Human/Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N‑Terminus Antibody Summary
15% cross‑reactivity with recombinant mouse (rm) Dhh N‑Terminus and rmIhh N-Terminus is observed.
Cys25-Gly198 (Lys122Arg)
Accession # Q62226
*Small pack size (-SP) is supplied either lyophilized or as a 0.2 µm filtered solution in PBS.
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
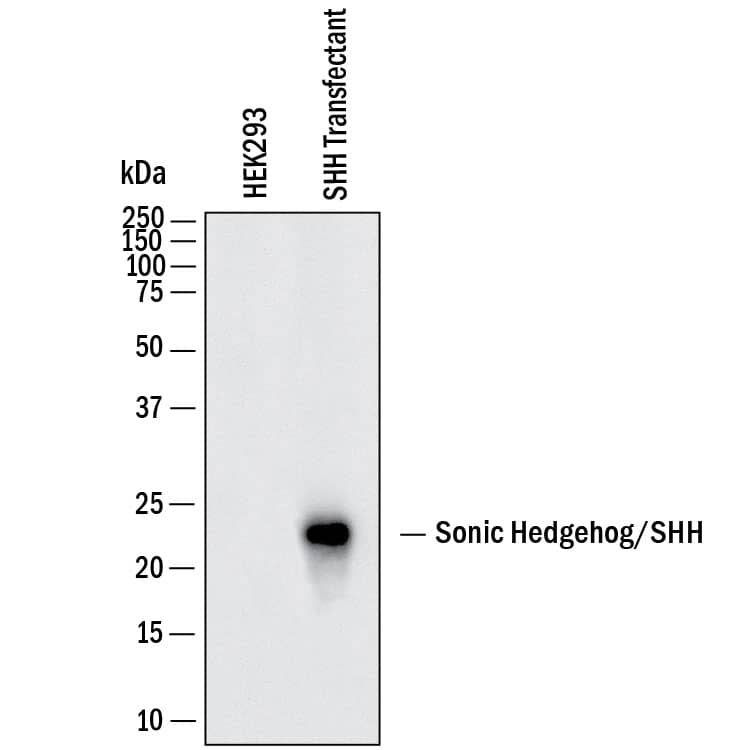
Detection of Human Sonic Hedgehog/Shh by Western Blot. Western Blot shows lysates of HEK293 human embryonic kidney cell line either mock transfected or transfected with mouse Sonic Hedgehog/SHH. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/ml of Goat Anti-Human/Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N-Terminus Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF464) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for Sonic Hedgehog/Shh at approximately 23 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Western Blot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
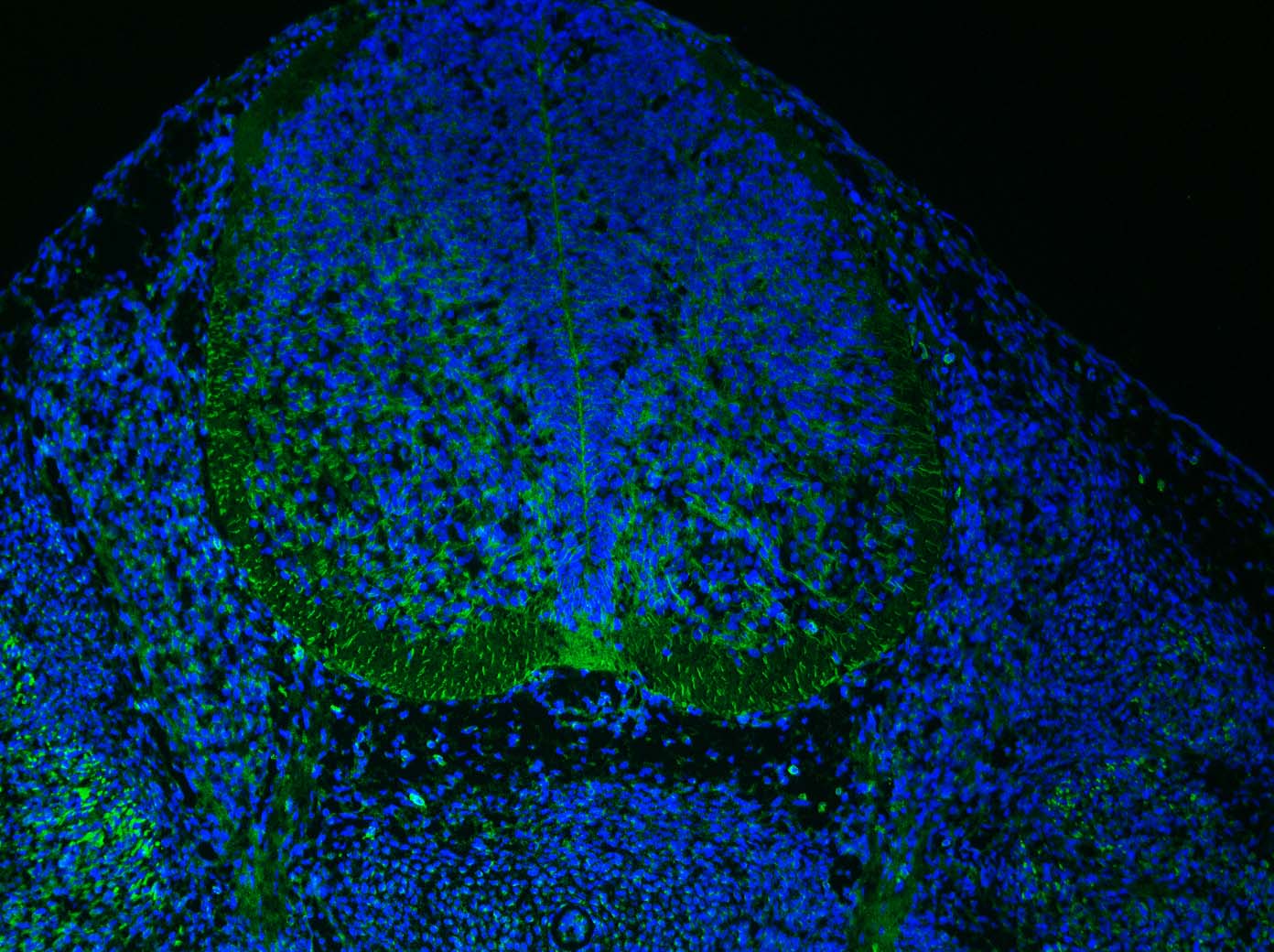
Sonic Hedgehog/Shh in Mouse Embryo. Sonic Hedgehog/Shh was detected in immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse embryo (13 d.p.c.) using Goat Anti-Human/Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N-Terminus Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF464) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to developing brain. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
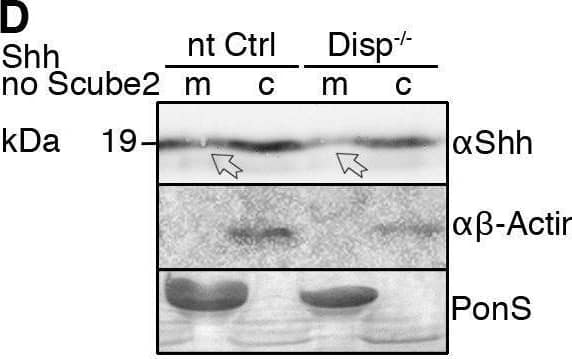
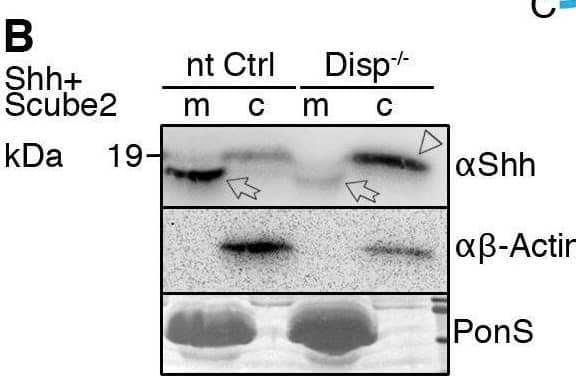
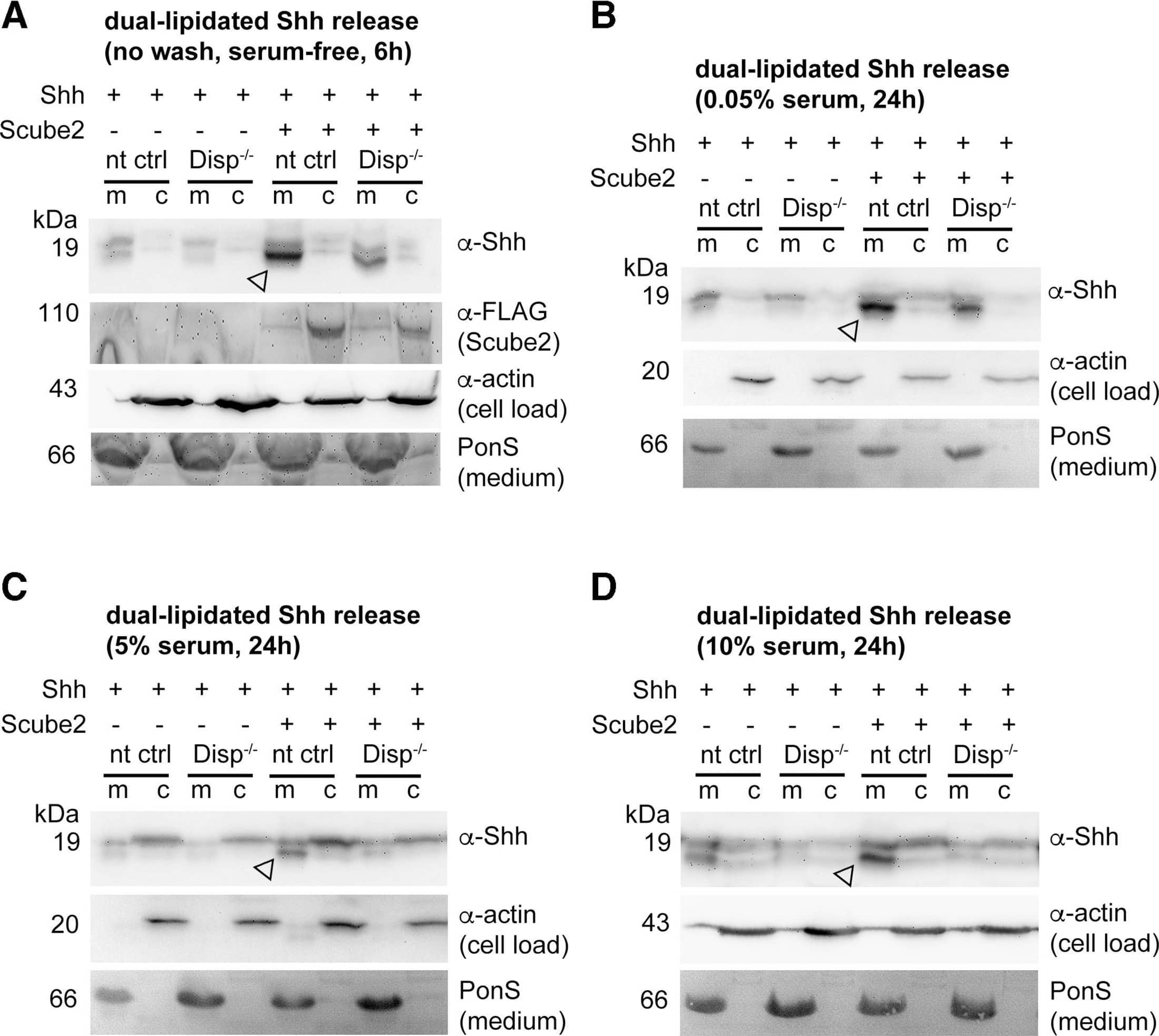
Detection of Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N-Terminus by Western Blot Impaired Shh release from Disp−/− cells. (A) Alignment of targeted disp gene sequences from Disp−/− cells and from non-targeted (nt Ctrl) cells. (A′) Schematic representation of the Disp protein structure. An asterisk indicates the CRISPR/Cas9-generated stop codon introduced at position 323, deleting 11 of 12 TM domains that together represent ∼80% of the protein sequence. L1 and L2 indicate extracellular loops. TM2–TM6 (colored red) constitute the SSD. (B,C) Immunoblots of cellular (c) and released (into the medium, m) Shh (B) and unlipidated control C25SShhN (C) in nt Ctrl and Disp−/− cells in the presence of Scube2. Arrows indicate solubilized Shh and the arrowhead indicates accumulated cellular material in Disp−/− cells. (D) In the absence of Scube2, Shh processing into serum-free medium was abolished in nt Ctrl and Disp−/− cells. Instead, both cell types released similar amounts of unprocessed protein. In B,C,D, anti-beta -actin blots ( alpha beta -actin) and Ponceau S staining of residual serum albumin (PonS) serve as loading controls. (B′,C′,D′) Quantifications of relative Shh (B′,D′) and C25SShhN (C′) release from nt Ctrl and Disp−/− cells. Ratios of solubilized versus cellular Shh were determined and expressed relative to Shh release from nt Ctrl cells (black bars). Data are mean±s.d. n=21 in B′, n=8 in C′ and n=5 in D′. ****P<0.0001; ns, not significant (two-tailed unpaired t-test). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34308968), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
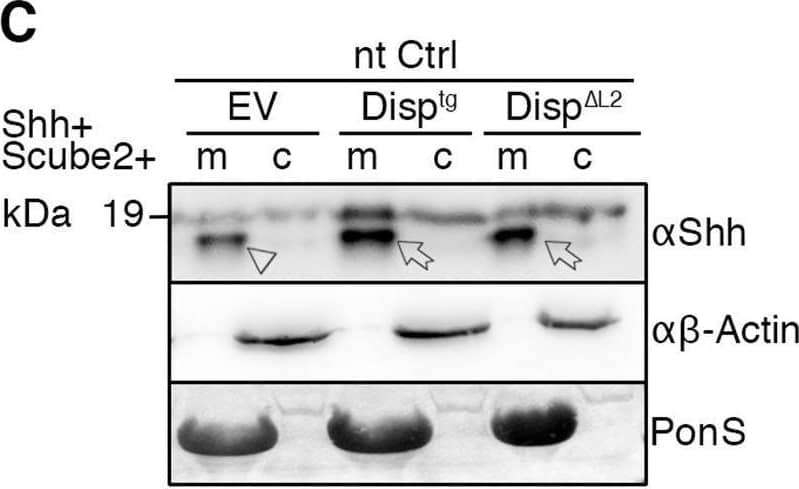
Detection of Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N-Terminus by Western Blot Overexpressed Disptg locates to the cell surface and restores Shh release from Disp−/− cells. (A,A′) Representative confocal planes of Disp−/− cells expressing Shh (A, red) or Disptg (A′, red). Both transgenes were secreted to the cell surface. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Dashed lines indicate the border of cytoplasmic eGFP signals (green). Images are representative of three experiments. Scale bars: 2 µm. (B) Co-expressed transgenic Disptg enhanced processed Shh release from Disp−/− cells (c) into the medium (m). Transgenic Disp delta L2, which lacks most of the second extracellular loop, did not release significantly increased amounts of truncated Shh. Empty-vector (EV)-transfected Disp−/− cells served as negative controls. (B′) Quantified relative processed Shh release, as shown in B. Data are mean±s.d. n=10. **P<0.01; ns, not significant; P=0.377 for Disp delta L2 (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison post hoc test). (C) Co-expressed transgenic Disptg or Disp delta L2 did not significantly increase Shh release from nt Ctrl cells. (C′) Quantified relative processed Shh release as shown in C. Data are mean±s.d. n=14. ns, not significant (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison post hoc test). In B and C, arrows indicate solubilized truncated Shh from Disptg- or Disp delta L2-expressing cells and the arrowhead indicates solubilized Shh from EV-transfected cells. Anti-beta -actin blots ( alpha beta -actin) and Ponceau S staining of residual serum albumin (PonS) serve as loading controls. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34308968), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
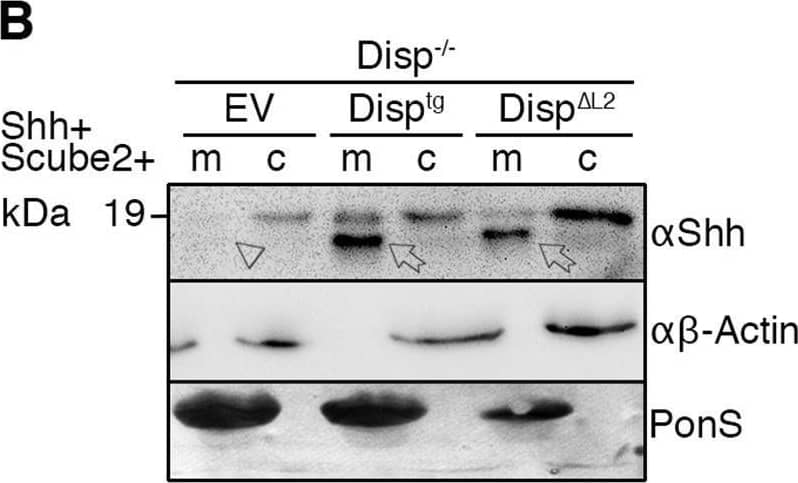 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N-Terminus by Western Blot Overexpressed Disptg locates to the cell surface and restores Shh release from Disp−/− cells. (A,A′) Representative confocal planes of Disp−/− cells expressing Shh (A, red) or Disptg (A′, red). Both transgenes were secreted to the cell surface. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Dashed lines indicate the border of cytoplasmic eGFP signals (green). Images are representative of three experiments. Scale bars: 2 µm. (B) Co-expressed transgenic Disptg enhanced processed Shh release from Disp−/− cells (c) into the medium (m). Transgenic Disp delta L2, which lacks most of the second extracellular loop, did not release significantly increased amounts of truncated Shh. Empty-vector (EV)-transfected Disp−/− cells served as negative controls. (B′) Quantified relative processed Shh release, as shown in B. Data are mean±s.d. n=10. **P<0.01; ns, not significant; P=0.377 for Disp delta L2 (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison post hoc test). (C) Co-expressed transgenic Disptg or Disp delta L2 did not significantly increase Shh release from nt Ctrl cells. (C′) Quantified relative processed Shh release as shown in C. Data are mean±s.d. n=14. ns, not significant (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison post hoc test). In B and C, arrows indicate solubilized truncated Shh from Disptg- or Disp delta L2-expressing cells and the arrowhead indicates solubilized Shh from EV-transfected cells. Anti-beta -actin blots ( alpha beta -actin) and Ponceau S staining of residual serum albumin (PonS) serve as loading controls. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34308968), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
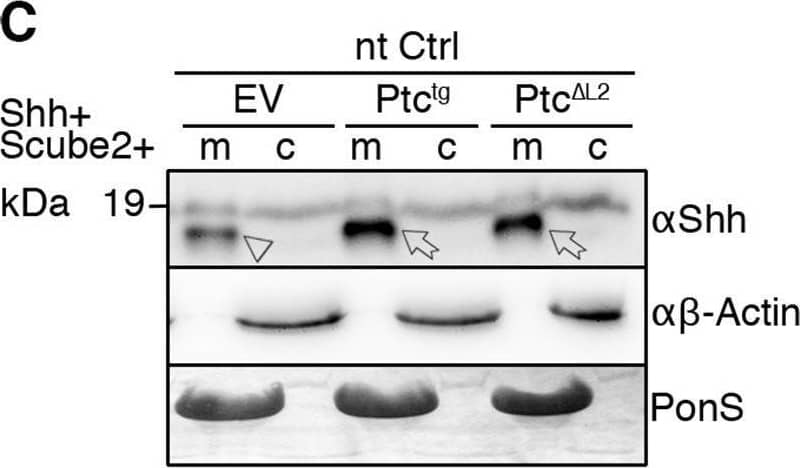
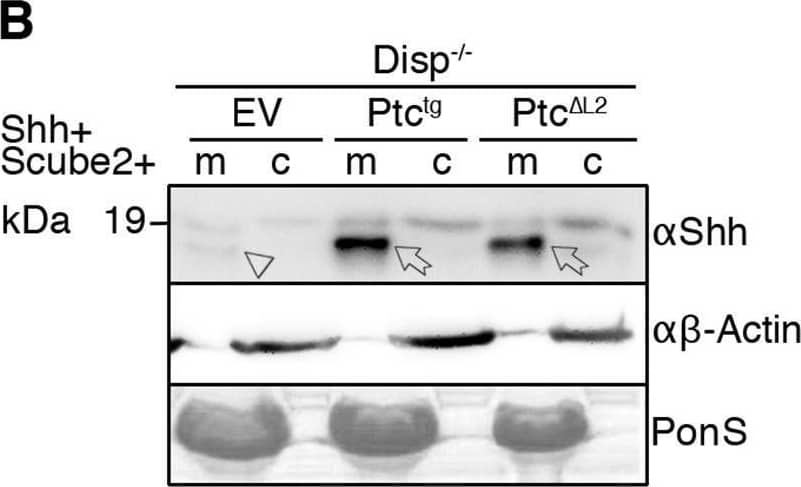
Detection of Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N-Terminus by Western Blot Overexpressed Ptctg restores Shh release from Disp−/− cells. (A,A′) Schematic representations of Disp (blue) and Ptc (green). Twelve transmembrane domains (TM1–TM12), two extracellular loops (L1 and L2), and the N- and C-termini are labeled. Conserved SSDs (TM2–TM6) are highlighted in red. Disp delta L2 and Ptc delta L2 lack most of the second extracellular loops (L2). (B,C) Co-expression of transgenic Ptctg or Ptc delta L2 increases Shh shedding from Disp−/− (B) and nt Ctrl (C) cells (c, cellular Shh; m, Shh released into the medium). Arrows indicate solubilized processed Shh from Ptctg- or Ptc delta L2-expressing cells, and arrowheads indicate reduced amounts of solubilized Shh from empty vector (EV)-transfected cells. Anti-beta -actin blots ( alpha beta -actin) and Ponceau S staining of residual serum albumin (PonS) serve as loading controls. (B′,C′) Quantification of relative processed Shh release as shown in B and C. Data are mean±s.d. n=6 in B′, n=9 in C′. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison post hoc test). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34308968), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N-Terminus by Western Blot Impaired Shh release from Disp−/− cells. (A) Alignment of targeted disp gene sequences from Disp−/− cells and from non-targeted (nt Ctrl) cells. (A′) Schematic representation of the Disp protein structure. An asterisk indicates the CRISPR/Cas9-generated stop codon introduced at position 323, deleting 11 of 12 TM domains that together represent ∼80% of the protein sequence. L1 and L2 indicate extracellular loops. TM2–TM6 (colored red) constitute the SSD. (B,C) Immunoblots of cellular (c) and released (into the medium, m) Shh (B) and unlipidated control C25SShhN (C) in nt Ctrl and Disp−/− cells in the presence of Scube2. Arrows indicate solubilized Shh and the arrowhead indicates accumulated cellular material in Disp−/− cells. (D) In the absence of Scube2, Shh processing into serum-free medium was abolished in nt Ctrl and Disp−/− cells. Instead, both cell types released similar amounts of unprocessed protein. In B,C,D, anti-beta -actin blots ( alpha beta -actin) and Ponceau S staining of residual serum albumin (PonS) serve as loading controls. (B′,C′,D′) Quantifications of relative Shh (B′,D′) and C25SShhN (C′) release from nt Ctrl and Disp−/− cells. Ratios of solubilized versus cellular Shh were determined and expressed relative to Shh release from nt Ctrl cells (black bars). Data are mean±s.d. n=21 in B′, n=8 in C′ and n=5 in D′. ****P<0.0001; ns, not significant (two-tailed unpaired t-test). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34308968), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
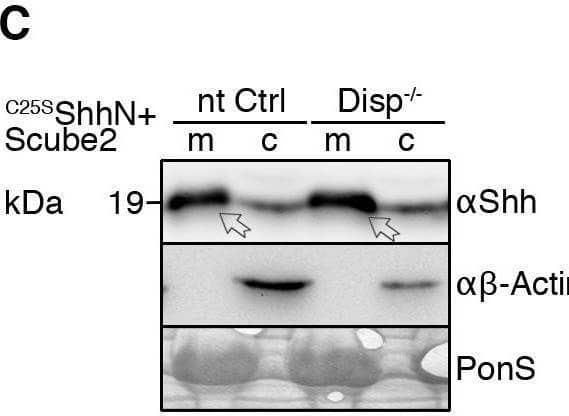 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N-Terminus by Western Blot Impaired Shh release from Disp−/− cells. (A) Alignment of targeted disp gene sequences from Disp−/− cells and from non-targeted (nt Ctrl) cells. (A′) Schematic representation of the Disp protein structure. An asterisk indicates the CRISPR/Cas9-generated stop codon introduced at position 323, deleting 11 of 12 TM domains that together represent ∼80% of the protein sequence. L1 and L2 indicate extracellular loops. TM2–TM6 (colored red) constitute the SSD. (B,C) Immunoblots of cellular (c) and released (into the medium, m) Shh (B) and unlipidated control C25SShhN (C) in nt Ctrl and Disp−/− cells in the presence of Scube2. Arrows indicate solubilized Shh and the arrowhead indicates accumulated cellular material in Disp−/− cells. (D) In the absence of Scube2, Shh processing into serum-free medium was abolished in nt Ctrl and Disp−/− cells. Instead, both cell types released similar amounts of unprocessed protein. In B,C,D, anti-beta -actin blots ( alpha beta -actin) and Ponceau S staining of residual serum albumin (PonS) serve as loading controls. (B′,C′,D′) Quantifications of relative Shh (B′,D′) and C25SShhN (C′) release from nt Ctrl and Disp−/− cells. Ratios of solubilized versus cellular Shh were determined and expressed relative to Shh release from nt Ctrl cells (black bars). Data are mean±s.d. n=21 in B′, n=8 in C′ and n=5 in D′. ****P<0.0001; ns, not significant (two-tailed unpaired t-test). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34308968), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N-Terminus by Western Blot Overexpressed Ptctg restores Shh release from Disp−/− cells. (A,A′) Schematic representations of Disp (blue) and Ptc (green). Twelve transmembrane domains (TM1–TM12), two extracellular loops (L1 and L2), and the N- and C-termini are labeled. Conserved SSDs (TM2–TM6) are highlighted in red. Disp delta L2 and Ptc delta L2 lack most of the second extracellular loops (L2). (B,C) Co-expression of transgenic Ptctg or Ptc delta L2 increases Shh shedding from Disp−/− (B) and nt Ctrl (C) cells (c, cellular Shh; m, Shh released into the medium). Arrows indicate solubilized processed Shh from Ptctg- or Ptc delta L2-expressing cells, and arrowheads indicate reduced amounts of solubilized Shh from empty vector (EV)-transfected cells. Anti-beta -actin blots ( alpha beta -actin) and Ponceau S staining of residual serum albumin (PonS) serve as loading controls. (B′,C′) Quantification of relative processed Shh release as shown in B and C. Data are mean±s.d. n=6 in B′, n=9 in C′. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison post hoc test). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34308968), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
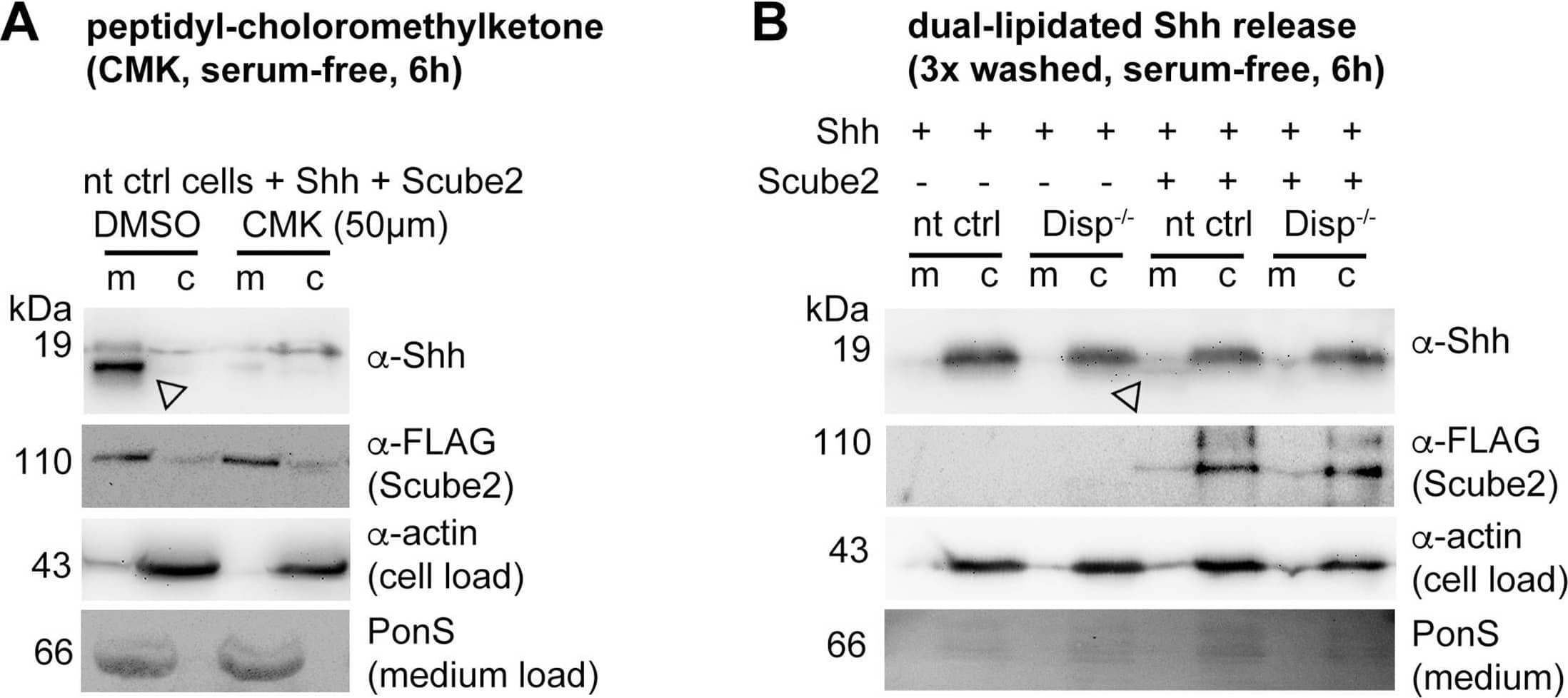
Detection of Human Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N-Terminus by Western Blot Loading controls.(A–D) Actin, PonceauS, and FLAG-tagged Scube2 loading controls for blots shown in Figure 3. Arrowheads indicate Shh specifically solubilized by Disp and Scube2.Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1.Uncropped western blots for Figure 3—figure supplement 1.Uncropped western blots for Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39297609), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
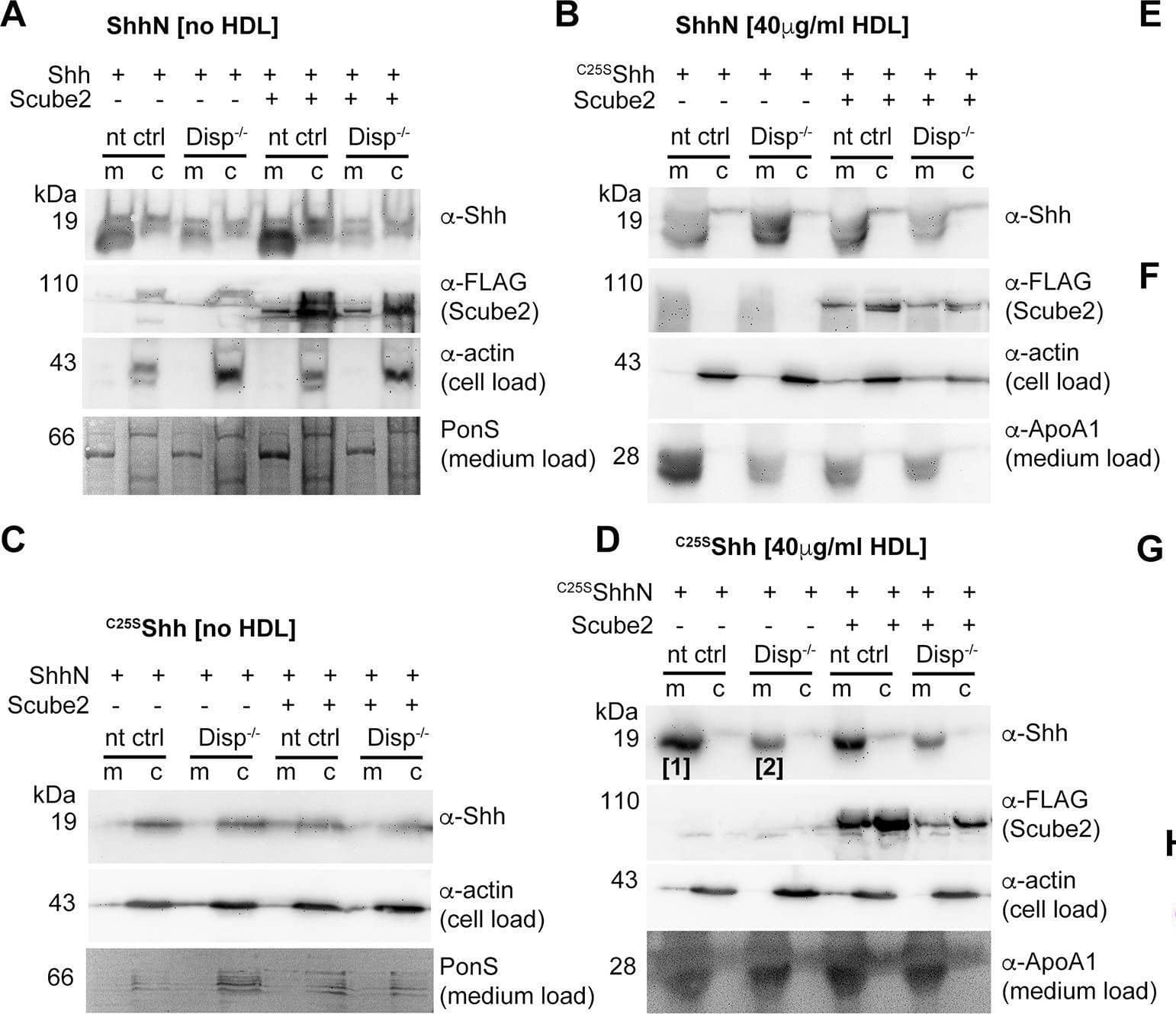
Detection of Human Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N-Terminus by Western Blot Loading controls.(A–D) Actin, PonceauS, and FLAG-tagged Scube2 loading controls for the blots shown in Figure 6A and B. (E, F) Reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) profiles of samples [1] and [2] shown in (D). Note that proteins released from non-targeting control (nt ctrl) cells and Disp-/- cells are both cholesterylated. This suggests that overexpressed monolipidated Shh is only loosely associated with the plasma membrane and can ‘leak out’, or desorb, and thereby associate with high-density lipoprotein (HDL) in a non-enzymatic manner. (G) Purified commercial 8908-SH Shh and HDL were mixed, incubated for 10 min, and analyzed by size-exclusion chromatography (SEC). This revealed rapid spontaneous association and explains the background desorption of dual-lipidated Shh in our cellular assays. Note the excellent 8908-SH Shh co-elution with the ApoE4-bearing HDL fraction, suggesting that this mobile apolipoprotein may have facilitated spontaneous 8908-SH Shh association, or that other properties of ApoE-bearing ‘late’ HDL (Sacks and Jensen, 2018) somehow facilitate Shh association. (H) Dual-lipidated mCherry is efficiently secreted to the outer plasma membrane leaflet of producing Bosc23 cells. Intracellular mCherry fluorescence is shown in white, alpha -mCherry antibody binding to the surface of non-permeabilized cells is shown in magenta, and DAPI staining of the nucleus is shown in blue. Scale bar: 10 μm.Figure 7—figure supplement 1—source data 1.Uncropped western blots of Figure 7—figure supplement 1.Uncropped western blots of Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39297609), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N-Terminus by Western Blot Loading controls.(A, B) Actin, PonceauS, and FLAG-tagged Scube2 loading controls for (the same stripped) blots shown in Figure 2.Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1.Uncropped western blots of Figure 2—figure supplement 1.Uncropped western blots of Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39297609), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Sonic Hedgehog/Shh
The hedgehog (hh) gene encoding a secreted protein was originally identified in Drosophila as a segment polarity gene. The vertebrate homologues of Hh comprise several proteins including sonic hedgehog (Shh), Indian hedgehog (Ihh), and Desert hedgehog (Dhh). Hedgehog proteins are important signaling molecules during embryonic development. Shh genes are highly conserved and have been identified in a variety of species including human, mouse, frog, fish, and chicken. Mouse and human Shh are 92% identical at the amino acid sequence level. Shh is expressed in key embryonic tissues such as the Hensen’s node, the zone of polarizing activity in the posterior limb bud, the notochord, and the floor plate of the neural tube. Shh is involved in regulating the patterning of the developing central nervous system, somite, and limb. Shh plays an important role in the development of particular tissues such as whisker, hair, foregut, tooth and bone. Evidence also suggests that Shh is involved in regulating stem cell fates of neural and hematopoeitic lineages, and that aberrant Shh signaling is implicated in basal cell carcinomas and other diseases.
Mouse Shh cDNA encodes a 437 amino acid residue with a predicted 24 aa residue signal peptide that is cleaved to generate a 413 aa residue precursor protein. An autocatalytic reaction yields a 19 kDa amino-terminal domain Shh-N protein containing cholesterol and palmitate, and a 27 kDa carboxy-terminal domain Shh-C protein. The N-terminal domain retains all known signaling capabilities, while the C-terminal domain is responsible for the intramolecular processing, acting as a cholesterol transferase. Shh can act as both a short-range contact dependent factor and as a long-range, diffusible morphogen. At the cell surface, Shh activity is mediated by a multicomponent receptor complex involving the 12-pass transmembrane protein Patched (Ptc) which binds Shh with high affinity and Smoothened (Smo), a signaling seven transmembrane G-protein coupled receptor. In the absence of Shh, Ptc represses Smo activity. The binding of Shh to Ptc, releases the basal repression of Smo by Ptc (1‑5).
- Carpenter, D. et al. (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:13630.
- Perrimon, N. (1995) Cell 80:517.
- Weed, M. et al. (1997) Matrix Biol. 16:53.
- Mullor, J. et al. (2002) Trends Cell Biol. 12:562.
- Ingham, P. and A. McMahon (2001) Genes & Dev. 15:3059.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human/Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N‑Terminus Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
37
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Disrupting Hedgehog Cardin–Weintraub sequence and positioning changes cellular differentiation and compartmentalization in vivo
Authors: Philipp Kastl, Dominique Manikowski, Georg Steffes, Sabine Schürmann, Shyam Bandari, Christian Klämbt et al.
Development
-
Timing of Smarcb1 and Nf2 inactivation determines schwannoma versus rhabdoid tumor development
Authors: Vitte J, Gao F, Coppola G et al.
Nat Commun
-
Multiple Shh signaling centers participate in fungiform papilla and taste bud formation and maintenance.
Authors: Liu HX, Ermilov A, Grachtchouk M et al.
Dev Biol
-
Unique lingual expression of the Hedgehog pathway antagonist Hedgehog-interacting protein in filiform papillae during homeostasis and ectopic expression in fungiform papillae during Hedgehog signaling inhibition
Authors: Kumari A, Li L, Ermilov AN et al.
Developmental dynamics : an official publication of the American Association of Anatomists
-
Early taste buds are from Shh+ epithelial cells of tongue primordium in distinction from mature taste bud cells which arise from surrounding tissue compartments
Authors: Naomi Kramer, Guiqian Chen, Mohamed Ishan, Xiaogang Cui, Hong-Xiang Liu
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications
-
Proteolytic processing of palmitoylated Hedgehog peptides specifies the 3-4 intervein region of the Drosophila wing
Authors: Sabine Schürmann, Georg Steffes, Dominique Manikowski, Philipp Kastl, Ursula Malkus, Shyam Bandari et al.
eLife
-
Conserved cholesterol-related activities of Dispatched 1 drive Sonic hedgehog shedding from the cell membrane
Authors: Kristina Ehring, Dominique Manikowski, Jonas Goretzko, Jurij Froese, Fabian Gude, Petra Jakobs et al.
Journal of Cell Science
-
Reduced Salivary Gustin and Statherin in Long-COVID Cohort with Impaired Bitter Taste
Authors: Chowdary, H;Riley, N;Patel, P;Gossweiler, AG;Running, CA;Srinivasan, M;
Journal of clinical medicine
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Immunocytochemistry -
Taste papilla cell differentiation requires tongue mesenchyme via ALK3-BMP signaling to regulate the production of secretory proteins
Authors: M Ishan, Z Wang, P Zhao, Y Yao, S Stice, L Wells, Y Mishina, HX Liu
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology, 2023-04-04;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Probing the multimodal fungiform papilla: complex peripheral nerve endings of chorda tympani taste and mechanosensitive fibers before and after Hedgehog pathway inhibition
Authors: Donnelly CR, Kumari A, Li L et al.
Cell and Tissue Research
-
Wnt Inhibitory Factor 1 Binds to and Inhibits the Activity of Sonic Hedgehog
Authors: K Kerekes, M Trexler, L Bányai, L Patthy
Cells, 2021-12-10;10(12):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Protein
Applications: Western Blot -
Complex Evaluation of Tissue Factors in Pediatric Cholesteatoma
Authors: Kristaps Dambergs, Gunta Sumeraga, Māra Pilmane
Children (Basel)
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Sonic hedgehog signalling as a potential endobronchial biomarker in COPD
Authors: J Ancel, R Belgacemi, JM Perotin, Z Diabasana, S Dury, M Dewolf, A Bonnomet, N Lalun, P Birembaut, M Polette, G Deslée, V Dormoy
Respir. Res., 2020-08-07;21(1):207.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Airway epithelial cell differentiation relies on deficient Hedgehog signalling in COPD
Authors: R Belgacemi, E Luczka, J Ancel, Z Diabasana, JM Perotin, A Germain, N Lalun, P Birembaut, X Dubernard, JC Mérol, G Delepine, M Polette, G Deslée, V Dormoy
EBioMedicine, 2019-12-23;51(0):102572.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Early taste buds are from Shh+ epithelial cells of tongue primordium in distinction from mature taste bud cells which arise from surrounding tissue compartments
Authors: Naomi Kramer, Guiqian Chen, Mohamed Ishan, Xiaogang Cui, Hong-Xiang Liu
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Functionally Distinctive Ptch Receptors Establish Multimodal Hedgehog Signaling in the Tooth Epithelial Stem Cell Niche
Authors: M Binder, P Chmielarz, PJ Mckinnon, LC Biggs, I Thesleff, A Balic
Stem Cells, 2019-06-10;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Species generalization and differences in Hedgehog pathway regulation of fungiform and circumvallate papilla taste function and somatosensation demonstrated with sonidegib
Authors: A Kumari, Y Yokota, L Li, RM Bradley, CM Mistretta
Sci Rep, 2018-11-01;8(1):16150.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Maintenance of Taste Organs Is Strictly Dependent on Epithelial Hedgehog/GLI Signaling
PLoS Genet, 2016-11-28;12(11):e1006442.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Ectoderm mesenchymal stem cells promote differentiation and maturation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells
Authors: Zhijian Zhang
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, 2016-10-28;0(0):.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates, Whole Cells
Applications: ICC, Western Blot -
Smoothened Agonist Reduces Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown in Humanized Mice
Authors: Vir B Singh
Sci Rep, 2016-05-31;6(0):26876.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Transcription factor 7-like 1 is involved in hypothalamo-pituitary axis development in mice and humans.
Authors: Gaston-Massuet C, McCabe M, Scagliotti V, Young R, Carreno G, Gregory L, Jayakody S, Pozzi S, Gualtieri A, Basu B, Koniordou M, Wu C, Bancalari R, Rahikkala E, Veijola R, Lopponen T, Graziola F, Turton J, Signore M, Mousavy Gharavy S, Charolidi N, Sokol S, Andoniadou C, Wilson S, Merrill B, Dattani M, Martinez-Barbera J
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2016-01-13;113(5):E548-57.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Prospectively isolated NGN3-expressing progenitors from human embryonic stem cells give rise to pancreatic endocrine cells.
Authors: Cai, Qing, Bonfanti, Paola, Sambathkumar, Rangaraj, Vanuytsel, Kim, Vanhove, Jolien, Gysemans, Conny, Debiec-Rychter, Maria, Raitano, Susanna, Heimberg, Harry, Ordovas, Laura, Verfaillie, Catherin
Stem Cells Transl Med, 2014-02-03;3(4):489-99.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Loss of the transcription factor GLI1 identifies a signaling network in the tumor microenvironment mediating KRAS oncogene-induced transformation.
Authors: Mills, Lisa D, Zhang, Yaqing, Marler, Ronald J, Herreros-Villanueva, Marta, Zhang, Lizhi, Almada, Luciana, Couch, Fergus, Wetmore, Cynthia, Pasca di Magliano, Marina, Fernandez-Zapico, Martin E
J Biol Chem, 2013-03-12;288(17):11786-94.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Separate and distinctive roles for Wnt5a in tongue, lingual tissue and taste papilla development
Authors: Hong-Xiang Liu, Ann S. Grosse, Ken Iwatsuki, Yuji Mishina, Deborah L. Gumucio, Charlotte M. Mistretta
Developmental Biology
Species: Mouse, Rat
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Heparan sulfate-modulated, metalloprotease-mediated sonic hedgehog release from producing cells.
Authors: Dierker T, Dreier R, Petersen A, Bordych C, Grobe K
J. Biol. Chem., 2009-01-27;284(12):8013-22.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Recombinant Protein
Applications: Western Blot -
Involvement of the Edar signaling in the control of hair follicle involution (catagen).
Authors: Fessing MY, Sharova TY, Sharov AA, Atoyan R, Botchkarev VA
Am. J. Pathol., 2006-12-01;169(6):2075-84.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr -
Neuroprotective properties of cultured neural progenitor cells are associated with the production of sonic hedgehog.
Authors: Rafuse VF, Soundararajan P, Leopold C, Robertson HA
Neuroscience, 2005-01-01;131(4):899-916.
Species: Chicken, Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Sonic hedgehog exerts distinct, stage-specific effects on tongue and taste papilla development.
Authors: Liu HX, MacCallum DK, Edwards C, Gaffield W, Mistretta CM
Dev. Biol., 2004-12-15;276(2):280-300.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Cyclopamine and jervine in embryonic rat tongue cultures demonstrate a role for Shh signaling in taste papilla development and patterning: fungiform papillae double in number and form in novel locations in dorsal lingual epithelium.
Authors: Mistretta CM, Liu HX, Gaffield W, MacCallum DK
Dev. Biol., 2003-02-01;254(1):1-18.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Sonic hedgehog regulates gastric gland morphogenesis in man and mouse.
Authors: van den Brink GR, Hardwick JC, Tytgat GN, Brink MA, Ten Kate FJ, Van Deventer SJ, Peppelenbosch MP
Gastroenterology, 2001-08-01;121(2):317-28.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Probing the multimodal fungiform papilla: complex peripheral nerve endings of chorda tympani taste and mechanosensitive fibers before and after Hedgehog pathway inhibition
Authors: Donnelly CR, Kumari A, Li L et al.
Cell and Tissue Research
-
Sonic hedgehog promotes autophagy of vascular smooth muscle cells
Authors: Haijie Li, Jingjing Li, Yuenan Li, Pavneet Singh, Liang Cao, Li-juan Xu et al.
American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology
-
Interaction between hedgehog signalling and PAX6 dosage mediates maintenance and regeneration of the corneal epithelium
Authors: Romana Kucerova, Natalie Dorà, Richard L. Mort, Karen Wallace, Lucy J. Leiper, Christina Lowes et al.
Mol Vis
-
Sonic Hedgehog acts as a macrophage chemoattractant during regeneration of the gastric epithelium
Authors: Chakrabarti J, Dua-Awereh M, Schumacher M et al.
NPJ Regenerative medicine
-
Increased activity of mesenchymal ALK2‐BMP signaling causes posteriorly truncated microglossia and disorganization of lingual tissues
Authors: Mohamed Ishan, Guiqian Chen, Chenming Sun, Shi‐You Chen, Yoshihiro Komatsu, Yuji Mishina et al.
genesis
-
Increased Programmed Death-Ligand 1 is an Early Epithelial Cell Response to Helicobacter pylori Infection
Authors: Holokai L, Chakrabarti J, Broda T et al.
PLoS Pathog.
-
Separate and distinctive roles for Wnt5a in tongue, lingual tissue and taste papilla development
Authors: Hong-Xiang Liu, Ann S. Grosse, Ken Iwatsuki, Yuji Mishina, Deborah L. Gumucio, Charlotte M. Mistretta
Developmental Biology
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human/Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N‑Terminus Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 2 Reviews)
Have you used Human/Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh N‑Terminus Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
H9 cells were fixed in 4%PFA. Nanog antibody (15ug/ml) was incubated overnight at 4 °C. Secondary antibody was donkey anti- goat 488 (Invitrogen).