Human/Mouse/Rat MuRF1/TRIM63 Antibody Summary
Met1-Gly325
Accession # Q969Q1
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human/Mouse/Rat MuRF1 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of human heart, mouse heart, and rat muscle tissue. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat MuRF1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF5366) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF019). A specific band was detected for MuRF1 at approximately 41-44 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 8.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human MuRF1/TRIM63 by Simple WesternTM. Simple Western lane view shows lysates of human heart tissue, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for MuRF1/TRIM63 at approximately 46 kDa (as indicated) using 10 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat MuRF1/TRIM63 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF5366) followed by 1:50 dilution of HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF109). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230 kDa separation system.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Zebrafish MuRF1/TRIM63 by Western Blot Blocking MuRF1-mediated proteasome degradation preserves myofibril integrity in tre/ncx1 deficient hearts.(A) Z-lines were visualized by alpha -actinin staining. By 72 hpf, sarcomeres are disassembled in hearts of uninjected (tre) and control morpholino-injected (tre +ctlMO) tremblor embryos. Murf1a/murf1 b knockdown does not affect sarcomere integrity in wild type embryos (WT +MO), but prevents sarcomere degradation in tre (tre +MO). Similarly, treatment with a proteasome inhibitor, MG132, preserves myofibril integrity in tre cardiomyocytes (tre +MG132). Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Graph shows % of embryos with periodic alpha -actinin staining at 72 hpf. (C) Western blot detecting MuRF1 and beta -actin proteins in uninjected control (WT control) and murf1a/murf1 b knockdown (MuRF1 MO) embryos. Chi-squared test, *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28826496), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse MuRF1/TRIM63 by Western Blot The qPCR (quantitative real-time PCR) (A) and Western blot analysis (B,C) showed the mRNA (A) and protein (B,C) expressions of TRAF6, MAFBx, and MuRF1 in the TA muscle of mice injected with vehicle (saline, control) or Dex (dexamethasone sodium phosphate in saline, 10 mg/kg) respectively. Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 9 per animal group, * p < 0.05 versus control. Also shown (B) is a representative Western blot image. GAPDH and tubulin were used as a loading control in qPCR and Western blot analysis. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/15/6/11126), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse MuRF1/TRIM63 by Western Blot (A) Micrograph showed the morphology of C2C12 myotubes cultured in vehicle (0.1% ethanol-containing plain medium, control) or stimulated by Dex (dexamethasone in vehicle) respectively. Scale bar = 100 μm; (B) Bar graph compared the diameter of C2C12 myotubes cultured in vehicle (control) or stimulated by Dex respectively; and (C,D) Representative Western blot image and Bar graphs displayed the protein expression of TRAF6, MAFBx, MuRF1, and desmin in C2C12 myotubes cultured in vehicle (control) or stimulated by Dex respectively. Tubulin were used as a loading control in Western blot analysis. All data in bar graphs are presented as mean ± SEM (standard error of the mean) from three independent experiments, * p < 0.05 versus control. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/15/6/11126), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse MuRF1/TRIM63 by Western Blot The qPCR (A) and Western blot analysis (B,C) showed that C2C12 myotubes were transfected with TRAF6-siRNA or control-siRNA; Micrographs (D) showed the morphology of Dex- or vehicle-treated C2C12 myotubes after transfection with TRAF6-siRNA and control-siRNA respectively. Scale bar = 100 μm; Bar graph (E) showed the diameter of Dex- or vehicle-treated C2C12 myotubes after transfection with TRAF6-siRNA and control-siRNA respectively; The qPCR and Western blot analysis showed the mRNA (F) and protein (G,H) expressions of TRAF6, MAFBx, and MuRF1, as well as the protein expression of pFOXO-1 in Dex- or vehicle-treated C2C12 myotubes after transfection with TRAF6-siRNA and control-siRNA respectively. GAPDH and tubulin were used as a loading control in qPCR and Western blot analysis. All data in bar graphs are presented as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments, * p < 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/15/6/11126), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse MuRF1/TRIM63 by Western Blot (A) Masson trichrome staining image of the TA muscle from mice co-injected with both Dex and control-siRNA, with both Dex and TRAF6-siRNA, with both vehicle and control-siRNA, or with both vehicle and TRAF6-siRNA, respectively, for 14 days; (B,C) Bar graphs showed the weight (B) and cross sectional area (CSA, C) of the TA muscle from mice co-injected with each of the above four combinations respectively. Scale bar =20 μm; (D–F) The qPCR and Western blot analysis showed the comparison in the mRNA (D) and protein; and (E,F) expression of TRAF6, MAFBx, and MuRF1, as well as the protein expression of pFOXO-1 in the TA muscle of mice co-injected with each of the above four combinations respectively. GAPDH and tubulin were used as a loading control in qPCR and Western blot analysis, respectively. All data in bar graphs are presented as mean ± SD, n = 9 per animal group,* p < 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/15/6/11126), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
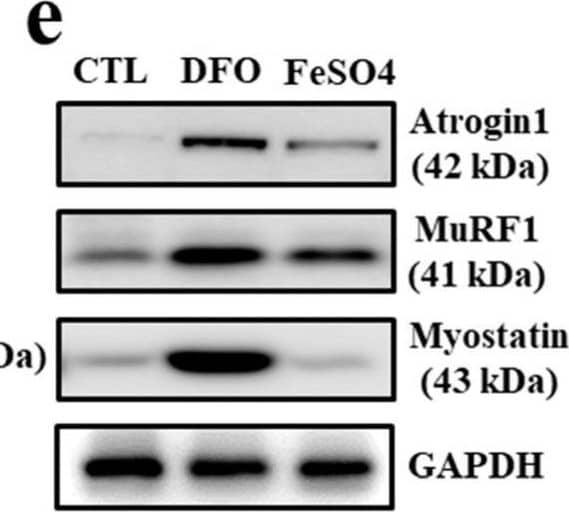
Detection of MuRF1/TRIM63 by Western Blot Muscle atrophy-associated gene expression under iron deficiency in myocytes. (a) mRNA expression of ferroportin, ferritin and N-Myc downstream regulated 1 (NDGR1) in C2C12 myotubes treated with deferoxamine (DFO) (100 μM/mL) and FeSO4 (400 μM /mL) for 24 h. (b) mRNA expression of myogenic and muscle atrophy-associated factors in C2C12 myotubes treated with DFO and FeSO4 for 48 h. Myf5: myogenic factor 5; MyoD: myoblast determination protein 1; MuRF1: muscle RING-finger protein-1. (c) Protein expression of ferroportin, ferritin and NDGR1 in C2C12 myotubes treated with DFO and FeSO4. GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (d) Protein expression of myogenic factors in C2C12 myotubes treated with DFO and FeSO4. (e) Protein expression of muscle atrophy-associated factors in C2C12 myotubes treated with DFO and FeSO4. (f) Expression of myostatin mRNA in C2C12 myotubes treated with different doses of DFO and FeSO4. (g) Expression of myostatin mRNA in C2C12 myotubes treated with DFO in the presence or absence of FeSO4. Data represent mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36139428), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
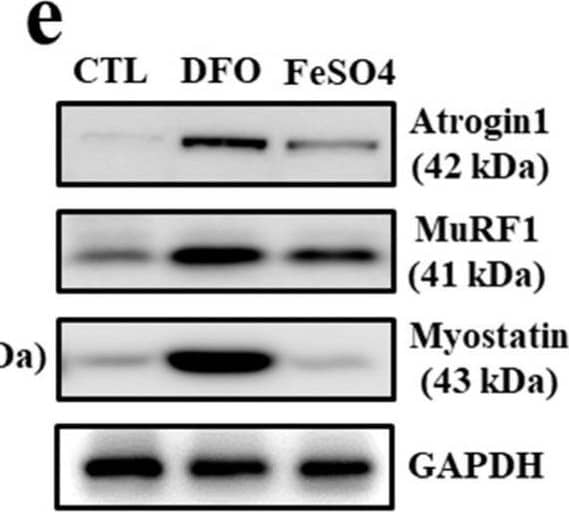
Detection of MuRF1/TRIM63 by Western Blot Muscle atrophy-associated gene expression under iron deficiency in myocytes. (a) mRNA expression of ferroportin, ferritin and N-Myc downstream regulated 1 (NDGR1) in C2C12 myotubes treated with deferoxamine (DFO) (100 μM/mL) and FeSO4 (400 μM /mL) for 24 h. (b) mRNA expression of myogenic and muscle atrophy-associated factors in C2C12 myotubes treated with DFO and FeSO4 for 48 h. Myf5: myogenic factor 5; MyoD: myoblast determination protein 1; MuRF1: muscle RING-finger protein-1. (c) Protein expression of ferroportin, ferritin and NDGR1 in C2C12 myotubes treated with DFO and FeSO4. GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (d) Protein expression of myogenic factors in C2C12 myotubes treated with DFO and FeSO4. (e) Protein expression of muscle atrophy-associated factors in C2C12 myotubes treated with DFO and FeSO4. (f) Expression of myostatin mRNA in C2C12 myotubes treated with different doses of DFO and FeSO4. (g) Expression of myostatin mRNA in C2C12 myotubes treated with DFO in the presence or absence of FeSO4. Data represent mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36139428), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of MuRF1/TRIM63 by Western Blot Iron deficiency-induced myostatin regulation by DAX1. (a) Expression of myostatin mRNA in C2C12 myotubes transfected with a nuclear receptor for 48 h. AR: androgen receptor; CAR: constitutive androstane receptor; DAX1: dosage-sensitive sex reversal, adrenal hypoplasia congenita critical region, on chromosome X, gene 1; ER alpha : estrogen receptor alpha ; ERR alpha / beta / gamma : estrogen-related receptor alpha / beta / gamma ; FXR: farnesoid X receptor; GR: glucocorticoid receptor; HNF4 alpha : hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha ; LRH-1: liver receptor homolog-1; LXR alpha : liver X receptor alpha ; PXR: pregnane X receptor; ROR alpha : RAR-related orphan receptor alpha ; SF-1: steroidogenic factor 1; SHP: small heterodimer partner; THR alpha : thyroid hormone receptor alpha ; TR4: testicular receptor 4. (b) Expression of DAX1 mRNA in C2C12 myotubes treated with different doses of deferoxamine (DFO) and FeSO4. (c) Expression of DAX1 mRNA in C2C12 myotubes with DFO in the presence or absence of FeSO4. (d) Adenoviral overexpression of DAX1 and mRNA expression of myogenic and muscle atrophy-associated factors. C2C12 myotubes were infected with an adenovirus expressing DAX1 (Ad-DAX 1) or control vector (Ad-CTL) at 100 multiplicity of infection for 48 h. Myf5: myogenic factor 5; MyoD: myoblast determination protein 1; MuRF1: muscle RING-finger protein-1. (e) Protein expression of muscle atrophy-associated factors in C2C12 myotubes infected with Ad-DAX 1. GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. A densitometric analysis of the Western blots is shown in the graph on the right. Data represent mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36139428), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of MuRF1/TRIM63 by Western Blot Iron deficiency-induced myostatin regulation by DAX1. (a) Expression of myostatin mRNA in C2C12 myotubes transfected with a nuclear receptor for 48 h. AR: androgen receptor; CAR: constitutive androstane receptor; DAX1: dosage-sensitive sex reversal, adrenal hypoplasia congenita critical region, on chromosome X, gene 1; ER alpha : estrogen receptor alpha ; ERR alpha / beta / gamma : estrogen-related receptor alpha / beta / gamma ; FXR: farnesoid X receptor; GR: glucocorticoid receptor; HNF4 alpha : hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha ; LRH-1: liver receptor homolog-1; LXR alpha : liver X receptor alpha ; PXR: pregnane X receptor; ROR alpha : RAR-related orphan receptor alpha ; SF-1: steroidogenic factor 1; SHP: small heterodimer partner; THR alpha : thyroid hormone receptor alpha ; TR4: testicular receptor 4. (b) Expression of DAX1 mRNA in C2C12 myotubes treated with different doses of deferoxamine (DFO) and FeSO4. (c) Expression of DAX1 mRNA in C2C12 myotubes with DFO in the presence or absence of FeSO4. (d) Adenoviral overexpression of DAX1 and mRNA expression of myogenic and muscle atrophy-associated factors. C2C12 myotubes were infected with an adenovirus expressing DAX1 (Ad-DAX 1) or control vector (Ad-CTL) at 100 multiplicity of infection for 48 h. Myf5: myogenic factor 5; MyoD: myoblast determination protein 1; MuRF1: muscle RING-finger protein-1. (e) Protein expression of muscle atrophy-associated factors in C2C12 myotubes infected with Ad-DAX 1. GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. A densitometric analysis of the Western blots is shown in the graph on the right. Data represent mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36139428), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: MuRF1/TRIM63
TRIM63 (Tripartite motif-containing protein 63; also MURF-1, SMRZ and RING finger protein 28) is a 41 kDa member of the RING finger-B-box-coiled-coil family of proteins. It is a striated muscle protein that is found in both cytoplasm and nucleus. TRIM63 has multiple finctions, among which are the inhibition of PKC epsilon -mediated cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and the maintenance of skeletal muscle M-line integrity. Human TRIM63 is 353 amino acids (aa) in length. It contains one RING finger domain (aa 23‑82), a B-Box type zinc-finger region (aa 117‑159), a coiled-coil region (aa 207‑269) and a C-terminal COS domain. Isoforms of TRIM63 show one potential alternate start site at Met14, a deletion of aa 105‑132 and a 21 aa substitution for aa 326‑353. Over aa 1‑325, human TRIM63 exhibits 93% aa identity with mouse TRIM63.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human/Mouse/Rat MuRF1/TRIM63 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
26
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Leucine supplementation stimulates protein synthesis and reduces degradation signal activation in muscle of newborn pigs during acute endotoxemia
Authors: Hernandez-Garcia AD, Columbus DA, Manjarin R et al.
Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.
-
Diggin' on U(biquitin): A Novel Method for the Identification of Physiological E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Substrates.
Authors: Rubel CE, Schisler JC, Hamlett ED et al.
Cell Biochem Biophys.
-
Effects of RAGE inhibition on the progression of the disease in hSOD1G93A ALS mice
Authors: Liu L, Killoy Km, Vargas Mr Et Al.
Pharmacol Res Perspect
-
CARM1 drives mitophagy and autophagy flux during fasting-induced skeletal muscle atrophy
Authors: Stouth, DW;vanLieshout, TL;Mikhail, AI;Ng, SY;Raziee, R;Edgett, BA;Vasam, G;Webb, EK;Gilotra, KS;Markou, M;Pineda, HC;Bettencourt-Mora, BG;Noor, H;Moll, Z;Bittner, ME;Gurd, BJ;Menzies, KJ;Ljubicic, V;
Autophagy
Species: Human
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
A synergistic blend of Garcinia mangostana fruit rind and Cinnamomum tamala leaf extracts enhances myogenic differentiation and mitochondrial biogenesis in vitro and muscle growth and strength in mice
Authors: Sinha, S;Alluri, KV;Somepalli, V;Golakoti, T;Sengupta, K;
Food & nutrition research
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Prematurity blunts protein synthesis in skeletal muscle independently of body weight in neonatal pigs
Authors: Marko Rudar, Jane K. Naberhuis, Agus Suryawan, Hanh V. Nguyen, Marta L. Fiorotto, Teresa A. Davis
Pediatric Research
-
A Novel Muscle Atrophy Mechanism: Myocyte Degeneration Due to Intracellular Iron Deprivation
Authors: DK Suh, WY Lee, WJ Yeo, BS Kyung, KW Jung, HK Seo, YS Lee, DW Suh
Cells, 2022-09-13;11(18):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
-
High-Intensity Aerobic Exercise Suppresses Cancer Growth by Regulating Skeletal Muscle-Derived Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors
Authors: Hyunseok Jee, Eunmi Park, Kyunghoon Hur, Minjeong Kang, Yoosik Kim
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences
-
Intermittent bolus feeding does not enhance protein synthesis, myonuclear accretion, or lean growth more than continuous feeding in a premature piglet model
Authors: Marko Rudar, Jane K. Naberhuis, Agus Suryawan, Hanh V. Nguyen, Barbara Stoll, Candace C. Style et al.
American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism
-
MyD88‐mediated signaling intercedes in neurogenic muscle atrophy through multiple mechanisms
Authors: Arshiya Parveen, Kyle R. Bohnert, Meiricris Tomaz Tomaz da Silva, Yefei Wen, Raksha Bhat, Anirban Roy et al.
The FASEB Journal
-
The Paradoxical Effect of PARP Inhibitor BGP-15 on Irinotecan-Induced Cachexia and Skeletal Muscle Dysfunction
Authors: DG Campelj, CA Timpani, AC Petersen, A Hayes, CA Goodman, E Rybalka
Cancers, 2020-12-17;12(12):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
&beta-Cryptoxanthin Improves p62 Accumulation and Muscle Atrophy in the Soleus Muscle of Senescence-Accelerated Mouse-Prone 1 Mice
Authors: M Noguchi, T Kitakaze, Y Kobayashi, K Mukai, N Harada, R Yamaji
Nutrients, 2020-07-22;12(8):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Doxorubicin induces cardiomyocyte apoptosis and atrophy through cyclin-dependent kinase 2-mediated activation of forkhead box O1
Authors: P Xia, J Chen, Y Liu, M Fletcher, BC Jensen, Z Cheng
J. Biol. Chem., 2020-02-19;0(0):.
Species: Mouse, Rat
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Vamorolone treatment improves skeletal muscle outcome in a critical illness myopathy rat model
Authors: Hazem Akkad, Nicola Cacciani, Monica Llano-Diez, Rebeca Corpeno Kalamgi, Tamara Tchkonia, James L. Kirkland et al.
Acta Physiol (Oxf)
-
Decreased abundance of eIF4F subunits predisposes low birth weight neonatal pigs to reduced muscle hypertrophy
Authors: Samer Wassim El-Kadi, Ying Chen, Sydney R. McCauley, Kacie A. Seymour, Sally E. Johnson, Robert P. Rhoads
Journal of Applied Physiology
-
Protein arginine methyltransferase expression, localization, and activity during disuse-induced skeletal muscle plasticity
Authors: Derek W. Stouth, Alexander Manta, Vladimir Ljubicic
American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology
-
Buyang Huanwu Tang improves denervation-dependent muscle atrophy by increasing ANGPTL4, and increases NF-?B and MURF1 levels
Authors: L Zhou, Y Huang, H Xie, X Mei
Mol Med Rep, 2017-12-19;0(0):.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
The Calcineurin-FoxO-MuRF1 signaling pathway regulates myofibril integrity in cardiomyocytes
Authors: H Shimizu, AD Langenbach, J Huang, K Wang, G Otto, R Geisler, Y Wang, JN Chen
Elife, 2017-08-19;6(0):.
Species: Zebrafish
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Effect of 20-Hydroxyecdysone on Proteolytic Regulation in Skeletal Muscle Atrophy
Authors: Apichart Suksamrarn
In Vivo, 2016-11-12;30(6):869-877.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Forkhead box O1 and muscle RING finger 1 protein expression in atrophic and hypertrophic denervated mouse skeletal muscle
Authors: Ann-Kristin Fjällström, Kim Evertsson, Marlene Norrby, Sven Tågerud
Journal of Molecular Signaling
-
TRAF6 inhibition rescues dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy.
Authors: Sun, Hualin, Gong, Yanpei, Qiu, Jiaying, Chen, Yanfei, Ding, Fei, Zhao, Qing
Int J Mol Sci, 2014-06-20;15(6):11126-41.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Masseter muscle myofibrillar protein synthesis and degradation in an experimental critical illness myopathy model.
Authors: Akkad, Hazem, Corpeno, Rebeca, Larsson, Lars
PLoS ONE, 2014-04-04;9(4):e92622.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
The posterior cricoarytenoid muscle is spared from MuRF1-mediated muscle atrophy in mice with acute lung injury.
Authors: Files D, Xiao K, Zhang T, Liu C, Qian J, Zhao W, Morris P, Delbono O, Feng X
PLoS ONE, 2014-01-31;9(1):e87587.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Muscle RING finger-1 attenuates IGF-I-dependent cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by inhibiting JNK signaling.
Authors: Wadosky K, Rodriguez J, Hite R, Min J, Walton B, Willis M
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2014-01-14;306(7):E723-39.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Protein synthesis in skeletal muscle of neonatal pigs is enhanced by administration of beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate.
Authors: Wheatley S, El-Kadi S, Suryawan A, Boutry C, Orellana R, Nguyen H, Davis S, Davis T
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2013-11-05;306(1):E91-9.
Species: Porcine
Sample Types: Protein
Applications: Western Blot -
MuRF1 mono-ubiquitinates TRalpha to inhibit T3-induced cardiac hypertrophy in vivo.
Authors: Wadosky KM, Berthiaume JM, Tang W et al.
J Mol Endocrinol
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human/Mouse/Rat MuRF1/TRIM63 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human/Mouse/Rat MuRF1/TRIM63 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human/Mouse/Rat MuRF1/TRIM63 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image

