Mouse SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 Antibody Summary
Ile17-Phe650
Accession # P70663
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
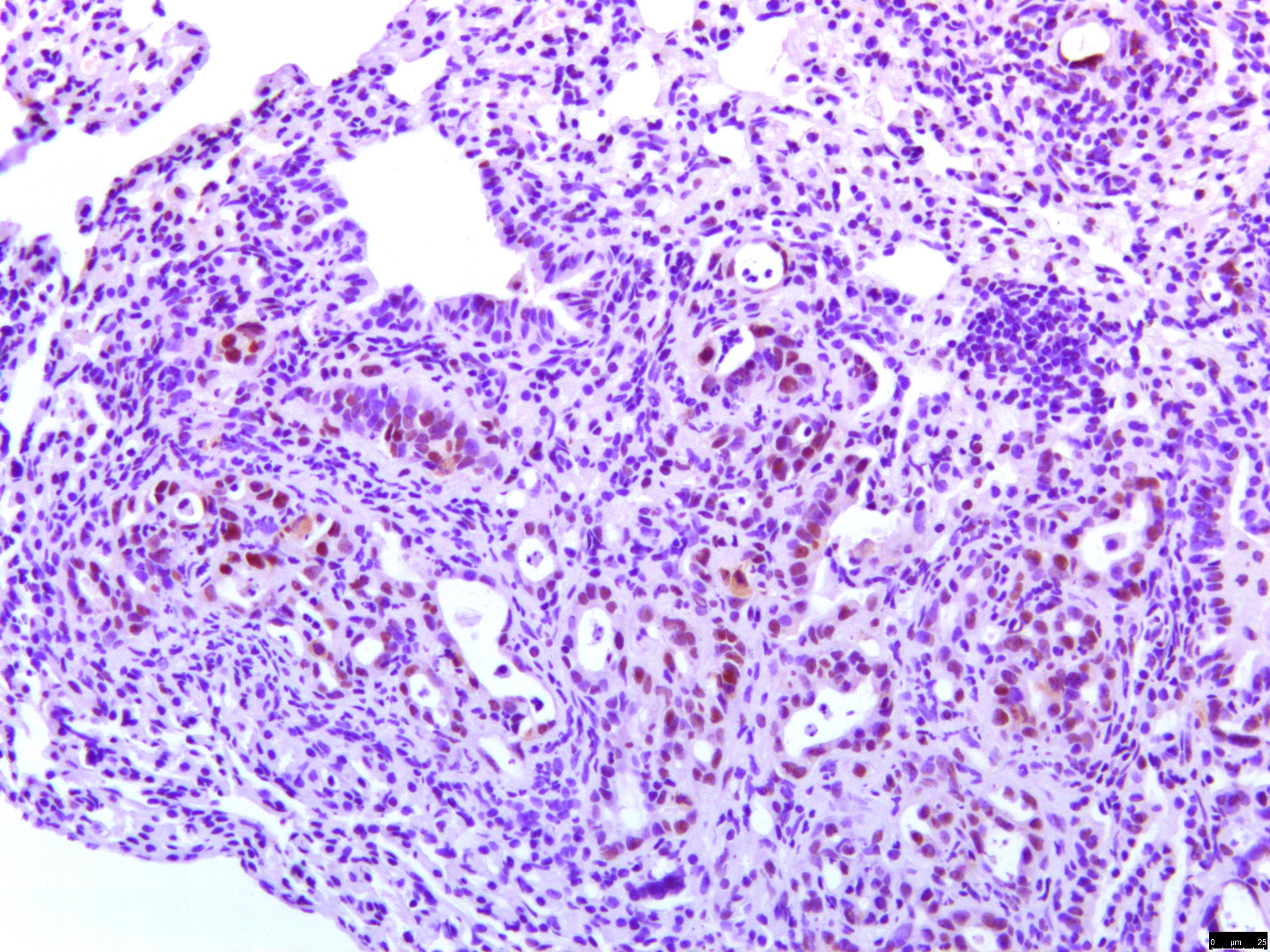
Detection of Mouse SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Hevin expression by astrocytes is developmentally regulated in the cortex.(A) Representative Western blots showing the developmental timeline for hevin expression in mouse cortex and hippocampus (tubulin was used as a loading control). (B) Quantification of Western blot analysis of hevin expression shows high expression between P15–P25. Data is presented as fold change compared to P1 levels (n = 3 animals per age; p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test). (C) Schematic diagram of a coronal slice through mouse brain shows the synaptic zone of primary visual cortex (V1) where EM, IHC and Golgi-cox staining analyses were performed. Layer II/III neurons of the visual cortex heavily project their dendrites to this region (D) IHC staining reveals that hevin expression (green) overlaps with all astrocytes (left, arrow) and a small subset of neurons (middle, asterisk) in V1, with no overlap seen with microglia (right, arrowhead). Cell-specific markers in red: Aldh1L1-EGFP for astrocytes, NeuN for neurons, Iba1 for microglia. Scale bar, 50 µm. (E) The rarely occurring GFAP+ astrocytes (red) in healthy visual cortex also express hevin (green). Scale bar, 10 µm.DOI:https://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.04047.003 Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25517933), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 by Western Blot Hevin expression by astrocytes is developmentally regulated in the cortex.(A) Representative Western blots showing the developmental timeline for hevin expression in mouse cortex and hippocampus (tubulin was used as a loading control). (B) Quantification of Western blot analysis of hevin expression shows high expression between P15–P25. Data is presented as fold change compared to P1 levels (n = 3 animals per age; p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test). (C) Schematic diagram of a coronal slice through mouse brain shows the synaptic zone of primary visual cortex (V1) where EM, IHC and Golgi-cox staining analyses were performed. Layer II/III neurons of the visual cortex heavily project their dendrites to this region (D) IHC staining reveals that hevin expression (green) overlaps with all astrocytes (left, arrow) and a small subset of neurons (middle, asterisk) in V1, with no overlap seen with microglia (right, arrowhead). Cell-specific markers in red: Aldh1L1-EGFP for astrocytes, NeuN for neurons, Iba1 for microglia. Scale bar, 50 µm. (E) The rarely occurring GFAP+ astrocytes (red) in healthy visual cortex also express hevin (green). Scale bar, 10 µm.DOI:https://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.04047.003 Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25517933), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Hevin expression by astrocytes is developmentally regulated in the cortex.(A) Representative Western blots showing the developmental timeline for hevin expression in mouse cortex and hippocampus (tubulin was used as a loading control). (B) Quantification of Western blot analysis of hevin expression shows high expression between P15–P25. Data is presented as fold change compared to P1 levels (n = 3 animals per age; p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test). (C) Schematic diagram of a coronal slice through mouse brain shows the synaptic zone of primary visual cortex (V1) where EM, IHC and Golgi-cox staining analyses were performed. Layer II/III neurons of the visual cortex heavily project their dendrites to this region (D) IHC staining reveals that hevin expression (green) overlaps with all astrocytes (left, arrow) and a small subset of neurons (middle, asterisk) in V1, with no overlap seen with microglia (right, arrowhead). Cell-specific markers in red: Aldh1L1-EGFP for astrocytes, NeuN for neurons, Iba1 for microglia. Scale bar, 50 µm. (E) The rarely occurring GFAP+ astrocytes (red) in healthy visual cortex also express hevin (green). Scale bar, 10 µm.DOI:https://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.04047.003 Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25517933), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1
SPARCL1 (Secreted Protein, Acidic and Rich in Cysteines-like 1), also known as hevin, SC1 or MAST9, is a member of the SPARC family of extracellular glycoproteins (1, 2). SPARCL1 is an anti-adhesive protein that is widely expressed in tissues such as brain, heart, lung, muscle and kidney, but not liver (3, 4). Mouse SPARCL1 contains a 16 amino acid (aa) signal sequence and a 634 aa mature region that contains four domains: a 403 aa N-terminal acidic region, a 23 aa follistatin-like domain, a 55 aa kazal-like segment and a 148 aa calcium binding domain that contains two EF hand motifs (3, 4). Mouse mature SPARCL1 shares 89%, 67%, 63%, 61%, 60%, and 58% aa identity with rat, human, equine, canine, porcine, and bovine SPARCL1, respectively. The follistatin-like, kazal-like and calcium-binding domains of SPARCL1 show 61% aa identity with corresponding regions of SPARC. SPARCL1 is predicted at 75 kDa, but migrates at ~130 kDa, which has been explained either by disulfide-linked homodimerization or by glycosylation and high acidity (3 - 5). Some truncated forms have been reported. In mouse, a 55 kDa C‑terminal fragment is the only form in kidney and represent a portion of SPARCL1 in other tissues (6). In humans, a 25 kDa form is increased in liver tumors that are encapsulated, while the full-length form is downregulated in many epithelial cell-derived tumors (7, 8). SPARCL1 inhibits adhesion and spreading on a variety of substrates (5, 9). It is thought to cause antiadhesive signaling that terminates neuronal migration, consistent with production by glial and neuronal cells during development or in response to trauma (10). In tonsillar high endothelial venules (HEV), SPARCL1 may induce endothelial cell dissociation, promoting extravasation (3). SPARCL1 binds collagen; in mice, deletion causes dermal collagen fibrils that are smaller in diameter and deficient in decorin (6, 11).
- Framson, P.E. and E.H. Sage (2004) J. Cell. Biochem. 92:679.
- Sullivan, M.M. and E.H. Sage (2004) Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 36:991.
- Girard, J.P. and T.A. Springer (1995) Immunity 2:113.
- Bendik, I. et al. (1998) Cancer Res. 58:626.
- Brekken, R.A. et al. (2004) J. Histochem. Cytochem. 52:735.
- Hambrock, H.O. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:11351.
- Lau, C.P. et al. (2006) J. Pathol. 210:469.
- Isler, S.G. et al. (2001) Int. J. Oncol. 18:521.
- Girard, J.P. and T.A. Springer (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:4511.
- Gongidi, V. et al. (2004) Neuron 41:57.
- Sullivan, M.M. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:27621.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
17
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Synaptic hyperexcitability of cytomegalic pyramidal neurons contributes to epileptogenesis in tuberous sclerosis complex
Authors: Wu X, Sosunov AA, Lado W et al.
Cell reports
-
Astrocyte modulation of synaptic plasticity mediated by activity-dependent Sonic hedgehog signaling
Authors: Le, AD;Fu, M;Kumar, R;Zacharias, G;Garcia, ADR;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Abnormal Morphology and Synaptogenic Signaling in Astrocytes Following Prenatal Opioid Exposure
Authors: Niebergall, EB;Weekley, D;Mazur, A;Olszewski, NA;DeSchepper, KM;Radant, N;Vijay, AS;Risher, WC;
Cells
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Comprehensive Profiling of Early Neoplastic Gastric Microenvironment Modifications and Biodynamics in Impaired BMP-Signaling FoxL1+-Telocytes
Authors: AB Alfonso, V Pomerleau, VR Nicolás, J Raisch, CM Jurkovic, FM Boisvert, N Perreault
Biomedicines, 2022-12-22;11(1):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenate
Applications: Western Blot -
SOX2 is essential for astrocyte maturation and its deletion leads to hyperactive behavior in mice
Authors: Y Wang, S Zhang, Z Lan, V Doan, B Kim, S Liu, M Zhu, VL Hull, S Rihani, CL Zhang, JA Gray, F Guo
Cell Reports, 2022-12-20;41(12):111842.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Cocaine preference and neuroadaptations are maintained by astrocytic NMDA receptors in the nucleus accumbens
Authors: GP Shelkar, PJ Gandhi, J Liu, SM Dravid
Science Advances, 2022-07-22;8(29):eabo6574.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Autism-associated mutation in Hevin/Sparcl1 induces endoplasmic reticulum stress through structural instability
Authors: T Taketomi, T Yasuda, R Morita, J Kim, Y Shigeta, C Eroglu, R Harada, F Tsuruta
Scientific Reports, 2022-07-13;12(1):11891.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: ICC, Western Blot -
Gene silencing by EZH2 suppresses TGF-beta activity within the decidua to avert pregnancy-adverse wound healing at the maternal-fetal interface
Authors: I Osokine, J Siewiera, D Rideaux, S Ma, T Tsukui, A Erlebacher
Cell Reports, 2022-02-01;38(5):110329.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Lineage-tracing and translatomic analysis of damage-inducible mitotic cochlear progenitors identifies candidate genes regulating regeneration
Authors: T Udagawa, PJ Atkinson, B Milon, JM Abitbol, Y Song, M Sperber, E Huarcaya N, M Scheibinge, R Elkon, R Hertzano, AG Cheng
PloS Biology, 2021-11-10;19(11):e3001445.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Matricellular Protein SPARCL1 Regulates Blood Vessel Integrity and Antagonizes Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Authors: Daniela Regensburger, Clara Tenkerian, Victoria Pürzer, Benjamin Schmid, Thomas Wohlfahrt, Iris Stolzer et al.
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
-
Spatiotemporal dynamics of inner ear sensory and non-sensory cells revealed by single-cell transcriptomics
Authors: TA Jan, Y Eltawil, AH Ling, L Chen, DC Ellwanger, S Heller, AG Cheng
Cell Reports, 2021-07-13;36(2):109358.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: ICC, IHC, RNAScope -
Greater epithelial ridge cells are the principal organoid-forming progenitors of the mouse cochlea
Authors: M Kubota, M Scheibinge, TA Jan, S Heller
Cell Reports, 2021-01-19;34(3):108646.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) knockout mice have greater outflow facility
Authors: L Yu, Y Zheng, BJ Liu, MH Kang, JC Millar, DJ Rhee
PLoS ONE, 2020-11-04;15(11):e0241294.
Species: Mouse, Transgenic Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC, Western Blot -
Species-, organ- and cell-type-dependent expression of SPARCL1 in human and mouse tissues
Authors: A Klingler, D Regensburg, C Tenkerian, N Britzen-La, A Hartmann, M Stürzl, E Naschberge
PLoS ONE, 2020-05-21;15(5):e0233422.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Astrocytes refine cortical connectivity at dendritic spines.
Authors: Risher, W Christ, Patel, Sagar, Kim, Il Hwan, Uezu, Akiyoshi, Bhagat, Srishti, Wilton, Daniel K, Pilaz, Louis-Ja, Singh Alvarado, Jonnatha, Calhan, Osman Y, Silver, Debra L, Stevens, Beth, Calakos, Nicole, Soderling, Scott H, Eroglu, Cagla
Elife, 2014-12-17;3(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Processing of the matricellular protein hevin in mouse brain is dependent on ADAMTS4.
Authors: Weaver MS, Workman G, Cardo-Vila M, Arap W, Pasqualini R, Sage EH
J. Biol. Chem., 2009-12-15;285(8):5868-77.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Single-cell RNA-Seq resolves cellular complexity in sensory organs from the neonatal inner ear.
Authors: Burns JC, Kelly MC, Hoa M et al.
Nat Commun
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Mouse SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: