Mouse/Rat P-Selectin/CD62P Antibody Summary
Trp42-Ala709
Accession # Q01102
*Small pack size (-SP) is supplied either lyophilized or as a 0.2 µm filtered solution in PBS.
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse and Rat P-Selectin/CD62P by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of mouse platelets and rat platelets. PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Mouse/Rat P-Selectin/CD62P Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF737) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for P-Selectin/CD62P at approximately 140-150 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
P‑Selectin/CD62P in Mouse Liver.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Rat P-Selectin/CD62P by Simple WesternTM. Simple Western lane view shows lysates of rat platelets, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for P-Selectin/CD62P at approximately 197 kDa (as indicated) using 20 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Mouse P-Selectin/CD62P Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF737) followed by 1:50 dilution of HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF109). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230 kDa separation system.
 View Larger
View Larger
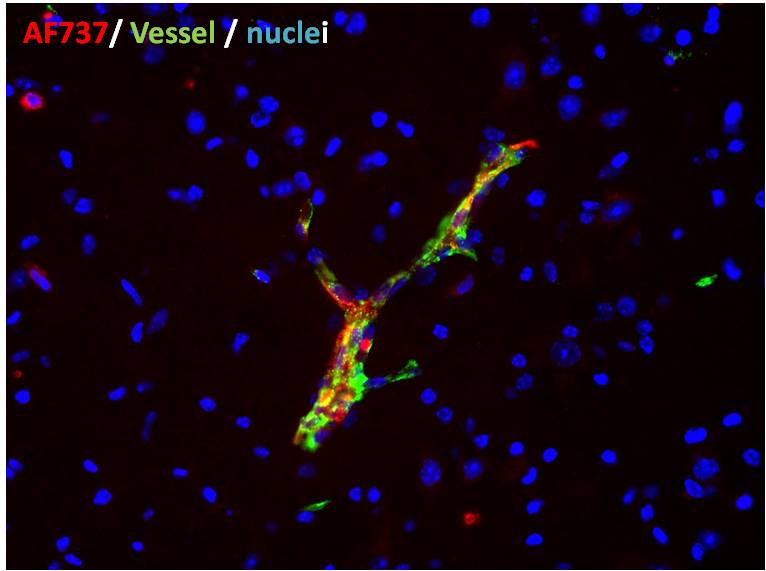
Detection of Mouse P-Selectin/CD62P by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence In-vivo targeting of BYL719-loaded nanoparticles prepared with either fucoidan (Fi) or dextran sulfate (Dex).(a) Representative ex vivo fluorescence images of mice organs 24 h after i.v. administration of FiBYL719 or DexBYL719 nanoparticles, and pre-treated with anti-P-selectin antibody (Ab). (b) Nanoparticle biodistribution in organs and tumour, calculated from ex vivo fluorescence images shown in a as total fluorescence efficiency divided by organ weight (n=3). (c) Representative immunofluorescence staining for CD-31 (red), P-selectin (green) and DAPI (blue) in Cal-33 xenografts before and after a single dose of ionizing radiation (4 Gy). Scale bars, 50 μm. (d) Quantification of double-staining positive endothelial cells per tumour shown in c (n=3). (e) In vivo fluorescence imaging of Cal-33 xenograft-bearing mice 24 h after treatment with FiBYL719 or 4 Gy RT followed by FiBYL719. (f) Quantification of total fluorescence efficiency of tumours shown e (n=10). (g) Representative immunofluorescence stains of tumour sections for P-selectin (green), NIR (red) and DAPI (blue) from H22 xenografts 24 h after treatments. Scale bars, 50 μm. In b,d,f error bars indicate mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01; by Mann–Whitney U-test in b or one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test in d,f. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms14292), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse P-Selectin/CD62P by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence In-vivo targeting of BYL719-loaded nanoparticles prepared with either fucoidan (Fi) or dextran sulfate (Dex).(a) Representative ex vivo fluorescence images of mice organs 24 h after i.v. administration of FiBYL719 or DexBYL719 nanoparticles, and pre-treated with anti-P-selectin antibody (Ab). (b) Nanoparticle biodistribution in organs and tumour, calculated from ex vivo fluorescence images shown in a as total fluorescence efficiency divided by organ weight (n=3). (c) Representative immunofluorescence staining for CD-31 (red), P-selectin (green) and DAPI (blue) in Cal-33 xenografts before and after a single dose of ionizing radiation (4 Gy). Scale bars, 50 μm. (d) Quantification of double-staining positive endothelial cells per tumour shown in c (n=3). (e) In vivo fluorescence imaging of Cal-33 xenograft-bearing mice 24 h after treatment with FiBYL719 or 4 Gy RT followed by FiBYL719. (f) Quantification of total fluorescence efficiency of tumours shown e (n=10). (g) Representative immunofluorescence stains of tumour sections for P-selectin (green), NIR (red) and DAPI (blue) from H22 xenografts 24 h after treatments. Scale bars, 50 μm. In b,d,f error bars indicate mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01; by Mann–Whitney U-test in b or one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test in d,f. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms14292), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse P-Selectin/CD62P by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence In-vivo targeting of BYL719-loaded nanoparticles prepared with either fucoidan (Fi) or dextran sulfate (Dex).(a) Representative ex vivo fluorescence images of mice organs 24 h after i.v. administration of FiBYL719 or DexBYL719 nanoparticles, and pre-treated with anti-P-selectin antibody (Ab). (b) Nanoparticle biodistribution in organs and tumour, calculated from ex vivo fluorescence images shown in a as total fluorescence efficiency divided by organ weight (n=3). (c) Representative immunofluorescence staining for CD-31 (red), P-selectin (green) and DAPI (blue) in Cal-33 xenografts before and after a single dose of ionizing radiation (4 Gy). Scale bars, 50 μm. (d) Quantification of double-staining positive endothelial cells per tumour shown in c (n=3). (e) In vivo fluorescence imaging of Cal-33 xenograft-bearing mice 24 h after treatment with FiBYL719 or 4 Gy RT followed by FiBYL719. (f) Quantification of total fluorescence efficiency of tumours shown e (n=10). (g) Representative immunofluorescence stains of tumour sections for P-selectin (green), NIR (red) and DAPI (blue) from H22 xenografts 24 h after treatments. Scale bars, 50 μm. In b,d,f error bars indicate mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01; by Mann–Whitney U-test in b or one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test in d,f. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms14292), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
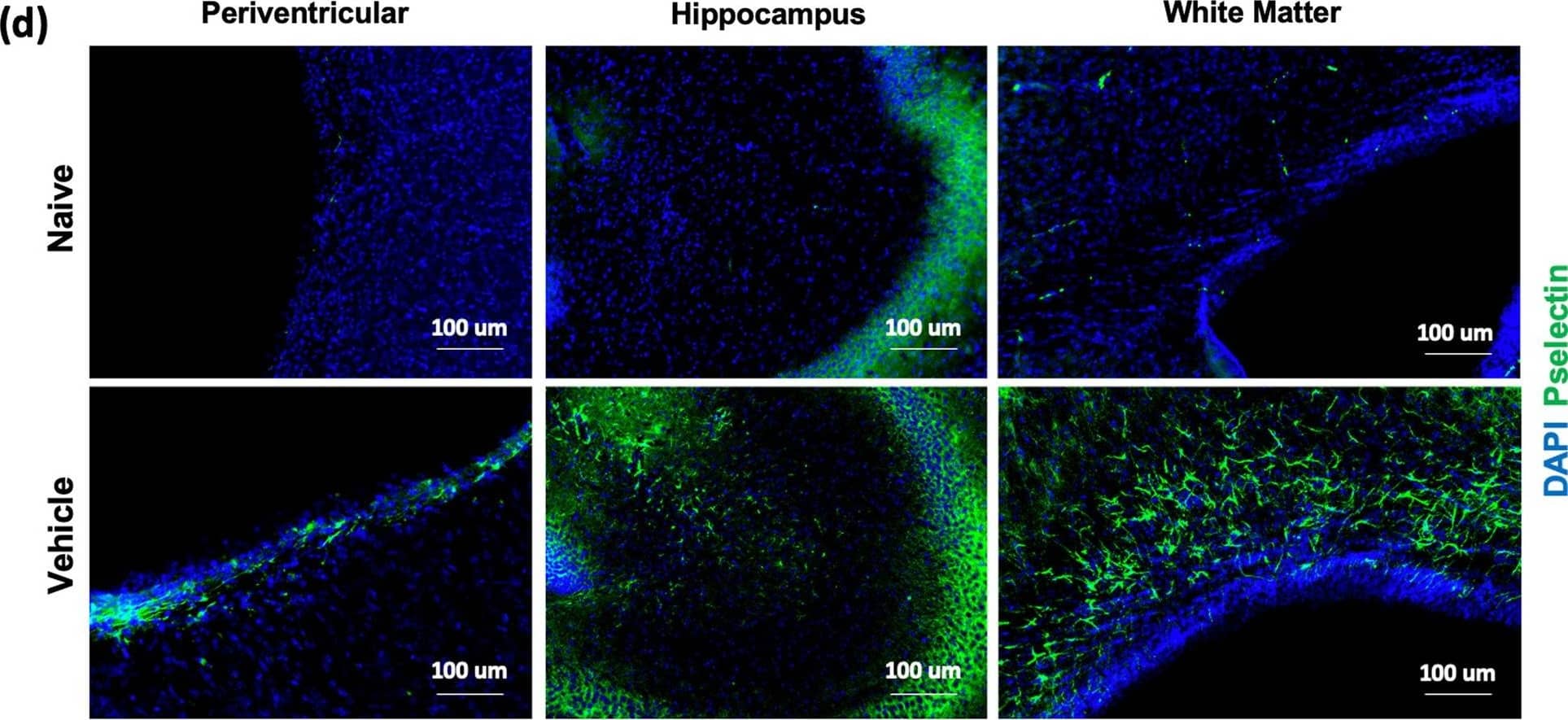
Detection of P-Selectin/CD62P by Immunohistochemistry Expression of P-selectin in different brain regions following GMH. P14 brain sections stained for P-selectin (CD62p) and quantified in 3 specific brain regions of each experimental group as indicated (a, b, c). One-way ANOVA with Turkey’s correction for multiple comparisons. ****p < 0.0001. Error bars = mean ± SEM. d 40 × representative images of P-selectin staining (green) and DAPI (blue) within each brain region for naïve and GMH animals Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37322469), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
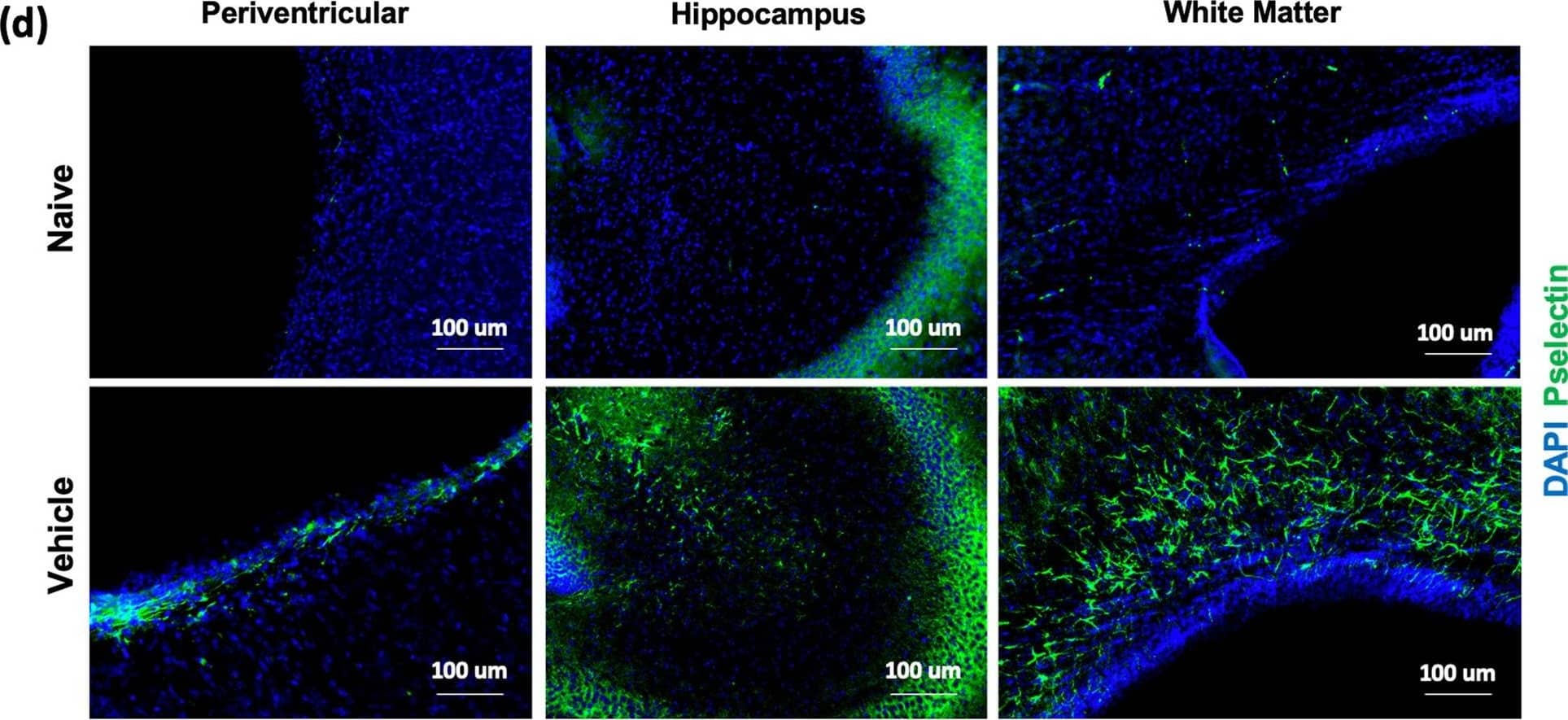
Detection of P-Selectin/CD62P by Immunohistochemistry Expression of P-selectin in different brain regions following GMH. P14 brain sections stained for P-selectin (CD62p) and quantified in 3 specific brain regions of each experimental group as indicated (a, b, c). One-way ANOVA with Turkey’s correction for multiple comparisons. ****p < 0.0001. Error bars = mean ± SEM. d 40 × representative images of P-selectin staining (green) and DAPI (blue) within each brain region for naïve and GMH animals Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37322469), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: P-Selectin/CD62P
Mouse P-Selectin (GMP-140, LECAM-3, PADGEM, CD62P), a member of the Selectin family, is a cell surface glycoprotein expressed by activated platelets and endothelial cells. P-Selectin is translocated to the cell surface within minutes, from alpha granules of platelets or Weibel-Palade bodies of endothelial cells, following stimulation with thrombin, histamine, PMA or peroxides. P-Selectin binds to a 106 kDa protein present on myeloid cells, neutrophils, monocytes and lymphocytes, termed PSGL-1 (P-Selectin glycoprotein ligand-1).
P-Selectin plays a role in the adhesion of leukocytes and neutrophils to the endothelium. Acting in cooperation with L-Selectin, P-Selectin mediates the initial interaction of circulating leukocytes with endothelial cells that produces a characteristic ‘rolling’ of the leukocytes on the endothelium. This initial interaction is followed by a stronger interaction involving E-Selectin, and later ICAM-1 and VCAM-1, that leads eventually to extravasation of the white blood cell through the blood vessel wall into the extracellular matrix tissue.
Mouse P-Selectin cDNA encodes a 768 amino acid (aa) residue type I transmembrane protein with a 41 aa signal peptide, a 668 aa extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain and a short (35 aa) cytoplasmic domain. The extracellular domain has an NH2-terminal C-type lectin domain and an EGF-like domain followed by a series of complement factor A repeat homology domains. The extracellular domains of human and mouse P-Selectin share approximately 73% sequence homology.
- Kansas, G.S. (1996) Blood 88:3259.
- McEver, R.P. and R.D. Cummings (1997) J. Clin. Invest. 100:485.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse/Rat P-Selectin/CD62P Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
25
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Longitudinal Molecular Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Endothelial Activation after Severe Traumatic Brain Injury
Authors: Gloria Vegliante, Daniele Tolomeo, Antoine Drieu, Marina Rubio, Edoardo Micotti, Federico Moro et al.
Journal of Clinical Medicine
-
P-selectin is a nanotherapeutic delivery target in the tumor microenvironment
Authors: Yosi Shamay, Moshe Elkabets, Hongyan Li, Janki Shah, Samuel Brook, Feng Wang et al.
Science Translational Medicine
-
Humanized Anti-RGMa Antibody Treatment Promotes Repair of Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier Under Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in Mice
Authors: Takeshi Hirata, Takahide Itokazu, Atsushi Sasaki, Fuminori Sugihara, Toshihide Yamashita
Frontiers in Immunology
-
A cellular and spatial map of the choroid plexus across brain ventricles and ages
Authors: Neil Dani, Rebecca H. Herbst, Cristin McCabe, Gilad S. Green, Karol Kaiser, Joshua P. Head et al.
Cell
-
Fucosyltransferase Induction during Influenza Virus Infection Is Required for the Generation of Functional Memory CD4+ T Cells
Authors: Roberto Tinoco, Florent Carrette, Monique L. Henriquez, Yu Fujita, Linda M. Bradley
The Journal of Immunology
-
Carfilzomib Delivery by Quinic Acid-Conjugated Nanoparticles: Discrepancy Between Tumoral Drug Accumulation and Anticancer Efficacy in a Murine 4T1 Orthotopic Breast Cancer Model
Authors: Yearin Jun, Jun Xu, Hyungjun Kim, Ji Eun Park, Yoo-Seong Jeong, Jee Sun Min et al.
Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences
-
Critical role of C5a in sickle cell disease
Authors: Gregory M. Vercellotti, Agustin P. Dalmasso, Terry R. Schaid, Julia Nguyen, Chunsheng Chen, Marna E. Ericson et al.
American Journal of Hematology
-
Central nervous system-associated macrophages modulate the immune response following stroke in aged mice
Authors: Levard, D;Seillier, C;Bellemain-Sagnard, M;Fournier, AP;Lemarchand, E;Dembech, C;Riou, G;McDade, K;Smith, C;McQuaid, C;Montagne, A;Amann, L;Prinz, M;Vivien, D;Rubio, M;
Nature neuroscience
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
LRRC8 complexes are adenosine nucleotide release channels regulating platelet activation and arterial thrombosis
Authors: Tranter, JD;Mikami, RT;Kumar, A;Brown, G;
bioRxiv
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
A dhesion analysis via a tumor vasculature-like microfluidic device identifies CD8+ T�cells with enhanced tumor homing to improve cell therapy
Authors: CP Camargo, AK Muhuri, Y Alapan, LF Sestito, M Khosla, MP Manspeaker, AS Smith, CM Paulos, SN Thomas
Cell Reports, 2023-02-26;42(3):112175.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors promotes renal cancer progression through MCPIP1 tumor-suppressor downregulation and c-Met activation
Authors: P Marona, J Górka, O Kwapisz, J Jura, J Rys, RM Hoffman, K Miekus
Cell Death & Disease, 2022-09-22;13(9):814.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Disrupting tumour vasculature and recruitment of aPDL1-loaded platelets control tumour metastasis
Authors: H Li, Z Wang, Z Chen, T Ci, G Chen, D Wen, R Li, J Wang, H Meng, R Bryan Bell, Z Gu, G Dotti, Z Gu
Nature Communications, 2021-05-13;12(1):2773.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: Flow Cytometry, IHC -
Angiopoietin-2 blockade ameliorates autoimmune neuroinflammation by inhibiting leukocyte recruitment into the CNS
Authors: Z Li, EA Korhonen, A Merlini, J Strauss, E Wihuri, H Nurmi, S Antila, J Paech, U Deutsch, B Engelhardt, S Chintharla, GY Koh, A Flügel, K Alitalo
J. Clin. Invest., 2020-04-01;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Alcohol exposure-induced neurovascular inflammatory priming impacts ischemic stroke and is linked with brain perivascular macrophages
Authors: A Drieu, A Lanquetin, D Levard, M Glavan, F Campos, A Quenault, E Lemarchand, M Naveau, AL Pitel, J Castillo, D Vivien, M Rubio
JCI Insight, 2020-02-27;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC, In Vivo -
Critical role of C5a in sickle cell disease
Authors: Gregory M. Vercellotti, Agustin P. Dalmasso, Terry R. Schaid, Julia Nguyen, Chunsheng Chen, Marna E. Ericson et al.
American Journal of Hematology
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Dose-Dependent Influences of Ethanol on Ischemic Stroke: Role of Inflammation
Authors: G Xu, C Li, AL Parsiola, J Li, KD McCarter, R Shi, WG Mayhan, H Sun
Front Cell Neurosci, 2019-02-12;13(0):6.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Fucosyltransferase Induction during Influenza Virus Infection Is Required for the Generation of Functional Memory CD4+ T Cells
Authors: Roberto Tinoco, Florent Carrette, Monique L. Henriquez, Yu Fujita, Linda M. Bradley
The Journal of Immunology
Species: Transgenic Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates, Whole Tissue
Applications: Flow Cytometry, Immunohistochemistry -
Prediction of disease activity in models of multiple sclerosis by molecular magnetic resonance imaging of P-selectin
Authors: AP Fournier, A Quenault, S Martinez d, M Gauberti, G Defer, D Vivien, F Docagne, R Macrez
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2017-05-22;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Tumour-specific PI3K inhibition via nanoparticle-targeted delivery in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Authors: A Mizrachi, Y Shamay, J Shah, S Brook, J Soong, VK Rajasekhar, JL Humm, JH Healey, SN Powell, J Baselga, DA Heller, A Haimovitz-, M Scaltriti
Nat Commun, 2017-02-13;8(0):14292.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Molecular magnetic resonance imaging discloses endothelial activation after transient ischaemic attack
Authors: Aurélien Quenault
Brain, 2016-11-08;140(0):146-157.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Complex Sample Type, Whole Tissue
Applications: Functional Assay, IHC -
Expression of the cysteine protease legumain in vascular lesions and functional implications in atherogenesis.
Authors: Clerin V, Shih HH, Deng N, Hebert G, Resmini C, Shields KM, Feldman JL, Winkler A, Albert L, Maganti V, Wong A, Paulsen JE, Keith JC, Vlasuk GP, Pittman DD
Atherosclerosis, 2008-02-21;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Reduced plaque formation induced by rosiglitazone in an STZ-diabetes mouse model of atherosclerosis is associated with downregulation of adhesion molecules.
Authors: Tikellis C, Jandeleit-Dahm KA, Sheehy K, Murphy A, Chin-Dusting J, Kling D, Sebokova E, Cooper ME, Mizrahi J, Woollard KJ
Atherosclerosis, 2008-02-21;199(1):55-64.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
A TREM family member, TLT-1, is found exclusively in the alpha-granules of megakaryocytes and platelets.
Authors: Washington AV, Schubert RL, Quigley L, Disipio T, Feltz R, Cho EH, McVicar DW
Blood, 2004-04-20;104(4):1042-7.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Quinic Acid‐Conjugated Nanoparticles Enhance Drug Delivery to Solid Tumors via Interactions with Endothelial Selectins
Authors: Jun Xu, Steve Seung‐Young Seung-Young Lee, Howon Seo, Liang Pang, Yearin Jun, Ruo‐Yu Zhang et al.
Small
-
Endothelial TLR4 Expression Mediates Vaso-Occlusive Crisis in Sickle Cell Disease
Authors: Joan D. Beckman, Fuad Abdullah, Chunsheng Chen, Rachel Kirchner, Dormarie Rivera-Rodriguez, Zachary M. Kiser et al.
Frontiers in Immunology
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse/Rat P-Selectin/CD62P Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Mouse/Rat P-Selectin/CD62P Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: