Mouse/Rat GRIN1/NMDAR1 C1 Splice Variant Antibody Summary
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
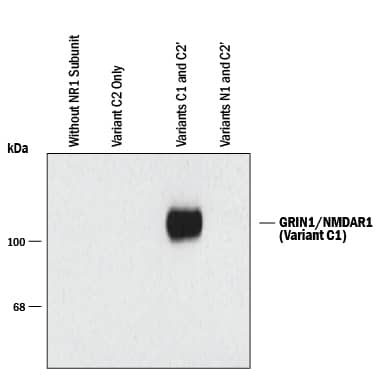
Detection of GRIN1/NMDAR1 C1 Splice Variant by Western Blot Western blot of HEK 293 cells: Lane 1 - HEK Cells without NR1 expression (Mock); Lane 2 - NR1 subunit containing only the C2 Splice Variant; Lane 3 - NR1 subunit containing the C1 and C2' splice variants; Lane 4 - NR1 subunit containing the N1 and C2' Splice Variant specific immunolabeling on approximately 120 kDa NR1 subunit of the NMDA Receptor containing the C1 Splice Variant in lane 3 only, demonstrates specificity for the C1 Splice Variant.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
Background: GRIN1/NMDAR1
NMDA (N-Methyl D-Aspartate) receptors are members of the glutamate receptor family of ligand-gated ion channels. The functional NMDA receptor is a heteromultimer of at least two NR1 (NMDA receptor-1) subunits and two NR2 subunits. Regulation of the NMDA complex by external factors such as zinc, PKC and polyamines is mediated by NR1 subunits. Upon glycine binding to NR1 and glutamate binding to NR2, the NMDA channel is opened allowing calcium and sodium influx into the cell. NR1 is a 120 kDa, 938 amino acid (aa), three transmembrane (TM) glycoprotein that contains a 541 aa extracellular domain and a 105 aa cytoplasmic region. The molecule is described as 4-TM. However, the second-TM segment is only partial (or reenterant), and this makes the C-terminus intracellular. Differential splicing of three exons generates up to nine isoforms of NR1. These exons encode a 21 amino acid N-terminal domain (N1) and adjacent sequences in the C-terminus (C1 and C2). Splicing out the C2 cassette eliminates the first stop codon and produces a new reading frame that generates a new sequence of 22 amino acids (C2'). Eight are integral membrane proteins. At the N-terminus, four isoforms show a 21 aa insertion between aa 190 - 191, and four do not. This is compounded by at least four possible variants between aa 864 - 938 in the cytoplasmic tail that impact potential serine phosphorylation sites. To date, all are believed to be physiologically active. There is one potentially “soluble” form that is only 181 aa in length. Its function is unknown.
- Stephenson, F.A. (2001) Curr. Drug Targets 2:233.
- Sugihara, H. et al. (1992) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 185:826.
- Prybylowski, K. and R.J. Wenthold (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279:9673.
- Moriyoshi, K. et al. (1991) Nature 354:31.
Product Datasheets
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse/Rat GRIN1/NMDAR1 C1 Splice Variant Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Mouse/Rat GRIN1/NMDAR1 C1 Splice Variant Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Mouse/Rat GRIN1/NMDAR1 C1 Splice Variant Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image

