Human/Mouse HMGA2 Antibody Summary
Ser2-Asp109
Accession # P52926
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human and Mouse HMGA2 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, MDA-MD-231 human breast cancer cell line, NIH-3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line, and P19 mouse embryonal carcinoma cell line. PVDF Membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human/Mouse HMGA2 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3184) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF019). A specific band was detected for HMGA2 at approximately 21 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 8.
 View Larger
View Larger
HMGA2 in IMR‑90 Human Cell Line. HMGA2 was detected in immersion fixed IMR‑90 human lung fibroblast cell line using Goat Anti-Human/Mouse HMGA2 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3184) at 5 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell nuclei. Staining was performed using our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse HMGA2 by Simple WesternTM. Simple Western lane view shows lysates of NIH-3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for HMGA2 at approximately 30 kDa (as indicated) using 10 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human/Mouse HMGA2 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3184) followed by 1:50 dilution of HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF109). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230 kDa separation system.
 View Larger
View Larger
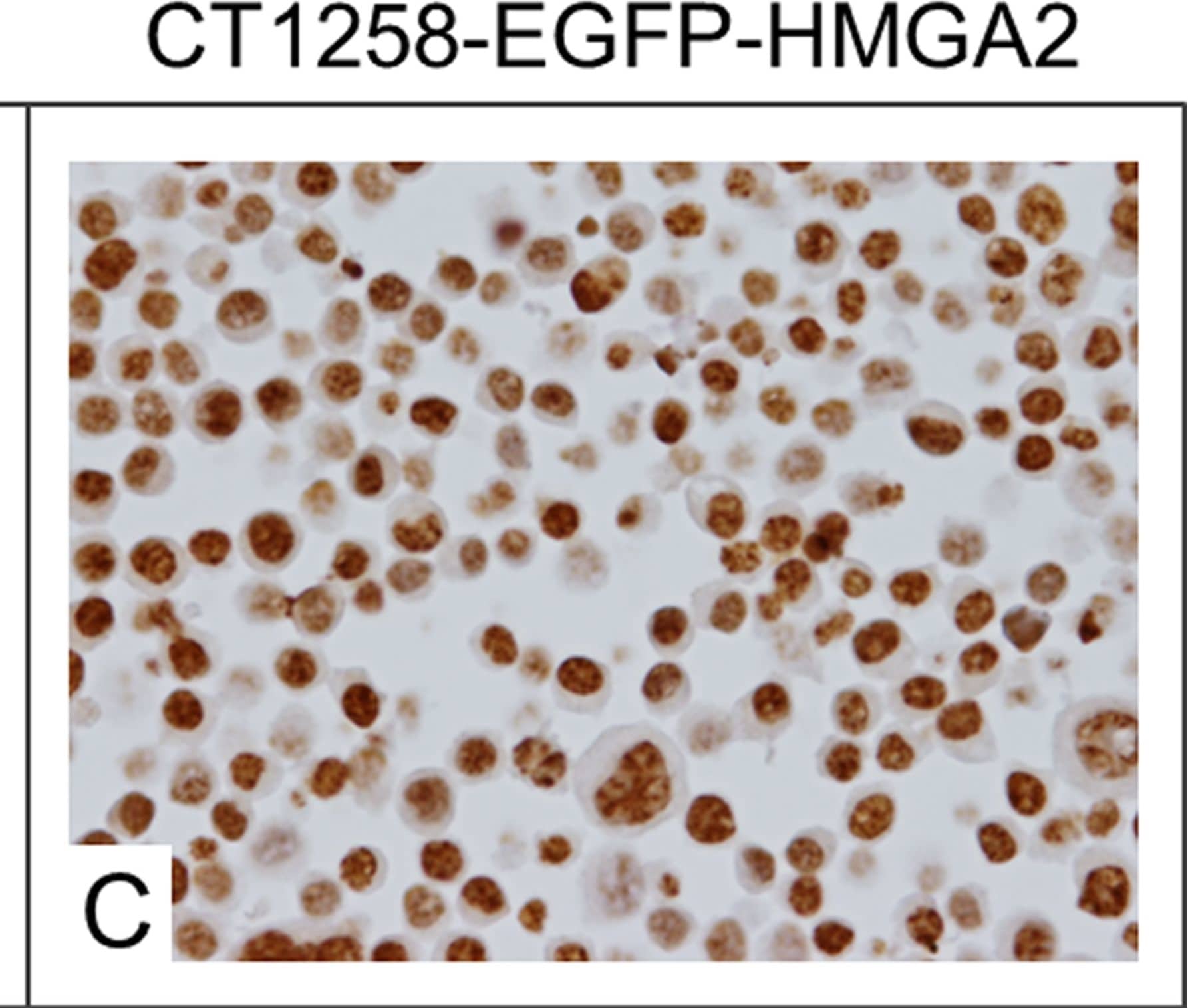
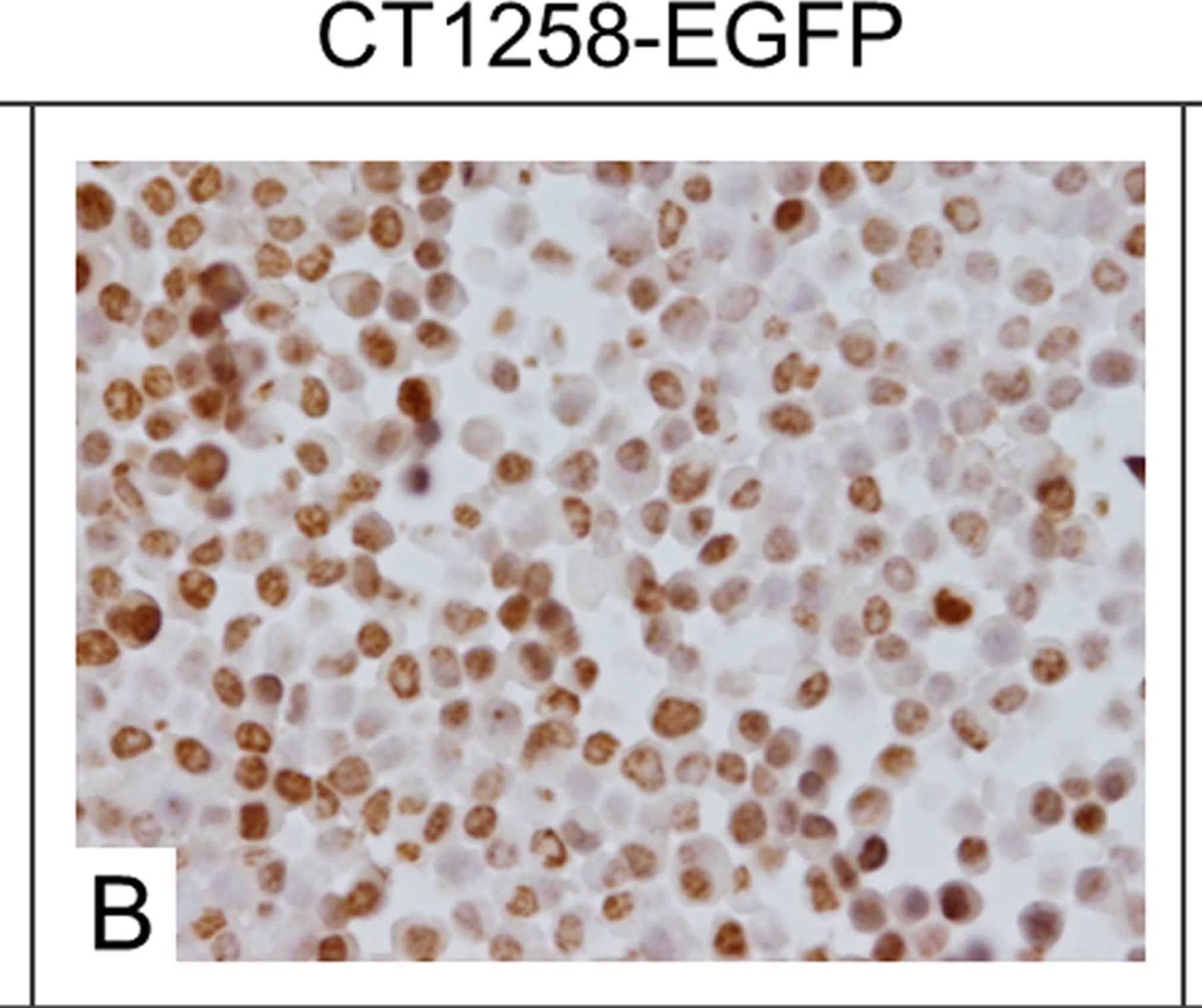
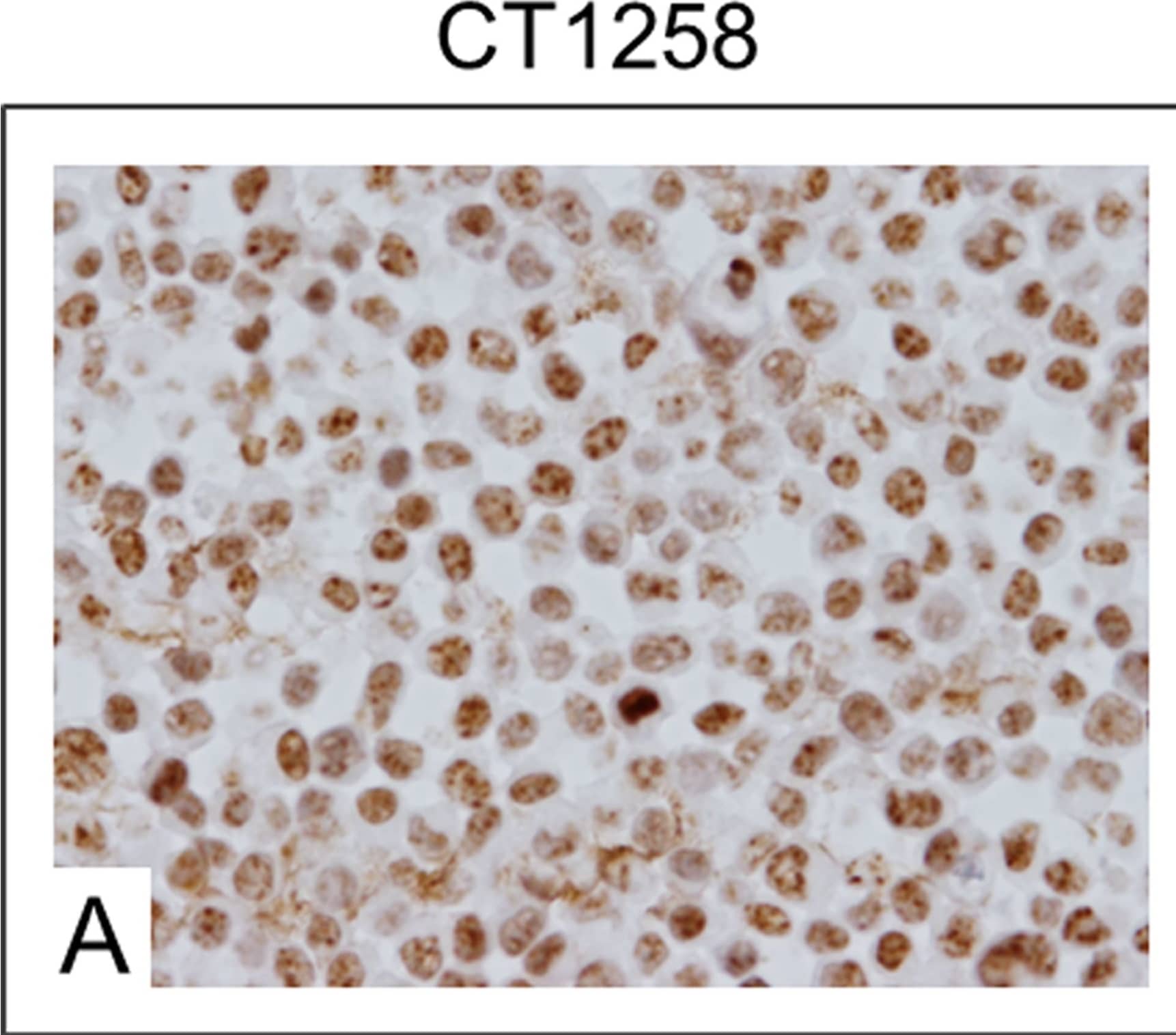
Detection of Canine HMGA2 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Immunocytochemical staining.A: Native CT1258 cells, B: CT1258-EGFP cells, C: CT1258-EGFP-HMGA2 cells. Approximately 50% of the native CT1258 cell line and of CT1258-EGFP cells showed a HMGA2-positive nuclear labelling. In approximately 70–80% of CT1258-EGFP-HMGA2 cells, a strong and exclusively nuclear labelling for HMGA2 was detectable. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24914948), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
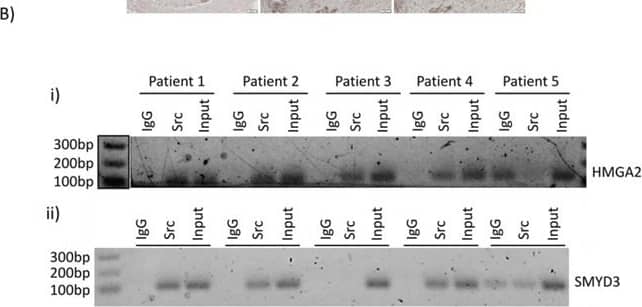
Detection of Human HMGA2 by Western Blot Nuclear Src activation and association with HMGA2 and SMYD3 gene promoters are observed in patient samples of PDACA Immunohistochemistry of human PDAC tumor samples. Human PDAC slides were immunostained for pY416Src (i) and (ii, left panels), HMGA2 (ii, middle panels), or SMYD3 (ii, right panels). Images were acquired at high (40X) magnification for pSrc (i), or low magnification (10X) of the same tumors for pSrc, HMGA2, or SMYD3 (ii). B. Pathology tissue-Chip (PAT-ChIP) of human PDAC samples derived from banked formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. Samples were subjected to chromatin immunoprecipitation assay using anti-Src antibody or IgG as control and amplified by PCR using specific primers for the HMGA2 (i) and SMYD3 (ii) promoters. Correct PCR product size is verified by DNA ladder. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.oncotarget.com/lookup/doi/10.18632/oncotarget.6635), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
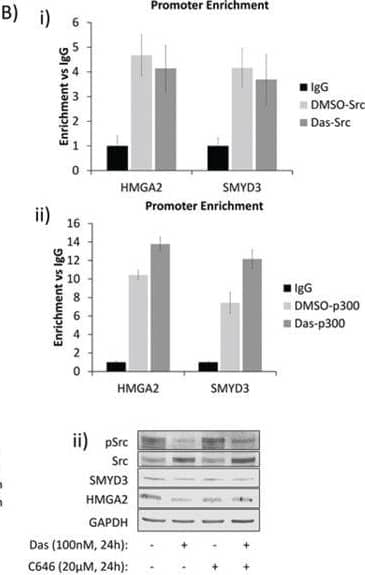
Detection of Human HMGA2 by Western Blot Nuclear Src and p300 associate with HMGA2 and SMYD3 gene promoters and regulate their expression in PDAC and MEF cellsA and B. Chromatin-immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and quantitative polymerase-chain reaction (qPCR) analyses of Src-associated genes in Panc-1 cells and the effects of dasatinib. (A) Untreated Panc-1 cells were subjected to ChIP analysis using anti–Src antibody and qPCR to quantify the immune-complex-associated ACTB, HMGA2, or SMYD3 promoters. Pre-immune IgG was used as control. (B) Panc-1 cells were treated for three hours with 100 nmol/L dasatinib or untreated (DMSO) and subjected to ChIP using anti-Src (i), anti-p300 (ii), or control IgG antibodies as indicated. Antibody-associated eluates were analyzed by qPCR using primers spanning the promoter regions of the indicated genes. PCR signals were normalized to individual sample inputs and compared to IgG control and plotted as enrichment vs IgG. C. Analysis of HMGA2 and SMYD3 expression in Panc-1 cells. Panc-1 cells were treated with 100 nmol/L dasatinib, 20 μmol/L C646, or 0.01% DMSO (control) for the indicated times. Total RNA was extracted from cells for mRNA expression analysis (i), or whole-cell lysates were prepared for immunoblotting analysis of HMGA2 or SMYD3 expression (ii). D. Promoter enrichment as detected by ChIP-qPCR of Src at the mouse HMGA2 promoter in the SYF+/+ and SYF-Src cell lines. PCR reactions were performed using specific primers for the mouse HMGA2 promoter region analogous to the Src-associated region in the human HMGA2 promoter. Data are normalized to individual inputs and are expressed as enrichment vs IgG. All qPCR data represent mean ±SEM of three independent experiments. E. Immunoprobes of Src, pSrc, HMGA2 or GAPDH from whole-cell lysates prepared from SYF+/+ and SYF-Src cells treated with 100 nmol/L dasatinib or 20 μmol/L C646 for 24 hours. Control (−) lanes represent cells treated with 0.05% DMSO. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.oncotarget.com/lookup/doi/10.18632/oncotarget.6635), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human HMGA2 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Immunocytochemical staining.A: Native CT1258 cells, B: CT1258-EGFP cells, C: CT1258-EGFP-HMGA2 cells. Approximately 50% of the native CT1258 cell line and of CT1258-EGFP cells showed a HMGA2-positive nuclear labelling. In approximately 70–80% of CT1258-EGFP-HMGA2 cells, a strong and exclusively nuclear labelling for HMGA2 was detectable. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24914948), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
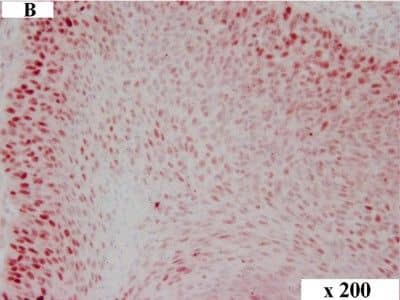
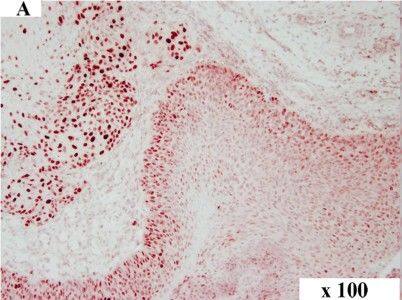
Detection of Canine HMGA2 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence HMGA2 immunohistochemistry in canine OSCC. Immunolabelling of a canine tumour grade II: overview (A), tumour centre (B) and invasive front (C). HMGA2 staining in the tumour centre (B) revealed approx. 25% tumour cells with nuclear immunolabelling while cells at the invasive front showed approx. 50% staining (C). Magnification: (A) 100x, (B) and (C) 200x. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25245141), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
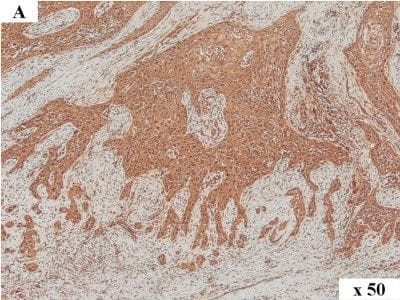
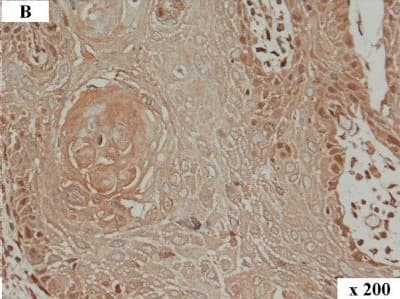
Detection of Human HMGA2 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence HMGA2 immunohistochemistry in human OSCC. Immunolabelling of a human tumour: overview (A), tumour centre (B) and invasive front (C). In the tumour centre (B) lower numbers of tumour cells with nuclear immunolabelling are present when compared to the respective invasive front (C). The invasive front shows numerous tumour cells exhibiting intense nuclear immunolabelling of HMGA2. Magnification: (A) 50x, (B) and (C) 200x. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25245141), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
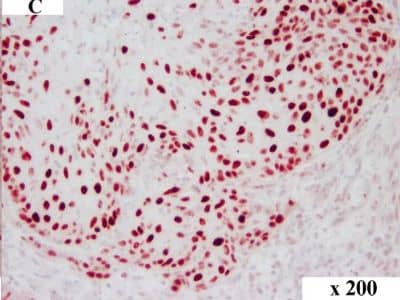
Detection of Canine HMGA2 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence HMGA2 immunohistochemistry in canine OSCC. Immunolabelling of a canine tumour grade II: overview (A), tumour centre (B) and invasive front (C). HMGA2 staining in the tumour centre (B) revealed approx. 25% tumour cells with nuclear immunolabelling while cells at the invasive front showed approx. 50% staining (C). Magnification: (A) 100x, (B) and (C) 200x. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25245141), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
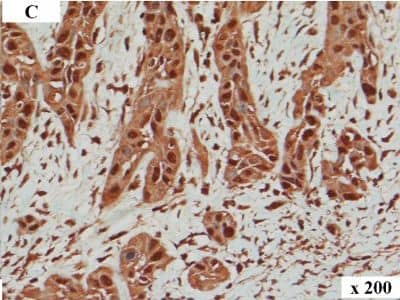
Detection of Human HMGA2 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence HMGA2 immunohistochemistry in human OSCC. Immunolabelling of a human tumour: overview (A), tumour centre (B) and invasive front (C). In the tumour centre (B) lower numbers of tumour cells with nuclear immunolabelling are present when compared to the respective invasive front (C). The invasive front shows numerous tumour cells exhibiting intense nuclear immunolabelling of HMGA2. Magnification: (A) 50x, (B) and (C) 200x. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25245141), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Canine HMGA2 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence HMGA2 immunohistochemistry in canine OSCC. Immunolabelling of a canine tumour grade II: overview (A), tumour centre (B) and invasive front (C). HMGA2 staining in the tumour centre (B) revealed approx. 25% tumour cells with nuclear immunolabelling while cells at the invasive front showed approx. 50% staining (C). Magnification: (A) 100x, (B) and (C) 200x. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25245141), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human HMGA2 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence HMGA2 immunohistochemistry in human OSCC. Immunolabelling of a human tumour: overview (A), tumour centre (B) and invasive front (C). In the tumour centre (B) lower numbers of tumour cells with nuclear immunolabelling are present when compared to the respective invasive front (C). The invasive front shows numerous tumour cells exhibiting intense nuclear immunolabelling of HMGA2. Magnification: (A) 50x, (B) and (C) 200x. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25245141), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Canine HMGA2 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Immunocytochemical staining.A: Native CT1258 cells, B: CT1258-EGFP cells, C: CT1258-EGFP-HMGA2 cells. Approximately 50% of the native CT1258 cell line and of CT1258-EGFP cells showed a HMGA2-positive nuclear labelling. In approximately 70–80% of CT1258-EGFP-HMGA2 cells, a strong and exclusively nuclear labelling for HMGA2 was detectable. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24914948), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: HMGA2
HMGA2, previously known as HMGI-C, belongs to the group of high mobility chromosomal proteins that have the AT-hook DNA-binding motif. It is highly and ubiquitously expressed during embryogenesis. Chromosomal rearrangements of the HMGA2 gene and overexpression are frequently associated with benign and malignant tumors, respectively. Human and mouse HMGA2 share 95% amino acid sequence identity.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human/Mouse HMGA2 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
11
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Novel roles for HMGA2 isoforms in regulating oxidative stress and sensitizing to RSL3-Induced ferroptosis in prostate cancer cells
Authors: T Campbell, O Hawsawi, V Henderson, P Dike, BJ Hwang, Y Liadi, EZ White, J Zou, G Wang, Q Zhang, N Bowen, D Scott, CV Hinton, V Odero-Mara
Heliyon, 2023-04-07;9(4):e14810.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC/IF -
Novel roles for HMGA2 isoforms in regulating oxidative stress and sensitizing to RSL3-Induced ferroptosis in prostate cancer cells
Authors: T Campbell, O Hawsawi, V Henderson, P Dike, BJ Hwang, Y Liadi, EZ White, J Zou, G Wang, Q Zhang, N Bowen, D Scott, CV Hinton, V Odero-Mara
Heliyon, 2023;9(4):e14810.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC/IF -
Multicolor quantitative confocal imaging cytometry
Authors: DL Coutu, KD Kokkaliari, L Kunz, T Schroeder
Nat. Methods, 2017-11-13;15(1):39-46.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
HMGA1 and HMGA2 expression and comparative analyses of HMGA2, Lin28 and let-7 miRNAs in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Authors: Sterenczak K, Eckardt A, Kampmann A, Willenbrock S, Eberle N, Langer F, Kleinschmidt S, Hewicker-Trautwein M, Kreipe H, Nolte I, Murua Escobar H, Gellrich N
BMC Cancer, 2014-09-23;14(0):694.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Generation and characterisation of a canine EGFP-HMGA2 prostate cancer in vitro model.
Authors: Willenbrock, Saskia, Wagner, Siegfrie, Reimann-Berg, Nicola, Moulay, Mohammed, Hewicker-Trautwein, Marion, Nolte, Ingo, Murua Escobar, Hugo
PLoS ONE, 2014-06-10;9(6):e98788.
Species: Canine
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: IHC-P -
MiRNA let-7g regulates skeletal myoblast motility via Pinch-2.
Authors: Boudoukha S, Rivera Vargas T, Dang I, Kropp J, Cuvellier S, Gautreau A, Polesskaya A
FEBS Lett, 2014-03-05;588(9):1623-9.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Downregulation of HMGA2 by the pan-deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat is dependent on hsa-let-7b expression in liver cancer cell lines.
Exp Cell Res, 2012-06-08;318(15):1832-43.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Subsets of very low risk wilms tumor show distinctive gene expression, histologic, and clinical features.
Authors: Sredni ST, Gadd S, Huang CC, Breslow N, Grundy P, Green DM, Dome JS, Shamberger RC, Beckwith JB, Perlman EJ
Clin. Cancer Res., 2009-11-10;15(22):6800-9.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Clinical significance of high mobility group A2 in human gastric cancer and its relationship to let-7 microRNA family.
Authors: Motoyama K, Inoue H, Nakamura Y, Uetake H, Sugihara K, Mori M
Clin. Cancer Res., 2008-04-15;14(8):2334-40.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Binding of high mobility group A proteins to the mammalian genome occurs as a function of AT-content
Authors: DF Colombo, L Burger, T Baubec, D Schübeler
PLoS Genet., 2017-12-21;13(12):e1007102.
-
A novel nuclear Src and p300 signaling axis controls migratory and invasive behavior in pancreatic cancer.
Authors: Paladino David, Yue Peibin, Furuya Hideki et al.
Oncotarget
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human/Mouse HMGA2 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human/Mouse HMGA2 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human/Mouse HMGA2 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
