Human/Mouse EBF-1 Antibody Summary
Arg416-Ser520
Accession # Q07802
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human/Mouse EBF‑1 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of Raji human Burkitt's lymphoma cell line, Daudi human Burkitt's lymphoma cell line, and CH-1 mouse B cell lymphoma cell line, and L1.2 mouse pro-B cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Human/Mouse EBF-1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF5165) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF109). A specific band was detected for EBF-1 at approximately 70 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
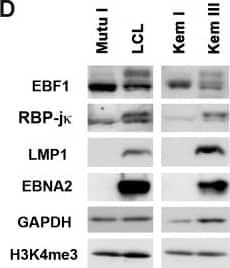
Detection of Human EBF-1 by Western Blot Differential binding of transcription factors on EBV genomes in type I and type III latency.(A) ChIP-Seq tracks mapped to EBV genome in LCL (red) or Mutu I (blue) for EBF1 or RBP-j kappa as indicated. EBNA2 ChIP-Seq for LCL (black). Y-axis represent raw read counts. (B) ChIP-qPCR for EBF1 or RBP-j kappa in LCL (red) or Mutu I (blue) at various EBV genome regulatory regions as indicated and Actin genomic region as negative control. (C) Same as in B, except for isogenic EBV positive BL cells Kem III (red) or Kem I (blue). Asterisk indicates p < 0.05. (D) Western blot of Mutu I, LCL, Kem I, and Kem III probed with antibody to EBF1, RBP-j kappa, LMP1, and EBNA2, with cellular loading controls for GAPDH and H3K4me3, as indicated. (E) RT-qPCR for EBV type III gene expression in LCL or Mutu I (left panel) or Kem I and Kem III (right panel). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26752713), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
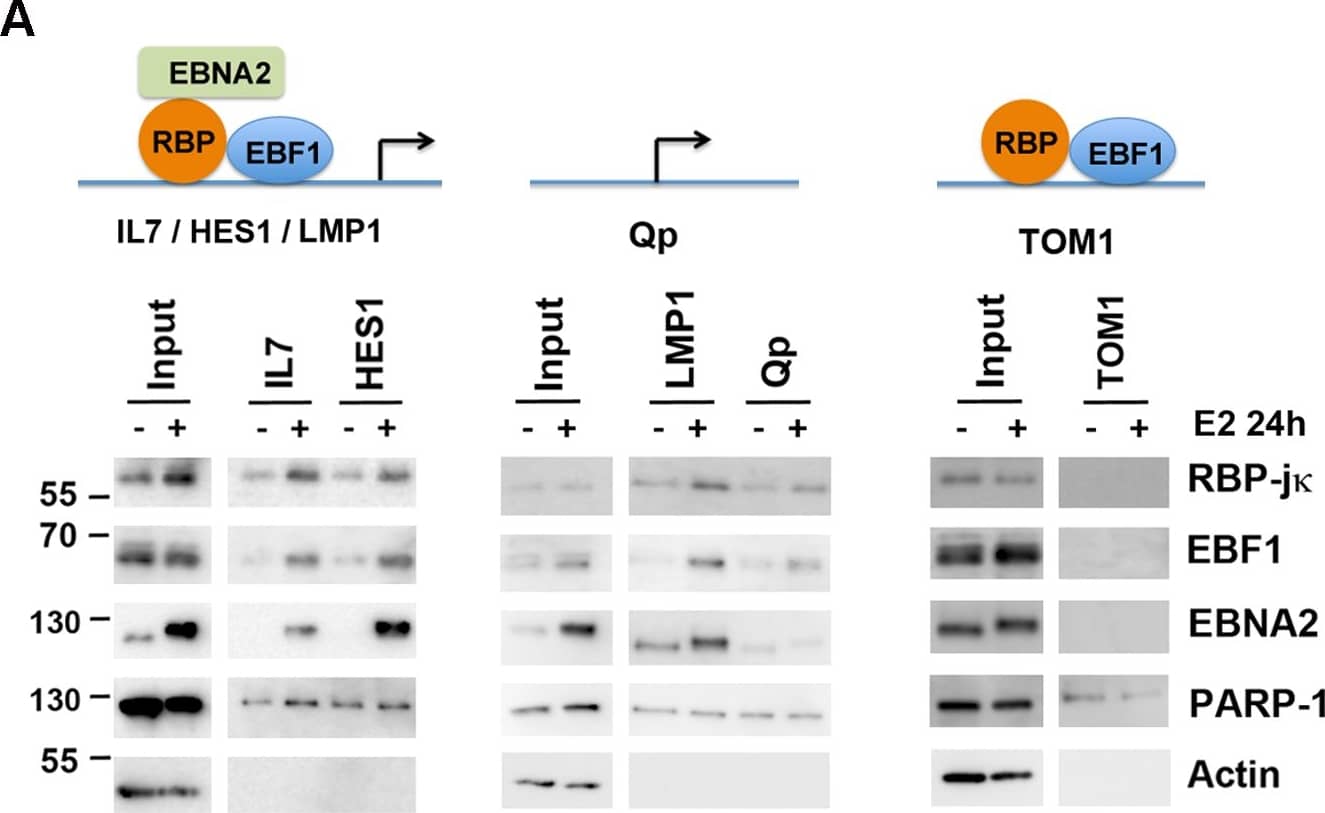
Detection of Human EBF-1 by Western Blot Cooperative binding and colocalization of EBF1, RBP-j kappa, and EBNA2 at DNA regulatory elements.(A) DNA-affinity binding assays with nuclear extracts from EREB2.5 cells with (+) or without (-) estradiol (E2) using DNA regulatory elements from IL7, HES1 (left), or LMP1, Qp (middle), or TOM1 (right). Input (10%) is indicated, and bound proteins were assayed by Western blot for EBF1, RBP-j kappa, EBNA2, and specificity controls for PARP1 and Actin. (B) ChIP-reChIP assays in LCLs with EBF1 as first ChIP, followed by a reChIP with either no antibody control or antibody to EBF1, RBP-j kappa or EBNA2. ReChIP DNA was quantified by qPCR at LMP1, IL7, and BDH2 (an EBF1 only site) binding sites. (C) Same as in B, except first ChIP was with RBP-j kappa followed by a ReChIP with no antibody control, or EBF1, RBP-j kappa, or EBNA2 antibody and assayed at LMP1, IL7, or LZTFL1 (an RBP-j kappa only site) binding sites. Asterisk indicates p < 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26752713), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
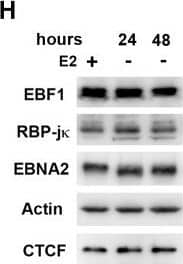
Detection of Human EBF-1 by Western Blot EBNA2-dependent transcription factor redistribution in chromatin occupancy.EREB2.5 cells were treated with (+) or without (-) estradiol (E2) for 24 or 48 hrs and then assayed by ChIP for binding to EBF1 (A and B), RBP-j kappa (C and D), or EBNA2 (E and F) at cellular (A, C, E) or EBV genome sites (B, D, F). Actin genomic region (cellular) or Qp (EBV) was used as negative binding control for EBF1, RBP-j kappa, ορ EBNA2 ChIP. (G) ChIP binding for CTCF, PU.1, or PAX5 in EREB2.5 cells treated (blue) or untreated (red) with E2 for 48 hrs. PPP1R1B or KCTD17 genomic region was negative binding control PU.1 or PAX5, respectively. Asterisk indicates p < 0.05. (H) Western blot showing protein levels for EBF1, RBP-j kappa, EBNA2, Actin, and CTCF in EREB2.5 cells at 24 and 48 hrs after E2 withdrawal. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26752713), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: EBF-1
EBF-1 (Early B cell Factor 1; also OLF1 and COE1) is a 65-70 kDa member of the COE family of transcription factors. Although expressed in adipocytes and neurons, it is best studied in B cells where IL-7 acts to promote EBF-1 in pre-proB cells, leading to proB stage development. Mouse EBF-1 is 591 amino acids (aa) in length. It contains one DNA-binding region with an embedded zinc-finger motif (aa 51‑235), a dimerization segment between aa 370‑430, and a Pro/Ser-rich transactivation domain (aa 462‑550). EBF-1 either homodimerizes, or heterodimerizes with EBF-2 and -3. There is an alternate start site at Met134, and an isoform that shows a one aa substitution for aa 252‑259. Over aa 416‑520, mouse EBF-1 shows absolute aa identity to the equivalent sequence in rat and human EBF-1.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human/Mouse EBF-1 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
3
Citations: Showing 1 - 3
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Chromatin restriction by the nucleosome remodeler Mi-2 beta and functional interplay with lineage-specific transcription regulators control B-cell differentiation
Authors: Toshimi Yoshida, Yeguang Hu, Zhihong Zhang, Akinola O. Emmanuel, Kiriaki Galani, Brejnev Muhire et al.
Genes & Development
-
Reduced IRF4 expression promotes lytic phenotype in Type 2 EBV-infected B cells
Authors: JA Bristol, J Brand, M Ohashi, MR Eichelberg, A Casco, SE Nelson, M Hayes, JC Romero-Mas, DC Baiu, JE Gumperz, EC Johannsen, HQ Dinh, SC Kenney
PloS Pathogens, 2022-04-26;18(4):e1010453.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
EBNA2 Drives Formation of New Chromosome Binding Sites and Target Genes for B-Cell Master Regulatory Transcription Factors RBP-jkappa and EBF1.
Authors: Lu F, Chen H, Kossenkov A, DeWispeleare K, Won K, Lieberman P
PLoS Pathog, 2016-01-11;12(1):e1005339.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human/Mouse EBF-1 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human/Mouse EBF-1 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human/Mouse EBF-1 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image

