Mouse CD36/SR-B3 Antibody Summary
Gly30-Lys439
Accession # Q3UAI3
Applications
Mouse CD36/SR-B3 Sandwich Immunoassay
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
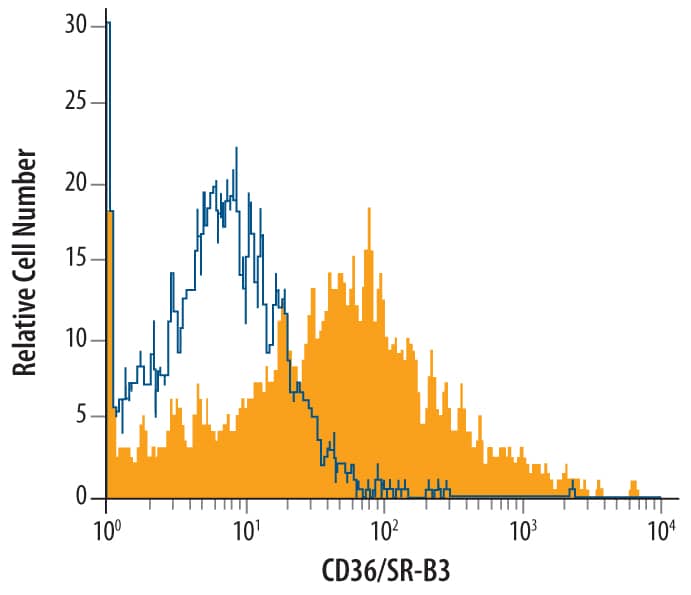
Detection of CD36/SR‑B3 in J774A.1 Mouse Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. J774A.1 mouse reticulum cell sarcoma macrophage cell line was stained with Goat Anti-Mouse CD36/SR-B3 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2519, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # AB-108-C, open histogram), followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0107).
 View Larger
View Larger
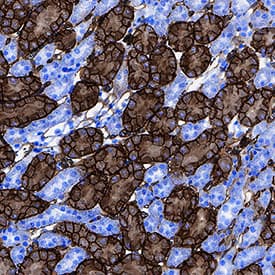
CD36/SR‑B3 in Mouse Kidney. CD36/SR-B3 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of mouse kidney using Goat Anti-Mouse CD36/SR-B3 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2519) at 3 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Goat IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC004). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm and plasma membrane. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
 View Larger
View Larger
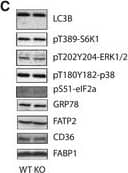
Detection of Mouse CD36/SR-B3 by Western Blot Liver GADD45 beta controls liver fatty acid handling by cytosolic FABP1 retentionA, BMale 12‐weeks‐old wild‐type (WT; C57Bl/6J) or obese/diabetic (db/db; BKS.Cg‐m+/+ Lepr DB/J) mice with (Ad‐G45b OE) or without (Ad‐NC) prior liver‐restricted GADD45 beta over‐expression were fasted and insulin was injected with livers harvested shortly thereafter and subsequently liver proteins were subjected to immunoblotting for insulin signalling proteins including phosphoprotein kinase B (PKB/Akt; A) and glycogen synthase kinase beta (GSK3b; B). Inserts show representative blots (n = 6/group).C, DRepresentative immunoblots (C) and relative abundance quantifications (D; n = 6) of proteins and phosphoproteins including light chain 3 isoform B (LC3B), S6 kinase 1 (S6K1), p42/44 mitogen activated protein kinase (ERK1/2), eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha (eIF2a), glucose regulated protein 78 (GRP78/HSPA5), fatty acid transport protein 2 (FATP2/SLC27A2), cluster determinant 36 (CD36/FAT) and fatty acid binding protein 1 (FABP1) from fasted GADD45 beta +/+ (WT) or GADD45 beta −/− (KO) mice.ERepresentative immunoblots of HNF4a (nuclear marker), BCKDE1A (mitochondrial marker), NTCP (microsomal marker) and ARG1 (cytosolic marker) from liver whole tissue lysate (W) as well as fractionated organelles/intraceuular structures including nuclei (N), mitochondria (MT), microsomes (MS) and cytoplasm (C), from GADD45 beta +/+ (WT) and GADD45 beta −/− (KO) mice.Data information: Data are mean ± SEM. The statistical test used and respective P‐value outputs can be found in Appendix Table S1. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27137487), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
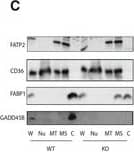
Detection of Mouse CD36/SR-B3 by Western Blot Liver GADD45 beta controls liver fatty acid handling by cytosolic FABP1 retentionA, BMale GADD45 beta +/+ (WT; n = 16) or GADD45 beta −/− (KO; n = 15) mice fasted for 24 h (fasted) with (AV‐G45b OE) or without (AV‐NC) liver‐restricted GADD45 beta over‐expression (n = 7–8/group). Liver mRNA expression of Gadd45b (A) as well as fatty acid metabolic genes (B) encompassing transport (Slc28a2, Slc27a5, Cd36), intracellular binding (Fabp1, Dbi) and metabolism (Acly, Dgat1, Atgl, Hsl).CRepresentative immunoblots of FATP2, CD36, FABP1 and GADD45 beta from liver whole tissue lysate (W) as well as fractionated organelles/intracellular structures including nuclei (N), mitochondria (MT), microsomes (MS) and cytoplasm (C), from GADD45 beta +/+ (WT) and GADD45 beta −/− (KO) mice.DQuantified band densities of FABP1 enrichment from fractions in C (n = 4/group).ELiver fraction enrichment of FABP1 from male GADD45 beta +/+ (WT) or GADD45 beta −/− (KO) mice fasted for 24 h with (AD‐G45b OE) or without (AD‐NC) liver‐restricted GADD45 beta over‐expression (n = 4/group). Insert shows a representative FABP1 immunoblot.FLiver fraction enrichment of FABP1 from obese/diabetic male db/db mice fasted for 24 h with (AD‐G45b OE) or without (AD‐NC) liver‐restricted GADD45 beta over‐expression (n = 4/group). Insert shows a representative FABP1 immunoblot.GFABP1 and GADD45B immunoblots from Flag immunoprecipitations (IP‐FLAG) or mock IP (IP‐HA) from liver input samples from mice with (AD‐G45b OE) or without (AD‐NC) liver‐restricted GADD45 beta over‐expression. Shown is a representative immunoblot from 3 separate experiments using 3 different input samples per condition.H–JLiver tissue long‐chain acyl‐CoA (LC‐acyl‐CoA) concentrations were determined in GADD45 beta +/+ (WT) or GADD45 beta −/− (KO) mice (H; n = 6/group) with (AD‐G45b OE) or without (AD‐NC) liver‐restricted GADD45 beta over‐expression (I; n = 5/group). Liver LC‐acyl‐CoA concentrations were determined in wild‐type (WT; C57Bl/6J) or obese/diabetic (db/db; BKS.Cg‐m+/+ Lepr DB/J) mice with (AD‐G45b OE) or without (AD‐NC) liver‐restricted GADD45 beta over‐expression (J; n = 4/group).Data information: Data are mean ± SEM. Effect of genotype, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Effect of viral manipulation: #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001. The statistical test used and respective P‐value outputs can be found in Appendix Table S1. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27137487), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
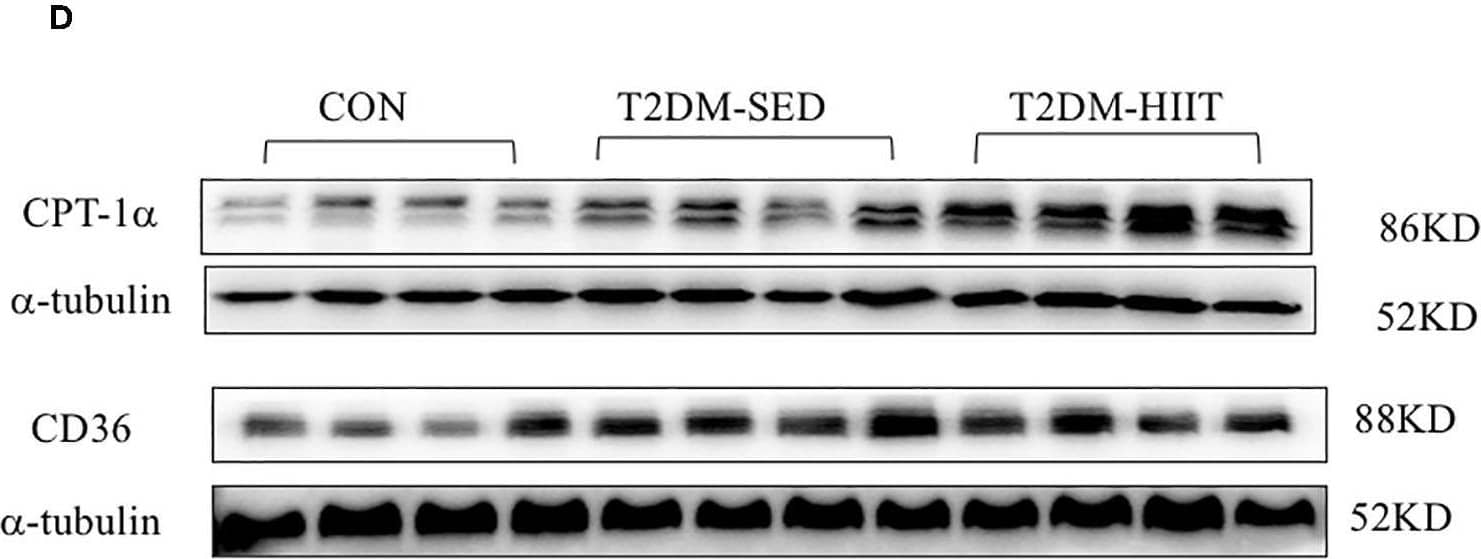 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse CD36/SR-B3 by Western Blot HIIT improves lipid metabolism of skeletal muscle in T2DM mice. (A,D) Protein expressions of ACC, HMGCR, CPT-1 alpha, CD36, and internal control alpha -tubulin in skeletal muscle. (B,C,E,F) Quantification of proteins described in (A,D) with normalization to protein levels of alpha -tubulin. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. n = 4 per group; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32922365), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: CD36/SR-B3
CD36 (alternatively known as platelet membrane glycoprotein IV (GPIV), thrombospondin receptor, fatty acid translocase (FAT), and scavenger receptor class B, member 3 (SR-B3)) is an 88 kDa, integral membrane glycoprotein that belongs to the class B scavenger receptor family (1, 2). The molecule is described as being ditopic, with two transmembrane segments connected by an extracellular loop (3). Mouse CD36 is synthesized as a 472 amino acid (aa) protein that contains a 6 aa N‑terminal cytoplasmic domain, a 22 aa N‑terminal transmembrane segment, a 420 aa extracellular “loop”, a 22 aa C‑terminal transmembrane segment, and a 9 aa C‑terminal cytoplasmic tail (4). Both cytoplasmic tails are palmitoylated, with the C‑terminal tail involved in oxidized LDL binding (5, 6). With respect to the extracellular loop, the N‑terminal region is believed to bind both thrombospondin-1 and Plasmodium-infected erythrocytes. Other ligands for CD36 include long-chain fatty acids, collagen, phospholipids and apoptotic cells (1). The extracellular loop of mouse CD36 is 94%, 92%, 84%, and 84% aa identical to the extracellular loops of rat, hamster, human, and bovine CD36, respectively. Cells known to express CD36 include capillary endothelium, adipocytes, skeletal muscle cells, intestinal epithelium, smooth muscle cells, and hematopoietic cells such as red blood cells, platelets, and monocytes (1). On the surface of cells, CD36 is suggested to exist as a dimer in response to ligation (7). CD36 is reported to regulate fatty uptake, act as an angiogenic with TSP-1, and participate in the clearance of apoptotic phagocytes (1, 8).
- Febbraio, M. et al. (2001) J. Clin. Invest. 108:795.
- Silverstein, R.L. and M. Febbraio (2000) Curr. Opin. Lipid. 11:483.
- Gruarin, P. et al. (2000) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 275:446.
- Endemann, G. et al. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268:11811.
- Malaud, E. et al. (2002) Biochem. J. 364:507.
- Tao, N. et al. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:22315.
- Daviet, L. et al. (1997) Thromb. Haemost. 78:897.
- Simantov, R. and R.L. Silverstein (2003) Front. Biosci. 8:s874.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse CD36/SR-B3 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
48
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Single-cell RNA-seq reveals cellular heterogeneity of mouse carotid artery under disturbed flow
Authors: Li F, Yan K, Wu L Et Al.
Cell death discovery
-
Increased retinoic acid catabolism in olfactory sensory neurons activates dormant tissue-specific stem cells and accelerates age-related metaplasia
Authors: S Håglin, A Berghard, S Bohm
J. Neurosci., 2020-05-08;0(0):.
-
L-PGDS-PGD2-DP1 Axis Regulates Phagocytosis by CD36+ MGs/M?s That Are Exclusively Present Within Ischemic Areas After Stroke
Authors: Nakagomi, T;Narita, A;Nishie, H;Nakano-Doi, A;Sawano, T;Fukuda, Y;Matsuyama, T;
Cells
Species: Transgenic Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Nalmefene, an opioid receptor modulator, aggravates atherosclerotic plaque formation in apolipoprotein E knockout mice by enhancing oxidized low-density lipoprotein uptake in macrophages
Authors: Koga, M;Inada, K;Yamada, A;Maruoka, K;Yamauchi, A;
Biochemistry and biophysics reports
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Microvascular insulin resistance associates with enhanced muscle glucose disposal in CD36 deficiency
Authors: Shibao, CA;Peche, VS;Williams, IM;Samovski, D;Pietka, TA;Abumrad, NN;Gamazon, E;Goldberg, I;Wasserman, D;Abumrad, NA;
medRxiv : the preprint server for health sciences
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Peroxisomal defects in microglial cells induce a disease-associated microglial signature
Authors: Quentin Raas, Ali Tawbeh, Mounia Tahri-Joutey, Catherine Gondcaille, Céline Keime, Romain Kaiser et al.
Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience
-
Differential Roles of CD36 in Regulating Muscle Insulin Response Depend on Palmitic Acid Load
Authors: J Sun, Y Su, J Chen, D Qin, Y Xu, H Chu, T Lu, J Dong, L Qin, W Li
Biomedicines, 2023-02-28;11(3):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Ganglioside GM3 prevents high fat diet-induced hepatosteatosis via attenuated insulin signaling pathway
Authors: O Tajima, Y Fujita, Y Ohmi, K Furukawa, K Furukawa
PLoS ONE, 2023-02-24;18(2):e0281414.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
A vein wall cell atlas of murine venous thrombosis determined by single-cell RNA sequencing
Authors: DeRoo E, Zhou T, Yang H et al.
Communications biology
-
Novel fat taste receptor agonists curtail progressive weight gain in obese male mice
Authors: AS Khan, A Hichami, B Murtaza, ML Louillat-H, C Ramseyer, M Azadi, S Yesylevsky, F Mangin, F Lirussi, J Leemput, JF Merlin, A Schmitt, M Suliman, J Bayardon, S Semnanian, S Jugé, NA Khan
Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2022-11-19;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Semaglutide May Alleviate Hepatic Steatosis in T2DM Combined with NFALD Mice via miR-5120/ABHD6
Authors: R Li, Z Ye, D She, P Fang, G Zong, K Hu, D Kong, W Xu, L Li, Y Zhou, K Zhang, Y Xue
Drug Design, Development and Therapy, 2022-10-12;16(0):3557-3572.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
CD36 deficiency inhibits proliferation by cell cycle control in skeletal muscle cells
Authors: Jingyu Sun, Yajuan Su, Yaning Xu, Duran Qin, Qianhui He, Haiping Qiu et al.
Frontiers in Physiology
-
Meflin defines mesenchymal stem cells and/or their early progenitors with multilineage differentiation capacity
Authors: Akitoshi Hara, Katsuhiro Kato, Toshikazu Ishihara, Hiroki Kobayashi, Naoya Asai, Shinji Mii et al.
Genes to Cells
-
Circulating CD36 is increased in hyperlipidemic mice: Cellular sources and triggers of release
Authors: Sudipta Biswas, Detao Gao, Jessica B. Altemus, Umar R. Rekhi, Ellen Chang, Maria Febbraio et al.
Free Radical Biology and Medicine
-
Sea-Buckthorn Seed Oil Induces Proliferation of both Normal and Dysplastic Keratinocytes in Basal Conditions and under UVA Irradiation
Authors: M Dudau, AC Vilceanu, E Codrici, S Mihai, ID Popescu, L Albulescu, I Tarcomnicu, G Moise, LC Ceafalan, ME Hinescu, AM Enciu, C Tanase
Journal of personalized medicine, 2021-04-07;11(4):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
CD36 and LC3B initiated autophagy in B cells regulates the humoral immune response
Authors: C He, S Wang, C Zhou, M He, J Wang, M Ladds, D Lianoudaki, SK Sedimbi, DP Lane, LS Westerberg, S Li, MCI Karlsson
Autophagy, 2021-02-16;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot -
Maternal and offspring high-fat diet leads to platelet hyperactivation in male mice offspring
Authors: RS Gaspar, AJ Unsworth, A Al-Dibouni, AP Bye, T Sage, M Stewart, S Wells, RD Cox, JM Gibbins, D Sellayah, C E Hughes
Scientific Reports, 2021-01-14;11(1):1473.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Plasma
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Effects of High-Intensity Exercise Training on Adipose Tissue Mass, Glucose Uptake and Protein Content in Pre- and Post-menopausal Women
Authors: Camilla M. Mandrup, Caroline B. Roland, Jon Egelund, Michael Nyberg, Lotte Hahn Enevoldsen, Andreas Kjaer et al.
Frontiers in Sports and Active Living
-
Hesperidin blocks varenicline-aggravated atherosclerotic plaque formation in apolipoprotein E knockout mice by downregulating net uptake of oxidized low-density lipoprotein in macrophages
Authors: M Koga, Y Kanaoka, K Inada, S Omine, Y Kataoka, A Yamauchi
J. Pharmacol. Sci., 2020-02-28;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Culture Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
IL-34 promotes foam cell formation by enhancing CD36 expression through p38 MAPK pathway
Authors: Q Liu, J Fan, J Bai, L Peng, T Zhang, L Deng, G Wang, Y Zhao, J Nong, M Zhang, Y Wang
Sci Rep, 2018-11-26;8(1):17347.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization, Western Blot -
Vimentin deficiency in macrophages induces increased oxidative stress and vascular inflammation but attenuates atherosclerosis in mice
Authors: L Håversen, JP Sundelin, A Mardinoglu, M Rutberg, M Ståhlman, U Wilhelmsso, LM Hultén, M Pekny, P Fogelstran, JF Bentzon, M Levin, J Borén
Sci Rep, 2018-11-19;8(1):16973.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr, Western Blot -
Metabolomic insights of macrophage responses to graphene nanoplatelets: Role of scavenger receptor CD36
Authors: SX Adamson, R Wang, W Wu, B Cooper, J Shannahan
PLoS ONE, 2018-11-07;13(11):e0207042.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Orosensory Detection of Dietary Fatty Acids Is Altered in CB1R−/− Mice
Authors: Léa Brissard, Julia Leemput, Aziz Hichami, Patricia Passilly-Degrace, Guillaume Maquart, Laurent Demizieux et al.
Nutrients
-
Endothelial cell CD36 optimizes tissue fatty acid uptake
Authors: Ni-Huiping Son, Debapriya Basu, Dmitri Samovski, Terri A. Pietka, Vivek S. Peche, Florian Willecke et al.
Journal of Clinical Investigation
-
Low-fat diet, and medium-fat diets containing coconut oil and soybean oil exert different metabolic effects in untrained and treadmill-trained mice
Authors: Mark Christian Manio, Shigenobu Matsumura, Kazuo Inoue
Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition
-
Inhibition of CD36 reduces visceral fat accumulation and improves insulin resistance in diet-induced obese BDNF Val66Met mice
Authors: J Yang, KW Park, S Cho
J. Biol. Chem., 2018-06-18;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
A novel role for scavenger receptor B1 as a contributor to the capture of specific volatile odorants in the nasal cavity
Authors: S Tsuzuki, Y Kimoto, S Lee, T Sugawara, Y Manabe, K Inoue
Biomed. Res., 2018-01-01;39(3):117-129.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
A role for scavenger receptor B1 as a captor of specific fatty acids in taste buds of circumvallate papillae
Authors: S Tsuzuki, S Lee, Y Kimoto, T Sugawara, Y Manabe, K Inoue
Biomed. Res., 2018-01-01;39(6):295-300.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Partitioning of adipose lipid metabolism by altered expression and function of PPAR isoforms after bariatric surgery
Authors: C Jahansouz, H Xu, AV Hertzel, S Kizy, KA Steen, R Foncea, FJ Serrot, N Kvalheim, G Luthra, K Ewing, DB Leslie, S Ikramuddin, DA Bernlohr
Int J Obes (Lond), 2017-08-14;42(2):139-146.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Protein
Applications: Western Blot -
CCN3 Regulates Macrophage Foam Cell Formation and Atherosclerosis
Authors: H Shi, C Zhang, V Pasupuleti, X Hu, DA Prosdocimo, W Wu, Y Qing, S Wu, H Mohammad, SL Gerson, B Perbal, PA Klenotic, N Dong, Z Lin
Am. J. Pathol., 2017-06-01;187(6):1230-1237.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
CD36 is essential for endurance improvement, changes in�whole-body metabolism, and efficient PPAR-related transcriptional responses in the muscle with exercise training
Authors: MCC Manio, S Matsumura, D Masuda, K Inoue
Physiol Rep, 2017-05-01;5(10):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
2Intestinal epithelial cell Caveolin 1 regulates fatty acid and lipoprotein cholesterol plasma levels
Authors: JP Otis, MC Shen, V Quinlivan, JL Anderson, SA Farber
Dis Model Mech, 2017-01-26;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Cell-surface CD36 in monocyte/macrophage contributes to phagocytosis during the resolution phase of ischemic stroke in mice
J Biol Chem, 2016-09-19;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
CD36 Differently Regulates Macrophage Responses to Smooth and Rough Lipopolysaccharide
Authors: R Biedro?, A Peru?, S Józefowski
PLoS ONE, 2016-04-13;11(4):e0153558.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Recombinant Protein
Applications: Binding Assay -
Expression of CD36 by Olfactory Receptor Cells and Its Abundance on the Epithelial Surface in Mice.
Authors: Lee S, Eguchi A, Tsuzuki S, Matsumura S, Inoue K, Iwanaga T, Masuda D, Yamashita S, Fushiki T
PLoS ONE, 2015-07-17;10(7):e0133412.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Regulation of AMPK activation by CD36 links fatty acid uptake to beta-oxidation.
Authors: Samovski D, Sun J, Pietka T, Gross R, Eckel R, Su X, Stahl P, Abumrad N
Diabetes, 2014-08-25;64(2):353-9.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
CD36 protein influences myocardial Ca2+ homeostasis and phospholipid metabolism: conduction anomalies in CD36-deficient mice during fasting.
Authors: Pietka, Terri A, Sulkin, Matthew, Kuda, Ondrej, Wang, Wei, Zhou, Dequan, Yamada, Kathryn, Yang, Kui, Su, Xiong, Gross, Richard, Nerbonne, Jeanne M, Efimov, Igor R, Abumrad, Nada A
J Biol Chem, 2012-09-27;287(46):38901-12.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
CD36 is Involved in Astrocyte Activation and Astroglial Scar Formation
Authors: Yi Bao, Luye Qin, Eunhee Kim, Sangram Bhosle, Hengchang Guo, Maria Febbraio et al.
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism
-
Native incretins prevent the development of atherosclerotic lesions in apolipoprotein E knockout mice.
Authors: Nagashima M, Watanabe T, Terasaki M
Diabetologia, 2011-07-24;54(10):2649-59.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Silencing of either SR-A or CD36 reduces atherosclerosis in hyperlipidaemic mice and reveals reciprocal upregulation of these receptors.
Authors: Makinen PI, Lappalainen JP, Heinonen SE, Leppanen P, Lahteenvuo MT, Aarnio JV, Heikkila J, Turunen MP, Yla-Herttuala S
Cardiovasc. Res., 2010-07-15;88(3):530-8.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, Western Blot -
Deficiency in the nuclear factor E2-related factor-2 transcription factor results in impaired adipogenesis and protects against diet-induced obesity.
Authors: Pi J, Leung L, Xue P, Wang W, Hou Y, Liu D, Yehuda-Shnaidman E, Lee C, Lau J, Kurtz TW, Chan JY
J. Biol. Chem., 2010-01-20;285(12):9292-300.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Cilostazol inhibits modified low-density lipoprotein uptake and foam cell formation in mouse peritoneal macrophages.
Authors: Okutsu R, Yoshikawa T, Nagasawa M, Hirose Y, Takase H, Mitani K, Okada K, Miyakoda G, Yabuuchi Y
Atherosclerosis, 2008-11-17;204(2):405-11.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
CD36/fatty acid translocase, an inflammatory mediator, is involved in hyperlipidemia-induced exacerbation in ischemic brain injury.
Authors: Kim E, Tolhurst AT, Qin LY, Chen XY, Febbraio M, Cho S
J. Neurosci., 2008-04-30;28(18):4661-70.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Transcriptional regulation of fatty acid translocase/CD36 expression by CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha.
Authors: Qiao L, Zou C, Shao P, Schaack J, Johnson PF, Shao J
J. Biol. Chem., 2008-02-08;283(14):8788-95.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Tetraspanin CD81 is required for the alpha v beta5-integrin-dependent particle-binding step of RPE phagocytosis.
Authors: Chang Y, Finnemann SC
J. Cell. Sci., 2007-08-07;120(0):3053-63.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Immunoprecipitation -
Malaria Parasites Hijack Host Receptors From Exosomes to Capture Lipoproteins
Authors: Iso-o N, Komatsuya K, Tokumasu F Et al.
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology
-
Blockade of Macrophage CD147 Protects Against Foam Cell Formation in Atherosclerosis
Authors: Lv JJ, Wang H, Cui HY, et al.
Frontiers in cell and developmental biology
-
A Systems Biology Approach to Deciphering the Etiology of Steatosis Employing Patient-Derived Dermal Fibroblasts and iPS Cells
Authors: Jozefczuk J, Kashofer K, Ummanni R et al.
Front Physiol
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse CD36/SR-B3 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Mouse CD36/SR-B3 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Mouse CD36/SR-B3 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image




