Human COMMD1 Antibody Summary
Ser37-Ser135
Accession # Q8N668
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human COMMD1 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of U2OS human osteosarcoma cell line, HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, and human placenta tissue. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.2 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human COMMD1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB7526) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF018). A specific band was detected for COMMD1 at approximately 20 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
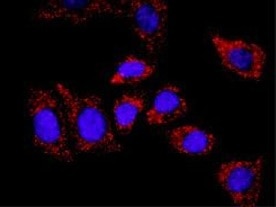
COMMD1 in U2OS Human Cell Line. COMMD1 was detected in immersion fixed U2OS human osteosarcoma cell line using Mouse Anti-Human COMMD1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB7526) at 8 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL007) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm and nuclei. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse COMMD1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence LDLR associates with COMMD1 and the WASH complex.(a) Human embryonic kidney 293T (HEK293T) cells were transfected with constructs expressing Flag-LDLR with either COMMD1-GST or GST alone. Interaction with COMMD1 was detected via pull-down assay using glutathione sepharose beads. (b) HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-LDLR vector, and interaction with endogenous COMMD1 was detected by immunoprecipitation with rabbit anti-Flag-antibody. (c) Colocalization of LDLR (red) and COMMD1 (green) in Commd1f/f MEFs examined by immunofluorescence staining. Representative images are shown; scale bar, 5μm. LDLR (red) and COMMD1 (green) was stained in COMMD1-deficient MEFs (Commd1−/−) and imaged by confocal fluorescence microscopy. COMMD1 levels in Commd1f/f and in Commd1−/− MEFs determined by immunoblot analysis. (d) Liver of a WT chow-fed mouse was homogenized and loaded on a continuous 10–40% sucrose gradient. Fractions were separated by ultracentrifugation and immunoblotted using antibodies against COMMD1, LDLR, WASH1, FAM21, VPS35 and CCDC22. The figure represents results of three independent experiments. (e) HEK293T cells were transfected with Ha-COMMD1 construct together with GST alone, GST-LDLRct (GST-tagged cytosolic domain of LDLR) or GST-LDLRct Y807A (GST-tagged mutated cytosolic domain of LDLR). Pull-down assay was performed to study the interaction between LDLRct and COMMD1. (f) Lysates of Flag-LDLR-transfected HEK293T cells were used for immunoprecipitation assays. Immunoprecipitates were washed, separated by SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotted as indicated. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms10961), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse COMMD1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence COMMD1 deficiency impairs the function of LDLR.(a) LDLR (green), COMMD1 (red) and VPS35 (pink) were stained in Commd1f/f and Commd1−/− MEFs and imaged by confocal microscopy. Representative images are shown; scale bar, 5μm. (b) Quantification of the colocalization of LDLR with COMMD1, VPS35, EEA1 and LAMP1 was performed by the analysis of 30–40 cells. (c) Total and plasma membrane LDLR levels of Commd1f/f and Commd1−/− MEFs determined by biotinylation assay. Data represent three independent experiments, and (d) the relative levels of LDLR at the cell surface are quantified in all experiments. (e) In vitro LDL and transferrin uptake assay. Dil-labelled LDL (5 μg ml−1) or Alexa-633-labelled transferrin (5 μg ml−1) was added to serum-depleted medium and incubated with MEFs at 4 °C for 1 h and subsequently at 37 °C for 5 min. Dil-labelled LDL and Alexa-633-labelled transferrin uptake was measured by FACS analysis, and the relative uptake in triplicate is shown. The results are presented as mean±s.e.m.; significance was calculated relative to the control group by unpaired Student's t-test; *P<0.05, ***P<0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms10961), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse COMMD1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence The WASH complex is essential for endosomal sorting of LDLR.(a) Cellular localization of LDLR (green), COMMD1 (red) and LAMP1 (pink) in Wash1f/f and Wash1−/− MEFs was determined by immunofluorescence staining. Representative images are shown; scale bar, 5 μm. Relative colocalization of (b) LDLR and (c) COMMD1 with VPS35, EEA1 and LAMP1 was quantified. (d) LDLR, WASH1, VPS35 and COMMD1 levels in Wash1f/f and Wash1−/− MEFs analysed by western blot. (e) Representative images (n=3) of immunoblot analysis of total LDLR levels in Wash1f/f and Wash1−/− MEFs treated with bafilomycin A (100 nM) for 0, 4 and 6 h. (f) Densitometry revealed the relative levels of LDLR in bafilomycin A-treated cells (n=3). (g) Representative images (n=3) of LDLR on the surface of Wash1f/f and Wash1−/− MEFs determined by surface biotinylation assay. (h) Densitometry revealed relative LDLR surface levels (n=3). (i) Wash1f/f and Wash1−/− MEFs were incubated with DiI-LDL for 30 min and imaged by fluorescence microscope. (j) Fluorescence intensity was quantified using ImageJ software and was normalized to the number of DAPI nuclei per image; >30 cells per condition were recorded. The results are presented as mean±s.e.m.; significance was calculated relative to the control group by unpaired Student's t-test; ***P<0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms10961), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: COMMD1
COMMD1, also known as MURR1 and the copper toxicosis gene product, is a ubiquitously expressed 21 kDa copper binding protein. It contains an N-terminal domain (aa 1-121) and C-terminal domain (aa 125-190) which are separated by a protease sensitive site. It forms high molecular weight oligomeric complexes both in solution and in association with phospholipid membranes. COMMD1 is found in the nucleus and cytoplasm as well as in endocytic vesicle membrane fractions. It binds and regulates the activity of a variety of proteins including the copper transporter Wilson disease protein (ATP7B), the delta ENaC epithelial cell sodium channel, the cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR), superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1), XIAP, HIF-1 alpha, and Cullin RING ubiquitin ligases. COMMD1 promotes the ubiquitination and degradation of the RelA subunit of NFkB, thereby inhibiting its chromatin association and nuclear targeting as well as the replication of HIV in resting T cells. Within aa 37-135, human COMMD1 shares 94% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat COMMD1.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human COMMD1 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
4
Citations: Showing 1 - 4
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
CCC- and WASH-mediated endosomal sorting of LDLR is required for normal clearance of circulating LDL.
Authors: Bartuzi P, Billadeau D, Favier R, Rong S, Dekker D, Fedoseienko A, Fieten H, Wijers M, Levels J, Huijkman N, Kloosterhuis N, van der Molen H, Brufau G, Groen A, Elliott A, Kuivenhoven J, Plecko B, Grangl G, McGaughran J, Horton J, Burstein E, Hofker M, van de Sluis B
Nat Commun, 2016-03-11;7(0):10961.
-
COMMD5/HCaRG Hooks Endosomes on Cytoskeleton and Coordinates EGFR Trafficking
Authors: CG Campion, K Zaoui, T Verissimo, S Cossette, H Matsuda, N Solban, P Hamet, J Tremblay
Cell Rep, 2018-07-17;24(3):670-684.e7.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
COMMD Family Regulates Plasma LDL Levels and Attenuates Atherosclerosis Through Stabilizing the CCC Complex in Endosomal LDLR Trafficking
Authors: A Fedoseienk, M Wijers, JC Wolters, D Dekker, M Smit, N Huijkman, N Kloosterhu, H Klug, A Schepers, K Willems va, JH Levels, DD Billadeau, MH Hofker, J van Deurse, M Westerterp, E Burstein, JA Kuivenhove, B van de Slu
Circ. Res., 2018-03-15;0(0):.
Species: Human, Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Immunoprecipitation -
Lipid kinases VPS34 and PIKfyve coordinate a phosphoinositide cascade to regulate retriever-mediated recycling on endosomes
Authors: Sai Srinivas Panapakkam Giridharan, Guangming Luo, Pilar Rivero-Rios, Noah Steinfeld, Helene Tronchere, Amika Singla et al.
eLife
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human COMMD1 Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human COMMD1 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: