C. difficile Toxin B/TcdB Antibody Summary
Ser2-Leu543
Accession # P18177
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection ofC. difficileToxin B/TcdB by Western Blot. Western blot shows recombinantC. difficileToxin B/TcdB (Catalog # 6246-GT). PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Sheep Anti-C. difficileToxin B/TcdB Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF6246) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF016). A specific band was detected for Toxin B/TcdB at approximately 75 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
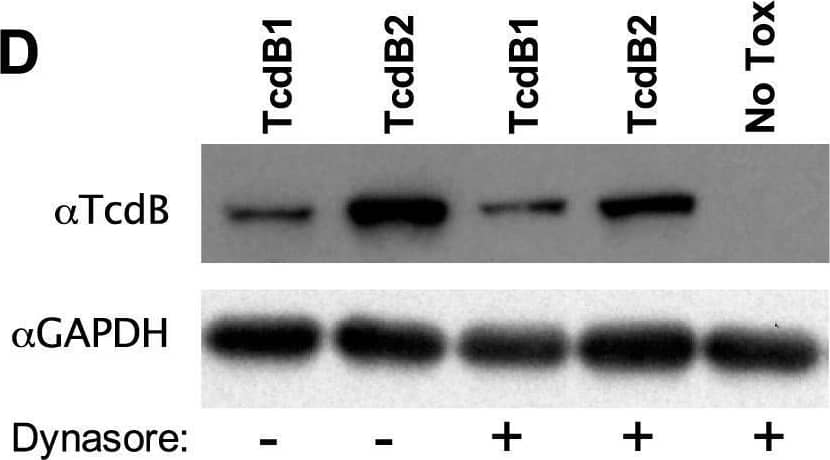
Detection of C. difficile Toxin B/TcdB by Western Blot Effective TcdB cell interactions correlate with endocytosis. (A, B) Representative confocal maximum-intensity projections of CHO-K1 cells stained with 250 nM Alexa Fluor 647-labeled TcdB1 B2′B3 (red) (A) or Alexa Fluor 647-labeled TcdB2 B2′B3 (red) (B). Ten micromolar calcein AM (green) was used to counterstain the cytoplasm of live cells with intact membranes, and 0.5 μg/ml Hoechst 33258 (blue) was used to visualize the nucleus. (C) Quantification of the images in panels A and B, expressed as corrected total cell fluorescence. (D) Representative immunoblotting of full-length TcdB1 and TcdB2 associated with CHO-K1 cells in the presence or absence the dynamin inhibitor dynasore (80 μM). Incubations were carried out for 30 min at 37°C. (E) Quantification of data presented in panel D, expressed as relative band density. (F) Representative immunoblotting of full-length TcdB1 and TcdB2 associated with CHO-K1 cells when incubations were carried out for 30 min at a temperature that permits (37°C) or inhibits (ice) endocytosis. (G) Quantification of data presented in panel F, expressed as relative band density. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28776043), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of C. difficile Toxin B/TcdB by Western Blot Mechanism-of-action of niclosamide inhibition of TcdB intoxication. c In vitro auto-processing assay. Compound or DMSO was added to 100 nM TcdB, and pre-incubated for 60 min. To initiate auto-processing, InsP6 was added (100 μM) and incubated @ 37 °C for 20 min before stopping with Laemlii sample buffer. Niclosamide at concentrations up to 10 μM did not affect auto-processing (n = 2). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30531960), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
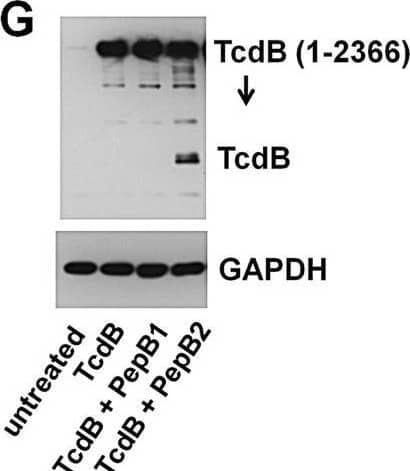
Detection of C. difficile Toxin B/TcdB by Western Blot Impact of PepB2 on TcdB enzymatic activity, thermal stability, and cell association. (G) Immunoblot analysis of TcdB associating with cells for 30 min. CHO-K1 cells were exposed at 37°C to 4 nM TcdB in the presence and absence of 50 µM peptide. The cells were then washed, and total cell lysates were examined by immunoblotting. In this figure, all bar graphs represent the mean densitometry value ± standard deviation, and asterisks indicate significant change. *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28512094), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
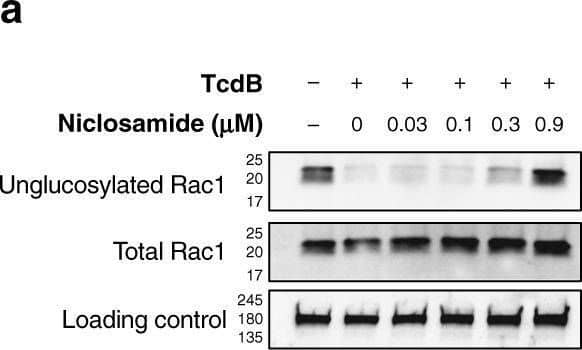
Detection of C. difficile Toxin B/TcdB by Western Blot Mechanism-of-action of niclosamide inhibition of TcdB intoxication. a Western blot image for intracellular Rac1 glucosylation (n = 3). IMR-90 cells were treated with niclosamide (doses indicated) for 15 min, followed by treatment with 0.5 pM TcdB. Cells were harvested as described in Methods. Mab102, which recognizes un-glucosylated Rac1 in cells, shows a dose-dependent re-appearance with increasing concentration of niclosamide, relative to total Rac1 levels (n = 2). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30531960), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Toxin B/TcdB
Clostridium difficile is the leading cause of hospital-acquired diarrhea, known as C. difficile-associated disease. The estimated number of cases of C. difficile-associated disease exceeds 250,000 per year (1), with health care costs approaching US $1 billion annually (2). The major virulence factors produced by C. difficile are two toxins, TcdA and TcdB. Both toxins can monoglucosylate and inactivate Rho family small GTPases within target cells, leading to disruption of vital signaling pathways in the cell, subsequently causing diarrhea, inflammation, and damage of colonic mucosa (3, 4, 5). Both toxins have a similar tripartite structure comprised of an N‑terminal glucosyltransferase domain, a C-terminal receptor binding domain, and a small hydrophobic span possibly involved in toxin translocation (6). Our recombinant TcdB consists of the enzymatic domain. Both TcdA and TcdB also have potassium-dependent UDP-Glc hydrolase activity, which is essentially glucosyltransferase activity with water as the acceptor molecule (7). Under same conditions, UDP-glucose hydrolysis by TcdB occurs at a rate about 5-fold greater than that of TcdA.
- Wilkins, T.D. and Lyerly, D.M. (2003) J. Clin. Microbiol 41:53.
- Kyne, L. et al. (2002) Clin. Infect. Dis. 34:346.
- Voth, D.E. and Ballard, J.D. (2005) Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 18:247.
- Chaves-Olarte, E. et al. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:6925.
- Just I, et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:13932.
- Hammond, G.A. and Johnson, J.L. (1995) Microb. Pathog. 19:203.
- Ciesla, W.P. Jr. and Bobak, D.A. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273:16021.
Product Datasheets
Citations for C. difficile Toxin B/TcdB Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
6
Citations: Showing 1 - 6
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Inhibition of EGFR/ErbB does not protect against C. difficile toxin B
Authors: Siddiqi, U;Lunnemann, HM;Childress, KO;Shupe, JA;Rutherford, SA;Farrow, MA;Washington, MK;Coffey, RJ;Lacy, DB;Markham, NO;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Immunocytochemistry -
Combined and Distinct Roles of Agr Proteins in Clostridioides difficile 630 Sporulation, Motility, and Toxin Production
Authors: Ahmed UKB, Shadid TM, Larabee JL, Ballard JD.
mBio
-
Intestinal bile acids directly modulate the structure and function of C. difficile TcdB toxin
Authors: J Tam, S Icho, E Utama, KE Orrell, RF Gómez-Biag, CM Theriot, HK Kroh, SA Rutherford, DB Lacy, RA Melnyk
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2020-03-09;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Host-targeted niclosamide inhibits C. difficile virulence and prevents disease in mice without disrupting the gut microbiota
Authors: J Tam, T Hamza, B Ma, K Chen, GL Beilhartz, J Ravel, H Feng, RA Melnyk
Nat Commun, 2018-12-07;9(1):5233.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Western Blot -
Amino Acid Differences in the 1753-to-1851 Region of TcdB Influence Variations in TcdB1 and TcdB2 Cell Entry
Authors: JJ Hunt, JL Larabee, JD Ballard
mSphere, 2017-08-02;2(4):.
Species: Chinese Hamster
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Intrinsic Toxin-Derived Peptides Destabilize and Inactivate Clostridium difficile TcdB
Authors: JL Larabee, SJ Bland, JJ Hunt, JD Ballard
MBio, 2017-05-16;8(3):.
Species: Hamster
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for C. difficile Toxin B/TcdB Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review C. difficile Toxin B/TcdB Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used C. difficile Toxin B/TcdB Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
