Human GATA-6 Antibody Summary
Met1-Thr449
Accession # Q92908
*Small pack size (-SP) is supplied either lyophilized or as a 0.2 µm filtered solution in PBS.
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human GATA‑6 by Western Blot. Western blot shows cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts from PC-3 human prostate cancer cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human GATA-6 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1700) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF017). A specific band was detected for GATA-6 at approximately 55 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
GATA‑6 in KATO-III Human Cell Line. GATA-6 was detected in immersion fixed KATO-III human gastric carcinoma cell line using 10 µg/mL Goat Anti-Human GATA-6 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1700) for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained with the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red, upper panel; NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue, lower panel). View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
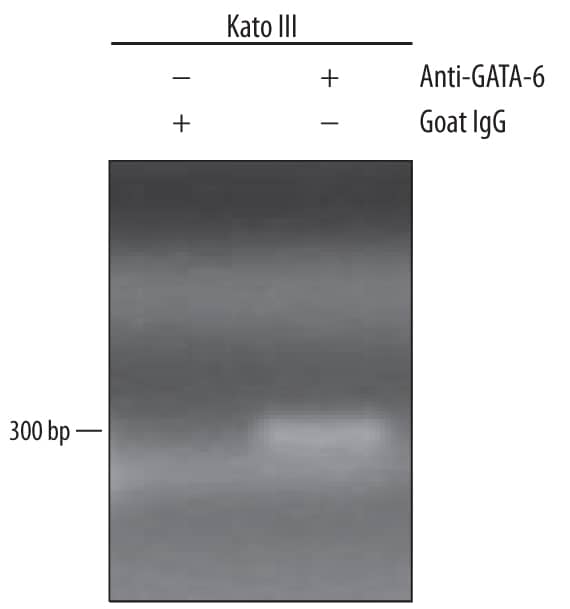
Detection of GATA‑6-regulated Genes by Chromatin Immunoprecipitation. KATO-III human gastric carcinoma cell line was fixed using formaldehyde, resuspended in lysis buffer, and sonicated to shear chromatin. GATA-6/DNA complexes were immunoprecipitated using 5 µg Goat Anti-Human GATA-6 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1700) or control antibody (AB-108-C) for 15 minutes in an ultrasonic bath, followed by Biotinylated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (BAF109). Immunocomplexes were captured using 50 µL of MagCellect Streptavidin Ferrofluid (MAG999) and DNA was purified using chelating resin solution. Themucin4promoter was detected by standard PCR.
 View Larger
View Larger
GATA‑6 in Human Intestine. GATA-6 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human intestine using Goat Anti-Human GATA-6 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1700) at 5 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; CTS008) and counter-stained with hematoxylin (blue). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
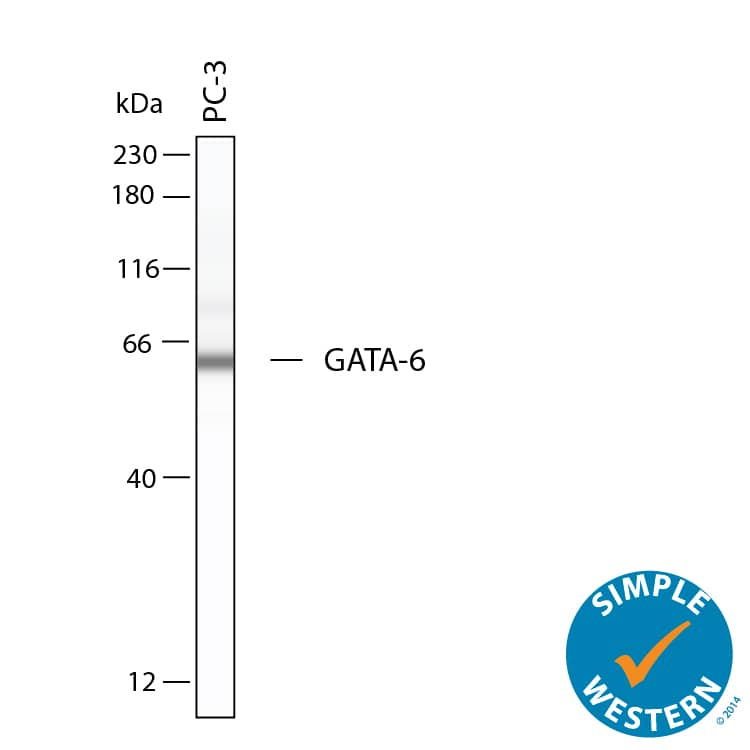
Detection of Human GATA‑6 by Simple WesternTM. Simple Western shows lysates of PC‑3 human prostate cancer cell line, loaded at 0.2 mg/ml. A specific band was detected for GATA‑6 at approximately 62 kDa (as indicated) using 10 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human GATA‑6 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1700). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230kDa separation system.
 View Larger
View Larger
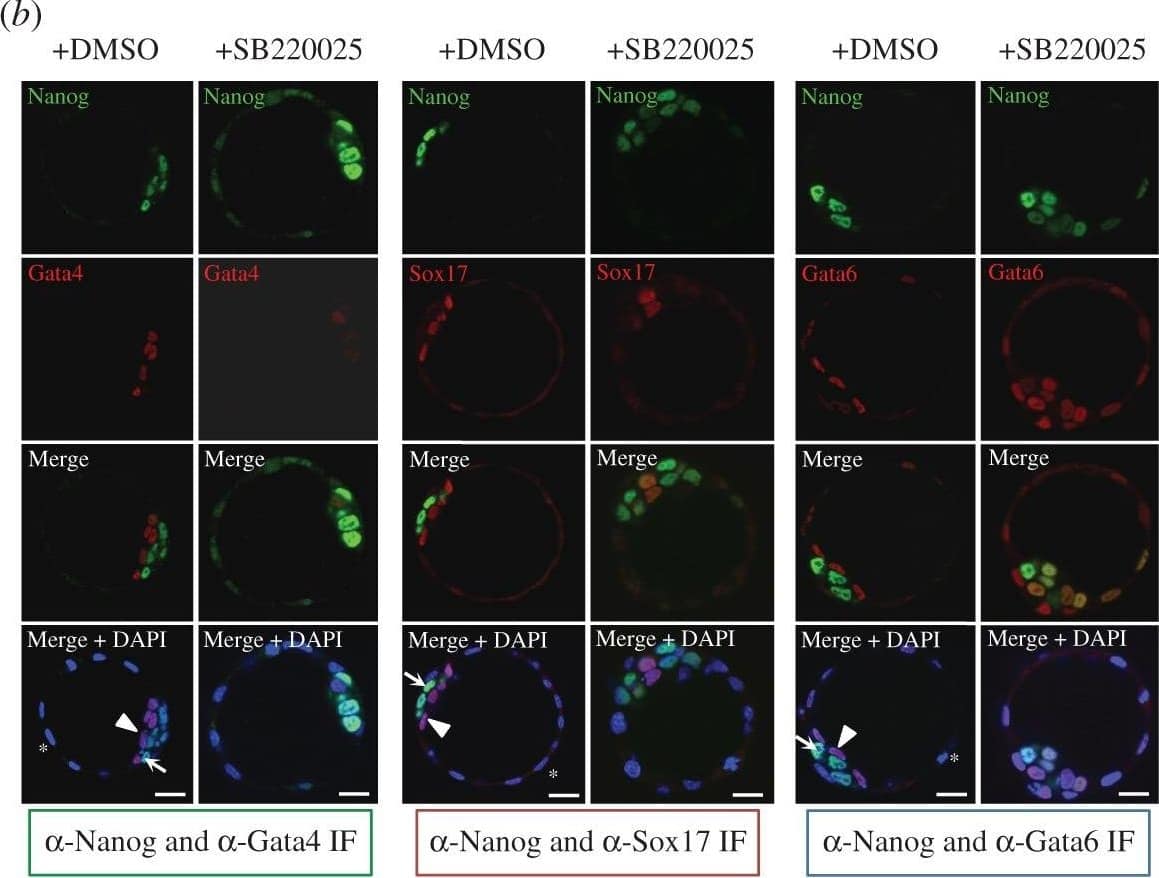
Detection of Mouse GATA-6 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence p38-Mapk14/11 inhibition during blastocyst maturation blocks PrE differentiation/maturation. (a) Experimental schema of p38-Mapk14/11 inhibition (+SB220025), plus vehicle control (+DMSO), and the details of antibodies used to analyse ICM cell lineage marker protein expression by immunofluorescence (IF) in late blastocysts (E4.5); Nanog and Gata4 (+DMSO n = 27, +SB220025 n = 33)—green, Nanog and Sox17 (+DMSO n = 18, +SB220025 n = 20)—red, and Nanog and Gata6 (+DMSO n = 24, +SB220025 n = 27)—blue. (b) Representative single confocal z-plane micrographs of vehicle control-treated (+DMSO) or p38-Mapk14/11 inhibited (+SB220025) late-blastocyst stage/equivalent embryos, immunofluorescently stained for indicated ICM cell lineage markers (Nanog in green and Gata4, Sox17 and Gata6 in red, plus DAPI DNA stain in blue). Examples of cells classified as TE, PrE and EPI are marked with an asterisk, arrowhead and arrow, respectively. Scale bar, 15 µm. (c) Pie charts of the relative cell lineage contribution in vehicle control (+DMSO) and p38-Mapk14/11 inhibited (+SB220025) blastocysts as judged by IF to detect the stated ICM lineage marker proteins. Blue, trophectoderm (TE); yellow, epiblast (EPI—ICM exhibiting exclusive Nanog expression); green, primitive endoderm (PrE—ICM exhibiting exclusive Gata4/6 or Sox17 expression, as appropriate); orange, uncommitted ICM cells (exhibiting co-expression of both Nanog and Gata4/6 or Sox17, as appropriate); and grey, ICM cells negative for either assayed marker. (d) Bar charts show average number of cells allocated to each specified ICM lineage, as judged by the indicated IF staining regime employed. Error bars represent s.e.m. and asterisks denote statistical significant differences in cell number between the vehicle control (+DMSO, black bars) and p38-Mapk14/11 inhibited (+SB220025, grey bars) embryo groups, according to two-tailed Student's t-test, with *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.005 confidence intervals. Yellow asterisk denotes increase in cells positively immunofluorescently staining for both EPI and PrE ICM markers using anti-Nanog and anti-Gata6 (an early PrE marker) antibodies. All individual embryo data used in the preparation of this figure are contained within the electronic supplementary material, table S3. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27605380), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
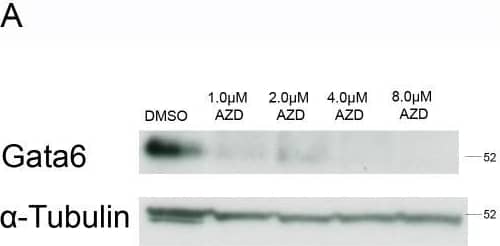
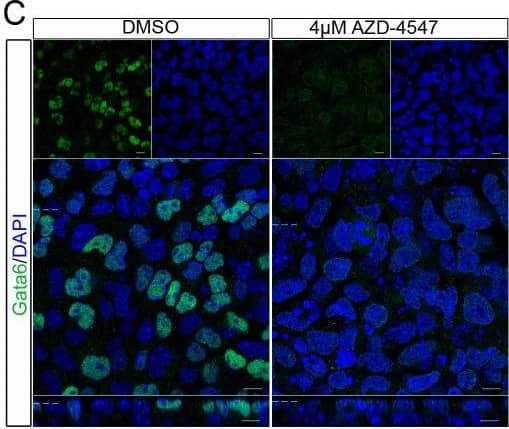
Detection of Mouse GATA-6 by Western Blot Reduced expression of the primitive endoderm markers Gata4 and Gata6 and increased expression of Nanog was observed in embryoid bodies following inhibitor of the Fgfr.Embryoid bodies were grown in different concentrations of AZD-4547 or 0.08% DMSO for 7 days. Expression levels of (A) Gata6, and (B) Gata4 were analysed using western blotting. A representative blot and quantification from 3 independent experiments is shown for each marker. A dose dependent decrease in expression of both proteins was observed. Statistical analysis is a one-way Anova with a Dunnett’s post-hoc test. Whole-mount immunostaining of (C) Gata6 and (D) Nanog after treatment of embryoid bodies with 4 µM AZD-4547 or 0.04% DMSO. A reduction in the percentage of nuclei expressing Gata6 was observed. The percentage of nuclei expressing Nanog increased. A representative image from 3 independent experiments is shown. Scale bars 10 µm. Dotted lines represent position that the relevant orthogonal or aerial images were taken. Statistical analysis is a paired t-test. Data is from 3 independent experiments, error bars represent SEM. (*P = 0.1–0.5, **p = 0.001–0.01, ***p<0.001). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095434), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
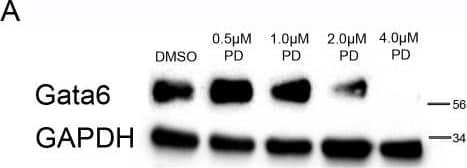
Detection of Mouse GATA-6 by Western Blot Reduced expression of primitive endoderm markers Gata4 and Gata6 and increased expression of Nanog was observed in embryoid bodies upon inhibition of Mek.Embryoid bodies were grown in different concentrations of PD-0325901 or 0.04% DMSO for 7 days. Expression levels of (A) Gata6, and (B) Gata4 were analysed using western blotting. A representative blot and quantification from 3 independent experiments is shown for each marker. A dose dependent decrease in expression of both proteins was observed. Statistical analysis is a one-way Anova with a Dunnett’s post-hoc test. Whole-mount immunostaining of (C) Gata6 and (D) Nanog after treatment of embryoid bodies with 4 µM PD-0325901. A reduction in the percentage of nuclei expressing Gata6 was observed whilst there was an increase in the percentage of nuclei expressing Nanog. A representative image from 3 independent experiments is shown. Scale bars 10 µm. Dotted lines represent position that the relevant orthogonal or aerial images were taken. Statistical test is a paired t-test. Data is from 3 independent experiments, error bars represent SEM. (*P = 0.1–0.5, **p = 0.001–0.01, ***p<0.001). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095434), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse GATA-6 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Reduced expression of the primitive endoderm markers Gata4 and Gata6 and increased expression of Nanog was observed in embryoid bodies following inhibitor of the Fgfr.Embryoid bodies were grown in different concentrations of AZD-4547 or 0.08% DMSO for 7 days. Expression levels of (A) Gata6, and (B) Gata4 were analysed using western blotting. A representative blot and quantification from 3 independent experiments is shown for each marker. A dose dependent decrease in expression of both proteins was observed. Statistical analysis is a one-way Anova with a Dunnett’s post-hoc test. Whole-mount immunostaining of (C) Gata6 and (D) Nanog after treatment of embryoid bodies with 4 µM AZD-4547 or 0.04% DMSO. A reduction in the percentage of nuclei expressing Gata6 was observed. The percentage of nuclei expressing Nanog increased. A representative image from 3 independent experiments is shown. Scale bars 10 µm. Dotted lines represent position that the relevant orthogonal or aerial images were taken. Statistical analysis is a paired t-test. Data is from 3 independent experiments, error bars represent SEM. (*P = 0.1–0.5, **p = 0.001–0.01, ***p<0.001). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095434), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
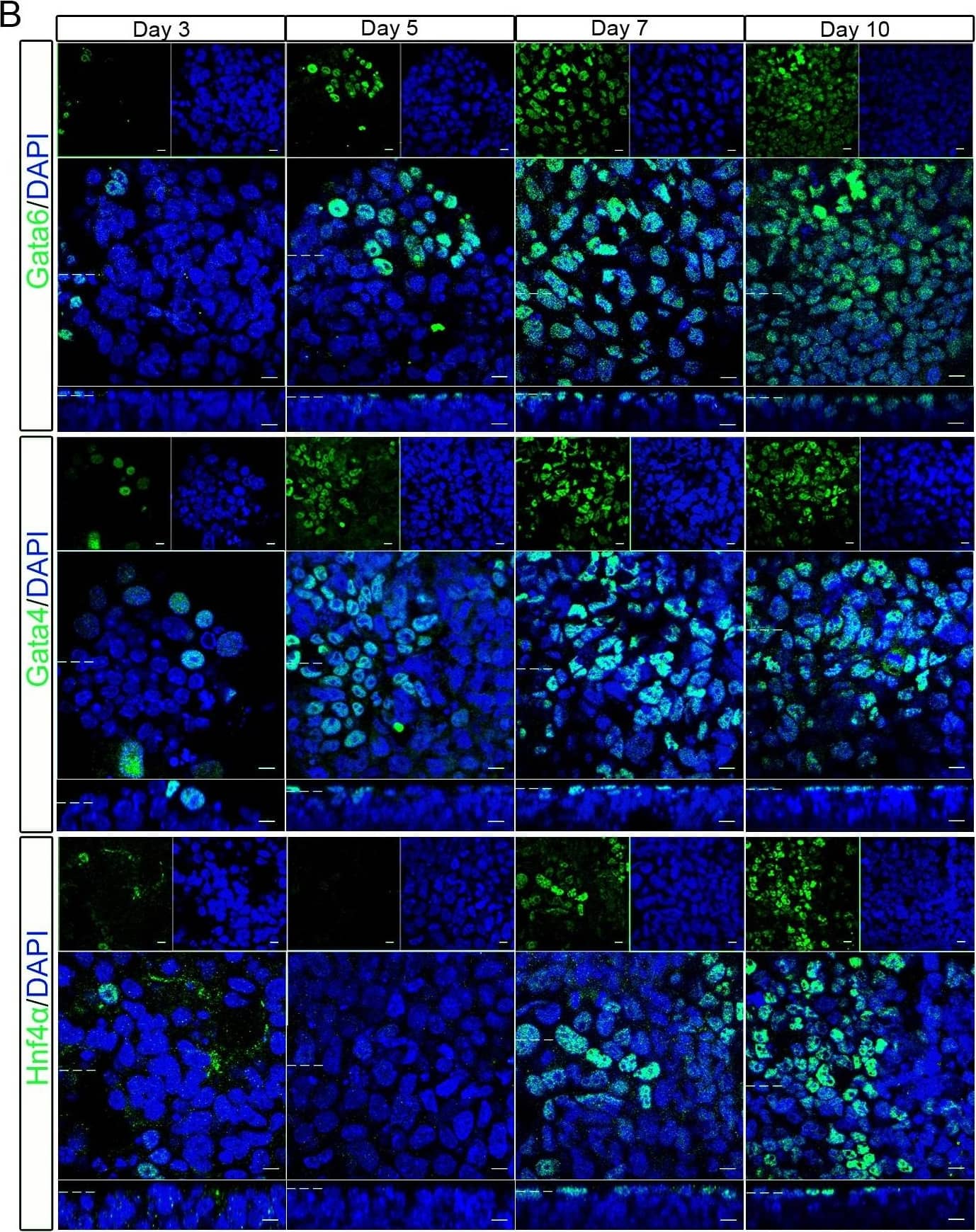
Detection of Mouse GATA-6 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence expression of primitive endoderm cell fate markers gradually increased and nanog decreased in developing embryoid bodies.Embryoid bodies were produced from R63 mES cells using the hanging drop method. Development of the embryoid body was monitored over ten days. (A) Light microscopy images show the gradual increase in size of the embryoid bodies as well as increased heterogeneity, loss of circularity and formation of cystic cavities at later timepoints. Scale bars 200 µm. (B) Whole-mount immunostaining showing nuclear localisation of Gata6, Gata4, and Hnf4 alpha on days 3, 5, 7, and 10 of embryoid body development. The percentage of positive nuclei for each protein is shown graphically. The number of positive nuclei increased, reaching a maximum on day 7. (C) Whole-mount immunostaining showing nuclear localisation of Nanog. The number of positive nuclei rapidly decreased, with no positive cells seen on days 7 or 10. The percentage of positive nuclei for each protein is shown graphically. Data is from at least 3 independent experiments, error bars are standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical analysis is a one-way Anova with a Tukey’s post-hoc test, (*P = 0.1–0.5, **p = 0.001–0.01, ***p<0.001). Dotted lines represent position that the relevant orthogonal or aerial images were taken. Scale bars 10 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095434), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
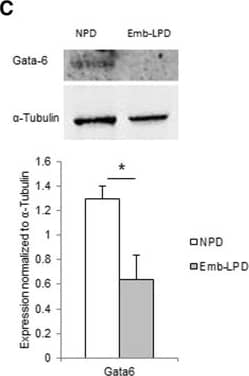
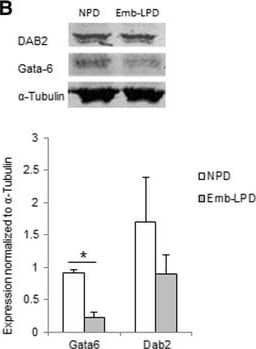
Detection of Mouse GATA-6 by Western Blot Gata factor expression in embryoid bodies (EBs) at day 5.5 culture and in ex vivo visceral yolk sac (VYS) at E17.5 in relation to maternal diet. (A) Expression of Gata4, Gata6 and Dab2 mRNA in EBs of Emb-LPD and NPD groups presented as ratio to the geometric mean of Gapdh and Ppib transcripts (n = 5 per treatment). (B) Expression of Gata6 and Dab2 protein in EBs from NPD and Emb-LPD groups (n = 6 cell lines per treatment). Upper: representative images of protein immunoblot bands. Lower: band intensity normalized to alpha -tubulin expression. (C) Expression of Gata6 protein in VYS from Emb-LPD, LPD and NPD group (n = 4 samples per treatment). Upper: representative images of protein immunoblot bands. Lower: band intensity normalized to alpha -tubulin expression. Values presented are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://bmcdevbiol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12861-015-0053-1), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
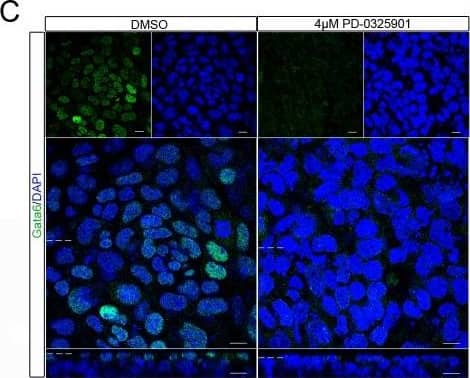
Detection of Mouse GATA-6 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Reduced expression of primitive endoderm markers Gata4 and Gata6 and increased expression of Nanog was observed in embryoid bodies upon inhibition of Mek.Embryoid bodies were grown in different concentrations of PD-0325901 or 0.04% DMSO for 7 days. Expression levels of (A) Gata6, and (B) Gata4 were analysed using western blotting. A representative blot and quantification from 3 independent experiments is shown for each marker. A dose dependent decrease in expression of both proteins was observed. Statistical analysis is a one-way Anova with a Dunnett’s post-hoc test. Whole-mount immunostaining of (C) Gata6 and (D) Nanog after treatment of embryoid bodies with 4 µM PD-0325901. A reduction in the percentage of nuclei expressing Gata6 was observed whilst there was an increase in the percentage of nuclei expressing Nanog. A representative image from 3 independent experiments is shown. Scale bars 10 µm. Dotted lines represent position that the relevant orthogonal or aerial images were taken. Statistical test is a paired t-test. Data is from 3 independent experiments, error bars represent SEM. (*P = 0.1–0.5, **p = 0.001–0.01, ***p<0.001). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095434), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human GATA-6 by Western Blot Gata factor expression in embryoid bodies (EBs) at day 5.5 culture and in ex vivo visceral yolk sac (VYS) at E17.5 in relation to maternal diet. (A) Expression of Gata4, Gata6 and Dab2 mRNA in EBs of Emb-LPD and NPD groups presented as ratio to the geometric mean of Gapdh and Ppib transcripts (n = 5 per treatment). (B) Expression of Gata6 and Dab2 protein in EBs from NPD and Emb-LPD groups (n = 6 cell lines per treatment). Upper: representative images of protein immunoblot bands. Lower: band intensity normalized to alpha -tubulin expression. (C) Expression of Gata6 protein in VYS from Emb-LPD, LPD and NPD group (n = 4 samples per treatment). Upper: representative images of protein immunoblot bands. Lower: band intensity normalized to alpha -tubulin expression. Values presented are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://bmcdevbiol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12861-015-0053-1), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: GATA-6
GATA-6 (also named GATA-GT1) is a zinc finger transcription activating protein that bins to a T/A-G-A-T-A-G/A DNA sequence motif in mesodermally and endodermally-derived tissue. There are two GATA-6 isoforms that arise from alternate start sites: a short form of 449 amino acids (aa), and a long form of 595 aa. The short form of human GATA-6 is 93%, 92% and 88% aa identical to GATA-6 in porcine, rat and mouse, respectively.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human GATA-6 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
144
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Distinct Molecular Trajectories Converge to Induce Naive Pluripotency
Authors: Hannah T. Stuart, Giuliano G. Stirparo, Tim Lohoff, Lawrence E. Bates, Masaki Kinoshita, Chee Y. Lim et al.
Cell Stem Cell
-
Characterization of multitype colonies originating from porcine blastocysts produced in vitro
Authors: Jong-Nam Oh, Jinsol Jeong, Mingyun Lee, Gyung Cheol Choe, Dong-Kyung Lee, Kwang-Hwan Choi et al.
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology
-
Spatial profiling of early primate gastrulation in utero
Authors: Sophie Bergmann, Christopher A. Penfold, Erin Slatery, Dylan Siriwardena, Charis Drummer, Stephen Clark et al.
Nature
-
Single-cell analysis of embryoids reveals lineage diversification roadmaps of early human development
Authors: Yi Zheng, Robin Zhexuan Yan, Shiyu Sun, Mutsumi Kobayashi, Lifeng Xiang, Ran Yang et al.
Cell Stem Cell
-
Generation of pancreatic ? cells from CD177(+) anterior definitive endoderm
Authors: Mahaddalkar PU, Scheibner K, Pfluger S et al.
Nature Biotechnology
-
GATA6 Is Required for Proliferation, Migration, Secretory Cell Maturation, and Gene Expression in the Mature Mouse Colon
Authors: Eva Beuling, Boaz E. Aronson, Luc M. D. Tran, Kelly A. Stapleton, Ellis N. ter Horst, Laurens A. T. M. Vissers et al.
Molecular and Cellular Biology
-
Morphogenesis of extra-embryonic tissues directs the remodelling of the mouse embryo at implantation
Authors: Neophytos Christodoulou, Antonia Weberling, Douglas Strathdee, Kurt I. Anderson, Paul Timpson, Magdalena Zernicka-Goetz
Nature Communications
-
An in vitro stem cell model of human epiblast and yolk sac interaction
Authors: KM Mackinlay, BA Weatherbee, V Souza Rosa, CE Handford, G Hudson, T Coorens, LV Pereira, S Behjati, L Vallier, MN Shahbazi, M Zernicka-G
Elife, 2021-08-17;10(0):.
-
Population-level antagonism between FGF and BMP signaling steers mesoderm differentiation in embryonic stem cells
Authors: Marina Gattiglio, Michelle Protzek, Christian Schröter
Biology Open
-
The interaction of LOXL2 with GATA6 induces VEGFA expression and angiogenesis in cholangiocarcinoma
Authors: Peng T, Deng X, Tian F et al.
Int. J. Oncol.
-
Histone methyltransferase Smyd3 regulates early embryonic lineage commitment in mice
Authors: Shinnosuke Suzuki, Yusuke Nozawa, Satoshi Tsukamoto, Takehito Kaneko, Hiroshi Imai, Naojiro Minami
REPRODUCTION
-
Bmi1 facilitates primitive endoderm formation by stabilizing Gata6 during early mouse development
Authors: Fabrice Lavial, Sylvain Bessonnard, Yusuke Ohnishi, Akiko Tsumura, Anil Chandrashekran, Mark A. Fenwick et al.
Genes & Development
-
Aldolase B-Mediated Fructose Metabolism Drives Metabolic Reprogramming of Colon Cancer Liver Metastasis
Authors: Pengcheng Bu, Kai-Yuan Chen, Kun Xiang, Christelle Johnson, Scott B. Crown, Nikolai Rakhilin et al.
Cell Metabolism
-
Gata6-Dependent GLI3 Repressor Function is Essential in Anterior Limb Progenitor Cells for Proper Limb Development
Authors: Shinichi Hayashi, Ryutaro Akiyama, Julia Wong, Naoyuki Tahara, Hiroko Kawakami, Yasuhiko Kawakami
PLOS Genetics
-
Efficient and scalable generation of primordial germ cells in 2D culture using basement membrane extract overlay
Authors: Arend W. Overeem, Yolanda W. Chang, Ioannis Moustakas, Celine M. Roelse, Sanne Hillenius, Talia Van Der Helm et al.
Cell Reports Methods
-
A combined human gastruloid model of cardiogenesis and neurogenesis
Authors: Olmsted ZT, Paluh JL.
iScience
-
A single cell characterisation of human embryogenesis identifies pluripotency transitions and putative anterior hypoblast centre
Authors: Matteo A. Molè, Tim H. H. Coorens, Marta N. Shahbazi, Antonia Weberling, Bailey A. T. Weatherbee, Carlos W. Gantner et al.
Nature Communications
-
3D time-lapse microscopy paired with endpoint lineage analysis in mouse blastocysts
Authors: Michael J. Pokrass, Sergi Regot
STAR Protocols
-
Characterization of porcine extraembryonic endoderm cells
Authors: Qiao‐Yan Shen, Shuai Yu, Ying Zhang, Zhe Zhou, Zhen‐Shuo Zhu, Qin Pan et al.
Cell Proliferation
-
Transcription factor GATA6: a novel marker and putative inducer of ductal metaplasia in biliary atresia
Authors: Tea Soini, Marjut Pihlajoki, Noora Andersson, Jouko Lohi, Kari A. Huppert, David A. Rudnick et al.
American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology
-
Rapid and efficient degradation of endogenous proteins in vivo identifies stage-specific roles of RNA Pol II pausing in mammalian development
Authors: Abderhman Abuhashem, Andrew S. Lee, Alexandra L. Joyner, Anna-Katerina Hadjantonakis
Developmental Cell
-
Farrerol directly activates the deubiqutinase UCHL3 to promote DNA repair and reprogramming when mediated by somatic cell nuclear transfer
Authors: W Zhang, M Wang, Z Song, Q Fu, J Chen, W Zhang, S Gao, X Sun, G Yang, Q Zhang, J Yang, H Tang, H Wang, X Kou, H Wang, Z Mao, X Xu, S Gao, Y Jiang
Nature Communications, 2023-04-03;14(1):1838.
-
Bilineage embryo-like structure from EPS cells can produce live mice with tetraploid trophectoderm
Authors: Kuisheng Liu, Xiaocui Xu, Dandan Bai, Yanhe Li, Yalin Zhang, Yanping Jia et al.
Protein & Cell
-
Epigenetic modifier balances Mapk and Wnt signalling in differentiation of goblet and Paneth cells
Authors: Johanna Grinat, Frauke Kosel, Neha Goveas, Andrea Kranz, Dimitra Alexopoulou, Klaus Rajewsky et al.
Life Science Alliance
-
The SP-C promoter facilitates alveolar type II epithelial cell-specific plasmid nuclear import and gene expression
Authors: James V. DeGiulio, Christopher D. Kaufman, David A. Dean
Gene Therapy
-
RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes breast tumor progression through inhibiting BNIP3
Authors: Y Niu, Z Lin, A Wan, H Chen, H Liang, L Sun, Y Wang, X Li, XF Xiong, B Wei, X Wu, G Wan
Mol. Cancer, 2019-03-28;18(1):46.
-
FGF signal-dependent segregation of primitive endoderm and epiblast in the mouse blastocyst
Authors: Yojiro Yamanaka, Fredrik Lanner, Janet Rossant
Development
-
Establishment of bovine extraembryonic endoderm cells
Authors: Ming, H;Scatolin, GN;Ojeda, A;Jiang, Z;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology
Species: Bovine
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Immunocytochemistry -
E-box independent chromatin recruitment turns MYOD into a transcriptional repressor
Authors: Nicoletti, C;Massenet, J;Pintado-Urbanc, AP;Connor, LJ;Nicolau, M;Sundar, S;Xu, M;Schmitt, A;Zhang, W;Fang, Z;Chan, TCI;Tapscott, SJ;Cheung, TH;Simon, MD;Caputo, L;Puri, PL;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Immunocytochemistry -
TASOR expression in naive embryonic stem cells safeguards their developmental potential
Authors: Pinzon-Arteaga, CA;O'Hara, R;Mazzagatti, A;Ballard, E;Hu, Y;Pan, A;Schmitz, DA;Wei, Y;Sakurai, M;Ly, P;Banaszynski, LA;Wu, J;
Cell reports
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Mechano-osmotic signals control chromatin state and fate transitions in pluripotent stem cells
Authors: McCreery, KP;Stubb, A;Stephens, R;Fursova, NA;Cook, A;Kruse, K;Michelbach, A;Biggs, LC;Keikhosravi, A;Nykänen, S;Hydén-Granskog, C;Zou, J;Lackmann, JW;Niessen, CM;Vuoristo, S;Miroshnikova, YA;Wickström, SA;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Embryo
Applications: Immunohistochemistry, Immunocytochemistry -
Cytokines and Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Exploring Their Relationship with Molecular Subtypes and Prognosis
Authors: Gutierrez-Sainz, L;Heredia-Soto, V;Rodríguez-García, AM;Crespo Sánchez, MG;Serrano-Olmedo, MG;Molero-Luis, M;Losantos-García, I;Ghanem, I;Pérez-Wert, P;Custodio, A;Mendiola, M;Feliu, J;
International journal of molecular sciences
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Tissue-intrinsic beta-catenin signals antagonize Nodal-driven anterior visceral endoderm differentiation
Authors: Schumacher, S;Fernkorn, M;Marten, M;Chen, R;Kim, YS;Bedzhov, I;Schröter, C;
Nature communications
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Immunocytochemistry -
Naive pluripotent stem cell-based models capture FGF-dependent human hypoblast lineage specification
Authors: Dattani, A;Corujo-Simon, E;Radley, A;Heydari, T;Taheriabkenar, Y;Carlisle, F;Lin, S;Liddle, C;Mill, J;Zandstra, PW;Nichols, J;Guo, G;
Cell stem cell
Species: Human
Sample Types: Embryo
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Reprogramming fibroblast into human iBlastoids
Authors: Tan, JP;Liu, X;Polo, JM;
Nature protocols
Species: Human
Sample Types: Embryoid Bodies
Applications: Immunocytochemistry -
Distinct pathways drive anterior hypoblast specification in the implanting human embryo
Authors: Weatherbee, BAT;Weberling, A;Gantner, CW;Iwamoto-Stohl, LK;Barnikel, Z;Barrie, A;Campbell, A;Cunningham, P;Drezet, C;Efstathiou, P;Fishel, S;Vindel, SG;Lockwood, M;Oakley, R;Pretty, C;Chowdhury, N;Richardson, L;Mania, A;Weavers, L;Christie, L;Elder, K;Snell, P;Zernicka-Goetz, M;
Nature cell biology
Species: Human, Mouse
Sample Types: Embryo
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Quiescence enables unrestricted cell fate in naive embryonic stem cells
Authors: Khoa, LTP;Yang, W;Shan, M;Zhang, L;Mao, F;Zhou, B;Li, Q;Malcore, R;Harris, C;Zhao, L;Rao, R;Iwase, S;Kalantry, S;Bielas, SL;Lyssiotis, CA;Dou, Y;
Nature communications
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Immunocytochemistry -
Molecular profiling of human blastocysts reveals primitive endoderm defects among embryos of decreased implantation potential
Authors: Chousal, JN;Morey, R;Srinivasan, S;Lee, K;Zhang, W;Yeo, AL;To, C;Cho, K;Garzo, VG;Parast, MM;Laurent, LC;Cook-Andersen, H;
Cell reports
Species: Human
Sample Types: Embryo
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Smad4 is essential for epiblast scaling and morphogenesis after implantation, but nonessential prior to implantation in the mouse
Authors: Kruger, RE;Frum, T;Brumm, AS;Hickey, SL;Niakan, KK;Aziz, F;Shammami, MA;Roberts, JG;Ralston, A;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
3D-cultured blastoids model human embryogenesis from pre-implantation to early gastrulation stages
Authors: Karvas, RM;Zemke, JE;Ali, SS;Upton, E;Sane, E;Fischer, LA;Dong, C;Park, KM;Wang, F;Park, K;Hao, S;Chew, B;Meyer, B;Zhou, C;Dietmann, S;Theunissen, TW;
Cell stem cell
Species: Human
Sample Types: Protein
Applications: Immunocytochemistry -
Large-scale production of human blastoids amenable to modeling blastocyst development and maternal-fetal cross talk
Authors: Yu, L;Logsdon, D;Pinzon-Arteaga, CA;Duan, J;Ezashi, T;Wei, Y;Ribeiro Orsi, AE;Oura, S;Liu, L;Wang, L;Liu, K;Ding, X;Zhan, L;Zhang, J;Nahar, A;Stobbe, C;Katz-Jaffe, M;Schoolcraft, WB;Tan, T;Hon, GC;Yuan, Y;Wu, J;
Cell stem cell
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC, IHC -
Influence of FGF4 and BMP4 on FGFR2 dynamics during the segregation of epiblast and primitive endoderm cells in the pre-implantation mouse embryo
Authors: Goissis, MD;Bradshaw, B;Posfai, E;Rossant, J;
PloS one
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Embryo
Applications: IHC -
Efficient and scalable generation of primordial germ cells in 2D culture using basement membrane extract overlay
Authors: Arend W. Overeem, Yolanda W. Chang, Ioannis Moustakas, Celine M. Roelse, Sanne Hillenius, Talia Van Der Helm et al.
Cell Reports Methods
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Immunocytochemistry -
Generation of pulsatile ERK activity in mouse embryonic stem cells is regulated by Raf activity
Authors: Toyooka, Y;Aoki, K;Usami, FM;Oka, S;Kato, A;Fujimori, T;
Scientific reports
Species: Transgenic Mouse
Sample Types: Embryo
Applications: ICC -
Bilineage embryo-like structure from EPS cells can produce live mice with tetraploid trophectoderm
Authors: Kuisheng Liu, Xiaocui Xu, Dandan Bai, Yanhe Li, Yalin Zhang, Yanping Jia et al.
Protein & Cell
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: Western Blot, Immunocytochemistry -
Single-cell analysis of bidirectional reprogramming between early embryonic states reveals mechanisms of differential lineage plasticities
Authors: V Garg, Y Yang, S Nowotschin, M Setty, YY Kuo, R Sharma, A Polyzos, E Salataj, D Murphy, A Jang, D Pe'er, E Apostolou, AK Hadjantona
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology, 2023-03-29;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: ChIP, Flow Cytometry, ICC -
The Wnt/TCF7L1 transcriptional repressor axis drives primitive endoderm formation by antagonizing naive and formative pluripotency
Authors: P Athanasoul, M Balli, A De Jaime-S, A Boel, S Papanikola, BK van der Ve, A Janiszewsk, T Vanhessche, A Francis, Y El Laithy, AL Nigro, F Aulicino, KP Koh, V Pasque, MP Cosma, C Verfaillie, A Zwijsen, B Heindryckx, C Nikolaou, F Lluis
Nature Communications, 2023-03-03;14(1):1210.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Efficient generation of ETX embryoids that recapitulate the entire window of murine egg cylinder development
Authors: C Dupont, OJM Schäffers, BF Tan, S Merzouk, EM Bindels, A Zwijsen, D Huylebroec, J Gribnau
Science Advances, 2023-01-18;9(3):eadd2913.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Embryoids
Applications: IHC -
An RNAi screen of RNA helicases identifies eIF4A3 as a regulator of embryonic stem cell identity
Authors: D Li, J Yang, V Malik, Y Huang, X Huang, H Zhou, J Wang
Nucleic Acids Research, 2022-11-28;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Extensive co-binding and rapid redistribution of NANOG and GATA6 during emergence of divergent lineages
Authors: JJ Thompson, DJ Lee, A Mitra, S Frail, RK Dale, PP Rocha
Nature Communications, 2022-07-23;13(1):4257.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: IHC -
A combined human gastruloid model of cardiogenesis and neurogenesis
Authors: Olmsted ZT, Paluh JL.
iScience
-
A gastruloid model of the interaction between embryonic and extra-embryonic cell types
Authors: NM Bérenger-C, M Mircea, E Adegeest, PR van den Be, M Feliksik, M Hochane, T Idema, SJ Tans, S Semrau
Journal of tissue engineering, 2022-06-11;13(0):2041731422110.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Organoids
Applications: IHC -
Cell fate roadmap of human primed-to-naive transition reveals preimplantation cell lineage signatures
Authors: Y Bi, Z Tu, J Zhou, X Zhu, H Wang, S Gao, Y Wang
Nature Communications, 2022-06-07;13(1):3147.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Identification of Carcinogenesis and Tumor Progression Processes in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Using High-Throughput Proteomics
Authors: L Trilla-Fue, A Gámez-Pozo, MI Lumbreras-, R López-Vaca, V Heredia-So, I Ghanem, E López-Cama, A Zapater-Mo, M Miguel, EM Peña-Burgo, E Palacios, M De Uribe, L Guerra, A Dittmann, M Mendiola, JÁ Fresno Var, J Feliu
Cancers, 2022-05-13;14(10):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Targeted Accumulation of Macrophages Induced by Microbeam Irradiation in a Tissue-Dependent Manner
Authors: V Trappetti, J Fazzari, C Fernandez-, L Smyth, M Potez, N Shintani, B de Breuyn, OA Martin, V Djonov
Biomedicines, 2022-03-22;10(4):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Klf4 methylated by Prmt1 restrains the commitment of primitive endoderm
Authors: ZY Zuo, GH Yang, HY Wang, SY Liu, YJ Zhang, Y Cai, F Chen, H Dai, Y Xiao, MB Cheng, Y Huang, Y Zhang
Nucleic Acids Research, 2022-02-28;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
ASPP2 maintains the integrity of mechanically stressed pseudostratified epithelia during morphogenesis
Authors: C Royer, E Sandham, E Slee, F Schneider, CB Lagerholm, J Godwin, N Veits, H Hathrell, F Zhou, K Leonaviciu, J Garratt, T Narendra, A Vincent, C Jones, T Child, K Coward, C Graham, M Fritzsche, X Lu, S Srinivas
Nature Communications, 2022-02-17;13(1):941.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
A balanced Oct4 interactome is crucial for maintaining pluripotency
Authors: D Han, G Wu, R Chen, HCA Drexler, CM MacCarthy, KP Kim, K Adachi, D Gerovska, L Mavrommati, I Bedzhov, MJ Araúzo-Bra, HR Schöler
Science Advances, 2022-02-16;8(7):eabe4375.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Embryos
Applications: IHC -
Generation of iPSC line (FAMRCi009-A) from patient with familial progressive cardiac conduction disorder carrying genetic variant FLNC p.Val2264Met
Authors: N Rodina, A Khudiakov, K Perepelina, A Muravyev, A Boytsov, A Zlotina, P Sokolnikov, A Kostareva
Stem Cell Research, 2021-12-27;59(0):102640.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, ICC -
Generation of iPSC line FAMRCi010-A from patient with restrictive cardiomyopathy carrying genetic variant FLNC p.Gly2011Arg
Authors: K Perepelina, A Khudiakov, N Rodina, A Boytsov, T Vavilova, A Zlotina, P Sokolnikov, A Kostareva
Stem Cell Research, 2021-12-21;59(0):102639.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, ICC -
The Long Terminal Repeats of ERV6 Are Activated in Pre-Implantation Embryos of Cynomolgus Monkey
Authors: K Duan, CY Si, SM Zhao, ZY Ai, BH Niu, Y Yin, LF Xiang, H Ding, Y Zheng
Cells, 2021-10-09;10(10):.
Species: Cynomolgus Monkey
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC/IF -
Orphan CpG islands amplify poised enhancer regulatory activity and determine target gene responsiveness
Authors: T Pachano, V Sánchez-Ga, T Ealo, M Mariner-Fa, T Bleckwehl, HG Asenjo, P Respuela, S Cruz-Molin, M Muñoz-San, E Haro, WFJ van IJcken, D Landeira, A Rada-Igles
Nature Genetics, 2021-06-28;53(7):1036-1049.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: IHC -
Chemical conversion of human epidermal stem cells into intestinal goblet cells for modeling mucus-microbe interaction and therapy
Authors: A Zhao, H Qin, M Sun, M Tang, J Mei, K Ma, X Fu
Science Advances, 2021-04-14;7(16):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Profiling of conditionally reprogrammed cell lines for in vitro chemotherapy response prediction of pancreatic cancer
Authors: HS Lee, E Kim, J Lee, SJ Park, HK Hwang, CH Park, SY Jo, CM Kang, SM Hong, H Kang, JH Jo, IR Cho, MJ Chung, JY Park, SW Park, SY Song, JM Han, S Kim, S Bang
EBioMedicine, 2021-02-25;65(0):103218.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Formative pluripotent stem cells show features of epiblast cells poised for gastrulation
Authors: X Wang, Y Xiang, Y Yu, R Wang, Y Zhang, Q Xu, H Sun, ZA Zhao, X Jiang, X Wang, X Lu, D Qin, Y Quan, J Zhang, N Shyh-Chang, H Wang, N Jing, W Xie, L Li
Cell Research, 2021-02-19;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: ICC, IHC -
Trophectoderm mechanics direct epiblast shape upon embryo implantation
Authors: A Weberling, M Zernicka-G
Cell Reports, 2021-01-19;34(3):108655.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Embryo
Applications: IHC -
Long noncoding RNA LINC00261 suppresses prostate cancer tumorigenesis through upregulation of GATA6-mediated DKK3
Authors: Y Li, H Li, X Wei
Cancer Cell Int, 2020-09-30;20(0):474.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: ChIP, Immunoprecipitation -
Reprogramming competence of OCT factors is determined by transactivation domains
Authors: KP Kim, Y Wu, J Yoon, K Adachi, G Wu, S Velychko, CM MacCarthy, B Shin, A Röpke, MJ Arauzo-Bra, M Stehling, DW Han, Y Gao, J Kim, S Gao, HR Schöler
Science Advances, 2020-09-02;6(36):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Generation of pancreatic ? cells from CD177(+) anterior definitive endoderm
Authors: Mahaddalkar PU, Scheibner K, Pfluger S et al.
Nature Biotechnology
-
Developmental potential of aneuploid human embryos cultured beyond implantation
Authors: MN Shahbazi, T Wang, X Tao, BAT Weatherbee, L Sun, Y Zhan, L Keller, GD Smith, A Pellicer, RT Scott, E Seli, M Zernicka-G
Nat Commun, 2020-08-10;11(1):3987.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: ICC, IHC -
Generation of two iPSC lines (FAMRCi007-A and FAMRCi007-B) from patient with Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy and heart rhythm abnormalities carrying genetic variant LMNA p.Arg249Gln
Authors: K Perepelina, A Kostina, P Klauzen, A Khudiakov, M Rabino, S Crasto, A Zlotina, Y Fomicheva, A Sergushich, M Oganesian, A Dmitriev, A Kostareva, E Di Pasqual, A Malashiche
Stem Cell Res, 2020-06-29;47(0):101895.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, ICC -
Intrauterine Pressures Adjusted by Reichert's Membrane Are Crucial for Early Mouse Morphogenesis
Authors: Y Ueda, C Kimura-Yos, K Mochida, M Tsume, Y Kameo, T Adachi, O Lefebvre, R Hiramatsu, I Matsuo
Cell Rep, 2020-05-19;31(7):107637.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Generation of two induced pluripotent stem cell lines (FAMRCi005-A and FAMRCi005-B) from patient carrying genetic variant LMNA p.Asp357Val
Authors: P Klauzen, K Perepelina, A Khudiakov, A Zlotina, Y Fomicheva, T Pervunina, T Vershinina, A Kostareva, A Malashiche
Stem Cell Res, 2020-02-05;43(0):101719.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Generation of two iPSC lines (FAMRCi004-A and FAMRCi004-B) from patient with familial progressive cardiac conduction disorder carrying genetic variant DSP p.His1684Arg
Authors: A Khudiakov, K Perepelina, P Klauzen, A Zlotina, K Gusev, E Kaznacheye, A Malashiche, A Kostareva
Stem Cell Res, 2020-02-04;43(0):101720.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, IF/ICC -
Generation of two iPSC lines (FAMRCi006-A and FAMRCi006-B) from patient with dilated cardiomyopathy and Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy associated with genetic variant LMNAp.Arg527Pro
Authors: K Perepelina, P Klauzen, A Khudiakov, A Zlotina, Y Fomicheva, D Rudenko, M Gordeev, A Sergushich, A Malashiche, A Kostareva
Stem Cell Res, 2020-01-31;43(0):101714.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Role of bulge epidermal stem cells and TSLP signaling in psoriasis
Authors: N Gago-Lopez, LF Mellor, D Megías, G Martín-Ser, A Izeta, F Jimenez, EF Wagner
EMBO Mol Med, 2019-09-26;0(0):e10697.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Distinct Molecular Trajectories Converge to Induce Naive Pluripotency
Authors: Hannah T. Stuart, Giuliano G. Stirparo, Tim Lohoff, Lawrence E. Bates, Masaki Kinoshita, Chee Y. Lim et al.
Cell Stem Cell
-
Molecular profiling of the basement membrane of pluripotent epiblast cells in post-implantation stage mouse embryos
Authors: S Futaki, I Nakano, M Kawasaki, N Sanzen, K Sekiguchi
Regen Ther, 2019-05-10;12(0):55-65.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr -
FGFR1 regulates trophectoderm development and facilitates blastocyst implantation
Authors: Agata Kurowski, Andrei Molotkov, Philippe Soriano
Developmental Biology
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Embryo
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
The BAF and PRC2 Complex Subunits Dpf2 and Eed Antagonistically Converge on Tbx3 to Control ESC Differentiation
Authors: W Zhang, C Chronis, X Chen, H Zhang, R Spalinskas, M Pardo, L Chen, G Wu, Z Zhu, Y Yu, L Yu, J Choudhary, J Nichols, MM Parast, B Greber, P Sahlén, K Plath
Cell Stem Cell, 2019-01-03;24(1):138-152.e8.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
yylncT Defines a Class of Divergently Transcribed lncRNAs and Safeguards the T-mediated Mesodermal Commitment of Human PSCs
Authors: S Frank, G Ahuja, D Bartsch, N Russ, W Yao, JC Kuo, JP Derks, VS Akhade, Y Kargapolov, T Georgomano, JE Messling, M Gramm, L Brant, R Rehimi, NE Vargas, A Kuroczik, TP Yang, RGA Sahito, J Franzen, J Hescheler, A Sachinidis, M Peifer, A Rada-Igles, M Kanduri, IG Costa, C Kanduri, A Papantonis, L Kurian
Cell Stem Cell, 2018-12-13;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Improving Cell Survival in Injected Embryos Allows Primed Pluripotent Stem Cells to Generate Chimeric Cynomolgus Monkeys
Authors: Y Kang, Z Ai, K Duan, C Si, Y Wang, Y Zheng, J He, Y Yin, S Zhao, B Niu, X Zhu, L Liu, L Xiang, L Zhang, Y Niu, W Ji, T Li
Cell Rep, 2018-11-27;25(9):2563-2576.e9.
Species: Primate - Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating Monkey or Cynomolgus Macaque)
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Combinatorial Smad2/3 Activities Downstream of Nodal Signaling Maintain Embryonic/Extra-Embryonic Cell Identities during Lineage Priming
Authors: AD Senft, I Costello, HW King, AW Mould, EK Bikoff, EJ Robertson
Cell Rep, 2018-08-21;24(8):1977-1985.e7.
-
The miR-590/Acvr2a/Terf1 Axis Regulates Telomere Elongation and Pluripotency of Mouse iPSCs
Authors: Q Liu, G Wang, Y Lyu, M Bai, Z Jiapaer, W Jia, T Han, R Weng, Y Yang, Y Yu, J Kang
Stem Cell Reports, 2018-06-14;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
OCT4/POU5F1 is required for NANOG expression in bovine blastocysts
Authors: K Simmet, V Zakhartche, J Philippou-, H Blum, N Klymiuk, E Wolf
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2018-02-26;0(0):.
Species: Bovine
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
GATA6 phosphorylation by Erk1/2 propels exit from pluripotency and commitment to primitive endoderm
Authors: Y Meng, R Moore, W Tao, ER Smith, JD Tse, C Caslini, XX Xu
Dev. Biol., 2018-02-15;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ChIP, IHC -
Probing GATA factor function in mouse Leydig cells via testicular injection of adenoviral vectors
Authors: Gervette M. Penny, Rebecca B. Cochran, Marjut Pihlajoki, Antti Kyrönlahti, Anja Schrade, Merja Häkkinen et al.
Reproduction
Species: Transgenic Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
ICM conversion to epiblast by FGF/ERK inhibition is limited in time and requires transcription and protein degradation
Authors: S Bessonnard, S Coqueran, S Vandormael, A Dufour, J Artus, M Cohen-Tann
Sci Rep, 2017-09-25;7(1):12285.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Direct Reprogramming of Fibroblasts via a Chemically Induced XEN-like State
Authors: X Li, D Liu, Y Ma, X Du, J Jing, L Wang, B Xie, D Sun, S Sun, X Jin, X Zhang, T Zhao, J Guan, Z Yi, W Lai, P Zheng, Z Huang, Y Chang, Z Chai, J Xu, H Deng
Cell Stem Cell, 2017-06-22;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Distinct Requirements for FGFR1 and FGFR2 in Primitive Endoderm Development and Exit from Pluripotency
Authors: A Molotkov, P Mazot, JR Brewer, RM Cinalli, P Soriano
Dev. Cell, 2017-05-25;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Lineage Establishment and Progression within the Inner Cell Mass of the Mouse Blastocyst Requires FGFR1 and FGFR2
Authors: M Kang, V Garg, AK Hadjantona
Dev. Cell, 2017-05-25;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
The chromatin modifier Satb1 regulates cell fate through Fgf signalling in the early mouse embryo
Authors: M Goolam, M Zernicka-G
Development, 2017-03-13;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Abrogation Of Gap Junctional Communication In Es Cells Results In A Disruption Of Primitive Endoderm Formation In Embryoid Bodies
Stem Cells, 2016-12-20;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: IHC-Fr -
Efficient derivation of extraembryonic endoderm stem cell lines from mouse postimplantation embryos
Sci Rep, 2016-12-19;6(0):39457.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Asynchronous fate decisions by single cells collectively ensure consistent lineage composition in the mouse blastocyst
Nat Commun, 2016-11-18;7(0):13463.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr -
p38 (Mapk14/11) occupies a regulatory node governing entry into primitive endoderm differentiation during preimplantation mouse embryo development
Open Biol, 2016-09-01;6(9):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Dynamic Heterogeneity of Brachyury in Mouse Epiblast Stem Cells Mediates Distinct Response to Extrinsic Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) Signaling
Authors: L Song, J Chen, G Peng, K Tang, N Jing
J. Biol. Chem., 2016-05-16;291(29):15212-25.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Epigenetic regulation of histone modifications and Gata6 gene expression induced by maternal diet in mouse embryoid bodies in a model of developmental programming.
Authors: Sun, Congshan, Denisenko, Oleg, Sheth, Bhavwant, Cox, Andy, Lucas, Emma S, Smyth, Neil R, Fleming, Tom P
BMC Dev Biol, 2015-01-21;15(0):3.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
GATA family members as inducers for cellular reprogramming to pluripotency.
Authors: Shu, Jian, Zhang, Ke, Zhang, Minjie, Yao, Anzhi, Shao, Sida, Du, Fengxia, Yang, Caiyun, Chen, Wenhan, Wu, Chen, Yang, Weifeng, Sun, Yingli, Deng, Hongkui
Cell Res, 2015-01-16;25(2):169-80.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Immunoprecipitation -
Loss of LKB1 leads to impaired epithelial integrity and cell extrusion in the early mouse embryo.
Authors: Krawchuk D, Anani S, Honma-Yamanaka N, Polito S, Shafik M, Yamanaka Y
J Cell Sci, 2015-01-14;128(5):1011-22.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Embryo
Applications: IHC -
Inhibition of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) signaling can substitute for Oct4 protein in reprogramming and maintain pluripotency.
Authors: Tan F, Qian C, Tang K, Abd-Allah S, Jing N
J Biol Chem, 2014-12-29;290(7):4500-11.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
BMP signalling regulates the pre-implantation development of extra-embryonic cell lineages in the mouse embryo.
Authors: Graham, Sarah J, Wicher, Krzyszto, Jedrusik, Agnieszk, Guo, Guoji, Herath, Wishva, Robson, Paul, Zernicka-Goetz, Magdalen
Nat Commun, 2014-12-16;5(0):5667.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
GATA6 levels modulate primitive endoderm cell fate choice and timing in the mouse blastocyst.
Authors: Schrode N, Saiz N, Di Talia S, Hadjantonakis A
Dev Cell, 2014-05-15;29(4):454-67.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Formation of a polarised primitive endoderm layer in embryoid bodies requires fgfr/erk signalling.
Authors: Doughton, Gail, Wei, Jun, Tapon, Nicolas, Welham, Melanie, Chalmers, Andrew D
PLoS ONE, 2014-04-21;9(4):e95434.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: ICC, Western Blot -
Mouse early extra-embryonic lineages activate compensatory endocytosis in response to poor maternal nutrition.
Authors: Sun, Congshan, Velazquez, Miguel A, Marfy-Smith, Stephani, Sheth, Bhavwant, Cox, Andy, Johnston, David A, Smyth, Neil, Fleming, Tom P
Development, 2014-02-06;141(5):1140-50.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: ICC, Western Blot -
Bmi1 facilitates primitive endoderm formation by stabilizing Gata6 during early mouse development
Authors: Fabrice Lavial, Sylvain Bessonnard, Yusuke Ohnishi, Akiko Tsumura, Anil Chandrashekran, Mark A. Fenwick et al.
Genes & Development
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells, Embryoid Bodies
Applications: Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot, Immunocytochemistry -
GATA6 Promotes Angiogenic Function and Survival in Endothelial Cells by Suppression of Autocrine Transforming Growth Factor beta/Activin Receptor-like Kinase 5 Signaling.
Authors: Froese N, Kattih B, Breitbart A, Grund A, Geffers R, Molkentin JD, Kispert A, Wollert KC, Drexler H, Heineke J
J. Biol. Chem., 2010-12-02;286(7):5680-90.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: ICC, Western Blot -
A role for PDGF signaling in expansion of the extra-embryonic endoderm lineage of the mouse blastocyst.
Authors: Artus J, Panthier JJ, Hadjantonakis AK
Development, 2010-09-08;137(20):3361-72.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
FGF signal-dependent segregation of primitive endoderm and epiblast in the mouse blastocyst
Authors: Yojiro Yamanaka, Fredrik Lanner, Janet Rossant
Development
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Embryo
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
A Gata6-Wnt pathway required for epithelial stem cell development and airway regeneration.
Authors: Zhang Y, Goss AM, Cohen ED, Kadzik R, Lepore JJ, Muthukumaraswamy K, Yang J, DeMayo FJ, Whitsett JA, Parmacek MS, Morrisey EE
Nat. Genet., 2008-06-08;40(7):862-70.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
New cell lines from mouse epiblast share defining features with human embryonic stem cells.
Authors: Tesar PJ, Chenoweth JG, Brook FA, Davies TJ, Evans EP, Mack DL, Gardner RL, McKay RD
Nature, 2007-06-27;448(7150):196-9.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
The human mucin MUC4 is transcriptionally regulated by caudal-related homeobox, hepatocyte nuclear factors, forkhead box A, and GATA endodermal transcription factors in epithelial cancer cells.
Authors: Jonckheere N, Vincent A, Perrais M, Ducourouble MP, Male AK, Aubert JP, Pigny P, Carraway KL, Freund JN, Renes IB, Van Seuningen I
J. Biol. Chem., 2007-06-06;282(31):22638-50.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: ChIP -
Inducible Stem-Cell-Derived Embryos Capture Mouse Morphogenetic Events In Vitro
Authors: Gianluca Amadei, Kasey Y.C. Lau, Joachim De Jonghe, Carlos W. Gantner, Berna Sozen, Christopher Chan et al.
Developmental Cell
-
Micropattern differentiation of mouse pluripotent stem cells recapitulates embryo regionalized cell fate patterning
Authors: Sophie M Morgani, Jakob J Metzger, Jennifer Nichols, Eric D Siggia, Anna-Katerina Hadjantonakis
eLife
-
Unique functions of Gata4 in mouse liver induction and heart development
Authors: Matthew J. Borok, Virginia E. Papaioannou, Lori Sussel
Developmental Biology
-
FGFR1 regulates trophectoderm development and facilitates blastocyst implantation
Authors: Agata Kurowski, Andrei Molotkov, Philippe Soriano
Developmental Biology
-
Gata6 restricts Isl1 to the posterior of nascent hindlimb buds through Isl1 cis-regulatory modules
Authors: Naoyuki Tahara, Ryutaro Akiyama, Joshua W. M. Theisen, Hiroko Kawakami, Julia Wong, Daniel J. Garry et al.
Developmental Biology
-
Mapping global changes in nuclear cytosine base modifications in the early mouse embryo.
Authors: Li Y, Seah MK, O'Neill C.
Reproduction.
-
Fast In Vitro Procedure to Identify Extraembryonic Differentiation Defect of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
Authors: Richard Patryk Ngondo, Michel Cohen-Tannoudji, Constance Ciaudo
STAR Protocols
-
Generation of human elongating multi-lineage organized cardiac gastruloids
Authors: Zachary T. Olmsted, Maria Belen Paredes-Espinosa, Janet L. Paluh
STAR Protocols
-
Self-Organization of Mouse Stem Cells into an Extended Potential Blastoid
Authors: Sozen B, Cox AL, De Jonghe J, et al.
Dev. Cell
-
A Gata4 nuclear GFP transcriptional reporter to study endoderm and cardiac development in the mouse
Authors: Claire S. Simon, Lu Zhang, Tao Wu, Weibin Cai, Nestor Saiz, Sonja Nowotschin et al.
Biology Open
-
Fibroblast GATA-4 and GATA-6 promote myocardial adaptation to pressure overload by enhancing cardiac angiogenesis
Authors: Gesine M. Dittrich, Natali Froese, Xue Wang, Hannah Kroeger, Honghui Wang, Malgorzata Szaroszyk et al.
Basic Research in Cardiology
-
A loss-of-function and H2B-Venus transcriptional reporter allele for Gata6 in mice
Authors: Laina Freyer, Christian Schröter, Néstor Saiz, Nadine Schrode, Sonja Nowotschin, Alfonso Martinez-Arias et al.
BMC Developmental Biology
-
CNOT3-Dependent mRNA Deadenylation Safeguards the Pluripotent State.
Authors: Zheng X, Yang P, Lackford B et al.
Stem Cell Reports
-
Functional Role of Mst1/Mst2 in Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation
Authors: Peng Li, Ying Chen, Kinglun Kingston Mak, Chun Kwok Wong, Chi Chiu Wang, Ping Yuan
PLoS ONE
-
The Mesenchymal Cap of the Atrial Septum and Atrial and Atrioventricular Septation
Authors: Deepe R, Fitzgerald E, Wolters R et al.
J Cardiovasc Dev Dis
-
GATA3 recruits UTX for gene transcriptional activation to suppress metastasis of breast cancer
Authors: W Yu, W Huang, Y Yang, R Qiu, Y Zeng, Y Hou, G Sun, H Shi, S Leng, D Feng, Y Chen, S Wang, X Teng, H Yu, Y Wang
Cell Death Dis, 2019-11-04;10(11):832.
-
In Vitro Characterization of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Isolated from Different Tissues with a Potential to Promote Complex Bone Regeneration
Authors: Áron Szepesi, Zsolt Matula, Anna Szigeti, György Várady, József Szalma, Gyula Szabó et al.
Stem Cells International
-
Zfp281 is essential for mouse epiblast maturation through transcriptional and epigenetic control of Nodal signaling
Authors: Xin Huang, Sophie Balmer, Fan Yang, Miguel Fidalgo, Dan Li, Diana Guallar et al.
eLife
-
Induced pluripotent stem cells and cerebral organoids from the critically endangered Sumatran rhinoceros
Authors: Vera Zywitza, Silke Frahm, Norman Krüger, Anja Weise, Frank Göritz, Robert Hermes et al.
iScience
-
In vivo partial reprogramming by bacteria promotes adult liver organ growth without fibrosis and tumorigenesis
Authors: Samuel Hess, Timothy J. Kendall, Maria Pena, Keitaro Yamane, Daniel Soong, Linda Adams et al.
Cell Reports Medicine
-
Cell-Cycle-Dependent ERK Signaling Dynamics Direct Fate Specification in the Mammalian Preimplantation Embryo
Authors: Michael J. Pokrass, Kathleen A. Ryan, Tianchi Xin, Brittany Pielstick, Winston Timp, Valentina Greco et al.
Developmental Cell
-
Live Visualization of ERK Activity in the Mouse Blastocyst Reveals Lineage-Specific Signaling Dynamics
Authors: Claire S. Simon, Shahadat Rahman, Dhruv Raina, Christian Schröter, Anna-Katerina Hadjantonakis
Developmental Cell
-
Single cell transcriptome analysis of human, marmoset and mouse embryos reveals common and divergent features of preimplantation development
Authors: Thorsten Boroviak, Giuliano G. Stirparo, Sabine Dietmann, Irene Hernando-Herraez, Hisham Mohammed, Wolf Reik et al.
Development
-
CTR9/PAF1c regulates molecular lineage identity, histone H3K36 trimethylation and genomic imprinting during preimplantation development
Authors: Kun Zhang, Jocelyn M. Haversat, Jesse Mager
Developmental Biology
-
A single-cell transcriptome atlas of marsupial embryogenesis and X inactivation
Authors: Shantha K. Mahadevaiah, Mahesh N. Sangrithi, Takayuki Hirota, James M. A. Turner
Nature
-
Progression of the pluripotent epiblast depends upon the NMD Factor UPF2
Authors: Chousal JN, Sohni A, Vitting-Seerup K et al.
Development (Cambridge, England)
-
Generation of Blastocyst-like Structures from Mouse Embryonic and Adult Cell Cultures
Authors: Ronghui Li, Cuiqing Zhong, Yang Yu, Haisong Liu, Masahiro Sakurai, Leqian Yu et al.
Cell
-
Distinct mechanisms for PDGF and FGF signaling in primitive endoderm development
Authors: Andrei Molotkov, Philippe Soriano
Developmental Biology
-
Probing GATA factor function in mouse Leydig cells via testicular injection of adenoviral vectors
Authors: Gervette M. Penny, Rebecca B. Cochran, Marjut Pihlajoki, Antti Kyrönlahti, Anja Schrade, Merja Häkkinen et al.
Reproduction
-
The Relationship between the Expression of GATA4 and GATA6 with the Clinical Characteristics and Prognosis of Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Authors: Victoria Heredia-Soto, Laura Gutiérrez-Sainz, Ismael Ghanem, Laura Guerra, Elena Palacios, Marta de Uribe et al.
Biomedicines
-
The miR-196b miRNA inhibits the GATA6 intestinal transcription factor and is upregulated in colon cancer patients
Authors: Sebastian Fantini, Valentina Salsi, Luca Reggiani, Antonino Maiorana, Vincenzo Zappavigna
Oncotarget
-
Human hypoblast formation is not dependent on FGF signalling
Authors: Mila Roode, Kathryn Blair, Philip Snell, Kay Elder, Sally Marchant, Austin Smith et al.
Developmental Biology
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human GATA-6 Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 2 Reviews)
Have you used Human GATA-6 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
Paraffin embedded tissue
Antibody dilution 1:1000