Recombinant Equine IL-6 Protein
Recombinant Equine IL-6 Protein Summary
Product Specifications
Phe26-Met208, with an N-terminal Met
Analysis
Product Datasheets
1886-EL/CF (carrier free)
Discontinued Product
1886-EL
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: IL-6
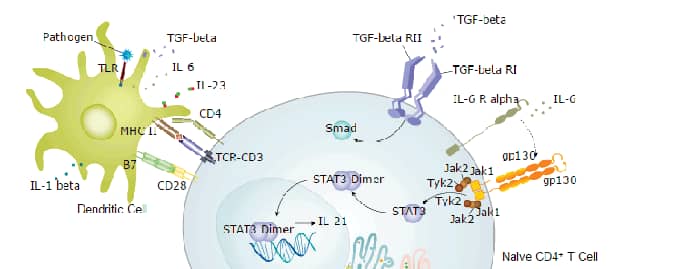
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a pleiotropic, alpha -helical, 22-28 kDa phosphorylated and variably glycosylated cytokine that plays important roles in the acute phase reaction, inflammation, hematopoiesis, bone metabolism, and cancer progression (1-5). Mature equine IL-6 is 181 amino acids (aa) in length and shares 59%, 39%, and 40% aa sequence identity with human, mouse, and rat IL-6, respectively IL-6 (6). IL-6 induces signaling through a cell surface heterodimeric receptor complex composed of a ligand binding subunit (IL-6 R alpha) and a signal transducing subunit (gp130). IL-6 binds to IL-6 R alpha, triggering IL-6 R alpha association with gp130 and gp130 dimerization (7). gp130 is also a component of the receptors for CLC, CNTF, CT-1, IL-11, IL-27, LIF, and OSM (8). Soluble forms of IL-6 R alpha are generated by both alternative splicing and proteolytic cleavage (5). In a mechanism known as trans-signaling, complexes of soluble IL-6 and IL-6 R alpha elicit responses from gp130-expressing cells that lack cell surface IL-6 R alpha (5). Trans-signaling enables a wider range of cell types to respond to IL-6, as the expression of gp130 is ubiquitous, while that of IL-6 R alpha is predominantly restricted to hepatocytes, monocytes, and resting lymphocytes (2, 5). Soluble splice forms of gp130 block trans-signaling from IL-6/IL-6 R alpha but not from other cytokines that use gp130 as a co-receptor (5, 9). IL-6, along with TNF-alpha and IL-1, drives the acute inflammatory response and the transition from acute inflammation to either acquired immunity or chronic inflammatory disease (1-5). When dysregulated, it contributes to chronic inflammation in obesity, insulin resistance, inflammatory bowel disease, arthritis, sepsis, and atherosclerosis (1, 2, 5). IL-6 can also function as an anti-inflammatory molecule, as in skeletal muscle where it is secreted in response to exercise (2). In addition, it enhances hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and the differentiation of Th17 cells, memory B cells, and plasma cells (1, 10).
- Mansell, A. and B.J. Jenkins (2013) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 24:249.
- Schuett, H. et al. (2009) Thromb. Haemost. 102:215.
- Erta, M. et al. (2012) Int. J. Biol. Sci. 8:1254.
- Garbers, C. et al. (2012) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 23:85.
- Mihara, M. et al. (2012) Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 122:143.
- Swiderski, C.E. et al. (2000) Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 77:213.
- Murakami, M. et al. (1993) Science 260:1808.
- Muller-Newen, G. (2003) Sci. STKE 2003:PE40.
- Mitsuyama, K. et al. (2006) Clin. Exp. Immunol. 143:125.
- Cerutti, A. et al. (1998) J. Immunol. 160:2145.
Citations for Recombinant Equine IL-6 Protein
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
6
Citations: Showing 1 - 6
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Interleukin-6 upregulates extracellular matrix gene expression and transforming growth factor ?1 activity of tendon progenitor cells
Authors: Altmann, N;Bowlby, C;Coughlin, H;Belacic, Z;Sullivan, S;Durgam, S;
BMC musculoskeletal disorders
Species: Equine
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Equine Arteritis Virus in Monocytic Cells Suppresses Differentiation and Function of Dendritic Cells
Authors: NA Moyo, D Westcott, R Simmonds, F Steinbach
Viruses, 2023-01-16;15(1):.
Species: Equine
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Infection of monocytes with European porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV-1) strain Lena is significantly enhanced by dexamethasone and IL-10
Authors: H Singleton, SP Graham, JP Frossard, KB Bodman-Smi, F Steinbach
Virology, 2018-03-02;0(0):.
Species: Porcine
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Effects of priming with cytokines on intracellular survival and replication of Rhodococcus equi in equine macrophages
Authors: LJ Berghaus, S Giguère, AI Bordin, ND Cohen
Cytokine, 2017-12-12;102(0):7-11.
Species: Equine
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Effects of high mobility group box protein-1, interleukin-1beta, and interleukin-6 on cartilage matrix metabolism in three-dimensional equine chondrocyte cultures.
Authors: Ley C, Svala E, Nilton A, Lindahl A, Eloranta ML, Ekman S, Skioldebrand E
Connect. Tissue Res., 2010-11-30;52(4):290-300.
Species: Equine
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-10 concentrations in normal and septic neonatal foals.
Authors: Burton AB, Wagner B, Erb HN, Ainsworth DM
Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol., 2009-05-18;132(2):122-8.
Species: N/A
Sample Types: Antibody
Applications: ELISA Standard
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Equine IL-6 Protein
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Equine IL-6 Protein and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Equine IL-6 Protein?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image