Human/Mouse/Rat FKBP12 Antibody Summary
Gly2-Glu108
Accession # P62942
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human/Mouse/Rat FKBP12 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of Neuro-2A mouse neuroblastoma cell line, Jurkat human acute T cell leukemia cell line, and MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL Rat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat FKBP12 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB3777) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Rat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF005). For additional reference, Recombinant Human FKBP12 (Catalog # 3777-FK), recombinant human FKBP12.6, and recombinant human FKBP13 (5 ng/lane) were included. A specific band for FKBP12 was detected at approximately 12 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 3.
 View Larger
View Larger
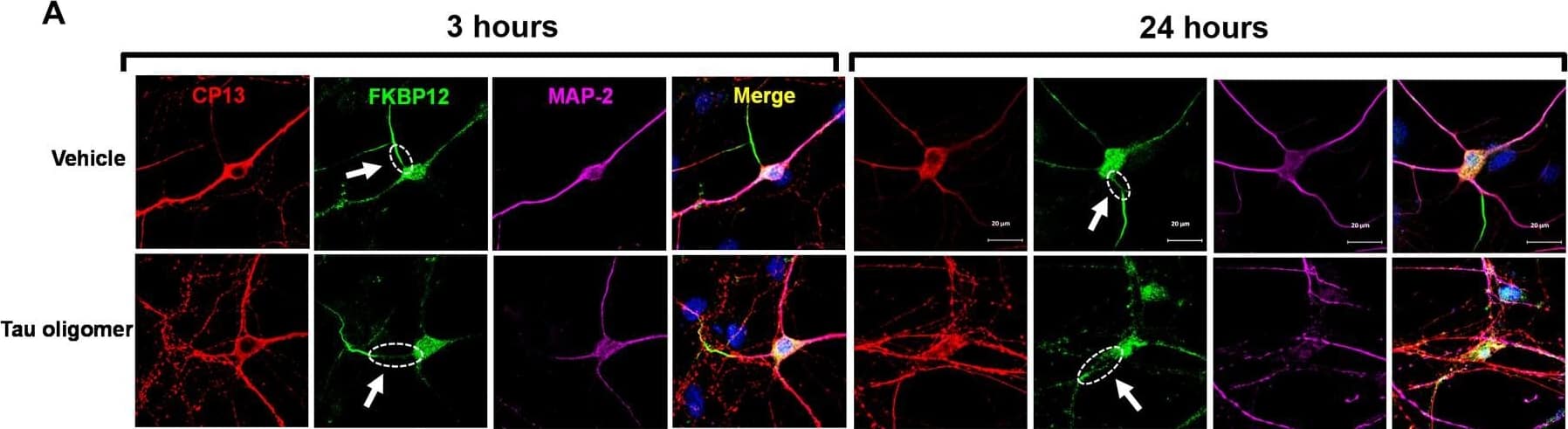
Detection of Mouse FKBP12 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence FKBP12 was translocated from axonal hillock to soma and colocalized to oTau.(A) Representative images of tau phosphorylation (CP13 antibody, red) and FKBP12 translocation in primary cortical neurons after induction of tau aggregation by oligomeric S1p fraction. Scale bars, 20 μm. (B) Representative images showed the high expression level of FKBP12 (green) in axonal hillock/axon initial segment (labeled by anti–ankyrin-G antibody, bright blue) under basal conditions whereas FKBP12 translocated to soma and dendrites when neurons bear tau aggregation. Scale bars, 20 μm. (C) Representative images showed the spatial colocalization of FKBP12 and aggregated Tau in the neurons after 24 hours of oTau seeding. Scale bars, 5 μm. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (D) Quantification of FKBP12 intensity in the axon hillock of the neurons at 3 and 24 hours of S1p treatment, respectively. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 10. Statistics by two-way ANOVA, post hoc multiple comparisons test by Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.005, and ****P < 0.001. (E and F) Quantification of granular intensity of CP13-labeled tau aggregates (E) and FKBP12 (F) in neurons at 3 and 24 hours of S1p treatment, respectively. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 10. Statistics by two-way ANOVA, and post hoc multiple comparisons test by Fisher’s LSD. ****P < 0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36724228), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
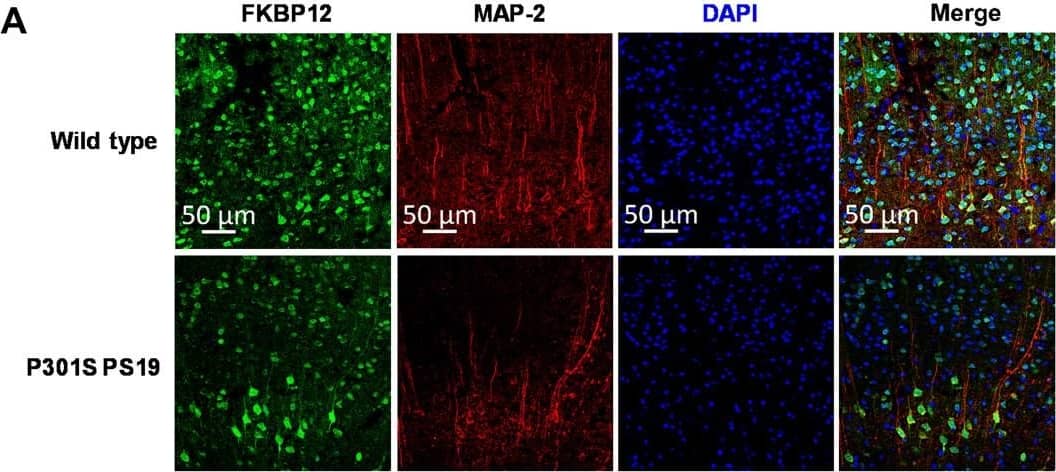
Detection of Mouse FKBP12 by Immunohistochemistry FKBP12 is decreased in PS19 mice brain.(A) Representative images showing the distribution of FKBP12 in entorhinal cortex of mouse brain. Scale bars, 50 μm. (B) Quantification of MAP-2 and FKBP12 fluorescence intensity in entorhinal cortex of PS19 mice brain in comparison to age-matched wild type (WT). Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 5. Statistics by unpaired t test, ***P < 0.005. (C) Representative Western blot showing high–molecular weight (HMW) tau aggregation in PS19 mice brain lysate and the decrease of FKBP12 in comparison to wild type. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (D) Quantification of the tau-5 band intensity showing the robust increase of the ratio between high–molecular weight tau to monomeric tau. (E) Quantification of the FKBP12 band intensity. (F) Representative Western blot images showing the expression level of phosphorylated tau (CP13 and PHF-1), FKBP12, and neuronal markers [postsynaptic density 95 (PSD-95) and MAP-2] in the brain lysate of 3-, 6-, and 9-month-old PS19 mice, respectively. (G) Quantification of the phosphorylated tau (CP13 and PHF-1) band intensity. Result was normalized by internal control of corresponding GAPDH band intensity. (H) Quantification of FKBP12 Western blot (WB) band intensity normalized by GAPDH and MAP-2, respectively. Statistics by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), post hoc multiple comparisons test by Tukey’s test. (I) Quantification for the band intensity of neuronal markers including PSD-95 and MAP-2, normalized by GAPDH. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 3. Statistics by two-way ANOVA, and post hoc multiple comparisons test by Tukey’s. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005, and ****P < 0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36724228), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
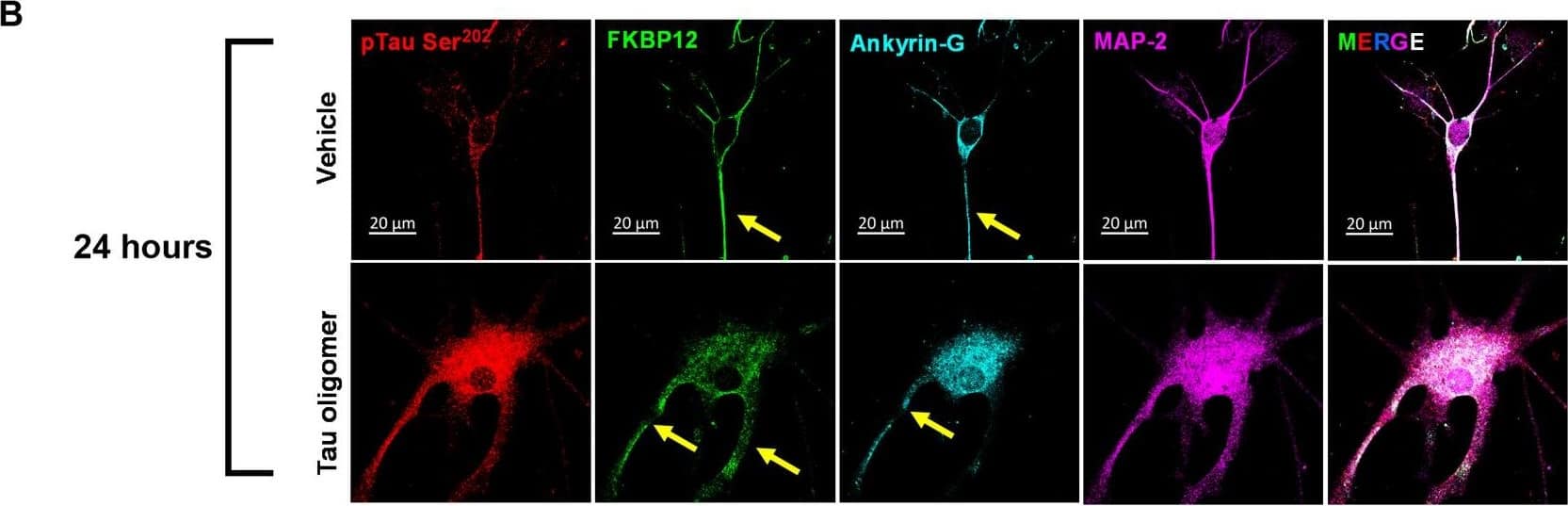
Detection of Mouse FKBP12 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence FKBP12 was translocated from axonal hillock to soma and colocalized to oTau.(A) Representative images of tau phosphorylation (CP13 antibody, red) and FKBP12 translocation in primary cortical neurons after induction of tau aggregation by oligomeric S1p fraction. Scale bars, 20 μm. (B) Representative images showed the high expression level of FKBP12 (green) in axonal hillock/axon initial segment (labeled by anti–ankyrin-G antibody, bright blue) under basal conditions whereas FKBP12 translocated to soma and dendrites when neurons bear tau aggregation. Scale bars, 20 μm. (C) Representative images showed the spatial colocalization of FKBP12 and aggregated Tau in the neurons after 24 hours of oTau seeding. Scale bars, 5 μm. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (D) Quantification of FKBP12 intensity in the axon hillock of the neurons at 3 and 24 hours of S1p treatment, respectively. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 10. Statistics by two-way ANOVA, post hoc multiple comparisons test by Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.005, and ****P < 0.001. (E and F) Quantification of granular intensity of CP13-labeled tau aggregates (E) and FKBP12 (F) in neurons at 3 and 24 hours of S1p treatment, respectively. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 10. Statistics by two-way ANOVA, and post hoc multiple comparisons test by Fisher’s LSD. ****P < 0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36724228), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
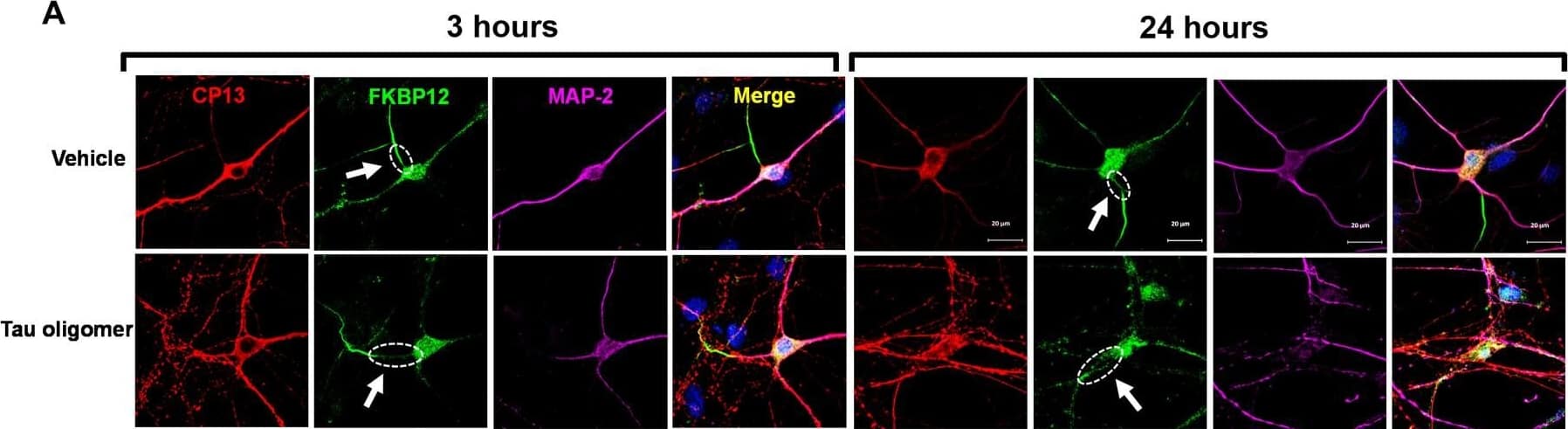
Detection of Mouse FKBP12 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence FKBP12 was translocated from axonal hillock to soma and colocalized to oTau.(A) Representative images of tau phosphorylation (CP13 antibody, red) and FKBP12 translocation in primary cortical neurons after induction of tau aggregation by oligomeric S1p fraction. Scale bars, 20 μm. (B) Representative images showed the high expression level of FKBP12 (green) in axonal hillock/axon initial segment (labeled by anti–ankyrin-G antibody, bright blue) under basal conditions whereas FKBP12 translocated to soma and dendrites when neurons bear tau aggregation. Scale bars, 20 μm. (C) Representative images showed the spatial colocalization of FKBP12 and aggregated Tau in the neurons after 24 hours of oTau seeding. Scale bars, 5 μm. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (D) Quantification of FKBP12 intensity in the axon hillock of the neurons at 3 and 24 hours of S1p treatment, respectively. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 10. Statistics by two-way ANOVA, post hoc multiple comparisons test by Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.005, and ****P < 0.001. (E and F) Quantification of granular intensity of CP13-labeled tau aggregates (E) and FKBP12 (F) in neurons at 3 and 24 hours of S1p treatment, respectively. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 10. Statistics by two-way ANOVA, and post hoc multiple comparisons test by Fisher’s LSD. ****P < 0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36724228), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
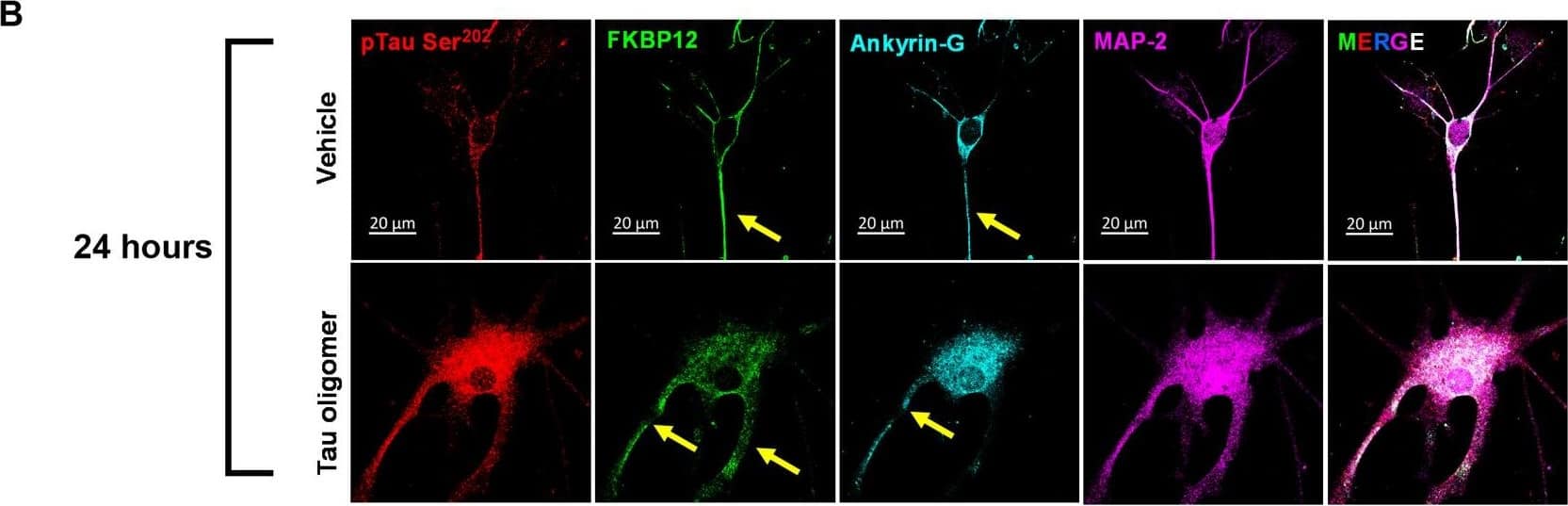 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse FKBP12 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence FKBP12 was translocated from axonal hillock to soma and colocalized to oTau.(A) Representative images of tau phosphorylation (CP13 antibody, red) and FKBP12 translocation in primary cortical neurons after induction of tau aggregation by oligomeric S1p fraction. Scale bars, 20 μm. (B) Representative images showed the high expression level of FKBP12 (green) in axonal hillock/axon initial segment (labeled by anti–ankyrin-G antibody, bright blue) under basal conditions whereas FKBP12 translocated to soma and dendrites when neurons bear tau aggregation. Scale bars, 20 μm. (C) Representative images showed the spatial colocalization of FKBP12 and aggregated Tau in the neurons after 24 hours of oTau seeding. Scale bars, 5 μm. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (D) Quantification of FKBP12 intensity in the axon hillock of the neurons at 3 and 24 hours of S1p treatment, respectively. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 10. Statistics by two-way ANOVA, post hoc multiple comparisons test by Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.005, and ****P < 0.001. (E and F) Quantification of granular intensity of CP13-labeled tau aggregates (E) and FKBP12 (F) in neurons at 3 and 24 hours of S1p treatment, respectively. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 10. Statistics by two-way ANOVA, and post hoc multiple comparisons test by Fisher’s LSD. ****P < 0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36724228), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
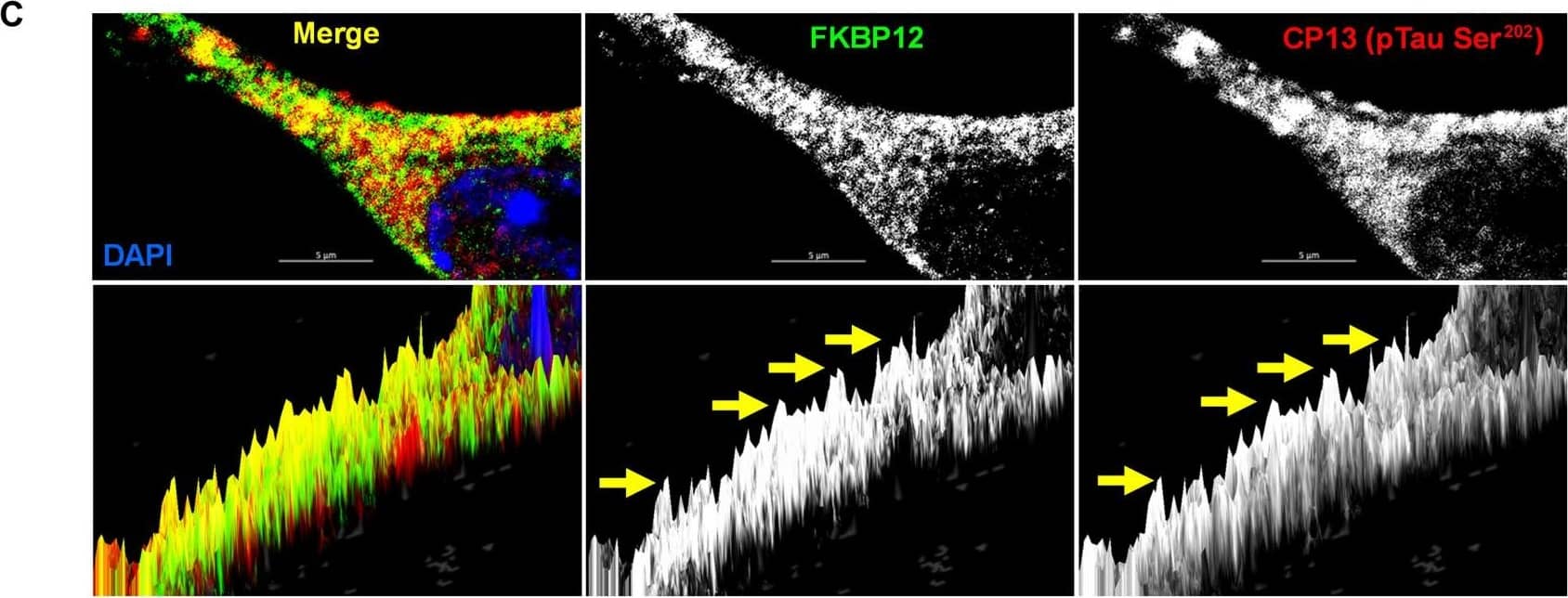 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse FKBP12 by Immunohistochemistry FKBP12 was translocated from axonal hillock to soma and colocalized to oTau.(A) Representative images of tau phosphorylation (CP13 antibody, red) and FKBP12 translocation in primary cortical neurons after induction of tau aggregation by oligomeric S1p fraction. Scale bars, 20 μm. (B) Representative images showed the high expression level of FKBP12 (green) in axonal hillock/axon initial segment (labeled by anti–ankyrin-G antibody, bright blue) under basal conditions whereas FKBP12 translocated to soma and dendrites when neurons bear tau aggregation. Scale bars, 20 μm. (C) Representative images showed the spatial colocalization of FKBP12 and aggregated Tau in the neurons after 24 hours of oTau seeding. Scale bars, 5 μm. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (D) Quantification of FKBP12 intensity in the axon hillock of the neurons at 3 and 24 hours of S1p treatment, respectively. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 10. Statistics by two-way ANOVA, post hoc multiple comparisons test by Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.005, and ****P < 0.001. (E and F) Quantification of granular intensity of CP13-labeled tau aggregates (E) and FKBP12 (F) in neurons at 3 and 24 hours of S1p treatment, respectively. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 10. Statistics by two-way ANOVA, and post hoc multiple comparisons test by Fisher’s LSD. ****P < 0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36724228), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
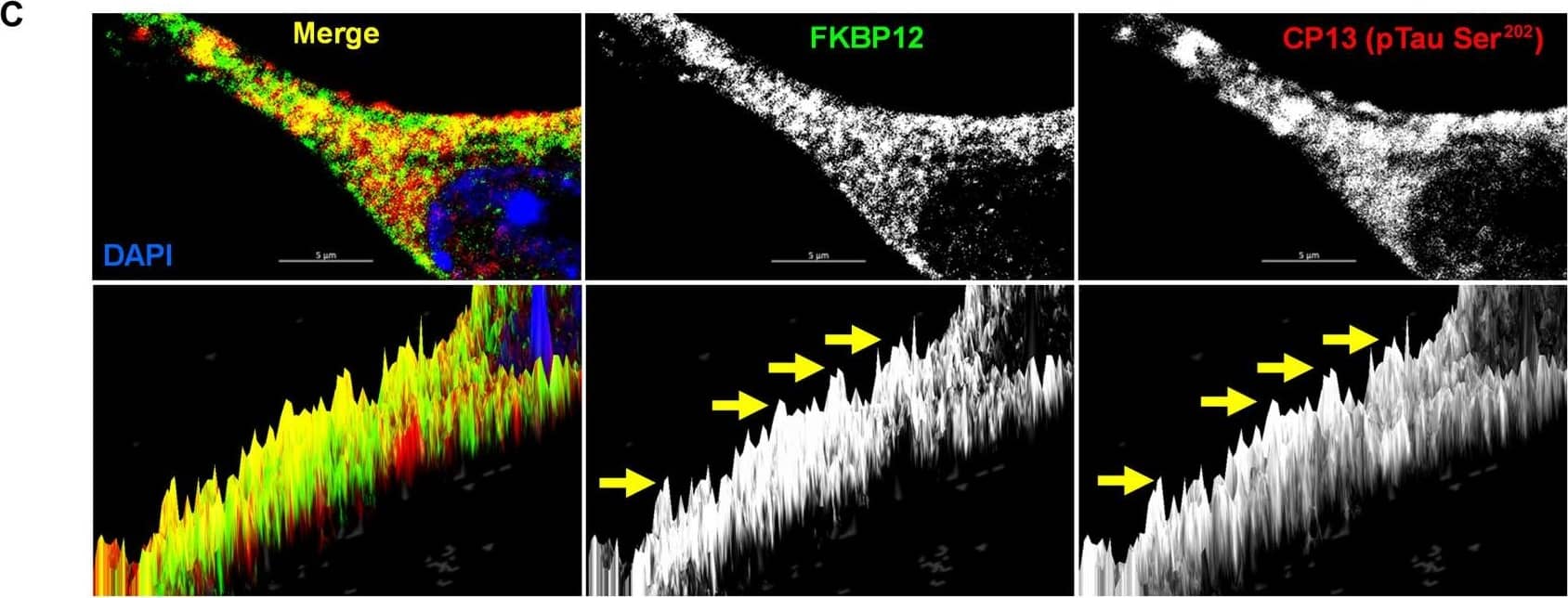 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse FKBP12 by Immunohistochemistry FKBP12 was translocated from axonal hillock to soma and colocalized to oTau.(A) Representative images of tau phosphorylation (CP13 antibody, red) and FKBP12 translocation in primary cortical neurons after induction of tau aggregation by oligomeric S1p fraction. Scale bars, 20 μm. (B) Representative images showed the high expression level of FKBP12 (green) in axonal hillock/axon initial segment (labeled by anti–ankyrin-G antibody, bright blue) under basal conditions whereas FKBP12 translocated to soma and dendrites when neurons bear tau aggregation. Scale bars, 20 μm. (C) Representative images showed the spatial colocalization of FKBP12 and aggregated Tau in the neurons after 24 hours of oTau seeding. Scale bars, 5 μm. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (D) Quantification of FKBP12 intensity in the axon hillock of the neurons at 3 and 24 hours of S1p treatment, respectively. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 10. Statistics by two-way ANOVA, post hoc multiple comparisons test by Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.005, and ****P < 0.001. (E and F) Quantification of granular intensity of CP13-labeled tau aggregates (E) and FKBP12 (F) in neurons at 3 and 24 hours of S1p treatment, respectively. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 10. Statistics by two-way ANOVA, and post hoc multiple comparisons test by Fisher’s LSD. ****P < 0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36724228), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
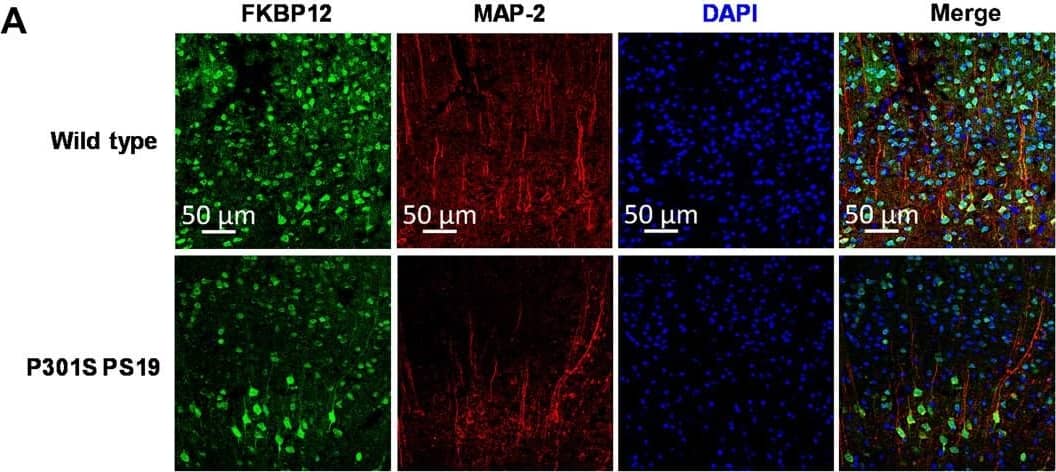 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse FKBP12 by Immunohistochemistry FKBP12 is decreased in PS19 mice brain.(A) Representative images showing the distribution of FKBP12 in entorhinal cortex of mouse brain. Scale bars, 50 μm. (B) Quantification of MAP-2 and FKBP12 fluorescence intensity in entorhinal cortex of PS19 mice brain in comparison to age-matched wild type (WT). Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 5. Statistics by unpaired t test, ***P < 0.005. (C) Representative Western blot showing high–molecular weight (HMW) tau aggregation in PS19 mice brain lysate and the decrease of FKBP12 in comparison to wild type. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (D) Quantification of the tau-5 band intensity showing the robust increase of the ratio between high–molecular weight tau to monomeric tau. (E) Quantification of the FKBP12 band intensity. (F) Representative Western blot images showing the expression level of phosphorylated tau (CP13 and PHF-1), FKBP12, and neuronal markers [postsynaptic density 95 (PSD-95) and MAP-2] in the brain lysate of 3-, 6-, and 9-month-old PS19 mice, respectively. (G) Quantification of the phosphorylated tau (CP13 and PHF-1) band intensity. Result was normalized by internal control of corresponding GAPDH band intensity. (H) Quantification of FKBP12 Western blot (WB) band intensity normalized by GAPDH and MAP-2, respectively. Statistics by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), post hoc multiple comparisons test by Tukey’s test. (I) Quantification for the band intensity of neuronal markers including PSD-95 and MAP-2, normalized by GAPDH. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 3. Statistics by two-way ANOVA, and post hoc multiple comparisons test by Tukey’s. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005, and ****P < 0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36724228), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: FKBP12
FK506 binding protein, 12 kilodalton molecular weight (FKBP12), also called FKBP1, was originally characterized as a peptidyl-prolyl isomerase that catalyzes the transition between cis- and trans-proline residues critical for proper folding of proteins. Proline isomerase activity was demonstrated but not used for quality control. The macrolide immunosuppressants FK506 (Tacrolimus) and rapamycin bind to FKBP12 with high affinity, while the structurally related compound cyclosporine binds with a much lower affinity (1). The binding of these drugs causes FKBP12 to become a potent inhibitor of calcineurin phosphatase activity (2) and TOR kinase activity (3). The inhibition of protein phosphatase activity is highly selective for calcineurin (2), making the FK506/FKBP12 complex a useful tool in the study of this enzyme. Knockout mice lacking FKBP12 are morphologically normal, but develop cardiomyopathies that may be related to dysregulation of ryanodyne receptors (4).
- Hamilton, G.S. and J.P. Steiner (1998) J. Med. Chem. 41:5119.
- Liu, J. et al. (1992) Biochemistry 31:3896.
- Toral-Barza, L. et al. (2005) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 332:304.
- Hamilton, S.L and M.M. Matzuk (1998) Nature 391:489.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human/Mouse/Rat FKBP12 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
4
Citations: Showing 1 - 4
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Chaperoning of specific tau structure by immunophilin FKBP12 regulates the neuronal resilience to extracellular stress
Authors: L Jiang, P Chakrabort, L Zhang, M Wong, SE Hill, CJ Webber, J Libera, LJ Blair, B Wolozin, M Zweckstett
Science Advances, 2023-02-01;9(5):eadd9789.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Development of NanoLuc-targeting protein degraders and a universal reporter system to benchmark tag-targeted degradation platforms
Authors: C Grohmann, CM Magtoto, JR Walker, NK Chua, A Gabrielyan, M Hall, SA Cobbold, S Mieruszyns, M Brzozowski, DS Simpson, H Dong, B Dorizzi, AV Jacobsen, E Morrish, N Silke, JM Murphy, JK Heath, A Testa, C Maniaci, A Ciulli, G Lessene, J Silke, R Feltham
Nature Communications, 2022-04-19;13(1):2073.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
An inducible, ligand-independent receptor activator of NF-kappaB gene to control osteoclast differentiation from monocytic precursors.
Authors: Rementer C, Wu M, Buranaphatthana W, Yang H, Scatena M, Giachelli C
PLoS ONE, 2013-12-27;8(12):e84465.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Designing Calcium Release Channel Inhibitors with Enhanced Electron Donor Properties: Stabilizing the Closed State of Ryanodine Receptor Type 1
Authors: Yanping Ye, Daniel Yaeger, Laura J. Owen, Jorge O. Escobedo, Jialu Wang, Jeffrey D. Singer et al.
Molecular Pharmacology
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human/Mouse/Rat FKBP12 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human/Mouse/Rat FKBP12 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human/Mouse/Rat FKBP12 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
