Mouse TNF RI/TNFRSF1A Antibody Summary
(rh) 4‑1BB, rhCD27, rhCD30, recombinant mouse (rm) CD27, rmCD30, rhCD40, rmCD40, rhDR3, rhDR6, rmEDAR, rhFas, rmFas, rhEDAR, rhGITR, rmGITR, rhHVEM, rhLT beta R, rmLT beta R, rhNGF R, rhOPG, rmOPG, rhRANK, rmRANK, rhTAJ, rhTNF RI, rhTNF RII or rmTNF RII is observed.
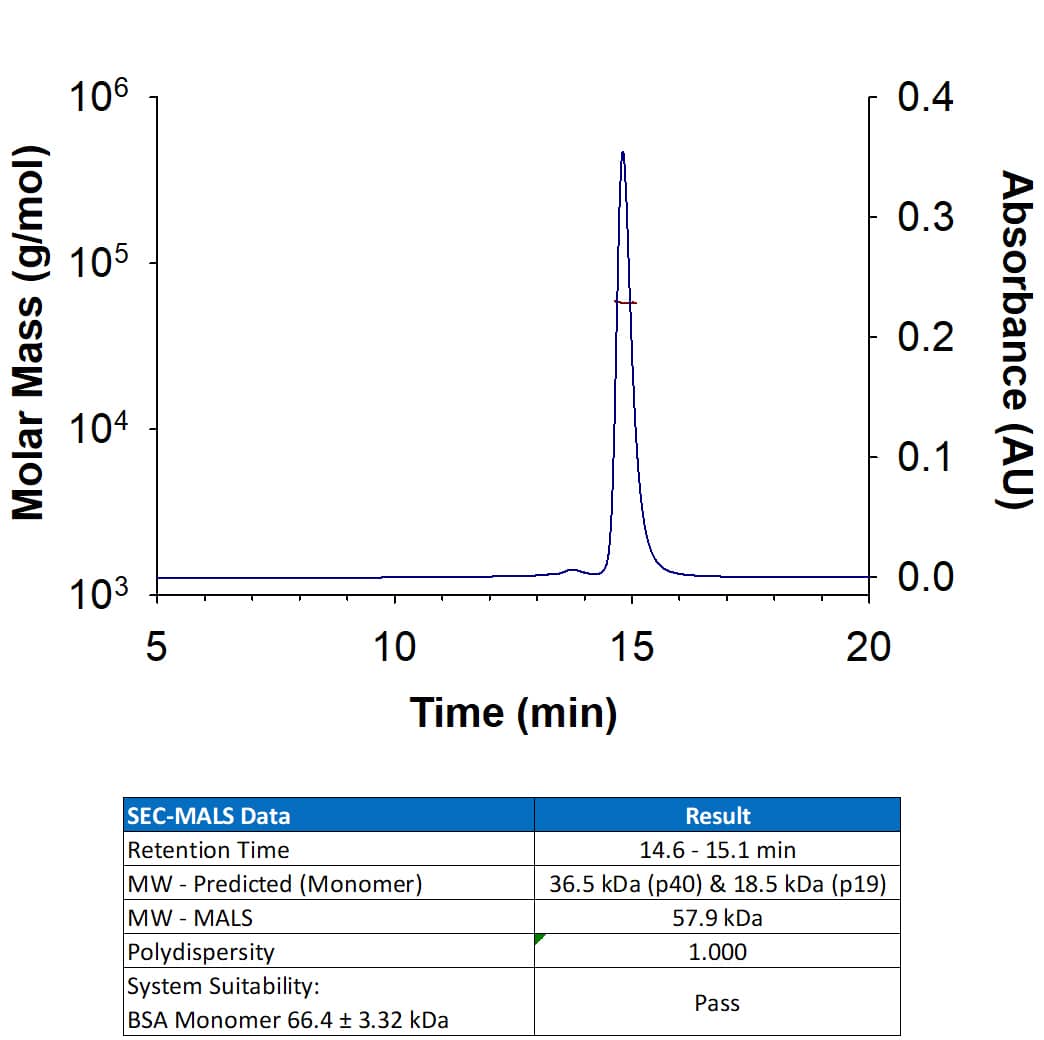
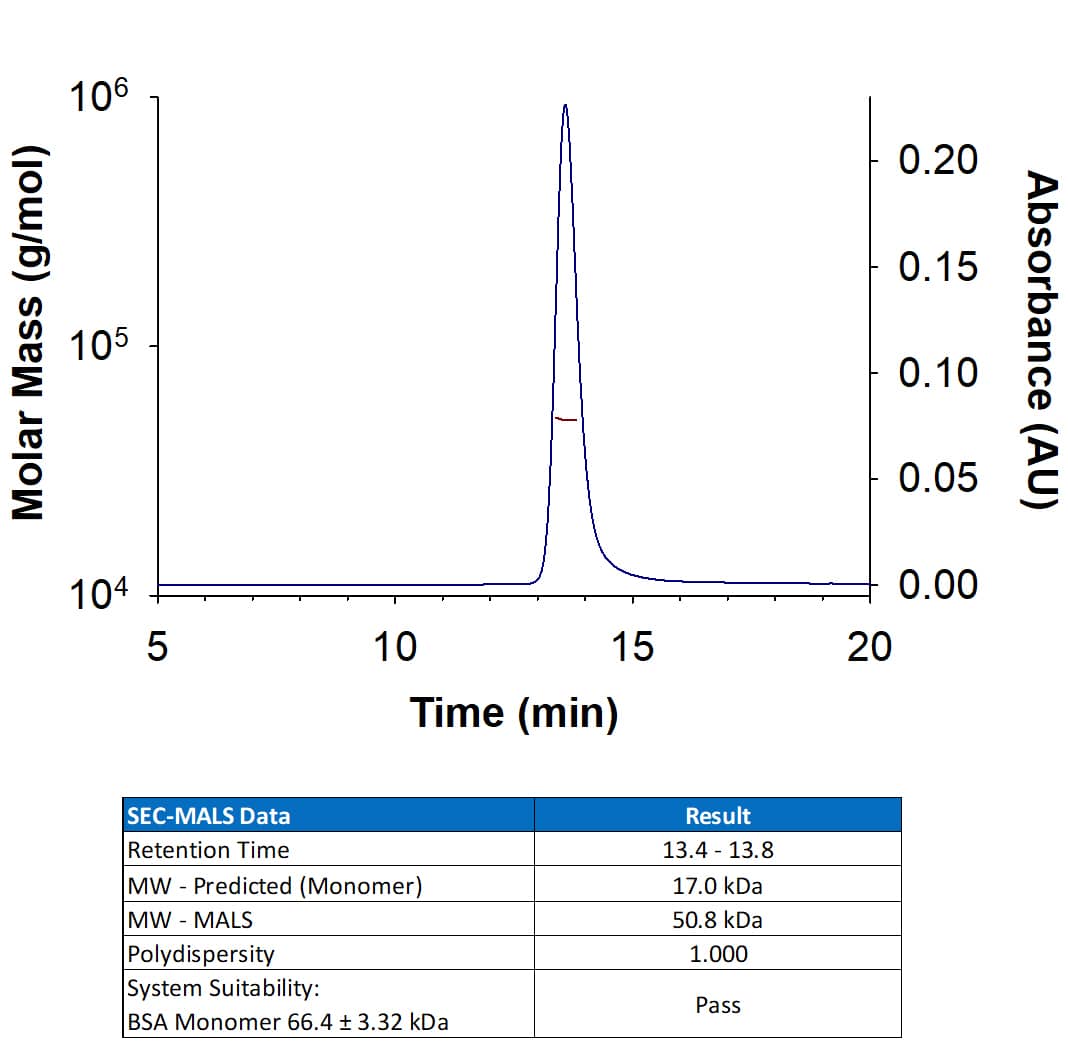
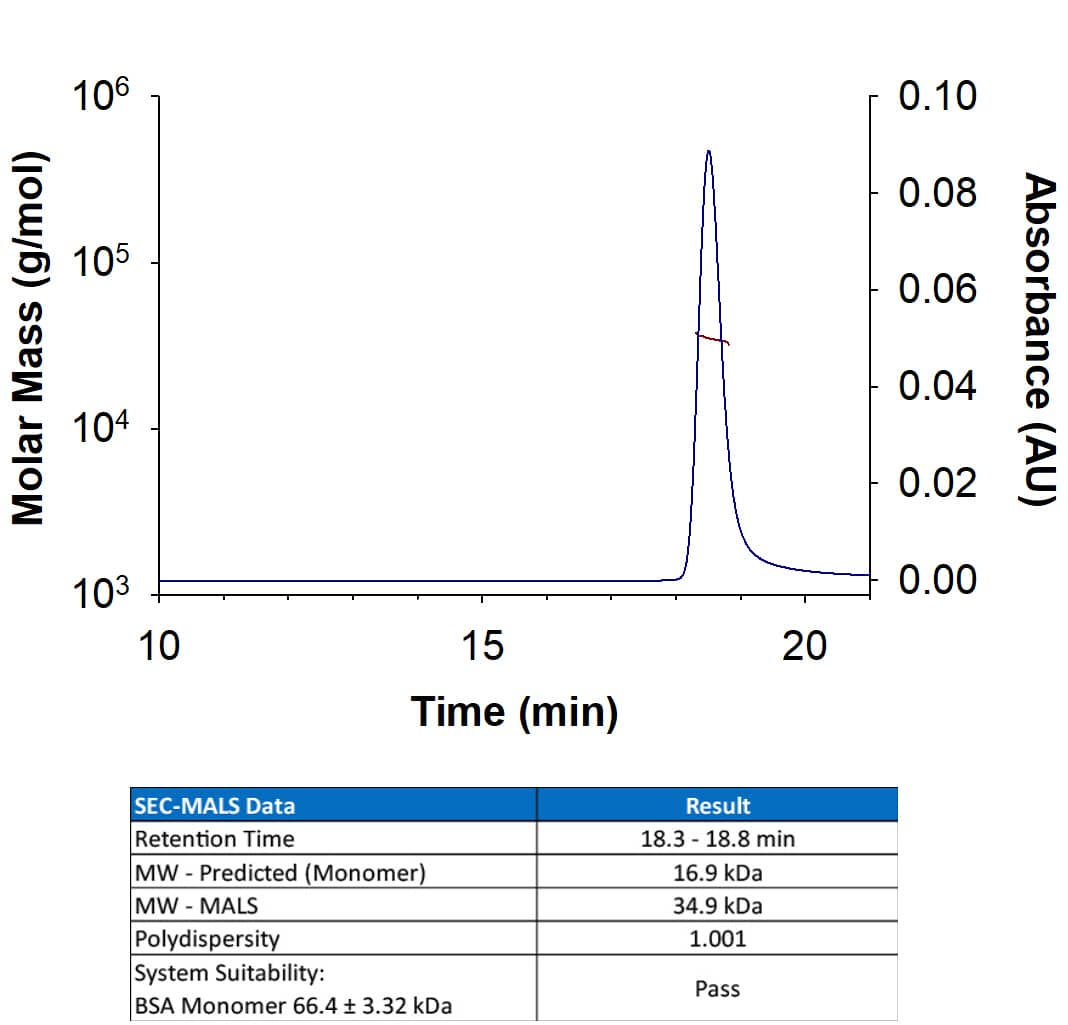
Extracellular domain
Customers also Viewed
Applications
under non-reducing conditions only
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
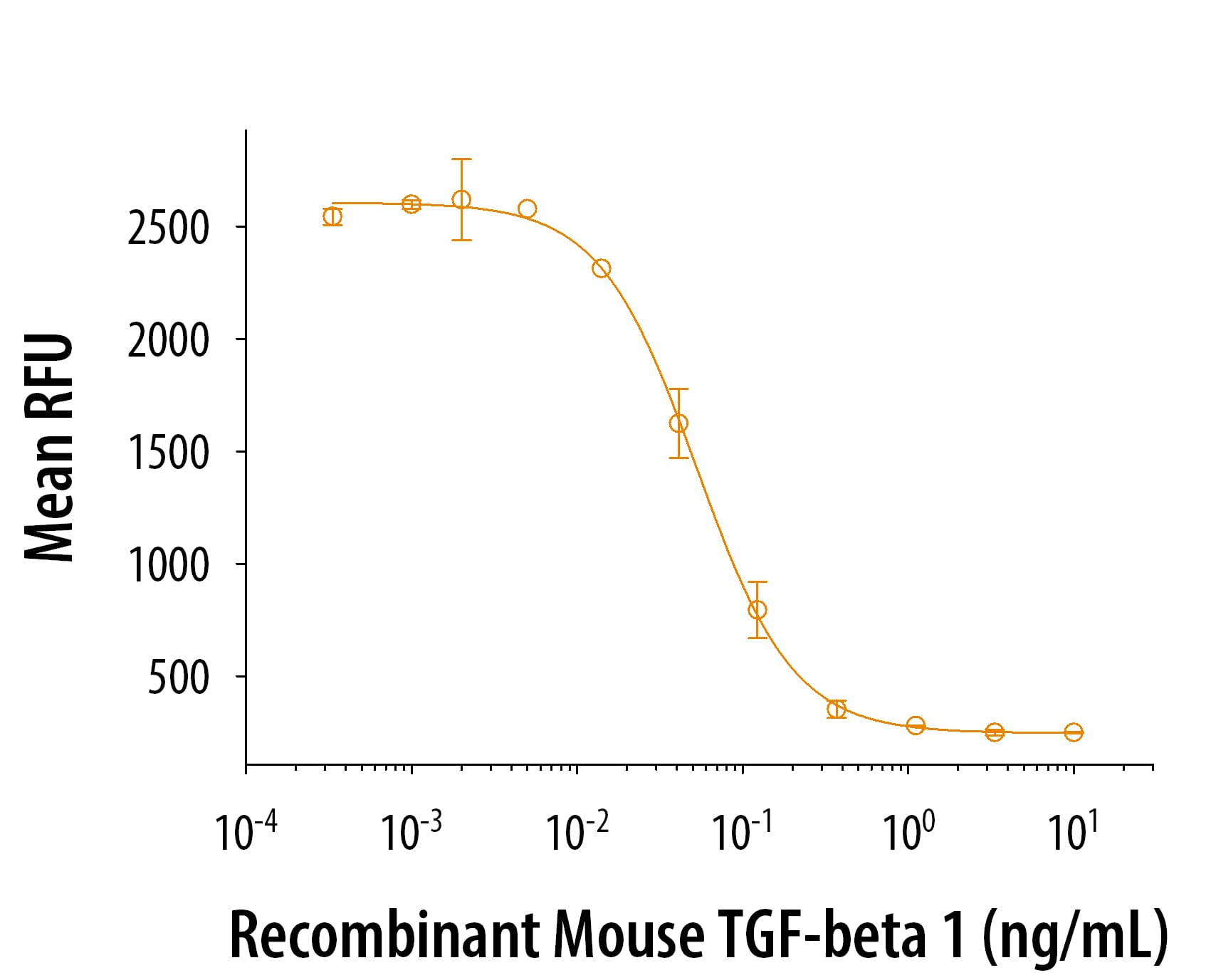
Cytotoxicity Induced by TNF‑ alpha and Neutralization by Mouse TNF RI/TNFRSF1A Antibody. Recombinant Mouse TNF-a (Catalog # 410-MT) induces cytotoxicity in the the L-929 mouse fibroblast cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Cytotoxicity elicited by Recombinant Mouse TNF-a (0.1 ng/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Hamster Anti-Mouse TNF RI/TNFRSF1A Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB430). The ND50 is typically 5-20 µg/mL in the presence of the metabolic inhibitor actinomycin D (1 µg/mL).
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: TNF RI/TNFRSF1A
TNF receptor 1 (TNF RI; also called TNF R-p55/p60 and TNFRSF1A) is a type I transmembrane protein member of the TNF receptor superfamily, designated TNFRSF1A (1, 2). Both TNF RI and TNF RII (TNFRSF1B) are widely expressed and contain four TNF-alpha trimer-binding cysteine-rich domains (CRD) in their extracellular domains (ECD). However, TNF RI is thought to mediate most of the cellular effects of TNF-alpha (3). It is essential for proper development of lymph node germinal centers and Peyer’s patches, and for combating intracellular pathogens such as Listeria (1‑3). TNF RI is also a receptor for TNF-beta /TNFSF1B (lymphotoxin-alpha ) (4). TNF RI is present on the cell surface as a trimer of 55 kDa subunits (4, 5). TNF-alpha induces sequestering of TNF RI in lipid rafts, where it activates NF kappa B and is cleaved by ADAM-17/TACE (9, 10). Release of the 28 - 34 kDa TNF RI ECD also occurs constitutively and in response to products of pathogens such as LPS, CpG DNA or S. aureus protein A (1, 6‑8). Full-length TNF RI may also be released in exosome-like vesicles (11). Release helps to resolve inflammatory reactions, since it down-regulates cell surface TNF RI and provides soluble TNF RI to bind TNF-alpha (6, 12, 13). Exclusion from lipid rafts causes endocytosis of TNF RI complexes and induces apoptosis (1). Mouse TNF RI is a 454 amino acid (aa) protein that contains a 21 aa signal sequence, a 191 aa ECD with a PLAD domain (5) that mediates constitutive trimer formation, followed by the four CRD, a 23 aa transmembrane domain, and a 219 aa cytoplasmic sequence that contains a neutral sphingomyelinase activation domain and a death domain (15). The ECD of mouse TNF RI shows 67%, 70%, 64%, 70% and 88% aa identity with canine, feline, porcine, human, and rat TNF RI, respectively; it shows 23% aa identity with the ECD of TNF RII.
- Pfeffer, K. (2003) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 14:185.
- Hehlgans, T. and K. Pfeffer (2005) Immunology 115:1.
- Peschon, J.J. et al. (1998) J. Immunol. 160:943.
- Banner, D.W et al. (1993) Cell 73: 431.
- Chan, F.K. et al. (2000) Science 288:2351.
- Xanthoulea, S. et al. (2004) J. Exp. Med. 200:367.
- Jin, L. et al. (2000) J. Immunol. 165:5153.
- Gomez, M.I. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:20190.
- Legler, D.F. et al. (2003) Immunity 18:655.
- Tellier, E. et al. (2006) Exp. Cell Res. 312:3969.
- Islam, A. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:6860.
- Garton, K.J. et al. (2006) J. Leukoc. Biol. 79:1105.
- McDermott, M.F. et al. (1999) Cell 97:133.
- Schneider-Brachert, W. et al. (2004) Immunity 21:415.
- Lewis, M. et al. (1991) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:2830.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse TNF RI/TNFRSF1A Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
18
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Caspase inhibition prolongs inflammation by promoting a signaling complex with activated RIPK1
Authors: Xinyue Huang, Shuixia Tan, Yanxia Li, Shuangyi Cao, Xingyan Li, Heling Pan et al.
Journal of Cell Biology
-
Microglial GPR56 is the molecular target of maternal immune activation-induced parvalbumin-positive interneuron deficits
Authors: Diankun Yu, Tao Li, Jean-Christophe Delpech, Beika Zhu, Priya Kishore, Tatsuhiro Koshi et al.
Science Advances
-
A novel role for the apoptosis inhibitor ARC in suppressing TNF alpha -induced regulated necrosis
Authors: G Kung, P Dai, L Deng, R N Kitsis
Cell Death & Differentiation
-
Microglial GPR56 is the molecular target of maternal immune activation-induced parvalbumin-positive interneuron deficits
Authors: D Yu, T Li, JC Delpech, B Zhu, P Kishore, T Koshi, R Luo, KJB Pratt, G Popova, TJ Nowakowski, SA Villeda, X Piao
Science Advances, 2022-05-06;8(18):eabm2545.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
The necroptotic cell death pathway operates in megakaryocytes, but not in platelet synthesis
Authors: D Moujalled, P Gangatirka, M Kauppi, J Corbin, M Lebois, JM Murphy, N Lalaoui, JM Hildebrand, J Silke, WS Alexander, EC Josefsson
Cell Death & Disease, 2021-01-28;12(1):133.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: ICC, IHC, Western Blot -
Targeting the Extrinsic Pathway of Hepatocyte Apoptosis Promotes Clearance of Plasmodium Liver Infection
Authors: G Ebert, S Lopaticki, MT O'Neill, RWJ Steel, M Doerflinge, P Rajasekara, ASP Yang, S Erickson, L Ioannidis, P Arandjelov, L Mackiewicz, C Allison, J Silke, M Pellegrini, JA Boddey
Cell Rep, 2020-03-31;30(13):4343-4354.e4.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Liver Protein Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Inflammation induced by incomplete radiofrequency ablation accelerates tumor progression and hinders PD-1 immunotherapy
Authors: L Shi, J Wang, N Ding, Y Zhang, Y Zhu, S Dong, X Wang, C Peng, C Zhou, L Zhou, X Li, H Shi, W Wu, X Long, C Wu, W Liao
Nat Commun, 2019-11-28;10(1):5421.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Cell Culture -
Cerebral ischemia-induced angiogenesis is dependent on tumor necrosis factor receptor 1-mediated upregulation of ?5?1 and ?V?3 integrins
J Neuroinflammation, 2016-09-01;13(1):227.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
Phosphorylation and linear ubiquitin direct A20 inhibition of inflammation.
Authors: Wertz I, Newton K, Seshasayee D, Kusam S, Lam C, Zhang J, Popovych N, Helgason E, Schoeffler A, Jeet S, Ramamoorthi N, Kategaya L, Newman R, Horikawa K, Dugger D, Sandoval W, Mukund S, Zindal A, Martin F, Quan C, Tom J, Fairbrother W, Townsend M, Warming S, DeVoss J, Liu J, Dueber E, Caplazi P, Lee W, Goodnow C, Balazs M, Yu K, Kolumam G, Dixit V
Nature, 2015-12-09;528(7582):370-5.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
TLR-mediated secretion of endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 from macrophages.
Authors: Goto Y, Ogawa K, Nakamura T, Hattori A, Tsujimoto M
J Immunol, 2014-03-31;192(9):4443-52.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
TNF-alpha induces matrix metalloproteinase-9-dependent soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 release via TRAF2-mediated MAPKs and NF-kappaB activation in osteoblast-like MC3T3-E1 cells.
Authors: Tsai C, Chen W, Hsieh H, Chi P, Hsiao L, Yang C
J Biomed Sci, 2014-02-05;21(0):12.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Lipopolysaccharide triggered TNF-alpha-induced hepatocyte apoptosis in a murine non-alcoholic steatohepatitis model.
Authors: Kudo H, Takahara T, Yata Y, Kawai K, Zhang W, Sugiyama T
J. Hepatol., 2009-05-03;51(1):168-75.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
IL-1beta augments TNF-alpha-mediated inflammatory responses from lung epithelial cells.
Authors: Saperstein S, Chen L, Oakes D, Pryhuber G, Finkelstein J
J Interferon Cytokine Res, 2009-05-01;29(5):273-84.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Hypoxia enhances lysosomal TNF-alpha degradation in mouse peritoneal macrophages.
Authors: Lahat N, Rahat MA, Kinarty A, Weiss-Cerem L, Pinchevski S, Bitterman H
Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol., 2008-04-23;295(1):C2-12.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Immunoprecipitation -
TLR-2 is upregulated and mobilized to the hepatocyte plasma membrane in the space of Disse and to the Kupffer cells TLR-4 dependently during acute endotoxemia in mice.
Authors: Ojaniemi M, Liljeroos M, Harju K, Sormunen R, Vuolteenaho R, Hallman M
Immunol. Lett., 2005-09-26;102(2):158-68.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
Oct4-Mediated Inhibition of Lsd1 Activity Promotes the Active and Primed State of Pluripotency Enhancers
Authors: Lama AlAbdi, Debapriya Saha, Ming He, Mohd Saleem Dar, Sagar M. Utturkar, Putu Ayu Sudyanti et al.
Cell Reports
-
TNF-alpha Downregulates Inhibitory Neurotransmission through Protein Phosphatase 1-Dependent Trafficking of GABAA Receptors.
Authors: Pribiag H, Stellwagen D.
J Neurosci.
-
TNFR1-mediated signaling is important to induce the improvement of liver fibrosis by bone marrow cell infusion
Authors: Takuro Hisanaga, Shuji Terai, Takuya Iwamoto, Taro Takami, Naoki Yamamoto, Tomoaki Murata et al.
Cell and Tissue Research
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReconstitution Buffers
Secondary Antibodies
Reviews for Mouse TNF RI/TNFRSF1A Antibody
Average Rating: 4.5 (Based on 2 Reviews)
Have you used Mouse TNF RI/TNFRSF1A Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
murine cross-reactivity studies