Human SPINK1 Antibody Summary
Asp24-Cys79
Accession # P00995
Customers also Viewed
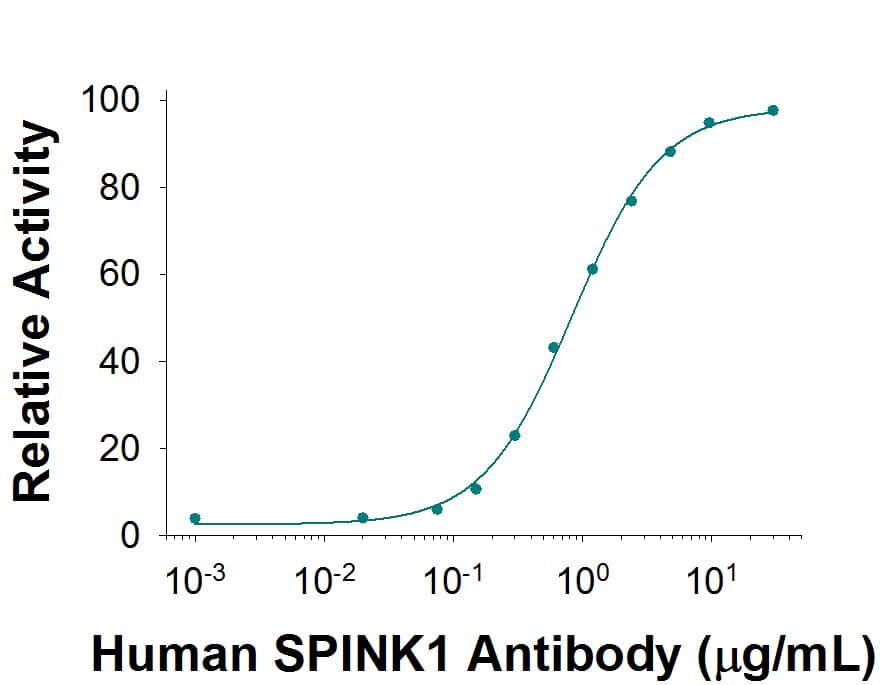
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
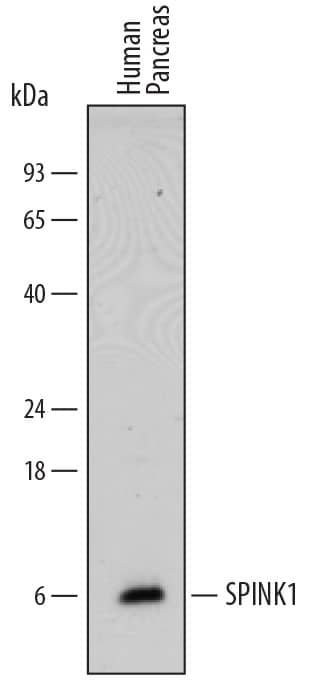
Detection of Human SPINK1 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of human pancreas tissue. PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human SPINK1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB7496) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF018). A specific band was detected for SPINK1 at approximately 6 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human SPINK1 by Simple WesternTM. Simple Western lane view shows lysates of human pancreas tissue, loaded at 0.5 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for SPINK1 at approximately 6 kDa (as indicated) using 100 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human SPINK1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB7496). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230 kDa separation system. Non-specific interaction with the 230 kDa Simple Western standard may be seen with this antibody.
 View Larger
View Larger
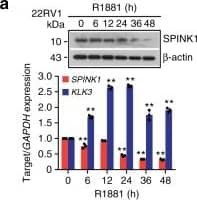
Detection of Human SPINK1 by Western Blot Androgen signaling negatively regulates SPINK1 expression in prostate cancer.a Immunoblot for SPINK1 in 22RV1 cells stimulated with R1881 (10 nM) (top). QPCR data showing relative expression of SPINK1&KLK3 in the same cells (bottom). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31959826), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human SPINK1 by Western Blot Reprogramming factor SOX2&AR transcriptional co-repressor REST modulate SPINK1 expression.a Schematic showing SOX2 binding elements (S1, S2,&S3) on the SPINK1 promoter (top). ChIP-qPCR data for SOX2 occupancy on the SPINK1 promoter in wildtype LNCaP&LNCaP-AI cells (androgen-deprived for 15 days) (bottom). b Same as in a, except 22RV1 cells. c ChIP-qPCR data for RNA Pol-II binding on the SPINK1 promoter using cells as a. d Same as c, except 22RV1 cells. e Immunoblot for SOX2&SPINK1 in siRNA mediated SOX2-silenced LNCaP-AI&control cells. f Same as e, except 22RV1 cells.Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31959826), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
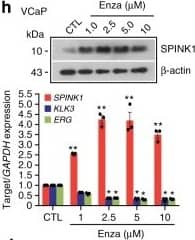
Detection of Human SPINK1 by Western Blot Androgen signaling negatively regulates SPINK1 expression in prostate cancer. h Immunoblot showing SPINK1 expression in VCaP cells treated with enzalutamide (top). QPCR data showing relative expression of SPINK1, KLK3,&ERG (bottom). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31959826), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
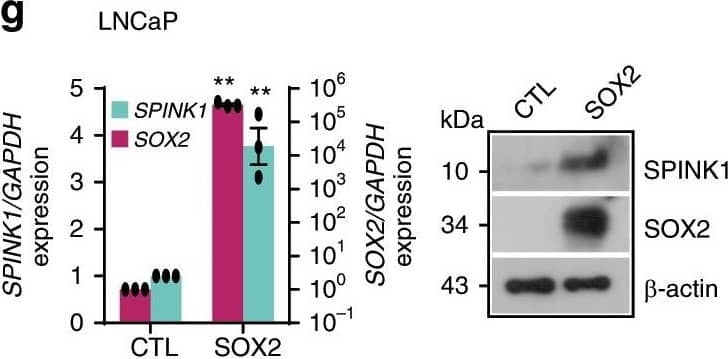 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human SPINK1 by Western Blot Reprogramming factor SOX2&AR transcriptional co-repressor REST modulate SPINK1 expression.a Schematic showing SOX2 binding elements (S1, S2,&S3) on the SPINK1 promoter (top). ChIP-qPCR data for SOX2 occupancy on the SPINK1 promoter in wildtype LNCaP&LNCaP-AI cells (androgen-deprived for 15 days) (bottom). b Same as in a, except 22RV1 cells. c ChIP-qPCR data for RNA Pol-II binding on the SPINK1 promoter using cells as a. d Same as c, except 22RV1 cells. e Immunoblot for SOX2&SPINK1 in siRNA mediated SOX2-silenced LNCaP-AI&control cells. f Same as e, except 22RV1 cells. g QPCR data showing relative expression of SOX2&SPINK1 upon transient SOX2 overexpression in LNCaP cells (left). Immunoblot for SOX2&SPINK1 expression(right). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31959826), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
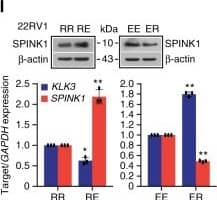 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human SPINK1 by Western Blot Androgen signaling negatively regulates SPINK1 expression in prostate cancer. l Immunoblot showing SPINK1 expression in 22RV1 cells as indicated in k (top). QPCR data showing relative expression of SPINK1&KLK3 using same cells in k (bottom)Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31959826), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
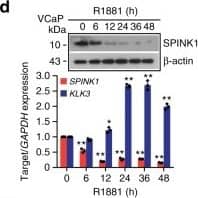 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human SPINK1 by Western Blot Androgen signaling negatively regulates SPINK1 expression in prostate cancer.a Immunoblot for SPINK1 in 22RV1 cells stimulated with R1881 (10 nM) (top). QPCR data showing relative expression of SPINK1&KLK3 in the same cells (bottom). b Immunostaining for SPINK1&AR in 22RV1 cells stimulated with R1881 (10 nM). c Same as b, except dot plot represents quantification for SPINK1 mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) per unit area shown as arbitrary units (AU). d Same as a, except VCaP cells used. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31959826), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
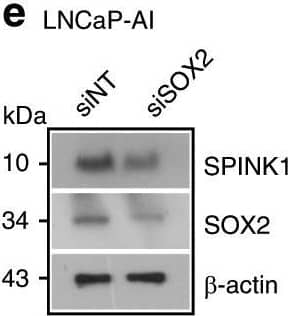 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human SPINK1 by Western Blot Reprogramming factor SOX2&AR transcriptional co-repressor REST modulate SPINK1 expression.a Schematic showing SOX2 binding elements (S1, S2,&S3) on the SPINK1 promoter (top). ChIP-qPCR data for SOX2 occupancy on the SPINK1 promoter in wildtype LNCaP&LNCaP-AI cells (androgen-deprived for 15 days) (bottom). b Same as in a, except 22RV1 cells. c ChIP-qPCR data for RNA Pol-II binding on the SPINK1 promoter using cells as a. d Same as c, except 22RV1 cells. e Immunoblot for SOX2&SPINK1 in siRNA mediated SOX2-silenced LNCaP-AI&control cells. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31959826), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
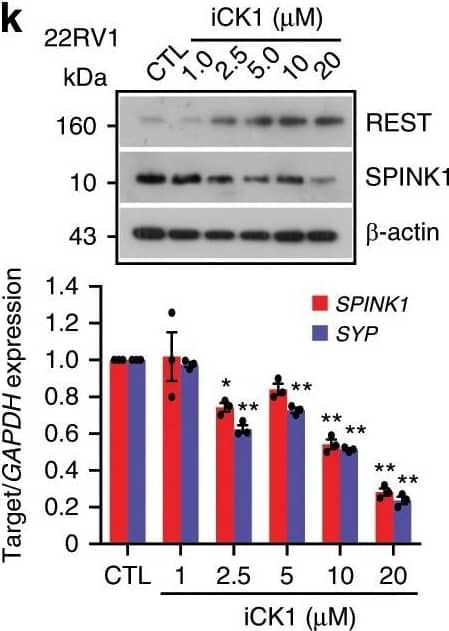
Detection of Human SPINK1 by Western Blot Reprogramming factor SOX2&AR transcriptional co-repressor REST modulate SPINK1 expression.k Immunoblot for the REST&SPINK1 levels in 22RV1 cells treated with Casein Kinase 1 inhibitor (iCK1) as indicated (top). QPCR data for relative SPINK1&SYP expression (bottom). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31959826), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
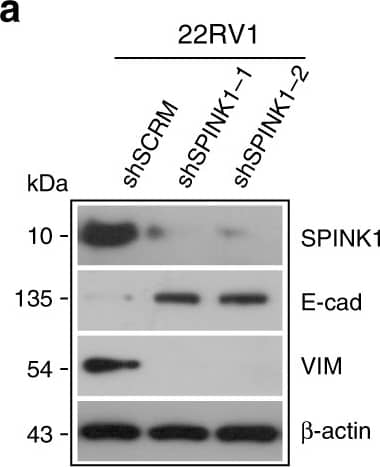
Detection of Human SPINK1 by Western Blot SPINK1 promotes EMT, stemness&chemoresistance in prostate cancer.a Immunoblot analysis for SPINK1, E-Cadherin&Vimentin levels in stable SPINK1-silenced (shSPINK1-1&shSPINK1-2)&control (shSCRM) 22RV1 cells. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31959826), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: SPINK1
SPINK1 (Serine Protease Inhibitor Kazal-type 1; also TATI and PST1) is a 6-7 kDa secreted polypeptide initially identified as a tumor-derived trypsin inhibitor. It is widely expressed and found in cells diverse as pancreatic acinar cells, columnar cells of the stomach, renal collecting duct epithelium, and ureteric transitional plus breast epithelium. SPINK1 is known to be secreted with pancreatic zymogens, and apparently inactivates prematurely-activated trypsin, thus protecting the pancreas from trypsin-mediated enzyme activation. It also is reported to regulate cell migration and proliferation, the latter effect attributed to its structural resemblance to EGF and its ability to bind to activate the EGFR. Mature human SPINK1 is 56 amino acids (aa) in length (aa 24-79). It contains one Kazal-like domain (aa 26-79) that possesses a potential proteolytic cleavage site between Lys41-Ile42. An 11-12 kDa form in SDS-PAGE has been reported for SPINK1, possibly reflecting dimerization. Mature human SPINK1 shares 66% aa sequence identity with mouse Spink3, the mouse equivalent to human SPINK1.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human SPINK1 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
4
Citations: Showing 1 - 4
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Keratin Profiling by Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing Identifies Human Prostate Stem Cell Lineage Hierarchy and Cancer Stem-Like Cells
Authors: Hu WY, Hu DP, Xie L et al.
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
-
Keratin Profiling by Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing Identifies Human Prostate Stem Cell Lineage Hierarchy and Cancer Stem-Like Cells
Authors: Hu WY, Hu DP, Xie L et al.
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
-
Androgen deprivation upregulates SPINK1 expression and potentiates cellular plasticity in prostate cancer
Authors: R Tiwari, N Manzar, V Bhatia, A Yadav, MA Nengroo, D Datta, S Carskadon, N Gupta, M Sigouros, F Khani, M Poutanen, A Zoubeidi, H Beltran, N Palanisamy, B Ateeq
Nat Commun, 2020-01-20;11(1):384.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Aberrant Activation of a Gastrointestinal Transcriptional Circuit in Prostate Cancer Mediates Castration Resistance
Authors: Shipra Shukla, Joanna Cyrta, Devan A. Murphy, Edward G. Walczak, Leili Ran, Praveen Agrawal et al.
Cancer Cell
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human SPINK1 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human SPINK1 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human SPINK1 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image