Human Urinary TIM-1/KIM-1/HAVCR ELISA Kit - Quantikine
Human Urinary TIM-1/KIM-1/HAVCR Quantikine ELISA Kit Summary
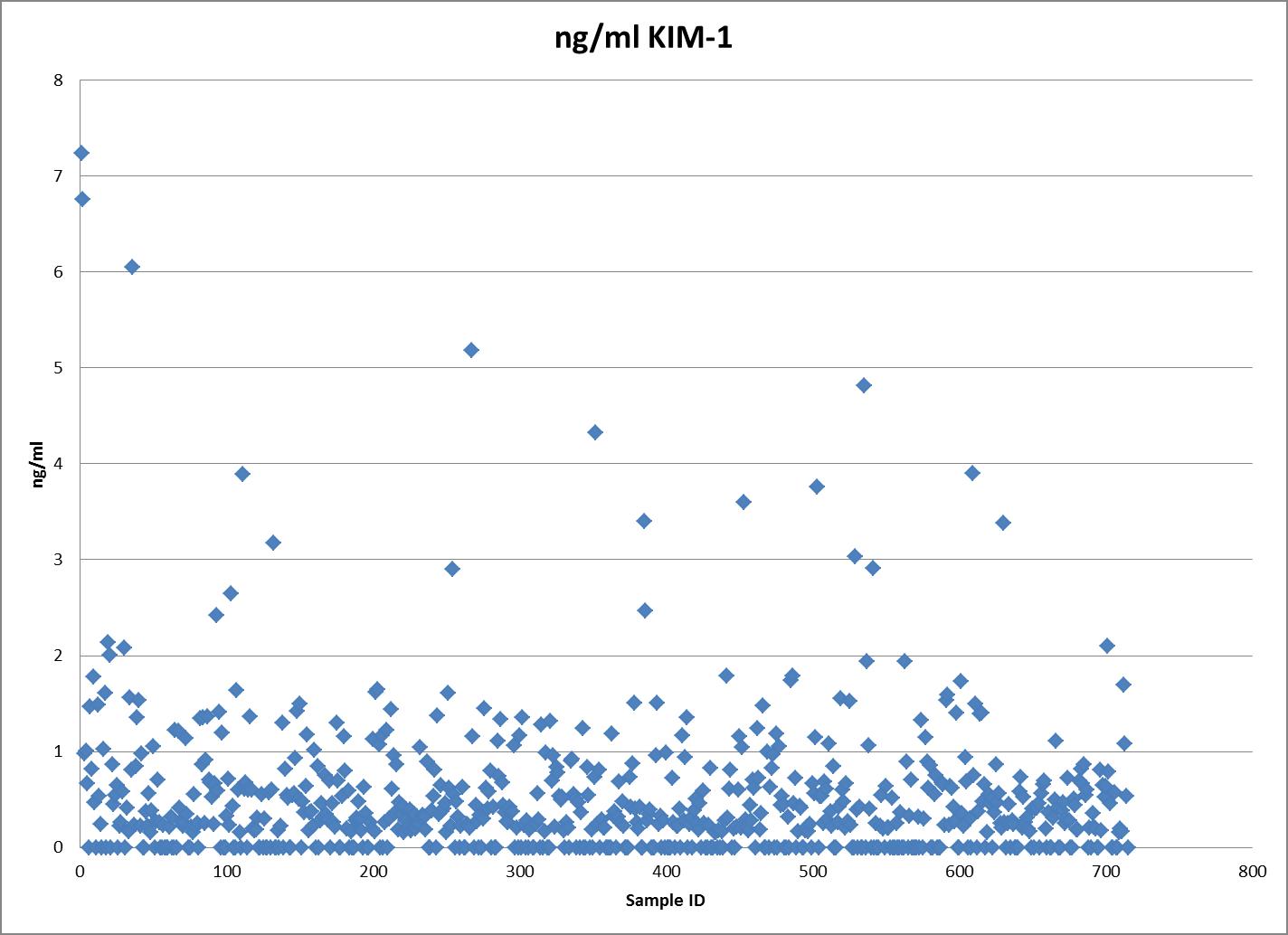
Sample Values
Urine - Twenty-six samples from apparently healthy volunteers were evaluated for the presence of human TIM-1 in this assay. No medical histories were available for the donors used in this study.| Sample Type | Mean | Range | Standard Deviation |
| TIM-1 (ng/mL) | 1.35 | 0.156-5.33 | 1.09 |
| TIM-1 (μg/g Creatinine) | 1.11 | 0.225-3.20 | 0.689 |
Product Summary
Precision
Urine
| Intra-Assay Precision | Inter-Assay Precision | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| n | 20 | 20 | 20 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| Mean (ng/mL) | 0.98 | 3.04 | 5.88 | 1.09 | 3.19 | 6.23 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.042 | 0.119 | 0.259 | 0.069 | 0.193 | 0.484 |
| CV% | 4.3 | 3.9 | 4.4 | 6.3 | 6 | 7.8 |
Recovery
The recovery of TIM-1 spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay was evaluated.
| Sample Type | Average % Recovery | Range % |
|---|---|---|
| Urine (n=20) | 104 | 94-112 |
Linearity
Scientific Data
Product Datasheets
Preparation and Storage
Background: TIM-1/KIM-1/HAVCR
T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 1 (TIM-1), also known as Kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1) and Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 1 (HAVcr1), is a member of the TIM family which is involved in the regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses (1, 2). TIM-1 is a type I transmembrane protein that contains an N-terminal immunoglobulin-like domain, a mucin domain with O- and N-linked glycosylations, a transmembrane segment, and a cytoplasmic signaling domain (3, 4). Multiple TIM-1 variants can be produced due to polymorphisms or alternative splicing resulting in deletions in the mucin domain (3). Some of these polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to atopy, autoimmunity, and severe hepatitis A virus infection in humans (5). Within the extracellular domain, human TIM-1 shares 41% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat TIM-1.
Assay Procedure
Refer to the product- Prepare all reagents, standard dilutions, and samples as directed in the product insert.
- Remove excess microplate strips from the plate frame, return them to the foil pouch containing the desiccant pack, and reseal.
- Add 100 µL of Assay Diluent to each well.
- Add 50 µL of Standard, control, or sample to each well. Cover with a plate sealer, and incubate at room temperature for 2 hours.
- Aspirate each well and wash, repeating the process 3 times for a total of 4 washes.
- Add 200 µL of Conjugate to each well. Cover with a new plate sealer, and incubate at room temperature for 2 hours.
- Aspirate and wash 4 times.
- Add 200 µL Substrate Solution to each well. Incubate at room temperature for 30 minutes. PROTECT FROM LIGHT.
- Add 50 µL of Stop Solution to each well. Read at 450 nm within 30 minutes. Set wavelength correction to 540 nm or 570 nm.



Citations for Human Urinary TIM-1/KIM-1/HAVCR Quantikine ELISA Kit
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
44
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Urinary biomarkers in prediction of subclinical acute kidney injury in pediatric oncology patients treated with nephrotoxic agents
Authors: Miloevski-Lomi?, G;Kotur-Stevuljevi?, J;Paripovi?, D;Nikolovski, S;Lazi?, J;Rodi?, P;Miloevi?, G;Mitrovi?, J;Vukmir, B;Petrovi?, A;Peco-Anti?, A;
BMC nephrology
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Urinary biomarkers for diagnosing acute kidney injury in sepsis in the emergency department
Authors: Baek, S;Park, I;Kim, S;Um, YW;Kim, HE;Lee, K;Lee, JH;Jo, YH;
Heliyon
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Serum and urinary biomarkers of vancomycin-induced acute kidney injury: A prospective, observational analysis
Authors: Park, SI;Yu, U;Oh, WS;Ryu, SW;Son, S;Lee, S;Baek, H;Park, JI;
Medicine
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Effects of high-intensity intermittent exercise versus moderate-intensity continuous exercise on renal hemodynamics assessed by ultrasound echo
Authors: Kawakami, S;Yasuno, T;Kawakami, S;Ito, A;Fujimi, K;Matsuda, T;Nakashima, S;Masutani, K;Uehara, Y;Higaki, Y;Michishita, R;
Physiological reports
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine, Whole Blood
-
Associations Between Characteristics of Individuals With Fontan Circulation With Blood and Urine Biomarkers of Kidney Injury and Dysfunction
Authors: Katz, DA;Gao, Z;Freytag, J;Mahendran, A;Szugye, C;Woodly, S;Alvarez, TCE;Lubert, AM;Alsaied, T;Goldstein, SL;Opotowsky, AR;
Journal of the American Heart Association
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
IL-17C neutralization protects the kidney against acute injury and chronic injury
Authors: Zhang, F;Yin, J;Liu, L;Liu, S;Zhang, G;Kong, Y;Wang, Y;Wang, N;Chen, X;Wang, F;
EBioMedicine
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Urine
-
Optimizing Vancomycin Therapy in Critically Ill Children: A Population Pharmacokinetics Study to Inform Vancomycin Area under the Curve Estimation Using Novel Biomarkers
Authors: Downes, KJ;Zuppa, AF;Sharova, A;Neely, MN;
Pharmaceutics
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Markers of Kidney Tubular Function Deteriorate While Those of Kidney Tubule Health Improve in Primary Aldosteronism After Targeted Treatments
Authors: VC Wu, CK Chan, JS Chueh, YM Chen, YH Lin, CC Chang, PC Lin, SD Chung, TAIPAI gro
Journal of the American Heart Association, 2023-02-15;12(4):e028146.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Cytokines and Immune Cell Phenotype in Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Authors: N Farooqui, M Zaidi, L Vaughan, TD McKee, E Ahsan, KD Pavelko, JC Villasboas, S Markovic, T Taner, N Leung, H Dong, MP Alexander, SM Herrmann
Kidney international reports, 2022-12-05;8(3):628-641.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Dicarbonyl-modified lipoproteins contribute to proteinuric kidney injury
Authors: J Zhong, HC Yang, EL Shelton, T Matsusaka, AJ Clark, V Yermalitsk, Z Mashhadi, LS May-Zhang, MF Linton, AB Fogo, A Kirabo, SS Davies, V Kon
JCI Insight, 2022-11-08;7(21):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Serum myo-inositol oxygenase levels at hospital discharge predict progression to chronic kidney disease in community-acquired acute kidney injury
Authors: TJ Kakkanattu, J Kaur, V Nagesh, M Kundu, K Kamboj, P Kaur, J Sethi, HS Kohli, KL Gupta, A Ghosh, V Kumar, AK Yadav, V Jha
Scientific Reports, 2022-08-02;12(1):13225.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
The moderate-intensity continuous exercise maintains renal blood flow and does not impair the renal function
Authors: S Kawakami, T Yasuno, S Kawakami, A Ito, K Fujimi, T Matsuda, S Nakashima, K Masutani, Y Uehara, Y Higaki, R Michishita
Physiological Reports, 2022-08-01;10(15):e15420.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Aristolochic acid I induces proximal tubule injury through ROS/HMGB1/mt DNA mediated activation of TLRs
Authors: R Upadhyay, V Batuman
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2022-06-28;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Exploration of a panel of urine biomarkers of kidney disease in two paediatric cohorts with Type 1 diabetes mellitus of differing duration
Authors: L Zeni, AGW Norden, E Prandi, C Canepa, K Burling, K Simpson, B Felappi, A Plebani, G Cancarini, PM Ferraro, D Fraser, RJ Unwin
Diabetology & metabolic syndrome, 2022-05-12;14(1):71.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Cell stress response impairs de novo NAD+ biosynthesis in the kidney
Authors: Y Bignon, A Rinaldi, Z Nadour, V Poindessou, I Nemazanyy, O Lenoir, B Fohlen, P Weill-Rayn, A Hertig, A Karras, P Galichon, M Naesens, D Anglicheau, PE Cippà, N Pallet
JCI Insight, 2022-01-11;7(1):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Effect of a 3% gelatin solution on urinary KIM-1 levels in patients after thyroidectomy: a preliminary randomized controlled trial
Authors: P Le?nik, E Wo?nica-Ni, J Janc, M Mierzcha?a, L ?ysenko
Scientific Reports, 2021-12-08;11(1):23617.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Kidney injury molecule‑1 levels are associated with therapeutic outcomes and renal tubulointerstitial injury severity in idiopathic membranous nephropathy
Authors: Yidan Zhang, Chunhong Xiang, Liying Gong, Yuanyuan Zhang, Junhui Zhen, Zhao Hu et al.
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Urine Biomarkers for the Assessment of Acute Kidney Injury in Neonates with Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy Receiving Therapeutic Hypothermia
Authors: J Rumpel, BJ Spray, VY Chock, MJ Kirkley, CL Slagle, A Frymoyer, SH Cho, KM Gist, R Blaszak, B Poindexter, SE Courtney
The Journal of pediatrics, 2021-09-20;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Organophosphate pesticides and progression of chronic kidney disease among children: A prospective cohort study
Authors: MH Jacobson, Y Wu, M Liu, K Kannan, AJ Li, M Robinson, BA Warady, S Furth, H Trachtman, L Trasande
Environment international, 2021-05-02;155(0):106597.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Effect of 0.9% NaCl compared to plasma-lyte on biomarkers of kidney injury, sodium excretion and tubular transport proteins in patients undergoing primary uncemented hip replacement - a randomized trial
Authors: AM Østergaard, AN Jørgensen, S Bøvling, NP Ekeløf, FH Mose, JN Bech
Bmc Nephrology, 2021-03-26;22(1):111.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Effect of balanced crystalloids versus saline on urinary biomarkers of acute kidney injury in critically ill adults
Authors: BE Funke, KE Jackson, WH Self, SP Collins, CT Saunders, L Wang, JD Blume, N Wickersham, RM Brown, JD Casey, GR Bernard, TW Rice, ED Siew, MW Semler, SMART Inve, Pragmatic
Bmc Nephrology, 2021-02-05;22(1):54.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Urine NGAL and KIM-1-Tubular Injury Biomarkers in Long-Term Survivors of Childhood Solid Tumors: A Cross-Sectional Study
Authors: E Latoch, K Kono?czuk, K Muszy?ska-, K Taranta-Ja, A Wasilewska, E Szymczak, J Trochim, M Krawczuk-R
Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2021-01-21;10(3):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Serially assessed bisphenol A and phthalate exposure and association with kidney function in children with chronic kidney disease in the US and Canada: A longitudinal cohort study
Authors: MH Jacobson, Y Wu, M Liu, TM Attina, M Naidu, R Karthikraj, K Kannan, BA Warady, S Furth, S Vento, H Trachtman, L Trasande
PLoS Med, 2020-10-14;17(10):e1003384.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
The Marker of Tubular Injury, Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1), in Acute Kidney Injury Complicating Acute Pancreatitis: A Preliminary Study
Authors: J Wajda, P Dumnicka, W Kolber, M Sporek, B Maziarz, P Ceranowicz, M Ku?niewski, B Ku?nierz-C
J Clin Med, 2020-05-13;9(5):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Renal tubular damage and worsening renal function in chronic heart failure: Clinical determinants and relation to prognosis (Bio-SHiFT study)
Authors: M Brankovic, KM Akkerhuis, EJ Hoorn, N van Boven, JC van den Be, A Constantin, J Brugts, J van Ramsho, T Germans, H Hillege, E Boersma, V Umans, I Kardys
Clin Cardiol, 2020-04-16;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Changes in Water Soluble Uremic Toxins and Urinary Acute Kidney Injury Biomarkers After 10- and 100-km Runs
Authors: W Wo?yniec, K Kasprowicz, J Giebu?towi, N Korytowska, K Zorena, M Bartoszewi, P Rita-Tkach, M Renke, W Ratkowski
Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2019-10-28;16(21):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Acute kidney injury during an ultra-distance race
Authors: R Jouffroy, X Lebreton, N Mansencal, D Anglicheau
PLoS ONE, 2019-09-25;14(9):e0222544.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Circulating kidney injury molecule-1 as a biomarker of renal parameters in diabetic kidney disease
Authors: T Gohda, N Kamei, T Koshida, M Kubota, K Tanaka, Y Yamashita, E Adachi, S Ichikawa, M Murakoshi, S Ueda, Y Suzuki
J Diabetes Investig, 2019-09-21;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Senescent Kidney Cells in Hypertensive Patients Release Urinary Extracellular Vesicles.
Authors: Santelli A, Sun I, Eirin A, Abumoawad A, Woollard J, Lerman A, Textor S, Puranik A, Lerman L
J Am Heart Assoc, 2019-06-01;8(11):e012584.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
The role of renal biomarkers to predict the need of surgery in congenital urinary tract obstruction in infants
Authors: D Kostic, GPNS Beozzo, SB do Couto, AHT Kato, L Lima, P Palmeira, VLJ Krebs, V Bunduki, RPV Francisco, M Zugaib, FT Dénes, WB de Carvalh, VHK Koch
J Pediatr Urol, 2019-03-16;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Baseline urinary KIM-1 concentration in detecting acute kidney injury should be interpreted with patient pre-existing nephropathy
Authors: Y Huang, Y Tian, S Likhodii, E Randell
Pract Lab Med, 2019-03-07;15(0):e00118.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Acute kidney injury in acute-on-chronic liver failure is different from in decompensated cirrhosis
Authors: QQ Jiang, MF Han, K Ma, G Chen, XY Wan, SB Kilonzo, WY Wu, YL Wang, J You, Q Ning
World J. Gastroenterol., 2018-06-07;24(21):2300-2310.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Urinary biomarkers predict advanced acute kidney injury after cardiovascular surgery
Authors: JJ Wang, NH Chi, TM Huang, R Connolly, LW Chen, SJ Chueh, WC Kan, CC Lai, VC Wu, JT Fang, TS Chu, KD Wu
Crit Care, 2018-04-26;22(1):108.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Follow Up of Value of the Intrarenal Resistivity Indices and Different Renal Biomarkers for Early Identification of Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 1 Diabetic Patients
Authors: SAE Dayem, AEME Bohy, M Hamed, S Ahmed
Open Access Maced J Med Sci, 2017-03-20;5(2):188-192.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Urinary kidney injury molecule?1 as an early diagnostic biomarker of obstructive acute kidney injury and development of a rapid detection method
Authors: Y Jin, X Shao, B Sun, C Miao, Z Li, Y Shi
Mol Med Rep, 2017-01-05;0(0):.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Urine
-
Kallistatin protects against diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice by suppressing AGE-RAGE-induced oxidative stress.
Authors: Yiu W, Wong D, Wu H, Li R, Yam I, Chan L, Leung J, Lan H, Lai K, Tang S
Kidney Int, 2016-02-01;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Angiopoietin/Tie2 Dysbalance Is Associated with Acute Kidney Injury after Cardiac Surgery Assisted by Cardiopulmonary Bypass.
Authors: Jongman R, van Klarenbosch J, Molema G, Zijlstra J, de Vries A, van Meurs M
PLoS ONE, 2015-08-26;10(8):e0136205.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Urinary kidney injury molecule-1 is related to pathologic involvement in IgA nephropathy with normotension, normal renal function and mild proteinuria.
Authors: Xu P, Wei L, Shang W, Tian S, Gu D, Yan T, Lin S
BMC Nephrol, 2014-07-07;15(0):107.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
A comparison of the ability of levels of urinary biomarker proteins and exosomal mRNA to predict outcomes after renal transplantation.
Authors: Peake, Philip W, Pianta, Timothy, Succar, Lena, Fernando, Mangalee, Pugh, Debbie J, McNamara, Kathleen, Endre, Zoltan H
PLoS ONE, 2014-06-11;9(2):e98644.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Autophagy activation reduces renal tubular injury induced by urinary proteins.
Authors: Liu, Wei Jing, Luo, Mian-Na, Tan, Jin, Chen, Wei, Huang, Lei-zhao, Yang, Chen, Pan, Qingjun, Li, Benyi, Liu, Hua-feng
Autophagy, 2013-11-26;10(2):243-56.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Urinary N-acetyl-beta-D glucosaminidase as a surrogate marker for renal function in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: 1 year prospective cohort study.
BMC Nephrol, 2012-08-30;13(0):93.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Measuring urinary tubular biomarkers in type 2 diabetes does not add prognostic value beyond established risk factors.
Kidney Int, 2012-06-20;82(7):812-8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Indomethacin reduces glomerular and tubular damage markers but not renal inflammation in chronic kidney disease patients: a post-hoc analysis.
Authors: de Borst MH, Nauta FL, Vogt L, Laverman GD, Gansevoort RT, Navis G
PLoS ONE, 2012-05-25;7(5):e37957.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
-
Urinary excretion of twenty peptides forms an early and accurate diagnostic pattern of acute kidney injury.
Authors: Metzger J, Kirsch T, Schiffer E, Ulger P, Mentes E, Brand K, Weissinger EM, Haubitz M, Mischak H, Herget-Rosenthal S
Kidney Int., 2010-09-08;78(12):1252-62.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all ELISA FAQsReviews for Human Urinary TIM-1/KIM-1/HAVCR Quantikine ELISA Kit
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 3 Reviews)
Have you used Human Urinary TIM-1/KIM-1/HAVCR Quantikine ELISA Kit?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
Obtained values in range when urine was diluted 3-fold.