Mouse JAM-C Antibody Summary
Val32-Asn241
Accession # Q9D8B7
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
JAM-C in Mouse Embryo. JAM-C was detected in immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse embryo (15 d.p.c.) using Goat Anti-Mouse JAM-C Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1213) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to muscle cells. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
JAM‑C in Mouse Splenocytes. JAM-C was detected in immersion fixed mouse splenocytes using Goat Anti-Mouse JAM-C Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1213) at 15 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.
 View Larger
View Larger
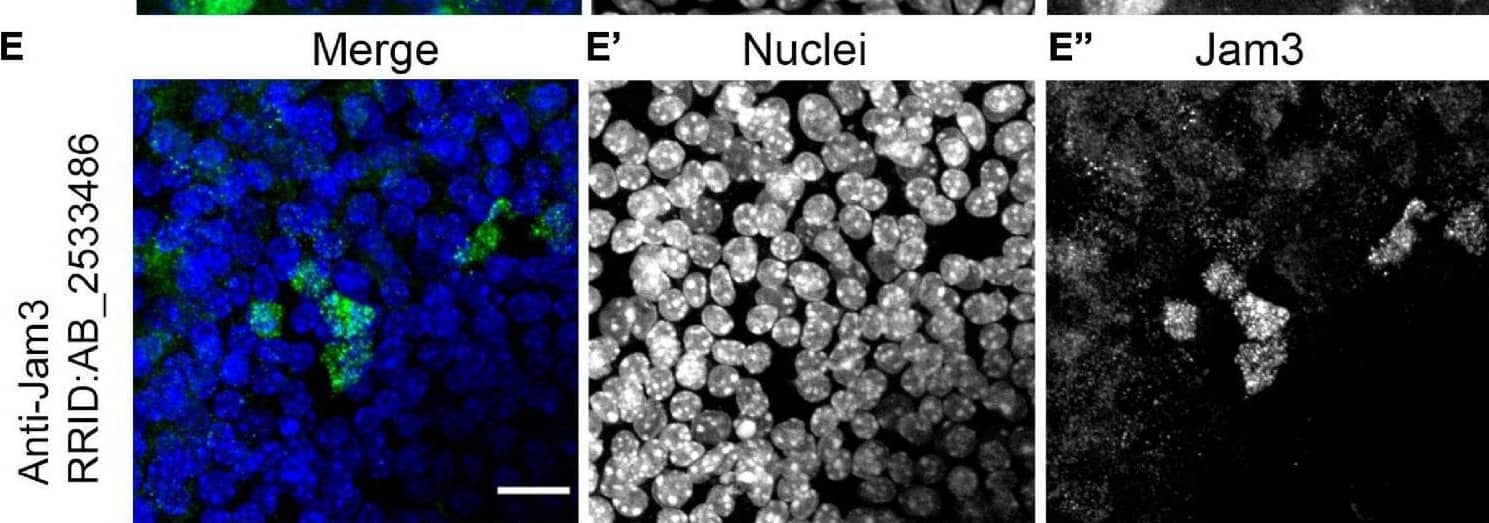
Detection of JAM-C by Immunohistochemistry Junctional adhesion molecule 3 (Jam3) is expressed in multiciliated cells in the mouse airway epithelium. (A) Immunohistochemistry of Jam3 in the mouse airway epithelium. Black arrows point to multiciliated cells, while black arrowheads point toward non-ciliated cells. (A’) A higher magnification image for a Jam3 immunohistochemistry in the mouse airway epithelium. (B’) A magnification of an immunohistochemistry image of Jam3 in the mouse airway epithelium. (B) Immunofluorescence in mouse whole-mount trachea for Jam3 in red (gray in panel B’), acetylated tubulin in green (gray in panel B’), and DAPI in blue (gray in panel B”). (C) Confocal image with higher magnification for Jam3 localization in whole-mount tracheas, Jam3 in red (gray in panel C’), and acetylated tubulin in green (gray in panel C”). (D,E) Jam3 immunofluorescence in MTECs differentiated for 14 days in vitro, nuclei in blue (gray in panels D’,E’), and Jam3 in green (gray in panels D’,E”) using two different antibodies. Scale bar represents 10 μm in panel (C), represents 10 μm, and represents 20 μm in panels (D,E). White arrowhead point a MCC with low Jam3 expression levels. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34395412), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
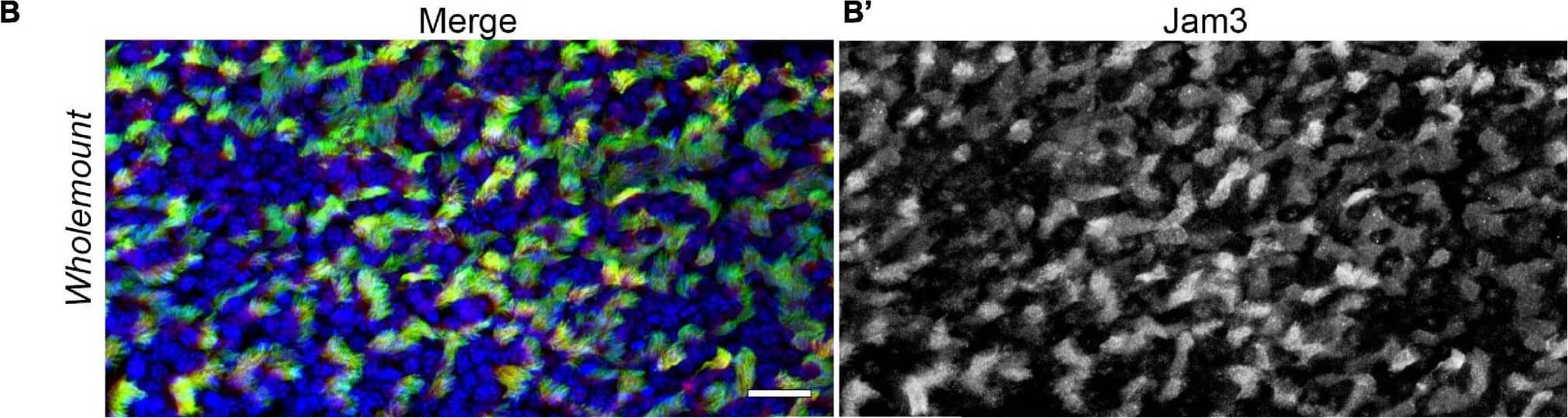
Detection of JAM-C by Immunohistochemistry Junctional adhesion molecule 3 (Jam3) is expressed in multiciliated cells in the mouse airway epithelium. (A) Immunohistochemistry of Jam3 in the mouse airway epithelium. Black arrows point to multiciliated cells, while black arrowheads point toward non-ciliated cells. (A’) A higher magnification image for a Jam3 immunohistochemistry in the mouse airway epithelium. (B’) A magnification of an immunohistochemistry image of Jam3 in the mouse airway epithelium. (B) Immunofluorescence in mouse whole-mount trachea for Jam3 in red (gray in panel B’), acetylated tubulin in green (gray in panel B’), and DAPI in blue (gray in panel B”). (C) Confocal image with higher magnification for Jam3 localization in whole-mount tracheas, Jam3 in red (gray in panel C’), and acetylated tubulin in green (gray in panel C”). (D,E) Jam3 immunofluorescence in MTECs differentiated for 14 days in vitro, nuclei in blue (gray in panels D’,E’), and Jam3 in green (gray in panels D’,E”) using two different antibodies. Scale bar represents 10 μm in panel (C), represents 10 μm, and represents 20 μm in panels (D,E). White arrowhead point a MCC with low Jam3 expression levels. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34395412), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
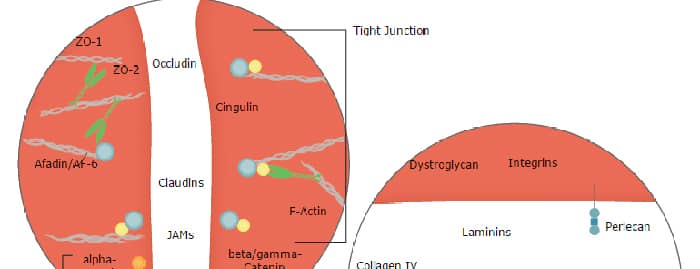
Background: JAM-C
The family of junctional adhesion molecules (JAM), comprised of at least three members, are type I transmembrane receptors belonging to the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily (1, 2). These proteins are localized in the tight junctions between endothelial cells or epithelial cells. Some family members are also found on blood leukocytes and platelets. Mouse JAM-C cDNA predicts a 310 amino acid (aa) residue precursor protein with a putative 31 aa signal peptide, a 210 aa extracellular region containing two Ig domains, an 18 aa transmembrane domain and a 51 aa cytoplasmic domain containing a PDZ-binding motif and a PKC phosphorylation site (3). Mouse JAM-C shares 86% aa sequence identity with its human homologue. It also shares approximately 31% and 35% aa sequence homology with mouse JAM-A and JAM-B, respectively (2). Mouse JAM-C is highly expressed during embryogenesis. In adult tissues, mouse JAM-C is restricted to endothelial cells, lymph endothelial cells in the kidney, lymph node and Peyer’s patches where the protein can be localized to the high endothelial venules (3). Although human JAM-C is expressed on human platelets and a subset of leukocytes, mouse JAM-C expression was not detected on any mouse lymphocytes (4). In contrast to human JAM-C which show weak homotypic interactions, mouse JAM-C was reported to exhibit homotypic interactions (3). Mouse JAM-C has also been shown to have heterotypic interaction with JAM-B. It is likely that mouse JAM-C may play a role in lymphocyte transendothelial migration (4).
The nomenclature used for the JAM family proteins is confusing. VE-JAM has been referred to in the literature variously as JAM-B or JAM-C. Until further clarification, R&D Systems has adopted the nomenclature where both mouse and human VE-JAM are referred to as JAM-B.
- Chavakis, T. et al. (2003) Thromb. Haemost. 89:13.
- Aurrand-Lions, M. et al. (2001) Blood 98:3699.
- Aurrand-Lions, M. et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:2733.
- Johnson-Leger, C. et al. (2002) Blood 100:25793.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse JAM-C Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
14
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Siah2 antagonism of Pard3/JamC modulates Ntn1-Dcc signaling to regulate cerebellar granule neuron germinal zone exit
Authors: Laumonnerie, C;Shamambo, M;Stabley, DR;Lewis, TL;Trivedi, N;Howell, D;Solecki, DJ;
Nature communications
Species: Transgenic Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Proximity Ligation Assay -
JAM-C Is Important for Lens Epithelial Cell Proliferation and Lens Fiber Maturation in Murine Lens Development
Authors: Sun, Q;Li, J;Ma, J;Zheng, Y;Ju, R;Li, X;Ren, X;Huang, L;Chen, R;Tan, X;Luo, L;
Investigative ophthalmology & visual science
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Macrophage fusion event as one prerequisite for inorganic nanoparticle-induced antitumor response
Authors: Chen S, Xing Z, Geng M et al.
Science advances
-
ADAM10 facilitates rapid neural stem cell cycling and proper positioning within the subventricular zone niche via JAMC/RAP1Gap signaling
Authors: N McMillan, GW Kirschen, S Desai, E Xia, SE Tsirka, A Aguirre
Neural regeneration research, 2022-11-01;17(11):2472-2483.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: IHC, Immunoprecipitation, Neutralization -
Deficiency of Jamc Leads to Congenital Nuclear Cataract and Activates the Unfolded Protein Response in Mouse Lenses
Authors: J Li, X Tan, Q Sun, X Li, R Chen, L Luo
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 2022-09-01;63(10):1.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Lysate
-
Junctional Adhesion Molecule 3 Expression in the Mouse Airway Epithelium Is Linked to Multiciliated Cells
Authors: Clara Maria Mateos-Quiros, Sergio Garrido-Jimenez, Guadalupe Álvarez-Hernán, Selene Diaz-Chamorro, Juan Francisco Barrera-Lopez, Javier Francisco-Morcillo et al.
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology
Species: Canine, Human, Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot, Immunocytochemistry -
Soluble JAM-C Ectodomain Serves as the Niche for Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells
Authors: Morio Yamazaki, Kotaro Sugimoto, Yo Mabuchi, Rina Yamashita, Naoki Ichikawa-Tomikawa, Tetsuharu Kaneko et al.
Biomedicines
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates, Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot -
Neutrophil‐endothelial interactions of murine cells is not a good predictor of their interactions in human cells
Authors: Fariborz Soroush, Yuan Tang, Omar Mustafa, Shuang Sun, Qingliang Yang, Laurie E. Kilpatrick et al.
The FASEB Journal
-
Genetic, structural, and chemical insights into the dual function of GRASP55 in germ cell Golgi remodeling and JAM-C polarized localization during spermatogenesis
Authors: Amandine Cartier-Michaud, Anne-Laure Bailly, Stéphane Betzi, Xiaoli Shi, Jean-Claude Lissitzky, Ana Zarubica et al.
PLOS Genetics
-
Murine junctional adhesion molecules JAM-B and JAM-C mediate endothelial and stellate cell interactions during hepatic fibrosis
Authors: E Hintermann, M Bayer, J Ehser, M Aurrand-Li, JM Pfeilschif, BA Imhof, U Christen
Cell Adh Migr, 2016-04-25;10(4):419-33.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Junctional adhesion molecule (JAM)-C deficient C57BL/6 mice develop a severe hydrocephalus.
Authors: Wyss L, Schafer J, Liebner S, Mittelbronn M, Deutsch U, Enzmann G, Adams R, Aurrand-Lions M, Plate K, Imhof B, Engelhardt B
PLoS ONE, 2012-09-18;7(9):e45619.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr -
Expression, localization, and function of junctional adhesion molecule-C (JAM-C) in human retinal pigment epithelium.
Authors: Economopoulou M, Hammer J, Wang F, Fariss R, Maminishkis A, Miller SS
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 2008-12-05;50(3):1454-63.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Junctional adhesion molecule-C promotes metastatic potential of HT1080 human fibrosarcoma.
Authors: Fuse C, Ishida Y, Hikita T, Asai T, Oku N
J. Biol. Chem., 2007-01-16;282(11):8276-83.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Junctional adhesion molecules (JAM)-B and -C contribute to leukocyte extravasation to the skin and mediate cutaneous inflammation.
Authors: Ludwig RJ, Zollner TM, Santoso S, Hardt K, Gille J, Baatz H, Johann PS, Pfeffer J, Radeke HH, Schon MP, Kaufmann R, Boehncke WH, Podda M
J. Invest. Dermatol., 2005-11-01;125(5):969-76.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr, Neutralization
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse JAM-C Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Mouse JAM-C Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Mouse JAM-C Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image