Human/Mouse Gremlin Antibody Summary
Lys25-Asp184
Accession # O70326
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Gremlin in Human Breast Cancer Tissue. Gremlin was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human breast cancer tissue using Goat Anti-Human/Mouse Gremlin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF956) at 3 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Goat IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC004). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
 View Larger
View Larger
Gremlin in Embryonic Mouse Ribs. Gremlin was detected in immersion fixed frozen sections of embryonic mouse ribs (15 d.p.c.) using 15 µg/mL Goat Anti-Human/Mouse Gremlin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF956) overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained with the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
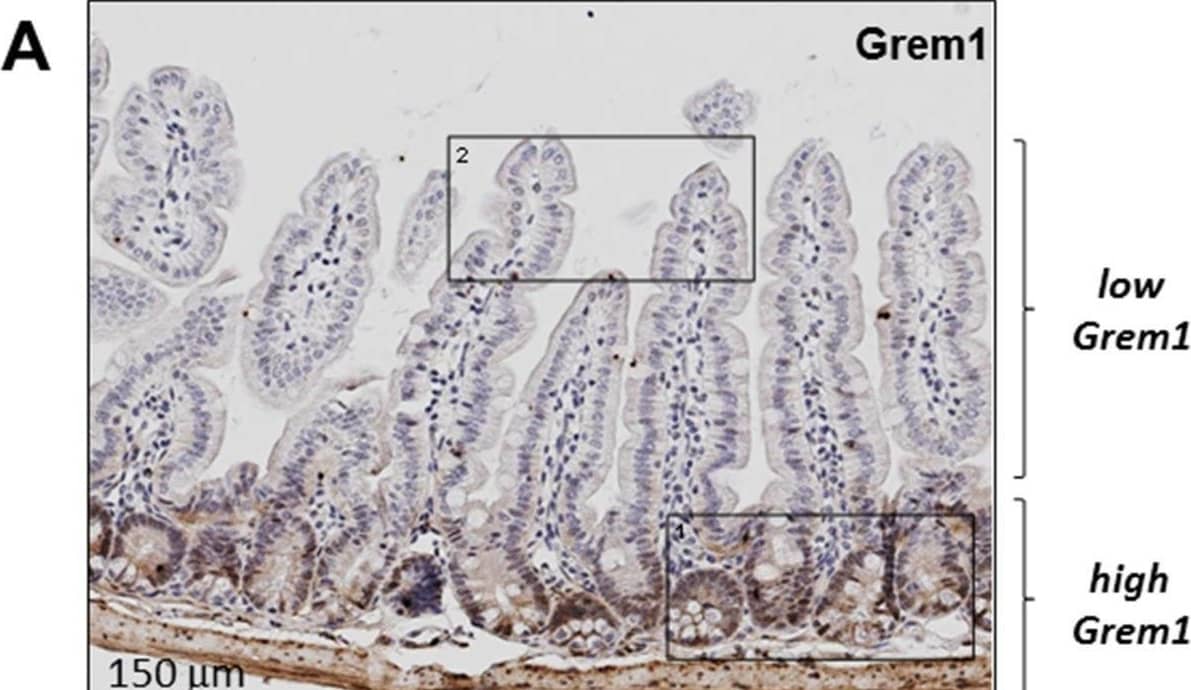
Detection of Gremlin by Immunohistochemistry Inverse relationship between expression of Grem1 protein and pSmad1/5 staining in mouse intestine. Sequential FFPE sections (5 μm) of mouse intestine were stained for Grem1 (A) or pSmad1/5 (B) as described in Methods. (C) Positively stained cells (empty bars) or villi tips (filled bars) were quantified in the indicated regions using Image J and data were plotted as mean pixel intensity –/+ SEM (n = 3 mice, 3 independent regions of intestine quantified per mouse). *p< 0.05, ***p< 0.001 using two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31384391), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
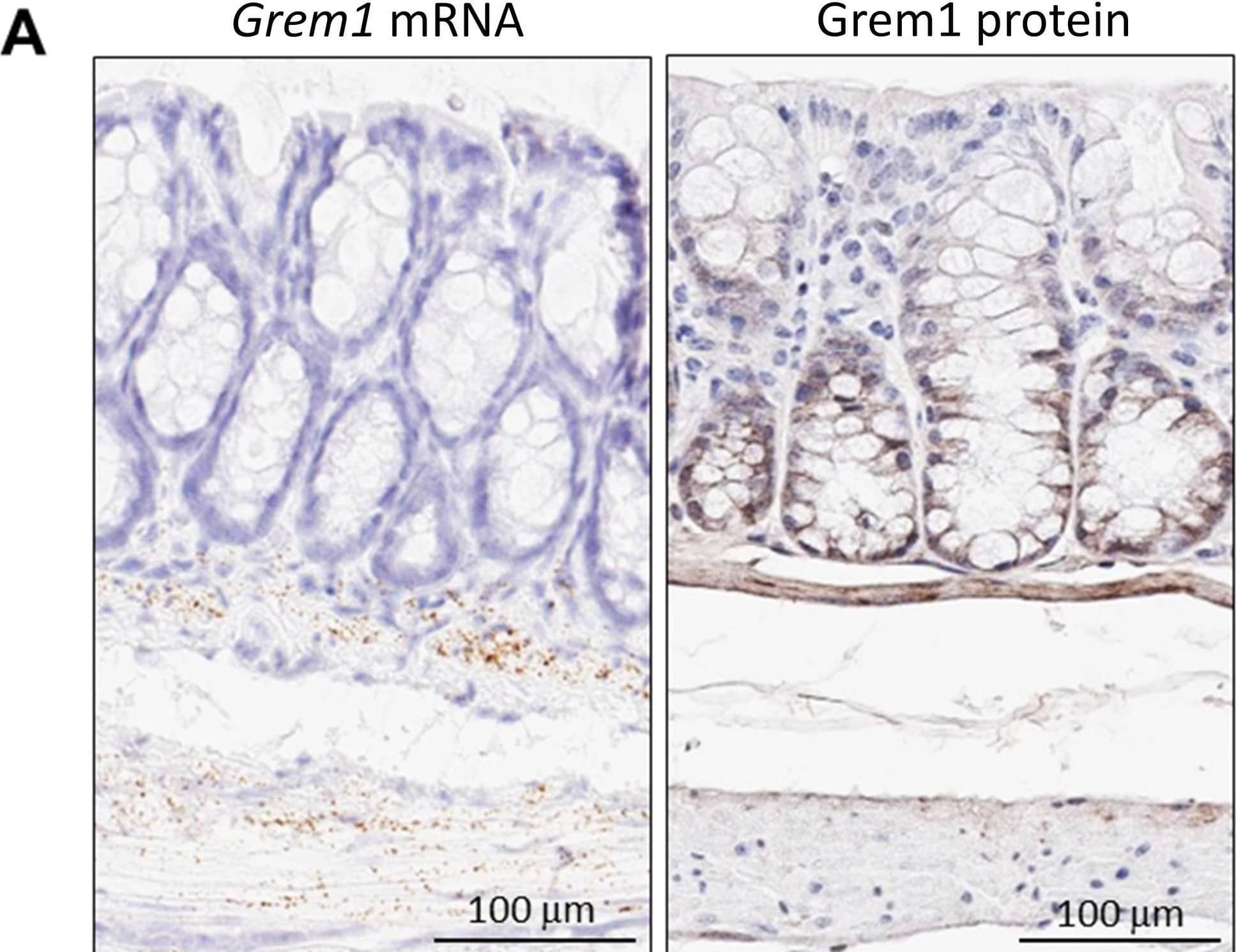
Detection of Gremlin by Immunohistochemistry Distinct pattern of endogenous Grem1 expression in mouse colon. Sections (5 μm) from FFPE colon samples (n = 4) from wild-type or Grem1-/- mice were processed for in situ hybridisation (A left) and immunohistochemistry (A right; B.) as described in Methods. Positive Grem1 mRNA and protein staining was imaged using DAB (brown) and sections were counterstained using haematoxylin and imaged using PathXL. (A) Grem1 mRNA is visible as brown, punctate staining in the muscularis mucosa layer. Scale bars 100 μm. (B) Grem1 protein staining is evident as brown staining in the muscularis layer and the base of the colonic crypts (left; scale bar 100 μm). Grem1 protein staining in the musclaris layer as well as cells of the colonic crypt. CBCC, crypt base columnar cells; P, Paneth cells; TA, transit-amplifying cells. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31384391), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
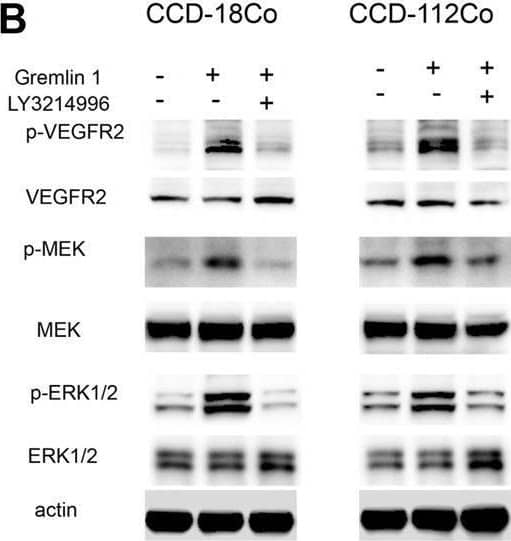
Detection of Gremlin by Western Blot VEGFR2-MEK-ERK axis mediated the enhancement of FAO from Gremlin 1. (A). Cell viability assay of human intestinal fibroblast cells CCD-18Co and CCD-112Co cells treated with 200 ng/ml Gremlin 1 and Rapamycin (10 nM), LY3214996 (10 nM) or stattic (10 μM) for 24 h. (B). Immunoblotting analysis of VEGFR2-MEK-ERK signaling in human intestinal fibroblast cells CCD-18Co and CCD-112Co cells treated with 200 ng/ml Gremlin 1 and LY3214996 (10 nM) for 24 h. Actin acted as loading control and re-used for illustrative purposes. (C). Immunofluorescence staining of a-SMA in human intestinal fibroblast cells CCD-18Co and CCD-112Co cells treated with 200 ng/ml Gremlin 1 and LY3214996 (10 nM). (D). The intensity statistical results of a-SMA immunofluorescence staining from five random fields of slides. E. OCR measurement of CCD-18Co and CCD-112Co cells treated with 200 ng/ml Gremlin 1 and LY3214996 (10 nM) for 24 h. p values are derived from one-way ANOVA analysis. Dunnett’s test was used to analysis the difference between control group to the other groups. **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33967807), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
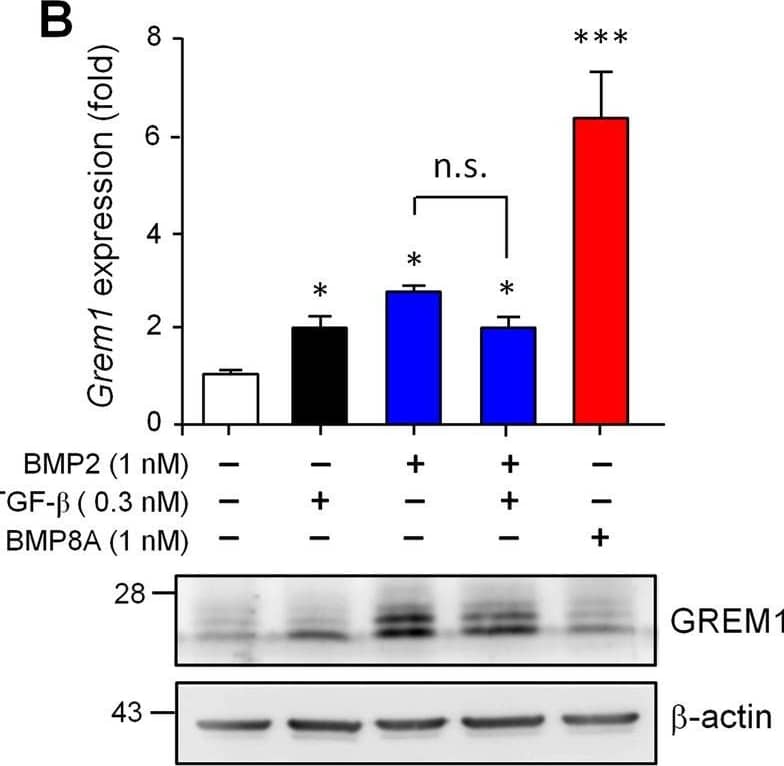
Detection of Gremlin by Western Blot BMP2, TGF-beta 1 and BMP8A show different effects on the expressional induction of Nog, Grem1 and Grem2. C3H10T1/2 cells were treated with BMP2 (1 nM), TGF-beta 1 (0.3 nM), BMP2 plus with TGF-beta 1 or BMP8A (1 nM) for 24 h. The transcript levels (upper panel) and encoding protein amounts (lower panel) of Nog (A), Grem1 (B) and Grem2 (C) were then evaluated. beta -actin amounts served as loading controls in immunoblotting. D To explore how BMP8A induces Grem1 expression, cells were treated with BMP8A in the absence or presence of SB431542 (SB) or dorsomorphin (DM) as indicated. Quantification data are presented as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 compared to no-treatment control. # P < 0.001 compared between indicated groups Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36443839), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
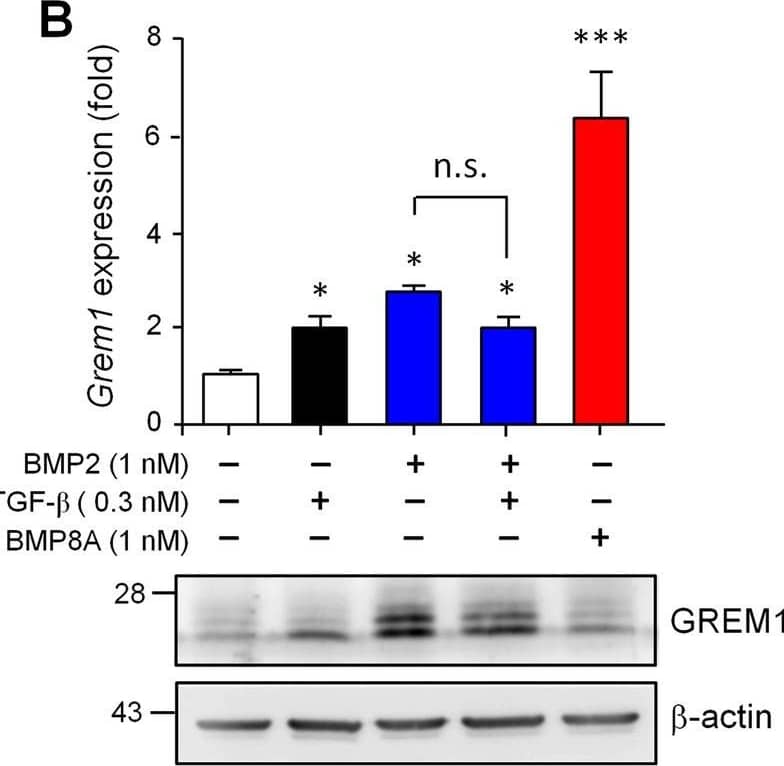
Detection of Gremlin by Western Blot BMP2, TGF-beta 1 and BMP8A show different effects on the expressional induction of Nog, Grem1 and Grem2. C3H10T1/2 cells were treated with BMP2 (1 nM), TGF-beta 1 (0.3 nM), BMP2 plus with TGF-beta 1 or BMP8A (1 nM) for 24 h. The transcript levels (upper panel) and encoding protein amounts (lower panel) of Nog (A), Grem1 (B) and Grem2 (C) were then evaluated. beta -actin amounts served as loading controls in immunoblotting. D To explore how BMP8A induces Grem1 expression, cells were treated with BMP8A in the absence or presence of SB431542 (SB) or dorsomorphin (DM) as indicated. Quantification data are presented as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 compared to no-treatment control. # P < 0.001 compared between indicated groups Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36443839), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Gremlin
Gremlin was identified in a Xenopus expression-cloning screen as a dorsalizing factor that can induce a secondary axis. A rat homolog, called Drm, was identified as a cDNA that was downregulated in v-mos transfected cells. Gremlin/Drm belongs to the DAN family of secreted glycoproteins that are BMP antagonists. Other members of the family include: cerberus, Dante, PRDC, caronte and DAN. DAN family members share a cysteine-rich domain that is structurally related to the cysteine-knot motif found in TGF-beta superfamily ligands. In vitro, Gremlin/Drm binds BMP-4 and BMP-2 indicating that it might interfere with BMP signaling. Gremlin/Drm acts as a BMP-2/4 antagonist in a variety of tissues and developmental processes including: Xenopus animal cap explants, chick limb bud outgrowth and chondrogenesis, murine lung branching morphogenesis, and osteogenic differentiation of mouse myoblasts and bone marrow stromal cells. In addition, expression of Gremlin/Drm has been shown to be downregulated in a wide range of human cancer cell lines. Mouse, human, chick and Xenopus homologs of Gremlin share over 80% amino acid identity. It is likely that various DAN family members and other BMP antagonists including Noggin, Chordin, Follistatin and TSG can selectively antagonize the activities of different subsets of TGF-beta superfamily ligands.
- Hsu, D.R. et al. (1998) Mol. Cell 1:673.
- Merino, R. et al. (1999) Development 126:5515.
- Shi, W. et al. (2001) Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 280:L1030.
- Topol, L.Z. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:8785.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human/Mouse Gremlin Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
21
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Fibroblast-derived Gremlin1 localises to epithelial cells at the base of the intestinal crypt
Authors: Louise R. Dutton, Owen P. Hoare, Amy M.B. McCorry, Keara L. Redmond, Noor Eisa Adam, Shannon Canamara et al.
Oncotarget
-
Gremlin-1 Overexpression in Mouse Lung Reduces Silica-Induced Lymphocyte Recruitment – A Link to Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis through Negative Correlation with CXCL10 Chemokine
Authors: Katri Koli, Eva Sutinen, Mikko Rönty, Pia Rantakari, Vittorio Fortino, Ville Pulkkinen et al.
PLOS ONE
-
The BMP antagonist gremlin 1 contributes to the development of cortical excitatory neurons, motor balance and fear responses
Authors: Mari Ichinose, Nobumi Suzuki, Tongtong Wang, Hiroki Kobayashi, Laura Vrbanac, Jia Q. Ng et al.
Development
-
Roles of Gremlin 1 and Gremlin 2 in regulating ovarian primordial to primary follicle transition
Authors: Eric E. Nilsson, Ginger Larsen, Michael K. Skinner
REPRODUCTION
-
Targeting Gremlin 1 Prevents Intestinal Fibrosis Progression by Inhibiting the Fatty Acid Oxidation of Fibroblast Cells
Authors: Yang Yang, Qi-Shan Zeng, Min Zou, Jian Zeng, Jiao Nie, DongFeng Chen et al.
Frontiers in Pharmacology
-
Excessive mechanical loading promotes osteoarthritis through the gremlin-1-NF- kappa B pathway.
Authors: Chang Song Ho, Mori Daisuke, Kobayashi Hiroshi et al.
Frontiers in Immunology
-
Evaluation of Gremlin-1 as a therapeutic target in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis
Authors: Horn, P;Norlin, J;Almholt, K;Viuff, BM;Galsgaard, ED;Hald, A;Zosel, F;Demuth, H;Poulsen, S;Norby, PL;Rasch, MG;Vyberg, M;Fleckner, J;Werge, MP;Gluud, LL;Rink, MR;Shepherd, E;Northall, E;Lalor, PF;Weston, CJ;Fog-Tonnesen, M;Newsome, PN;
eLife
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
TAF15 regulates the BRD4/GREM1 axis and activates the gremlin-1-NF-kappa B pathway to promote OA progression
Authors: Du, X;Xin, R;Chen, X;Wang, G;Huang, C;Zhou, K;Zhang, S;
Regenerative Therapy
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Dynamic and adaptive cancer stem cell population admixture in colorectal neoplasia
Authors: EG Vasquez, N Nasreddin, GN Valbuena, EJ Mulholland, HL Belnoue-Da, HR Eggington, RO Schenck, VM Wouters, P Wirapati, K Gilroy, TRM Lannagan, DJ Flanagan, AK Najumudeen, S Omwenga, AMB McCorry, A Easton, VH Koelzer, JE East, D Morton, L Trusolino, T Maughan, AD Campbell, MB Loughrey, PD Dunne, P Tsantoulis, DJ Huels, S Tejpar, OJ Sansom, SJ Leedham
Cell Stem Cell, 2022-08-04;29(8):1213-1228.e8.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
The BMP antagonist gremlin 1 contributes to the development of cortical excitatory neurons, motor balance and fear responses
Authors: Mari Ichinose, Nobumi Suzuki, Tongtong Wang, Hiroki Kobayashi, Laura Vrbanac, Jia Q. Ng et al.
Development
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Distinct fibroblast subsets regulate lacteal integrity through YAP/TAZ-induced VEGF-C in intestinal villi
Authors: SP Hong, MJ Yang, H Cho, I Park, H Bae, K Choe, SH Suh, RH Adams, K Alitalo, D Lim, GY Koh
Nat Commun, 2020-08-14;11(1):4102.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Vital Roles of Gremlin-1 in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Induced by Systemic-to-Pulmonary Shunts
Authors: L Meng, X Teng, Y Liu, C Yang, S Wang, W Yuan, J Meng, H Chi, L Duan, X Liu
J Am Heart Assoc, 2020-07-31;9(15):e016586.
Species: Human, Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: Functional Assay, IHC, Neutralization -
Fibroblast-derived Gremlin1 localises to epithelial cells at the base of the intestinal crypt
Authors: Louise R. Dutton, Owen P. Hoare, Amy M.B. McCorry, Keara L. Redmond, Noor Eisa Adam, Shannon Canamara et al.
Oncotarget
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
The role of Bmp2 in the maturation and maintenance of the murine knee joint
Authors: LW Gamer, S Pregizer, J Gamer, M Feigenson, A Ionescu, Q Li, L Han, V Rosen
J. Bone Miner. Res., 2018-06-13;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Multi-physics interactions drive VEGFR2 relocation on endothelial cells
Authors: V Damioli, A Salvadori, GP Beretta, C Ravelli, S Mitola
Sci Rep, 2017-12-01;7(1):16700.
Species: Bovine
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Gremlin-1 Overexpression in Mouse Lung Reduces Silica-Induced Lymphocyte Recruitment – A Link to Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis through Negative Correlation with CXCL10 Chemokine
Authors: Katri Koli, Eva Sutinen, Mikko Rönty, Pia Rantakari, Vittorio Fortino, Ville Pulkkinen et al.
PLOS ONE
Species: Transgenic Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Tubular overexpression of gremlin induces renal damage susceptibility in mice.
Authors: Droguett A, Krall P, Burgos M, Valderrama G, Carpio D, Ardiles L, Rodriguez-Diez R, Kerr B, Walz K, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J, Mezzano S
PLoS ONE, 2014-07-18;9(7):e101879.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
A concentration-dependent endocytic trap and sink mechanism converts Bmper from an activator to an inhibitor of Bmp signaling.
Authors: Kelley R, Ren R, Pi X, Wu Y, Moreno I, Willis M, Moser M, Ross M, Podkowa M, Attisano L, Patterson C
J. Cell Biol., 2009-02-16;184(4):597-609.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Bone morphogenic protein antagonist Drm/gremlin is a novel proangiogenic factor.
Authors: Stabile H, Mitola S, Moroni E, Belleri M, Nicoli S, Coltrini D, Peri F, Pessi A, Orsatti L, Talamo F, Castronovo V, Waltregny D, Cotelli F, Ribatti D, Presta M
Blood, 2006-10-31;109(5):1834-40.
Species: Bovine, Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P, Western Blot -
Unveiling the transcriptomic landscape and the potential antagonist feedback mechanisms of TGF-beta superfamily signaling module in bone and osteoporosis
Authors: Ying-Wen Wang, Wen-Yu Lin, Fang-Ju Wu, Ching-Wei Luo
Cell Communication and Signaling
-
Gremlin is a key pro-fibrogenic factor in chronic pancreatitis
Authors: Dustin Staloch, Xuxia Gao, Ka Liu, Meihua Xu, Xueping Feng, Judith F. Aronson et al.
Journal of Molecular Medicine
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human/Mouse Gremlin Antibody
Average Rating: 4 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human/Mouse Gremlin Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: