Search Conjugated Antibodies
Search Conjugated Antibodies
Conjugated Primary Antibodies
Conjugated Primary Antibodies
Contents
Contents
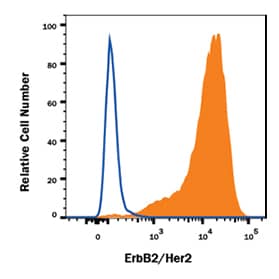
What Are Conjugated Antibodies?
What Are Conjugated Antibodies?
Fluorescent Dyes
Fluorescent Dyes
Chromogenic and Biotin Labels
Chromogenic and Biotin Labels
Isotype Controls and Secondary Reagents
Isotype Controls and Secondary Reagents
Additional Resources
Additional Resources
Featured Content
Featured Content
Featured Content
Do more with Bio-Techne Antibodies. Find mFluor™ Violet Conjugated Antibodies to over 14,000 targets.
Featured Content

Learn more about our extensive antibodies’ portfolio!
Featured Content

Explore a clear and easy to follow guide to flow cytometry suited for new researchers or experienced scientists
Featured Content

Generate reliable, reproducible data for every experiment with calibration, compensation and cell sorting beads