Human Sirtuin 2/SIRT2 Biotinylated Antibody Summary
Ala2-Gln389
Accession # Q8IXJ6
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
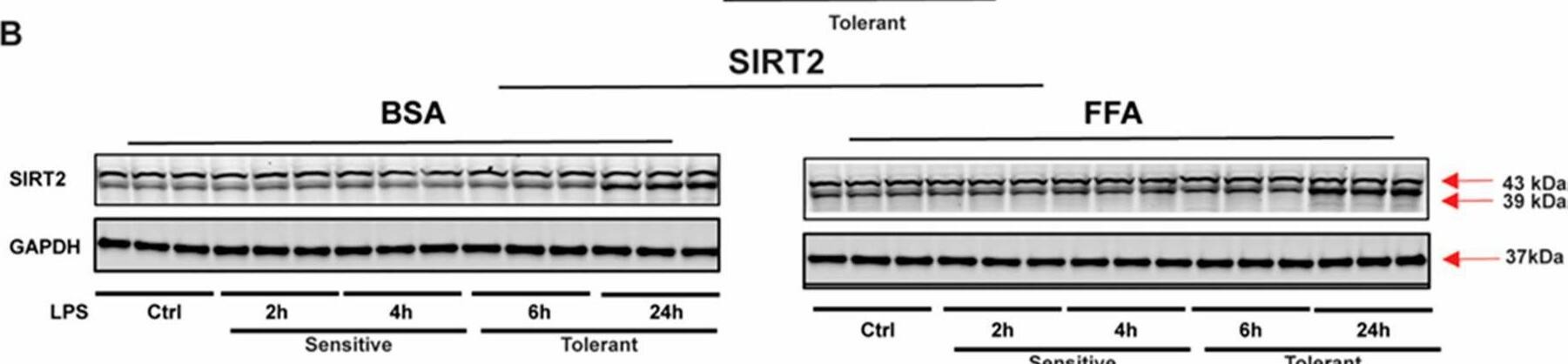
Detection of Sirtuin 2/SIRT2 by Western Blot SIRT2 expression is increased in free fatty acid (FFA)-exposed tolerant RAW 264.7 cell macrophages (RAW) cells. Bovine serum albumin (BSA: vehicle for free fatty acid) or stearic acid (free fatty acid: FFA)-exposed RAW264.7 cell macrophages (RAW) were stimulated with either one or two doses of the LPS; second dose at indicated time points after 1st LPS. (A) TNF-alpha mRNA expression was evaluated by qRT–PCR analysis. (B) SIRT2 protein expression was detected by Western blot in BSA- or FFA-exposed RAW cells following a single dose of the LPS stimulation for indicated time periods. GAPDH was used as the loading control. (C) Western blot image quantification using image-J software (n = 3 each group; * p < 0.05). SIRT2 protein expression was normalized to GAPDH. (D,E). To inhibit SIRT2, after 4 h of 1st LPS exposure, cells were treated with SIRT2 inhibitor AK-7 (25 µM) and incubated further for 20 h in the presence or absence of the second dose of the LPS. TNF-alpha protein released in the cell culture media from FFA-exposed sensitive and tolerant cells was evaluated by ELISA. (* p < 0.05). IL6 (Figure 1E) protein released in the cell culture media from FFA-exposed sensitive and tolerant cells evaluated by ELISA. (* p < 0.05). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33810233), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
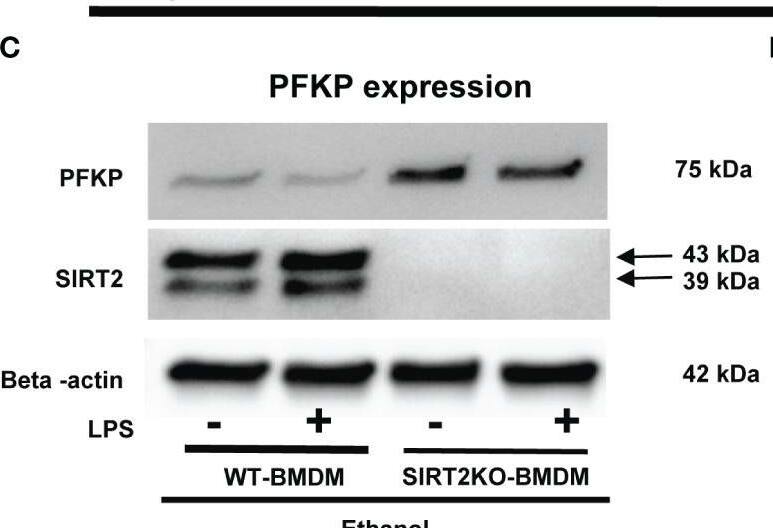
Detection of Sirtuin 2/SIRT2 by Western Blot The effect of acute ethanol-exposure-induced SIRT2 on PFKP expression in macrophages. (A) PFKP expression in WT-BMDM exposed to vehicle or ethanol ± LPS by western blot analysis. (B) PFKP western blot image quantification of PFKP protein in vehicle vs. ethanol exposed WT-BMDM, Y axis represents fold of vehicle-LPS (fold of vehicle control) (n = 4 blots; * p < 0.05). (C) PFKP expression in Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM and SIRT2KO-BMDM ± LPS. (D) Western blot image quantification of PFKP protein in ethanol exposed WT-BMDM and SIRT2KO-BMDM. Y axis represents fold of Ethanol-exposed WT-LPS (fold of WT- ethanol control) (n = 4 blots; * p < 0.05). (E) PFKP expression in Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM treated with AK-7 or DMSO ± LPS. (F) Western blot image quantification of PFKP in AK-7 vs. DMSO treated-Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM ± LPS, Y axis represents fold of Ethanol-exposed WT-LPS (fold of WT- ethanol control) (n = 4 blots; * p < 0.05). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36865524), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
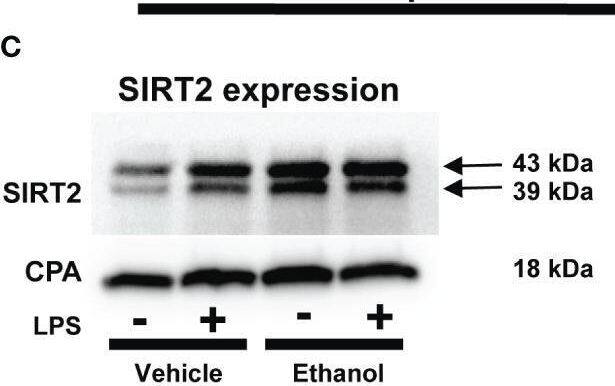
Detection of Sirtuin 2/SIRT2 by Western Blot The effect of acute ethanol-exposure on mouse bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM). Phagocytosis in BMDM exposed to vehicle or ethanol ± LPS to study phagocytosis using pHrodo bioparticles and SIRT2 expression. (A) Representative images of intracellular pHrodo bioparticles in vehicle or Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM ± LPS. (B) Fluorescence quantification of pHrodo bioparticles in WT-BMDM (n=4 repetitions/group; * p<0.05). (C) SIRT2 protein expression detected by western blot in Vehicle- or Ethanol-exposed BMDM cells ± LPS. (D) Western blot image quantification of SIRT2 protein blot in vehicle or ethanol-exposed BMDM cells ± LPS (n = 4 blots/group; * p < 0.05). (E) Representative images of pHrodo bioparticles in Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM and SIRT2KO-BMDM ± LPS. (F) Fluorescence quantification of pHrodo bioparticles in Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM, and SIRT2KO-BMDM ± LPS. * p < 0.05. (G) Representative images of pHrodo bioparticles in Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM, co-treated with SIRT2 inhibitor AK-7 or DMSO ± LPS. (H) Fluorescence quantification of pHrodo bioparticles in Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM with AK-7/DMSO ± LPS stimulation. * p < 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36865524), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
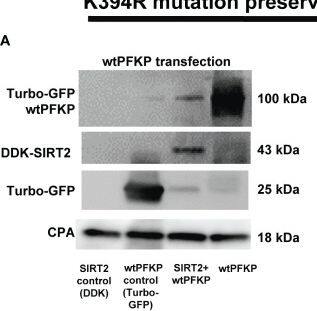
Detection of Sirtuin 2/SIRT2 by Western Blot Effect of K394R mutation on PFKP. (A, B) HEK293T cells transfected with wtPFKP/mtPFKP in the presence or absence of SIRT2. Western blot analysis of Turbo-GFP-wtPFKP, DDK-SIRT2, turbo-GFP (control for wtPFKP plasmid transfected) and CPA. (C) mtPFKP transfection and IP using turbo-GFP-trap in HEK293T cells, in presence or absence of SIRT2 followed by IB analysis of acetyl lysine, turbo-GFP-mtPFKP and turbo-GFP (control for wtPFKP plasmid transfected). Pulldown with HEK293T cell lysate without transfection was used as a negative control. (D) Western blot analysis of turbo-GFP mtPFKP, DDK-SIRT2, turbo-GFP and CPA in whole cell lysate, used as an input for the turbo-GFP IP. (E) mtPFKP transfection and IP using magnetic-TUBEs in HEK293T cells, in presence or absence of SIRT2 followed by IB analysis of ubiquitination. (F) Western blot analysis of turbo-GFP mtPFKP, DDK-SIRT2, turbo-GFP and CPA in whole cell lysate used as input for the TUBE IP. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36865524), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
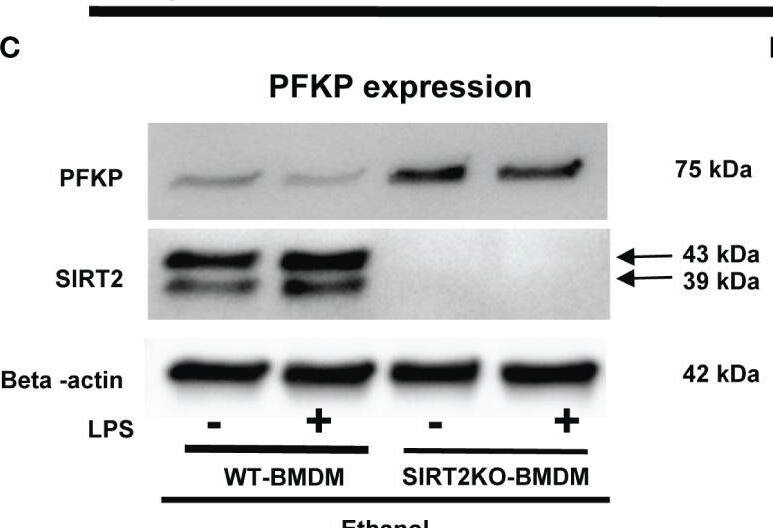
Detection of Sirtuin 2/SIRT2 by Western Blot The effect of acute ethanol-exposure-induced SIRT2 on PFKP expression in macrophages. (A) PFKP expression in WT-BMDM exposed to vehicle or ethanol ± LPS by western blot analysis. (B) PFKP western blot image quantification of PFKP protein in vehicle vs. ethanol exposed WT-BMDM, Y axis represents fold of vehicle-LPS (fold of vehicle control) (n = 4 blots; * p < 0.05). (C) PFKP expression in Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM and SIRT2KO-BMDM ± LPS. (D) Western blot image quantification of PFKP protein in ethanol exposed WT-BMDM and SIRT2KO-BMDM. Y axis represents fold of Ethanol-exposed WT-LPS (fold of WT- ethanol control) (n = 4 blots; * p < 0.05). (E) PFKP expression in Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM treated with AK-7 or DMSO ± LPS. (F) Western blot image quantification of PFKP in AK-7 vs. DMSO treated-Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM ± LPS, Y axis represents fold of Ethanol-exposed WT-LPS (fold of WT- ethanol control) (n = 4 blots; * p < 0.05). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36865524), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
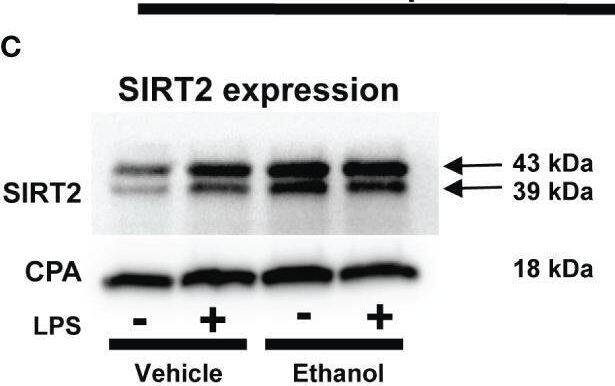
Detection of Sirtuin 2/SIRT2 by Western Blot The effect of acute ethanol-exposure on mouse bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM). Phagocytosis in BMDM exposed to vehicle or ethanol ± LPS to study phagocytosis using pHrodo bioparticles and SIRT2 expression. (A) Representative images of intracellular pHrodo bioparticles in vehicle or Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM ± LPS. (B) Fluorescence quantification of pHrodo bioparticles in WT-BMDM (n=4 repetitions/group; * p<0.05). (C) SIRT2 protein expression detected by western blot in Vehicle- or Ethanol-exposed BMDM cells ± LPS. (D) Western blot image quantification of SIRT2 protein blot in vehicle or ethanol-exposed BMDM cells ± LPS (n = 4 blots/group; * p < 0.05). (E) Representative images of pHrodo bioparticles in Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM and SIRT2KO-BMDM ± LPS. (F) Fluorescence quantification of pHrodo bioparticles in Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM, and SIRT2KO-BMDM ± LPS. * p < 0.05. (G) Representative images of pHrodo bioparticles in Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM, co-treated with SIRT2 inhibitor AK-7 or DMSO ± LPS. (H) Fluorescence quantification of pHrodo bioparticles in Ethanol-exposed WT-BMDM with AK-7/DMSO ± LPS stimulation. * p < 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36865524), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
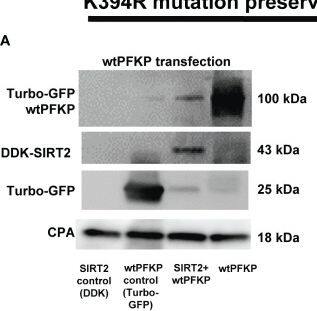
Detection of Sirtuin 2/SIRT2 by Western Blot Effect of K394R mutation on PFKP. (A, B) HEK293T cells transfected with wtPFKP/mtPFKP in the presence or absence of SIRT2. Western blot analysis of Turbo-GFP-wtPFKP, DDK-SIRT2, turbo-GFP (control for wtPFKP plasmid transfected) and CPA. (C) mtPFKP transfection and IP using turbo-GFP-trap in HEK293T cells, in presence or absence of SIRT2 followed by IB analysis of acetyl lysine, turbo-GFP-mtPFKP and turbo-GFP (control for wtPFKP plasmid transfected). Pulldown with HEK293T cell lysate without transfection was used as a negative control. (D) Western blot analysis of turbo-GFP mtPFKP, DDK-SIRT2, turbo-GFP and CPA in whole cell lysate, used as an input for the turbo-GFP IP. (E) mtPFKP transfection and IP using magnetic-TUBEs in HEK293T cells, in presence or absence of SIRT2 followed by IB analysis of ubiquitination. (F) Western blot analysis of turbo-GFP mtPFKP, DDK-SIRT2, turbo-GFP and CPA in whole cell lysate used as input for the TUBE IP. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36865524), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Sirtuin 2/SIRT2
Sirtuin 2, encoded by the SIRT2 gene, is also known as SIR2 (silent information regulator 2)-like protein 2. It is a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)-dependent histone/protein deacetylase (1, 2). The SIR2 family of enzymes is classified as class III histone deacetylases (HDACs) and has been implicated in many cellular processes that include histone deacetylation, gene silencing, chromosomal stability, and aging (3, 4). Unlike class I and class II HDACs, the enzymatic activity of class III HDACs is NAD dependent and insensitive to HDAC inhibitor trichostatin A (5).
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human Sirtuin 2/SIRT2 Biotinylated Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
2
Citations: Showing 1 - 2
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
SIRT2-PFKP interaction dysregulates phagocytosis in macrophages with acute ethanol-exposure
Authors: Gandhirajan A, Roychowdhury S, Kibler C et al.
Frontiers in Immunology
-
Sirtuin 2 Dysregulates Autophagy in High-Fat-Exposed Immune-Tolerant Macrophages
Authors: Sanjoy Roychowdhury, Anugraha Gandhirajan, Christopher Kibler, Xianfeng Wang, Vidula Vachharajani
Cells
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human Sirtuin 2/SIRT2 Biotinylated Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human Sirtuin 2/SIRT2 Biotinylated Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human Sirtuin 2/SIRT2 Biotinylated Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
