Mouse JAM-B/VE-JAM Antibody Summary
Phe29-Asn236 (predicted)
Accession # Q9JI59
Customers also Viewed
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Cell Adhesion Mediated by JAM‑B/VE‑JAM and Neutral-ization by Mouse JAM‑B/ VE‑JAM Antibody. Recombinant Mouse JAM-B/VE-JAM Fc Chimera (Catalog # 988-VJ), immobilized onto a microplate previously coated with Goat Anti-Human IgG Fc (Catalog # G-102-C), supports the adhesion of the J45.01 human acute lymphoblastic leukemia T lymphocyte cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line), as measured by endogenous cellular lysosomal acid phosphatase activity. Adhesion elicited by Recombinant Mouse JAM-B/VE-JAM Fc Chimera (0.2 µg/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Rat Anti-Mouse JAM-B/ VE-JAM Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB988). The ND50 is typically 0.1-0.5 µg/mL.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: JAM-B/VE-JAM
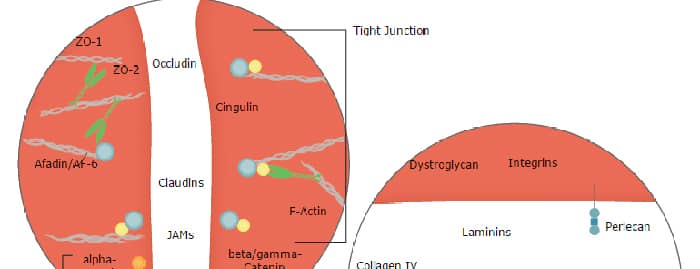
The family of juctional adhesion molecules (JAM), comprising at least three members, are type I transmembrane receptors belonging to the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily (1, 2). These proteins are localized in the tight junctions between endothelial cells or epithelial cells. Some family members are also found on blood leukocytes and platelets. JAM-B, alternatively named vascular endothelial JAM (VE-JAM), is expressed prominently on high endothelial venules of lymphoid organs where it is localized to the intercellular boundaries of high endothelial cells. It is also expressed on the endothelium of a variety of non-lymphoid organs, especially the heart and placenta (2, 3, 5). Mouse JAM-B/VE-JAM cDNA predicts a 298 amino acid (aa) precursor protein with a putative 28 aa signal peptide, a 209 aa extracellular region containing two Ig domains, a 23 aa transmembrane domain and a 38 aa cytoplasmic domain containing a PDZ-binding motif and a PKC phosphorylation site (2, 3). Mouse JAM-B shares approximately 79% aa sequence homology with its human homologue. It also shares approximately 35% aa sequence homology with mouse JAM-A or JAM‑C. JAM-B exhibits homotypic interactions, as well as heterotypic interactions with JAM‑C, but not JAM-A (4, 5, 7). It is also a ligand for the Integrin alpha4beta1. However, the JAM-B/alpha4beta1 interaction is facilitated only after prior adhesion of JAM-B to JAM‑C (6). Through its heterotypic interactions with JAM‑C, JAM-B is an adhesive ligand for T, NK, and dendritic cells, and may play a role in regulating leukocyte transmigration (5).
- Chavakis, T. et al. (2003) Thromb. Haemost. 89:13.
- Aurand-Lions, M. et al. (2001) Blood 98:3699.
- Palmeri, A. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:19139.
- Cunnigham, S. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:34750.
- Liang, T. et al. (2002) J. Immunol. 168:1618.
- Cunningham, A. et al. (2002) J Biol. Chem. 277:27589.
- Arrate, M. et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:45826.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse JAM-B/VE-JAM Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
3
Citations: Showing 1 - 3
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Impaired stem cell differentiation and somatic cell reprogramming in DIDO3 mutants with altered RNA processing and increased R-loop levels
Authors: A Fütterer, A Talavera-G, T Pons, J de Celis, J Gutiérrez, V Domínguez, C Martínez-A
Cell Death & Disease, 2021-06-21;12(7):637.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Soluble JAM-C Ectodomain Serves as the Niche for Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells
Authors: Morio Yamazaki, Kotaro Sugimoto, Yo Mabuchi, Rina Yamashita, Naoki Ichikawa-Tomikawa, Tetsuharu Kaneko et al.
Biomedicines
-
Junctional adhesion molecules (JAM)-B and -C contribute to leukocyte extravasation to the skin and mediate cutaneous inflammation.
Authors: Ludwig RJ, Zollner TM, Santoso S, Hardt K, Gille J, Baatz H, Johann PS, Pfeffer J, Radeke HH, Schon MP, Kaufmann R, Boehncke WH, Podda M
J. Invest. Dermatol., 2005-11-01;125(5):969-76.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse JAM-B/VE-JAM Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Mouse JAM-B/VE-JAM Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Mouse JAM-B/VE-JAM Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image