MagCellect Mouse Naive CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit Summary
Kit Summary
Specifications
Product Datasheets
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Enrichment of Naïve CD4+ T Cells from Mouse Splenocytes. Ficolled mouse splenocytes before (A) and after (B) processing with the MagCellect Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit. Cells were stained with FITC-conjugated Rat Anti-Mouse CD44 Monoclonal Antibody and PE-conjugated Rat Anti-Mouse CD62L Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB5761P).
Background: CD4
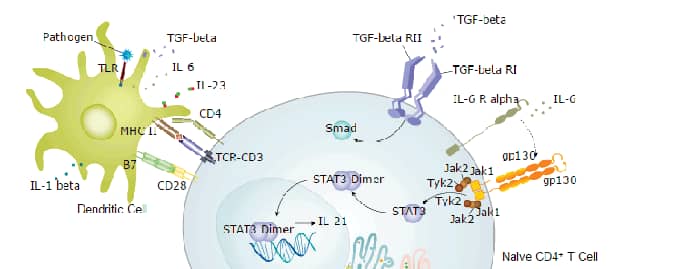
CD4 is a transmembrane glycoprotein that is expressed predominantly on thymocytes and a subset of mature T lymphocytes. It is a standard phenotype marker for the identification of T cell populations. CD4 is expressed along with CD8 on double positive T cells during their development in the thymus. Either CD4 or CD8 expression is then lost, giving rise to single positive (SP) CD4+ or CD8+ mature T cells. CD4+ SP cells, also known as T helper cells, further differentiate into multiple subsets of CD4+ cells including Th1, Th2, Th9, Th17,Th22, Tfh, and Treg cells which regulate humoral and cellular immunity. In human, CD4 is additionally expressed on macrophages, neutrophils, monocytes, NK cells, and neurons and glial cells in the brain. CD4 binds directly to MHC class II molecules on antigen presenting cells. This interaction contributes to the formation of the immunological synapse which is focused around the TCR-MHC class II-antigenic peptide interaction. CD4 also functions as a chemotactic receptor for IL-16 and, in human, as a coreceptor for the gp120 surface glycoprotein of HIV-1.
Assay Procedure
Refer to the product datasheet for complete product details.
Briefly, mouse naïve CD4+ T cells can be isolated using the following procedure:
- Incubate the single-cell suspension with the MagCellect Antibody Cocktail
- Add the MagCellect Streptavidin Ferrofluid
- Place the tube in a magnetic field
- Collect the desired cells while undesired cells remain attracted to the magnet
The MagCellect Mouse CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit (Catalog # MAGM205) contains the following reagents:
- MagCellect Mouse CD4+ T Cell Biotinylated Antibody Cocktail
- MagCellect Streptavidin Ferrofluid
- MagCellect Plus Buffer (10X)
This kit contains sufficient reagents to process up to 1 x 109 total cells.
Other Supplies Required
Reagents
- Ficoll-Hypaque™
- Hemocytometer
- Centrifuge
- Mouse Erythrocyte Lysing Kit (Catalog # WL2000)
- MagCellect Magnet (Catalog # MAG997) or equivalent
- 12 x 75 mm (5 mL) polystyrene round-bottom tubes
- Sterile Pasteur pipettes or transfer pipettes
NOTE: Reaction incubations must be carried out at 2 to 8° C in a refrigerator and not in an ice bath to avoid excessively low temperatures that can slow the kinetics of the optimized reactions.
Procedure Overview
R&D Systems Protocol for the Magnetic Isolation of Mouse Regulatory T Cells
PBMC Preparation
Prepare a single cell suspension of mononuclear cells.
Wash the cells once with excess PBS.
Centrifuge the cells for 10 minutes at 200 x g.

Decant the supernatant. If necessary, remove red blood cells using R&D Systems Mouse Erythrocyte Lysing Kit (Catalog # WL2000).
Resuspend the cells in a small volume of cold 1X MagCellect Plus Buffer.

Perform a cell count.
Adjust the cell concentration to at least 20 x 107 cells/mL with cold 1X MagCellect Plus Buffer.

Transfer 20 x 107 cells (1 mL) into a 5 mL polystyrene tube.
Add 200 μL of MagCellect Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Biotinylated Antibody Cocktail.
Mix the cell-antibody suspension and incubate at 2 °C to 8 °C for 15 minutes.

Add 250 μL of MagCellect Streptavidin Ferrofluid to the cell suspension.
Mix gently.
Incubate at 2 °C to 8 °C for 15 minutes.

Add 1.55 mL of MagCellect Plus Buffer.
Mix gently.

Place the reaction tube in the MagCellect Magnet.
Incubate for 6 minutes at room temperature (18 °C to 25 °C).
Transfer the supernatant containing the naïve CD4+ T cells into a new 5 mL tube.

Repeat the magnetic depletion with the new tube containing the recovered cells. The supernatant obtained at the end of this step is the final depleted cell fraction containing the desired enriched naïve CD4+ T cells.

Technical Hints
- If sterile cells are required following the cell selection, the entire procedure should be carried out in a laminar flow hood to maintain sterile conditions. Use sterile equipment when pipetting reagents that will be reused at a later date.
- Avoid antibody capping on cell surfaces and non-specific cell tagging by working fast, keeping cells and solutions cold through the use of pre-cooled solutions and by adhering to the incubation times and temperatures specified in the protocol. Increased temperature and prolonged incubation times may lead to non-specific cell labeling thus lowering cell purity and yield.
- When processing different numbers of cells observe the following guidelines: keep antibody cocktail and ferrofluid incubation times and temperatures the same; keep the cell density at 20 x 107 cells/mL; add 10 μL of the antibody cocktail per 1 x 107 cells being processed; add 10 μL of Streptavidin Ferrofluid per 1 x 107 cells being processed.
- When processing 20 x 107 cells or fewer, use the 12 x 75 mm (5 mL) tubes with the MagCellect Magnet horizontally positioned to accommodate up to six 5 mL tubes. Do not process more than 20 x 107 cells in each 5 mL tube and do not exceed a total reaction volume of 3 mL in each tube. A reaction volume of 2 mL is recommended for processing 10 x 107 cells. A reaction volume of 1 mL is recommended when processing 5 x 107 or fewer cells. Reaction volume adjustments must be made using 1X MagCellect Buffer just prior to the magnetic separation step.
- When processing greater than 20 x 107 cells, use the 17 x 100 mm (15 mL) tubes with the MagCellect magnet vertically positioned to accommodate up to two 15 mL tubes. Do not process more than 60 x 107 cells in each 15 mL tube and do not exceed a total reaction volume of 9 mL in each tube. When using this larger tube, increase the reaction volume before the magnetic separation step according to the following formula: 3 mL for each 20 x 107 cells processed. Also increase the magnetic incubation time described in to 8 minutes. Reaction volume adjustments must be made using 1X MagCellect Buffer just prior to the magnetic separation step.
Citations for MagCellect Mouse Naive CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
16
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Hemin-primed dendritic cells suppress allergic airway inflammation through releasing extracellular vesicles
Authors: Y Wu, Q Yu, M Zhang, Y Zhou, X Su, M Wu, J Lv, Z Xia
Journal of leukocyte biology, 2021-07-23;0(0):. 2021-07-23
-
CCL11 increases the proportion of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Treg cells and the production of IL?2 and TGF?&beta by CD4+ T�cells via the STAT5 signaling pathway
Authors: R Wang, K Huang
Mol Med Rep, 2020-04-01;0(0):. 2020-04-01
-
BATF3-dependent dendritic cells drive both effector and regulatory T-cell responses in bacterially infected tissues
Authors: IC Arnold, X Zhang, M Artola-Bor, A Fallegger, P Sander, P Johansen, A Müller
PLoS Pathog., 2019-06-12;15(6):e1007866. 2019-06-12
-
Enhanced susceptibility to chemically induced colitis caused by excessive endosomal TLR signaling in LRBA-deficient mice
Authors: KW Wang, X Zhan, W McAlpine, Z Zhang, JH Choi, H Shi, T Misawa, T Yue, D Zhang, Y Wang, S Ludwig, J Russell, M Tang, X Li, AR Murray, EMY Moresco, EE Turer, B Beutler
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2019-05-16;116(23):11380-11389. 2019-05-16
-
Critical role of Tim-3 mediated autophagy in chronic stress induced immunosuppression
Authors: A Qin, T Zhong, H Zou, X Wan, B Yao, X Zheng, D Yin
Cell Biosci, 2019-01-22;9(0):13. 2019-01-22
-
Environmental cues received during development shape dendritic cell responses later in life
Authors: JL Meyers, B Winans, E Kelsaw, A Murthy, S Gerber, BP Lawrence
PLoS ONE, 2018-11-09;13(11):e0207007. 2018-11-09
-
Integrated STAT3 and Ikaros Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Activities Regulate Bcl-6 Expression in CD4(+) Th Cells
Authors: KA Read, MD Powell, CE Baker, BK Sreekumar, VM Ringel-Sca, H Bachus, RE Martin, ID Cooley, IC Allen, A Ballestero, KJ Oestreich
J. Immunol., 2017-08-28;0(0):. 2017-08-28
-
Basophils as a primary inducer of the T helper type 2 immunity in ovalbumin-induced allergic airway inflammation.
Authors: Zhong W, Su W, Zhang Y, Liu Q, Wu J, Di C, Zhang Z, Xia Z
Immunology, 2014-06-01;142(2):202-15. 2014-06-01
-
Attenuation of experimental colitis in glutathione peroxidase 1 and catalase double knockout mice through enhancing regulatory T cell function.
Authors: Kim H, Lee A, Choi E, Kie J, Lim W, Lee H, Moon B, Seoh J
PLoS ONE, 2014-04-17;9(4):e95332. 2014-04-17
-
To investigate the necessity of STRA6 upregulation in T cells during T cell immune responses.
Authors: Terra R, Wang X, Hu Y, Charpentier T, Lamarre A, Zhong M, Sun H, Mao J, Qi S, Luo H, Wu J
PLoS ONE, 2013-12-31;8(12):e82808. 2013-12-31
-
TNF-like ligand 1A (TL1A) gene knockout leads to ameliorated collagen-induced arthritis in mice: implication of TL1A in humoral immune responses.
Authors: Wang X, Hu Y, Charpentier T, Lamarre A, Qi S, Wu J, Luo H
J Immunol, 2013-10-18;191(11):5420-9. 2013-10-18
-
Modeling and experimental methods to probe the link between global transcription and spatial organization of chromosomes.
Authors: Iyer K, Maharana S, Gupta S, Libchaber A, Tlusty T, Shivashankar G
PLoS ONE, 2012-10-01;7(10):e46628. 2012-10-01
-
Developmental heterogeneity in DNA packaging patterns influences T-cell activation and transmigration.
Authors: Gupta S, Marcel N, Talwar S, Garg M, R I, Perumalsamy L, Sarin A, Shivashankar G
PLoS ONE, 2012-09-05;7(9):e43718. 2012-09-05
-
The effect of conditional EFNB1 deletion in the T cell compartment on T cell development and function.
Authors: Jin W, Qi S, Luo H
BMC Immunol., 2011-12-19;12(0):68. 2011-12-19
-
Tolerogenic signals delivered by dendritic cells to T cells through a galectin-1-driven immunoregulatory circuit involving interleukin 27 and interleukin 10.
Authors: Ilarregui JM, Croci DO, Bianco GA, Toscano MA, Salatino M, Vermeulen ME, Geffner JR, Rabinovich GA
Nat. Immunol., 2009-08-09;10(9):981-91. 2009-08-09
-
Differential glycosylation of TH1, TH2 and TH-17 effector cells selectively regulates susceptibility to cell death.
Authors: Toscano MA, Bianco GA, Ilarregui JM, Croci DO, Correale J, Hernandez JD, Zwirner NW, Poirier F, Riley EM, Baum LG, Rabinovich GA
Nat. Immunol., 2007-06-24;8(8):825-34. 2007-06-24
FAQs
-
When using MacCellect Cell Isolation kits (MAGM*** or MAGH***), why is it important to lyse red blood cells before starting the cell isolation protocol?
It is important to remove red blood cells before the isolation protocol using MagCellect isolation kits because not doing so can cause a poorer yield of selected cells. Red blood cells become sticky during the incubation protocols and may interfere with the interactions needed for removal of unwanted populations.
Reviews for MagCellect Mouse Naive CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review MagCellect Mouse Naive CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit and earn rewards!
Have you used MagCellect Mouse Naive CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image