, a unique 15 amino acid peptide. Protein orientation will be uniform when bound to streptavidin-coated surface due to the precise control of biotinylation and the rest of the protein is unchanged so there is no interference in the protein's bioactivity.
- Tangye, S.G. (2015) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 34:107.
- Asao, H. et al. (2001) J. Immunol. 167:1.
- Habib, T. et al. (2002) Biochemistry 41:8725.
- Parrish-Novak, et al. (2000) Nature 408:57.
- Ozaki, K. et al. (2000) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:11439.
- Ozaki, K. et al. (2002) Science 298:1630.
- Rankin, A.L. et al. (2011) J. Immunol. 186:667.
- King, I.L. et al. (2010) J. Immunol. 185:6138.
- Kasaian, M.T. et al. (2002) Immunity 16:559.
- Frohlich, A. et al. (2009 Science 324:1576.
- Tortola, L. et al. (2010) Blood 116:5200.
- Lee, Y. et al. (2015) J. Clin. Invest. 125:4011.
- Moser, E.K. et al. (2015) PLoS One 10:e0120169.
- Jin, H. et al. (2009) J. Clin. Invest. 119:47.
- Sarosiek, K.A. et al. (2010) Blood 115:570.
Citation for Recombinant Human IL-21R His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
1 Citation: Showing 1 - 1
-
Potent antitumor activity of a designed interleukin-21 mimic
Authors: Chun, JH;Lim, BS;Roy, S;Walsh, MJ;Abhiraman, GC;Zhangxu, K;Atajanova, T;Revach, OY;Clark, EC;Li, P;Palin, CA;Khanna, A;Tower, S;Kureshi, R;Hoffman, MT;Sharova, T;Lawless, A;Cohen, S;Boland, GM;Nguyen, T;Peprah, F;Tello, JG;Liu, SY;Kim, CJ;Shin, H;Quijano-Rubio, A;Jude, KM;Gerben, S;Murray, A;Heine, P;DeWitt, M;Ulge, UY;Carter, L;King, NP;Silva, DA;Kueh, HY;Kalia, V;Sarkar, S;Jenkins, RW;Garcia, KC;Leonard, WJ;Dougan, M;Dougan, SK;Baker, D;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology
Species: N/A
Sample Types: Recombinant Protein
Applications: Bioassay
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsStaining Reagents
Supplemental Cell Selection Products
Supplemental ELISA Products
Reviews for Recombinant Human IL-21R His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Human IL-21R His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Human IL-21R His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image