Recombinant Human/Cynomolgus/Rhesus CD28 Fc Avi-tag, CF
Recombinant Human/Cynomolgus/Rhesus CD28 Fc Avi-tag, CF Summary
- R&D Systems CHO-derived Recombinant Human/Cynomolgus/Rhesus CD28 Fc Avi-tag (AVI342)
- Quality control testing to verify active proteins with lot specific assays by in-house scientists
- All R&D Systems proteins are covered with a 100% guarantee
Product Specifications
| Human/Cynomolgus Monkey/Rhesus Macaque CD28 (Asn19-Pro152) Accession # P10747.1 | DMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) | Avi-tag |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | ||
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
AVI342
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with dry ice or equivalent. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
When Recombinant Human B7-1/CD80 Fc Chimera Protein (Catalog # 10133-B1) is immobilized at 10 µg/mL (100 µL/well), the concentration of Biotinylated Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey/Rhesus Macaque CD28 Fc Chimera Avi-tag that produces a 50% optimal binding response is found to be 0.5-3 µg/mL.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: CD28
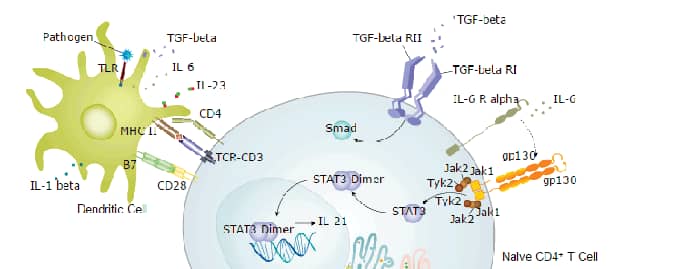
CD28 is the founding member of a subfamily of structurally homologous costimulatory or immune checkpoint molecules of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. The CD28/B7 pathway has been shown to play a central role in immune responses against infection, autoimmune diseases, and graft rejection (1). CD28 subfamily members, including ICOS, CTLA4, PD1, PD1H, and BTLA, are characterized by a single Ig V-like extracellular domain (ECD), a transmembrane domain and an intracellular domain with highly conserved tyrosine-based signaling motifs (2). CD28 and ICOS predominately enhance T-cell activation, while CTLA-4, PD-1 and BTLA are inhibitory (1-3). The mature ECD of human CD28 shares 65% and 66% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat CD28, respectively. CD28 and CTLA-4, together with their ligands, B7-1 and B7-2, constitute one of the dominant co-stimulatory pathways that regulate T and B cell responses. CD28 is expressed on approximately 80% of CD4+ T cells and 50% of CD8+ T cells in humans, with the proportion of CD28-positive T cells declining with age (1-4). CD28 expression has been identified on other cell lineages, including bone marrow stromal cells, plasma cells, neutrophils, and eosinophils (5). CD28 is expressed on the cell surface as a disulfide-linked homodimer and the covalent bond is required for maximum activity (6,7). Although both CTLA-4 and CD28 can bind to the same ligands, CTLA-4 binds to B7-1 and B7-2 with a 20-100 fold higher affinity than CD28. While, CD28 ligation is critical in promoting proliferation and effector function of conventional T cells, it also promotes the anti-inflammatory function of Treg cells. Thus, CD28 serves both pro- and anti-inflammatory roles depending on the cell type and context in which it is expressed (8). The CD28 pathway has effects both at amplifying signals initiated by the T cell receptor and on a variety of processes, including signaling, metabolism, transcription, epigenetic modifications, post-translational modifications, and RNA splicing (9).Our Avi-tag Biotinylated CD28 features biotinylation at a single site contained within the Avi-tag, a unique 15 amino acid peptide. Protein orientation will be uniform when bound to streptavidin-coated surface due to the precise control of biotinylation and the rest of the protein is unchanged so there is no interference in the protein's bioactivity.
- Sandigursky, S. et al. (2020). Clin Immunol. 217:108485l.
- Chen, L. and Flies D.B. (2013) Nat Rev Immunol. 13:227.
- Esensten, J.H. et al. (2016) Immunity. 44:973.
- Jonathan, H. et al. (2016) Immunity. 44:937.
- Boomer, J.S. and Green, J.M. (2010) Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2:a002436.
- Greene, J.L. et al. (1996) J Biol Chem. 271:26762.
- Lazar-Molnar, E. et al. (2006) Cell Immunol. 244:125.
- He, X. et al. (2017) Scientific Reports. 7:43003.
- West, S.M. et al. (2019) Exp Biol. Med. (Maywood) 244:1577.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human/Cynomolgus/Rhesus CD28 Fc Avi-tag, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Human/Cynomolgus/Rhesus CD28 Fc Avi-tag, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Human/Cynomolgus/Rhesus CD28 Fc Avi-tag, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image