Mouse Notch-1 PE-conjugated Antibody
Mouse Notch-1 PE-conjugated Antibody Summary
Accession # Q01705
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
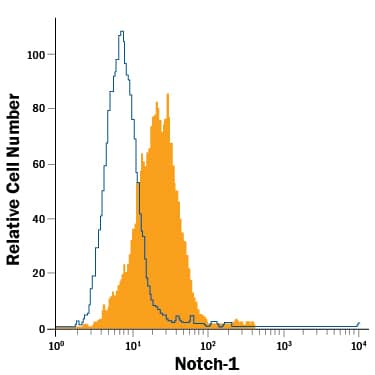
View Larger
Detection of Notch‑1 in RPMI 8226 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. RPMI 8226 human multiple myeloma cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Mouse Notch-1 PE-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # IC5267P, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC002P, open histogram). To facilitate intracellular staining, cells were fixed with Flow Cytometry Fixation Buffer (Catalog # FC004) and permeabilized with Flow Cytometry Permeabilization/Wash Buffer I (Catalog # FC005). View our protocol for Staining Intracellular Molecules.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
Background: Notch-1
Notch-1 is a 300 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein that is one of four Notch homologues involved in developmental processes (1-3). Notch signaling is important for maintaining stem cells and inducing differentiation, especially in the nervous system and lymphoid tissues (2-4). Notch can specify binary cell fates. For example, it promotes T cell over B cell development from a common precursor (2). Mouse Notch-1 is synthesized as a 2531 amino acid (aa) precursor that contains an 18 aa signal sequence, a 1707 aa extracellular domain (ECD) with 36 EGF-like repeats and three Lin-12/notch repeats (LNR), a 21 aa transmembrane (TM) segment and a 785 aa cytoplasmic domain that contains six ankyrin repeats, a glutamine-rich domain and a PEST sequence. The 11th and 12th EGF-like repeats, that bind ligands such as Jagged and Delta-like families in humans, correspond to aa 412-488 in mouse Notch-1 (6). Elongation of O-linked fucose chains by Fringe family members at a site within this region can inhibit the interaction of Notch with Jagged ligands, thereby promoting Delta-like ligand interactions (7). The Notch-1 receptor undergoes post-translational furin-type proteolytic cleavage, generating a heterodimer through the interaction of a hydrophobic area C-terminal to the LNR on the extracellular region with the transmembrane/cytoplasmic portion (8, 9). Upon ligand binding, additional sequential proteolysis by TNF-converting enzyme (ADAM17) and the presenilin-dependent gamma -secretase results in the release of the Notch intracellular domain (NICD) which translocates into the nucleus, activating transcription of Notch-responsive genes (10).
- Ellisen, L.W. et al. (1991) Cell 66:649.
- Dumortier, A. et al. (2005) Int. J. Hematol. 82:277.
- Yoon, K. and N. Gaiano (2005) Nat. Neurosci. 8:709.
- Androutsellis-Theotokis, A. et al. (2006) Nature 442:823.
- Weng, A.P. et al. (2004) Science 306:269.
- Hambleton, S. et al. (2004) Structure 12:2173.
- Yang, L. et al. (2005) Mol. Biol. Cell 16:927.
- Sanchez-Irizarry, C. et al. (2004) Mol. Cell. Biol. 24:9265.
- Logeat, F. et al. (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:8108.
- Mumm, J.S. and R. Kopan (2000) Dev. Biol. 228:151.
Product Datasheets
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse Notch-1 PE-conjugated Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Mouse Notch-1 PE-conjugated Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Mouse Notch-1 PE-conjugated Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image





