Human/Mouse FGF-8 Antibody Summary
Gln23-Arg215
Accession # NP_001159834
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
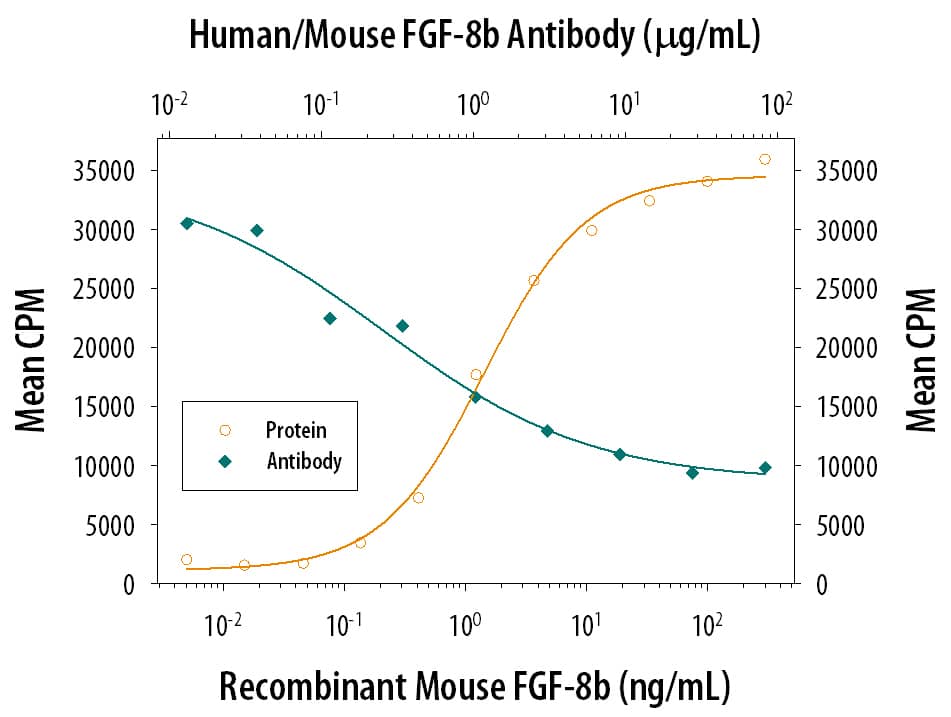
Cell Proliferation Induced by FGF‑8 and Neutralization by Human and Mouse FGF‑8 Antibody. Recombinant Mouse FGF-8 c Isoform (Catalog # 424-FC) stimulates proliferation in the the NR6R-3T3 mouse fibroblast cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Proliferation elicited by Recombinant Mouse FGF-8 c Isoform (125 ng/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse FGF-8 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB323). The ND50 is typically 0.25-0.75 µg/mL in the presence of heparin (0.1 µg/mL).
 View Larger
View Larger
FGF‑8 in Human Prostate. FGF-8 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human prostate using Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse FGF-8 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB323) at 25 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Mouse HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS002) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to stromal cell cytoplasm. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
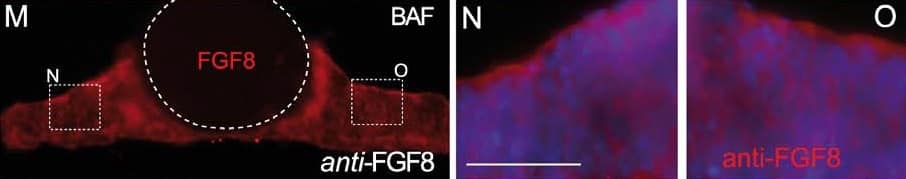
Detection of Human/Mouse FGF-8 by Immunohistochemistry Bafilomycin A1 (BAF) treatment demonstrates the polarization of ERK activity by FGF8 signal activity along the neuraltube. A-C) BAF amplifies ectopic ERK1/2 activity-related FGF8 induction revealing a clear polarized distribution of ERK1/2 activity around FGF8soaked beads depending of the implanted bead; rostral to IsO (C,D,G), or caudal to IsO (C,E). Nonetheles, isthmic organizer morphogenetic activityseems unaffected for Fgf8 (A) and negative regulator Sprouty 2 (B) expressions. Note that PBS bead implantation in control side (blue asterisk in C andF) did not show any ectopic induction. Two hours after bead implantation a clear amplified and almost non-homogeneous ERK1/2 activity wasdetected rostrally in the mesencephalon (rostral to the IsO), which was detected caudally when bead was placed in hindbrain (caudal to the IsO)territories (E). In telencephalic vesicles, caudal to the anr (H) the polarity of ERK activation was reversed. This polarized dpERK detection around thebead is lost at the zli (zona limitans intrathalamica) region (I). Similar symmetric ERK-related FGF8 signal found in zli was seen when placing a FGF8bead in the midbrain of Fgf8 hypomorphic mice (J,K). Importantly FGF8b protein distribution (M) was observed apparently in equal intensity andrange at rostral (N) and caudal (O) sides of the bead (for comparison with PBS bead in panel L). Scale bars are 0,5 mm in A, B, C, H, I, 200 mm in D, E, J,100 mm in F, G, K, L, M, and 50 mm in N, O. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3391221/), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
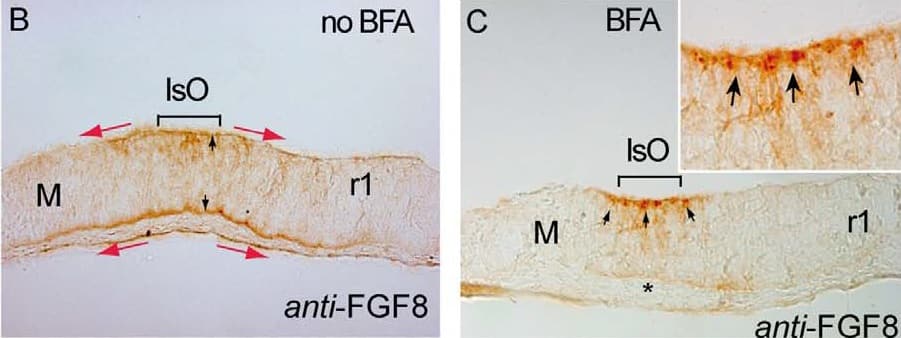
Detection of Human/Mouse FGF-8 by Immunohistochemistry Brefeldin A (BFA) treatment inhibits ERK1/2 activity & modulates differentially Fgf8 negative feed-back regulators. A, B & C) are 12 mM cryostat transversal sections of mouse ONTCs to the isthmic constriction. A & B) are control example before BFA administration to the culture medium showing an ISH for Fgf8 (A) & an Immunostaining for anti-FGF8 (B). Note different domains of expression of the transcript (solid line & arrows) & of the protein FGF8 (red arrows). FGF8 immunodetection is detected both at basal & ventricular sides of the ONTCs (black arrows in B). After 4 hours of BFA incubation (C-J) mRNA of Fgf8 was maintained at IsO (D) while the FGF8 protein profile changed dramatically being accumulated only at the ventricular side (D) as small vesicle-like, (arrows in fig. C & the magnified insert). Moreover, ERK1/2 activity disappears in Isthmic cells & nearby cells (E). Inside this negative gap, FGF8b beads still exerts polarizing ERK1/2 effects (F). Also inside this gap, genes such as Mkp3 (G) & Sef (H) disappear in mesencephalon while Sprouty family genes are maintained (I,J). K) represents experiments & model by which FGF8 planar induction activity coming from mouse FGF8-related secondary organizers (IsO & anr) exerts a different tissue preferential signaling effects (based on the activation of ERK1/2). The direction of polarized ERK1/2 activity depends on location of FGF8-related secondary organizers & the establishment of positional information signaling is dependent mainly on FGF8 negative modulator system, particularly Sprouty2 (blue gradient). FGF8 morphogenetic planar instruction signals coming from rostral (anr) & caudal (IsO) diminish & lose their polarization effect at the diencephalic region (zli) resulting in an equilibrium state. Scale bars is 100 mm. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3391221/), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
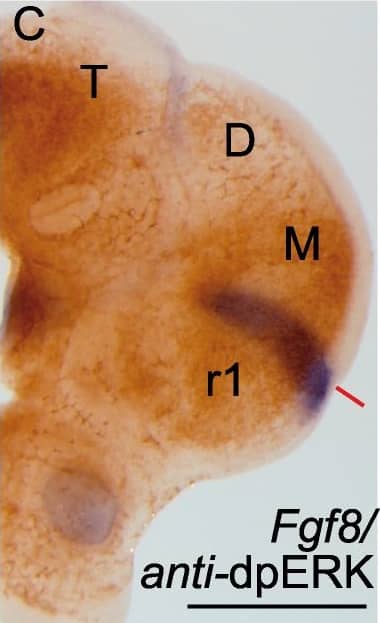
Detection of Mouse Human/Mouse FGF-8 Antibody by Immunohistochemistry Phosphorylation patterns of ERK1/2 (dpERK) enzymes in the anterior neural tube.Whole mount in situ hybridization (ISH) of E9.5 mouse embryo (A,B,B’) and corresponding organotypic neural tissue cultures of mouse E9.5 anterior neural tube (A’,B”,C-E”; ONTCs; [42]) where it shows the maintenance of gene expression profiles such us Fgf8, Tcf4 (A,A’) (used to delimit main brain subdivisions such the diencephalon (D; Tcf4 positive) and the mesencephalic anlage (M; negative staining), Pax6 D-D” (delimiting di-mesencephalic boundary and rhombomere 1–2 limits) and En2 E-E”. In B-B”) are photomicrographs of E9.5 mouse embryo with anti-dpERK Immunohistochemistry (IHC) taken from lateral (B) and caudal (B’) sides and the corresponding IHC in ONTCs. (C) double staining procedure: ISH (in blue) for Fgf8 and IHC for dpERK (dark brown) to localize inside the dpERK domain the position of the IsO, marked by the solid red line. (D-E”) photomicrographs of same ONTCs in which first a whole mount ISH for Pax6 (D) or Tcf4/En2 (E) were made and afterwards IHC against dpERK. (D’,E’ respectively). Dashed lines mark the main transversal (in black) and longitudinal (in red) brain subdivisions. These ONTCs were cut into transversal sections to the isthmic constriction (D”,E”) to proof that indeed dpERK expression reaches diencephalic anlage (D”; see asterisk; rostral is left) and has a wider expansion than En2 expression (E”; see asterisk; rostral is left). anr is anterior neural ridge secondary organizer; ba is branchial arch; IsO is isthmic organizer; os is optic stalk; ov is otic vesicle; r is rhombomere; T is telencephalon, D, diencephalon, M, mesencephalon. Scale bars are 0,5 mm except in D”, E” they are 100 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22792203), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: FGF-8
FGF-8 is a member of the fibroblast growth factor family that was originally discovered as a growth factor essential for the androgen-dependent growth of mouse mammary carcinoma cells (1-3). Alternate splicing of mouse FGF-8 mRNA generates eight secreted isoforms, designated a-h, but only FGF-8a, b, e and f exist in humans (4). FGF-8 contains a 22 amino acid (aa) signal sequence, an N‑terminal domain that varies according to the isoform (30 aa for FGF-8b; 20 aa for the shortest, FGF-8a), a 125 aa FGF domain and a 37 aa proline‑rich C‑terminal sequence. The FGF domain of FGF-8 shares the most aa identity with FGF17 (75%) and FGF-18 (67%), and the three form an FGF subfamily (2). Mouse FGF-8b shares 100% aa identity with human FGF-8b. FGF-8 is widely expressed during embryogenesis, and mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. It plays an organizing and inducing role during gastrulation, and regulates patterning of the midbrain/hindbrain, eye, ear, limbs and heart in the embryo (2, 5 - 8). The isoforms may play different roles in development. FGF-8b shows the strongest receptor affinity and oncogenic transforming capacity although FGF-8a and FGF-8e are also transforming and have been found in human prostate, breast or ovarian tumors (1, 5, 9-12). FGF-8 shows limited expression in the normal adult, but low levels are found in the reproductive and genitourinary tract, peripheral leukocytes and bone marrow hematopoietic cells (3, 9, 13).
- Mattila, M.M. and P.L. Harkonen (2007) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 18:257.
- Reuss, B. and O. von Bohlen und Halbach (2003) Cell Tiss. Res. 313:139.
- Tanaka, A. et al. (1992) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:8928.
- Gemel, J. et al. (1996) Genomics 35:253.
- Olsen, S.K. et al. (2006) Genes Dev. 20:185.
- Crossley, P.H. et al. (1996) Cell, 84:127.
- Heikinheimo, M. et al. (1994) Mech. Dev. 48:129.
- Sun, X. et al. (1999) Genes Dev. 13:1834.
- Ghosh, A.K. et al. (1996) Cell Growth Differ. 7:1425.
- Mattila, M.M. et al. (2001) Oncogene 20:2791.
- Valve, E. et al. (2000) Int. J. Cancer 88:718.
- Valve, E.M. et al. (2001) Lab. Invest. 81:815.
- Nezu, M. et al. (2005) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 335:843.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human/Mouse FGF-8 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
9
Citations: Showing 1 - 9
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Catalytically inactive Dnmt3b rescues mouse embryonic development by accessory and repressive functions
Authors: P Nowialis, K Lopusna, J Opavska, SL Haney, A Abraham, P Sheng, A Riva, A Natarajan, O Guryanova, M Simpson, R Hlady, M Xie, R Opavsky
Nat Commun, 2019-09-26;10(1):4374.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Specificity protein 7 is required for proliferation and differentiation of ameloblasts and odontoblasts
Authors: JM Bae, JC Clarke, H Rashid, MD Adhami, K McCullough, JS Scott, H Chen, KM Sinha, B de Crombru, A Javed
J. Bone Miner. Res., 2018-03-24;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P, Western Blot -
Fgf8 morphogen gradients are differentially regulated by heparan sulphotransferases Hs2st and Hs6st1 in the developing brain
Authors: Wai-Kit Chan, David J. Price, Thomas Pratt
Biology Open
-
Androgen Receptor Pathway-Independent Prostate Cancer Is Sustained through FGF Signaling
Authors: Eric G. Bluemn, Ilsa M. Coleman, Jared M. Lucas, Roger T. Coleman, Susana Hernandez-Lopez, Robin Tharakan et al.
Cancer Cell
-
Fibulin-1 Binds to Fibroblast Growth Factor 8 with High Affinity: Effects on Embryo Survival
J Biol Chem, 2016-07-08;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Protein
Applications: Western Blot -
Local apoptosis modulates early mammalian brain development through the elimination of morphogen-producing cells.
Authors: Nonomura K, Yamaguchi Y, Hamachi M, Koike M, Uchiyama Y, Nakazato K, Mochizuki A, Sakaue-Sawano A, Miyawaki A, Yoshida H, Kuida K, Miura M
Dev Cell, 2013-12-23;27(6):621-34.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Cell aggregation-induced FGF8 elevation is essential for P19 cell neural differentiation.
Authors: Wang C, Xia C, Bian W, Liu L, Lin W, Chen YG, Ang SL, Jing N
Mol. Biol. Cell, 2006-04-26;17(7):3075-84.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Regulation of avian cardiogenesis by Fgf8 signaling.
Authors: Alsan BH, 2019, Schultheiss TM
e0007247, 2002-04-01;129(8):1935-43.
Species: Chicken
Sample Types: In Ovo
Applications: In Ovo -
MiR-302/367 regulate neural progenitor proliferation, differentiation timing, and survival in neurulation.
Authors: Yang S, Yang M, Herrlinger S, Liang C, Lai F, Chen J
Dev Biol, 2015-10-09;408(1):140-50.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human/Mouse FGF-8 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human/Mouse FGF-8 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human/Mouse FGF-8 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image



