Human/Mouse/Rat CTGF/CCN2 Antibody
Human/Mouse/Rat CTGF/CCN2 Antibody Summary
Glu247-Ala349
Accession # P29279
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human, Mouse, and Rat CTGF/CCN2 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells, SVEC4-10 mouse vascular endothelial cell line, and Rat-2 rat embryonic fibroblast cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Rabbit Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat CTGF/CCN2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB91901) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Rabbit IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF008). A specific band was detected for CTGF/CCN2 at approximately 36 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
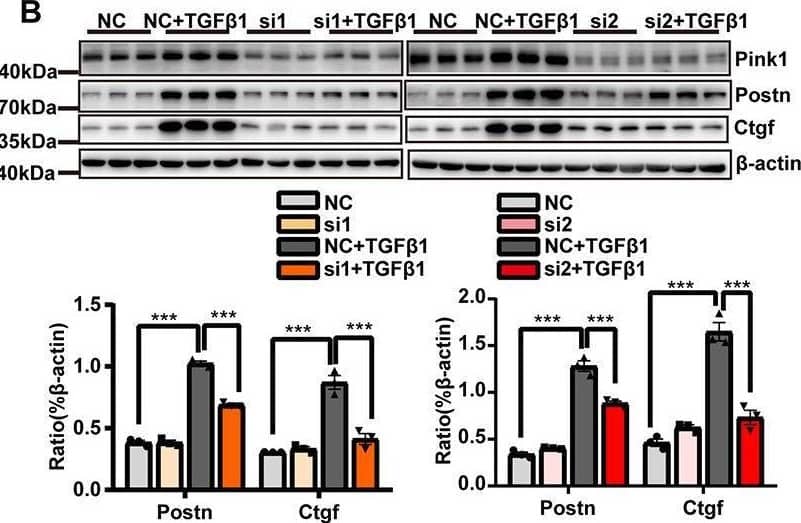
Detection of CTGF/CCN2 by Western Blot The suppression of mitophagy inhibited cardiac fibroblasts (CF) activation. CF were transfected with either Pink1 siRNA or negative control (NC) and then stimulated with TGF-beta 1. (A) alpha -SMA immunofluorescence staining and semi-quantitative analysis. (B) Immunoblot analyses and quantitative analyses of the markers of CF activation, Postn and Ctgf, among the different groups. EdU and vimentin staining (C) and the MTS cell proliferation assay (D) were used to evaluate CF proliferation. (E) A wound healing assay was performed to evaluate CF migratory capacity following the different treatments. (F) Measurement of lysyl oxidase (LOX) activity. (G) The relative expression levels of extracellular matrix (ECM)-related proteins normalized to that of beta-actin. (H) Cell apoptosis was compared among the different groups by flow cytometry. Data are shown as mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 3 independent cell isolations per group). Means were compared by one-way ANOVA, followed by the Student–Newman–Keuls (SNK) post hoc test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33585469), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
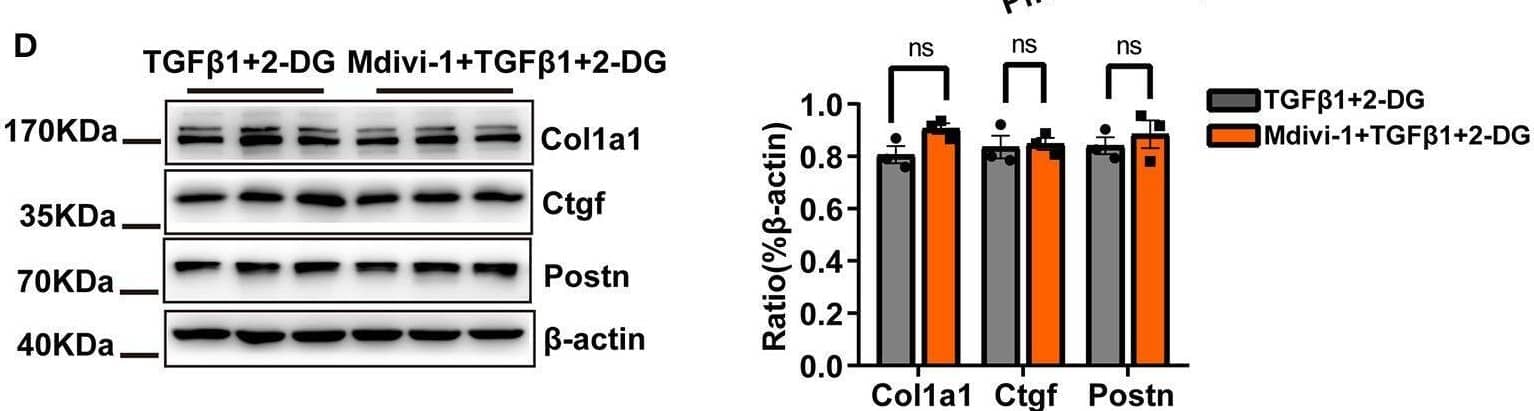
Detection of CTGF/CCN2 by Western Blot Reducing the cardiac fibroblasts (CF) glycolytic flux may be important for mitochondrial fission inhibition-induced suppression of CF activation. (A) Measurements of the extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) metabolic profile by Seahorse XF glycolytic rate assay kit and analyses of CF Proton Efflux Rate (PER) in basal glycolysis and glycolysis capacity. (B) The oxygen consumption rate (OCR) as measured using a Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit and analyses of the OCR under basal and maximum respiration. (C) Western blot analyses and quantification of key glycolytic enzymes under TGF-beta 1 plus mdivi-1 cotreatment. (D) The expression of CF activation-related markers was measured by immunoblotting following TGF-beta 1 plus mdivi-1 cotreatment and in the presence or absence of 2-DG. Data are shown as mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 3 independent cell isolations per group). Means were compared by one-way ANOVA, followed by the Student–Newman–Keuls (SNK) post hoc test. ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33585469), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
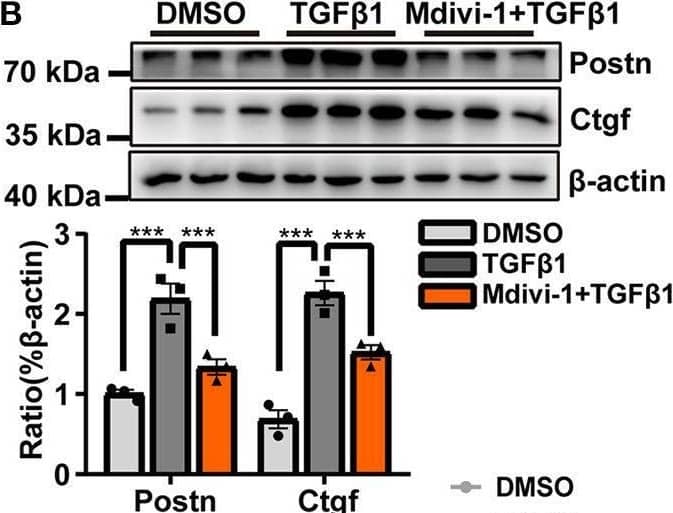
Detection of CTGF/CCN2 by Western Blot The inhibition of TGF-beta 1-induced mitochondrial fission abolished cardiac fibroblasts (CF) activation. (A) alpha -SMA immunofluorescence staining and semi-quantitative analysis. (B) The expression of the markers of CF activation, Postn and Ctgf, was measured by immunoblotting. EdU and vimentin staining (C) and an MTS assay (D) were used to observe CF proliferation. (E) Gelatin zymography was used to measure MMP-2 and MMP-9 activities. (F) The activity of lysyl oxidase (LOX) was used as an indicator of extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition. (G) Immunoblot of ECM-related proteins, with quantification, following TGF-beta 1 plus mdivi-1 cotreatment. (H) A wound healing assay was employed to evaluate CF migration. Data are shown as mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 3 independent cell isolations per group). Means were compared using one-way ANOVA, followed by the Student–Newman–Keuls (SNK) post hoc test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33585469), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
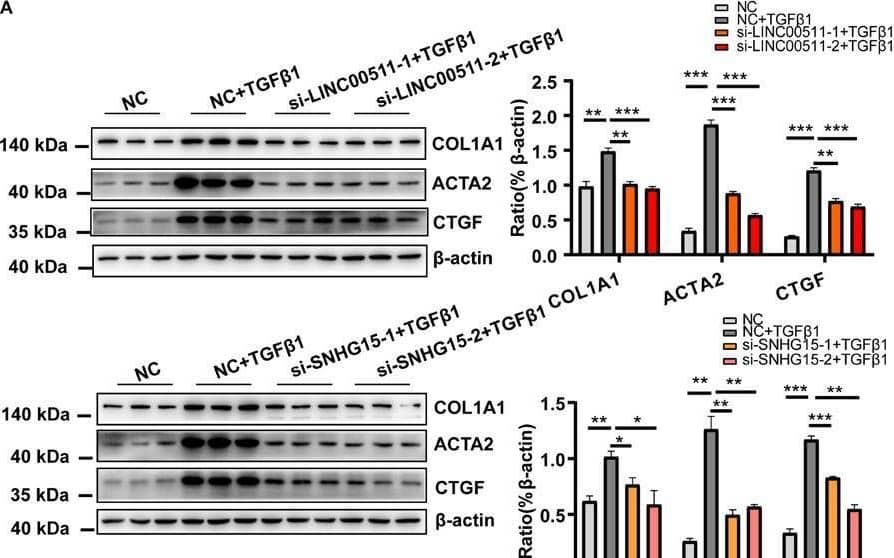
Detection of CTGF/CCN2 by Western Blot Functional validation of LINC00511 and SNHG15 in activation of cardiac fibroblasts. (A) Knockdown of expression of LINC00511 and SNHG15 reduced expression of myofibroblast-associated genes. (B) Depletion of LINC00511 and SNHG15 can reduce collagen secretion in HCF-cultured supernatants. (C) Depletion of LINC00511 and SNHG15 can reduce myofibroblast proliferation in 1 and 2 days, respectively. n = 3 per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33552116), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: CTGF/CCN2
CTGF belongs to the CCN (CYR61/CTGF/NOV) family of secreted proteins that share a common multimodular organization. Each protein contains IGF-binding protein domain, a von Willebrand factor type C domain, a thrombospondin type I domain, and a cysteine knot domain. The multimodular CTGF has the ability to bind multiple ligands and has numerous effects on development, differentation, and disease. The C-terminal cysteine knot motif contains the heparin and low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) binding sites that contributes to the adhesive and mitogenic properties of CTGF.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human/Mouse/Rat CTGF/CCN2 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
2
Citations: Showing 1 - 2
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Geniposide ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice by inhibiting TGF-?/Smad and p38MAPK signaling pathways
Authors: Yin, JB;Wang, YX;Fan, SS;Shang, WB;Zhu, YS;Peng, XR;Zou, C;Zhang, X;
PloS one
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Paracrine signalling between intestinal epithelial and tumour cells induces a regenerative programme
Authors: G Jacquemin, A Wurmser, M Huyghe, W Sun, Z Homayed, C Merle, M Perkins, F Qasrawi, S Richon, F Dingli, G Arras, D Loew, D Vignjevic, J Pannequin, S Fre
Elife, 2022-05-11;11(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Organoids
Applications: Neutralization
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human/Mouse/Rat CTGF/CCN2 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human/Mouse/Rat CTGF/CCN2 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human/Mouse/Rat CTGF/CCN2 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
