Human VCAM-1/CD106 Antibody Summary
Phe25-Glu698
Accession # P19320-1
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human VCAM‑1/CD106 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells untreated (-) or treated (+) with 10 ng/mL Recombinant Human TNF‑ alpha (210-TA) for 24 hours. PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human VCAM‑1/CD106 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB8091) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF018). A specific band was detected for VCAM‑1/CD106 at approximately 110 kDa (as indicated). GAPDH (MAB5718) is shown as a loading control. This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Western Blot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of VCAM‑1/CD106 in HuT 78 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. HuT 78 human cutaneous T cell lymphoma cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human VCAM-1/CD106 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB8091, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (MAB002, open histogram) followed by anti-Mouse IgG PE-conjugated Secondary Antibody (F0102B). Staining was performed using our Staining Membrane-associated Proteins protocol.
 View Larger
View Larger
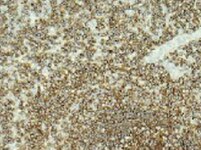
VCAM‑1/CD106 in Human Spleen. VCAM‑1/CD106 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human spleen using Mouse Anti-Human VCAM‑1/CD106 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB8091) at 5 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (VC001). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to splenocytes. Staining was performed using our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human VCAM‑1/CD106 by Simple WesternTM. Simple Western lane view shows lysates of HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells untreated (-) or treated (+) with 10 ng/ml Recombinant Human TNF‑ alpha (210-TA) for 24 hrs, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for VCAM‑1/CD106 at approximately 132 kDa (as indicated) using 20 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human VCAM‑1/CD106 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB8091). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230 kDa separation system.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: VCAM-1/CD106
VCAM-1, also known as CD106, is an immunoglobulin (Ig)-like adhesion molecule that is mainly expressed in endothelial cells and other cell types including macrophages, dendritic cells, neurons, smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, and oocytes (1, 2). It plays a critical role in inflammation by recruiting leukocytes to acute and chronic inflammation sites (3, 4). Alternatively-spliced forms are known to occur, but the most common form is a type I transmembrane protein with a 674 aa extracellular domain (ECD) that includes seven C2-type immunoglobulin domains, a 22 aa transmembrane segment, and a 19 amino acid (aa) cytoplasmic tail. Within the ECD, human VCAM-1 shares 75% and 76% aa sequence identity with the mouse and rat VCAM-1, respectively. VCAM-1 binds to leukocyte integrins alpha 4 beta 1 (VLA-4) and alpha 4 beta 7. During the inflammatory adhesion mechanism, activated integrins halt rolling leukocytes and attach them firmly to the vascular endothelium. The VCAM-1:VLA-4/ alpha 4 beta 7 interaction is also thought to be involved in the extravasation of white blood cells through the blood vessel wall to sites of inflammation (5). ELISA techniques have shown that detectable levels of soluble VCAM-1 are present in the biological fluids of apparently normal individuals, but elevated levels of serum VCAM-1 are indicative of future Atrial Fibrillation incident as well as liver disease (6, 7). Tumor cells use overexpression of VCAM-1 as means of escaping immune surveillance (8).
- Vonderheide, R.H. et al. (1994) J. Cell Biol. 125:215.
- Cybulsky, M.I. et al. (1991) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:7859.
- Luster, A.D. et al. (2005) Nat. Immunol. 6:1182.
- Osborn, L. et al. (1989) Cell 59:1203
- Langer. H.F. et al. 2009. J Cell Mol Med. 13:1211.
- Willeit.K. et al. 2017. JAMA Cardiol. 2:516.
- Lo Iacono.O. et al. 2008. Liver Int. 28:1129.
- Wu.T.C. et al. 2007. Cancer Research. 67:6003
Product Datasheets
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human VCAM-1/CD106 Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human VCAM-1/CD106 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: