Human VEGF-B167/186 Antibody Summary
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
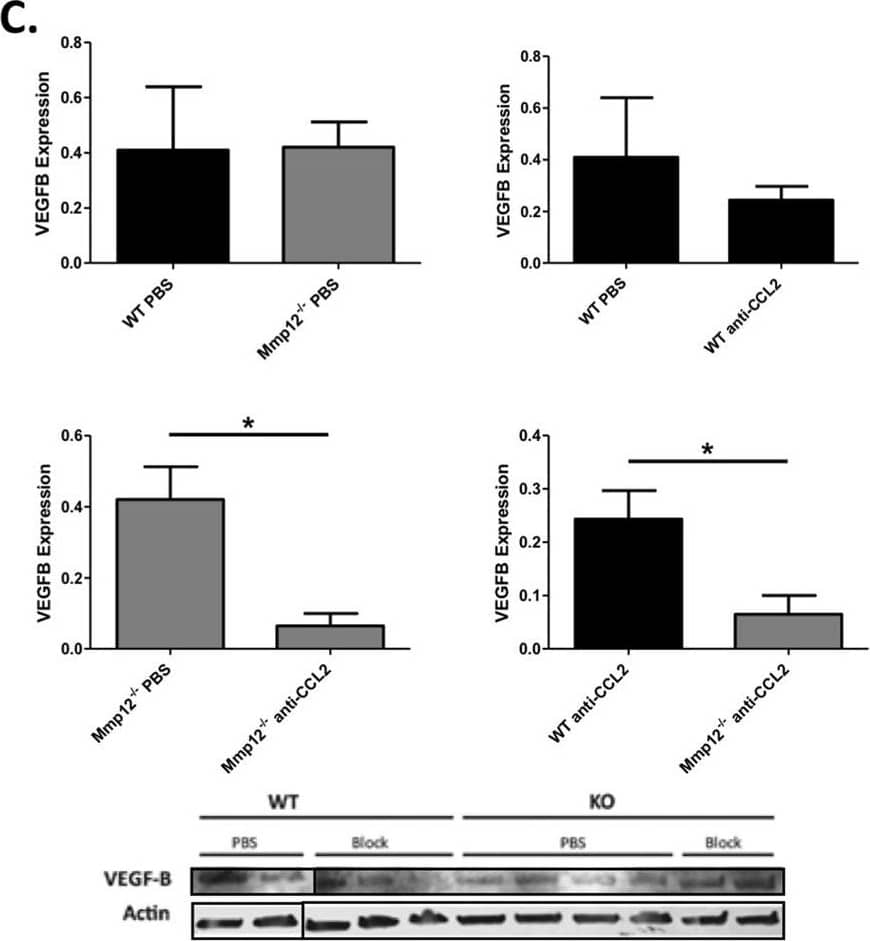
Detection of Mouse VEGF-B by Western Blot Expression patterns of CCR2, VEGFA, and VEGFB protein in wounded corneas of WT and MMP12 KO mice. (A) Protein expression levels of CCR2 and actin in unwounded and wounded corneas of WT (N = 8 per lane) and Mmp12−/− (N = 8 per lane) mice 1 and 6 days post-chemical injury, as determined by Western blot analysis. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 1A. (B,C) The effect of CCL2 neutralization on VEGFA and VEGFB protein expression in WT and Mmp12−/− mice at 7 days post-chemical injury. Treatment of WT and Mmp12−/− mice with PBS or anti-CCL2 antibody had no significant effect on VEGFA expression. Treatment of Mmp12−/− mice with anti-CCL2 significantly decreased VEGFB protein expression compared with PBS-treated Mmp12−/− mice (0.42 versus 0.065 respectively). VEGFB expression was decreased more in WT mice compared with Mmp12−/− mice following treatment with anti-CCL2 (0.24 versus 0.065 respectively). *P < 0.05. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 1B,C. While we had to use several gels to fit all samples, they all derive from the same experiment and gels/blots were processed in parallel. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31399604), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse VEGF-B by Western Blot Expression patterns of CCR2, VEGFA, and VEGFB protein in wounded corneas of WT and MMP12 KO mice. (A) Protein expression levels of CCR2 and actin in unwounded and wounded corneas of WT (N = 8 per lane) and Mmp12−/− (N = 8 per lane) mice 1 and 6 days post-chemical injury, as determined by Western blot analysis. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 1A. (B,C) The effect of CCL2 neutralization on VEGFA and VEGFB protein expression in WT and Mmp12−/− mice at 7 days post-chemical injury. Treatment of WT and Mmp12−/− mice with PBS or anti-CCL2 antibody had no significant effect on VEGFA expression. Treatment of Mmp12−/− mice with anti-CCL2 significantly decreased VEGFB protein expression compared with PBS-treated Mmp12−/− mice (0.42 versus 0.065 respectively). VEGFB expression was decreased more in WT mice compared with Mmp12−/− mice following treatment with anti-CCL2 (0.24 versus 0.065 respectively). *P < 0.05. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 1B,C. While we had to use several gels to fit all samples, they all derive from the same experiment and gels/blots were processed in parallel. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31399604), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: VEGF-B
Vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGF-B), also known as vascular endothelial growth factor-related factor (VRF), is a member of the VEGF family of growth factors that share structural and functional similarity (1, 2). Five mammalian members, including VEGF-A, -B, -C, -D and PlGF, have been identified. VEGF family members are disulfide-linked dimeric proteins that are important regulators of physiological and pathological vasculogenesis, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. VEGF-B is expressed in most tissues, especially in heart, skeletal muscle and pancreas. In many tissues, VEGF-B is co-expressed and can heterodimerize with VEGF (3). By alternative splicing, two isoforms of mature VEGF-B containing 167 or 186 amino acid (aa) residues exist (3, 4). The two VEGF-B isoforms have identical amino-terminal cysteine-knot VEGF homology domains but the carboxyl end of VEGF-B167 differs from that of VEGF-B186 by the presence of a highly basic cysteine-rich heparin binding domain. Whereas VEGF-B186 is a secreted diffusible protein, VEGF-B167 is sequestered into the cell matrix after secretion. Both VEGF-B isoforms bind VEGF receptor 1 (VEGF R1), but not VEGF R2 or VEGF R3 (5). On endothelial cells, ligation of VEGF R1 by VEGF-B has been shown to regulate the expression and activity of urokinase type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. VEGF-B167 and a proteolytically processed form of VEGF-B186 (VEGF-B127) also bind neuropilin-1 (NP-1), a type I transmembrane receptor for semaphorins/collapsins, ligands involved in neuron guidance (6). Besides VEGF-B, NP-1 has been shown to bind PLGF-2, VEGF165 and VEGF R1 (6, 7). The many interactions of NP-1 with VEGF ligands and receptor suggests that NP-1 may function as a regulator of angiogenesis (7).
- Li, X. and U. Eriksson (2001) Int. J. Biochem Cell Biol. 33:421.
- Olofsson, B. et al. (1999) Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 10:528.
- Olofsson, B. et al. (1996) Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 93:2576.
- Grimmond, S. et al. (1996) Benome Res. 6:124.
- Olofsson, B. et al. (1998) Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 95:11709.
- Makinen, T. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:21217.
- Fuh, G. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:26690.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human VEGF-B167/186 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
9
Citations: Showing 1 - 9
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
MMP12 Inhibits Corneal Neovascularization and Inflammation through Regulation of CCL2.
Authors: Wolf M, Clay S. M, et al.
Sci Rep
-
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-B Induces a Distinct Electrophysiological Phenotype in Mouse Heart
Authors: Nikolay Naumenko, Jenni Huusko, Tomi Tuomainen, Jussi T. Koivumäki, Mari Merentie, Erika Gurzeler et al.
Frontiers in Physiology
-
Chronic exposure of colorectal cancer cells to bevacizumab promotes compensatory pathways that mediate tumour cell migration.
Authors: Fan F, Samuel S, Gaur P
Br. J. Cancer, 2011-03-15;104(8):1270-7.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Effect of chemotherapeutic stress on induction of vascular endothelial growth factor family members and receptors in human colorectal cancer cells.
Authors: Fan F, Gray MJ, Dallas NA, Yang AD, Van Buren G, Camp ER, Ellis LM
Mol. Cancer Ther., 2008-09-01;7(9):3064-70.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Upregulation of VEGF-A without angiogenesis in a mouse model of dilated cardiomyopathy caused by mitochondrial dysfunction.
Authors: Tham E, Wang J, Piehl F, Weber G
J. Histochem. Cytochem., 2002-07-01;50(7):935-44.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Vascular endothelial growth factor ligands and receptors that regulate human cytotrophoblast survival are dysregulated in severe preeclampsia and hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets syndrome.
Authors: Zhou Y, 2019, McMaster M, Woo K, Janatpour M, Perry J, Karpanen T, Alitalo K, Damsky C, Fisher SJ
2002-04-01;160(4):1405-23.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8)-encoded cytokines induce expression of and autocrine signaling by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in HHV-8-infected primary-effusion lymphoma cell lines and mediate VEGF-independent antiapoptotic effects.
Authors: Okruzhnov Y, Nicholas J
J. Virol., 2001-11-01;75(22):10933-40.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Adenoviral VEGF-B186R127S gene transfer induces angiogenesis and improves perfusion in ischemic heart
Authors: Henna Korpela, Olli-Pekka Hätinen, Tiina Nieminen, Rahul Mallick, Pyry Toivanen, Jonna Airaksinen et al.
iScience
-
Optimized riboswitch-regulated AAV vector for VEGF-B gene therapy
Authors: Reetta A. E. Eriksson, Tiina Nieminen, Lionel Galibert, Sanna K. Peltola, Petra Tikkanen, Piia Käyhty et al.
Frontiers in Medicine
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human VEGF-B167/186 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human VEGF-B167/186 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human VEGF-B167/186 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
