Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey CD4 Fc Chimera Protein, CF Summary
- R&D Systems CHO-derived Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey CD4 Fc Chimera Protein (11145-CD)
- Quality control testing to verify active proteins with lot specific assays by in-house scientists
- All R&D Systems proteins are covered with a 100% guarantee
Product Specifications
| Cynomolgus Monkey CD4 (Lys26-Pro396) Accession # P79185.1 | IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | |
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
11145-CD
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
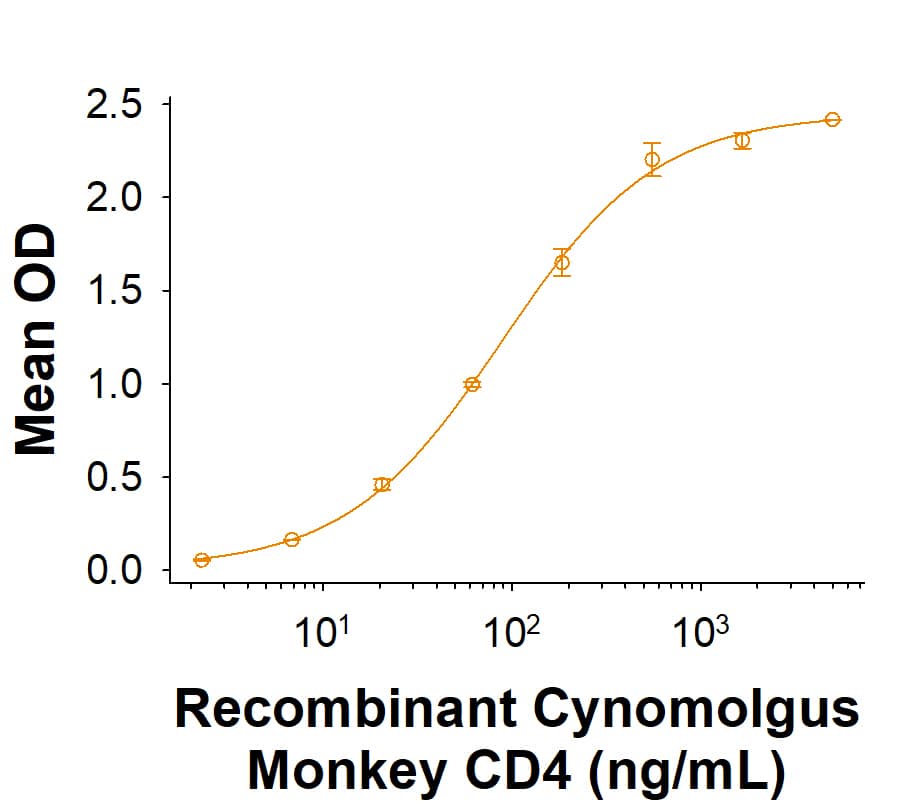
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA with Human CD4 Biotinylated Antibody (BAF379). The ED50 for this effect is 35.0-280 ng/mL.
 View Larger
View Larger
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey CD4 Fc Chimera Protein (Catalog # 11145-CD) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 80-88 kDa and 160-180 kDa, respectively.
Reconstitution Calculator
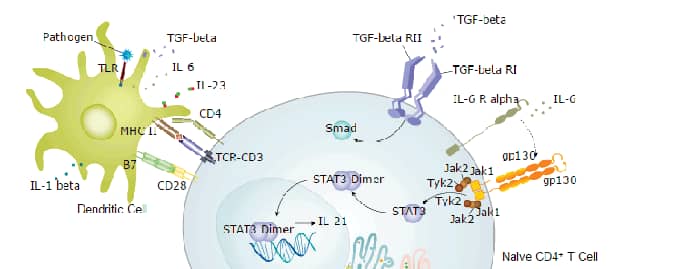
Background: CD4
CD4, also known as L3T4, T4, and W3/25, is an approximately 55 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein that is expressed predominantly on thymocytes and a subset of mature T lymphocytes. It is a standard phenotype marker for the identification of T cell populations (1). Mature cynomolgus monkey CD4 consists of a 371 amino acid (aa) extracellular region containing four immunoglobulin-like domains, a 22 aa transmembrane segment, and a 40 aa cytoplasmic domain (2). Within the ECD, cynomolgus monkey and human CD4 shares approximately 91% aa sequence identity. CD4 is expressed along with CD8 on double positive T cells during their development in the thymus. Either CD4 or CD8 expression is then lost, giving rise to single positive (SP) CD4+ or CD8+ mature T cells (3). CD4+ SP cells, also known as T helper cells, further differentiate into multiple subsets of CD4+ cells including Th1, Th2, Th17, Tfh, and Treg cells which regulate humoral and cellular immunity (4). CD4 is re-expressed on circulating CD8+ T cells upon activation and contributes to their cytotoxic effector activity (5). In human, CD4 is additionally expressed on macrophages, neutrophils, monocytes, NK cells, and neurons and glial cells in the brain (6-9). Similar CD4 distribution between species cannot be assumed as demonstrated by its presence on macrophages in human and rat but not in mouse (6). CD4 binds directly to MHC class II molecules on antigen presenting cells (10). This interaction contributes to the formation of the immunological synapse which is focused around the TCR-MHC class II-antigenic peptide interaction (1, 11). Palmitoylation of two cysteine residues in the cytoplasmic tail of CD4 promotes the localization of CD4 in lipid rafts and its ability to augment TCR signaling via activation of the tyrosine kinase Lck (12). CD4 also functions as a chemotactic receptor for IL-16 and, in human, as a co-receptor for the gp120 surface glycoprotein of HIV-1 (7, 13-15).
- Vignali, D.A.A. (2010) J. Immunol. 184:5933.
- Maddon, P.J. et al. (1985) Cell 42:93.
- Alarcon, B. and H.M. van Santen (2010) Sci. Signal. 3:pe11.
- Wan, Y.Y. and R.A. Flavell (2009) Mol. Cell Biol. 1:20.
- Kitchen, S.G. et al. (2005) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 102:3794.
- Crocker, P.R. et al. (1987) J. Exp. Med. 166:613.
- Biswas, P. et al. (2003) Blood 101:4452.
- Bernstein, H.B. et al. (2006) J. Immunol. 177:3669.
- Funke, I. et al. (1987) J. Exp. Med. 165:1230.
- Doyle, C. and J.L. Strominger (1987) Nature 330:256.
- Huppa, J.B. et al. (2010) Nature 463:963.
- Fragoso, R. et al. (2003) J. Immunol. 170:913.
- Cruikshank, W.W. et al. (1994) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 91:5109.
- Klatzmann, D. et al. (1984) Nature 312:767.
- Dagleish, A.G. et al. (1984) Nature 312:763.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey CD4 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey CD4 Fc Chimera Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey CD4 Fc Chimera Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image