Recombinant Human DPPIV/CD26 His-tag Protein, CF Summary
- R&D Systems HEK293-derived Recombinant Human DPPIV/CD26 His-tag Protein (11244-SE)
- Quality control testing to verify active proteins with lot specific assays by in-house scientists
- All R&D Systems proteins are covered with a 100% guarantee
Product Specifications
Asn29-Pro766 with a C-terminal DI and 6-His tag
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
11244-SE
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Tris and NaCl. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Assay Procedure
- Assay Buffer: 25 mM Tris, pH 8.0
- Recombinant Human DPPIV/CD26 His-tag (rhCD26) (Catalog # 11244-SE)
- Substrate: H-Gly-Pro-AMC, 10 mM stock in DMSO
- Black 96-well Plate
- Fluorescent Plate Reader
- Dilute rhCD26 to 0.1 ng/μL in Assay Buffer. Minimize the number of dilution steps to obtain the best activity results.
- Dilute Substrate to 200 μM in Assay Buffer.
- Load into a plate 50 μL of 0.1 ng/μL rhCD26 and start the reaction by adding 50 μL of 200 μM Substrate. Include a Substrate Blank containing 50 μL of Assay Buffer and 50 μL of 200 μM Substrate.
- Read at excitation and emission wavelengths of 380 nm and 460 nm, respectively, in kinetic mode for 5 minutes.
- Calculate specific activity:
Specific Activity (pmol/min/µg) = | Adjusted Vmax* (RFU/min) x Conversion Factor** (pmol/RFU) |
| amount of enzyme (µg) |
*Adjusted for Substrate Blank
- rhCD26: 0.005 μg
- Substrate: 100 μM
Scientific Data
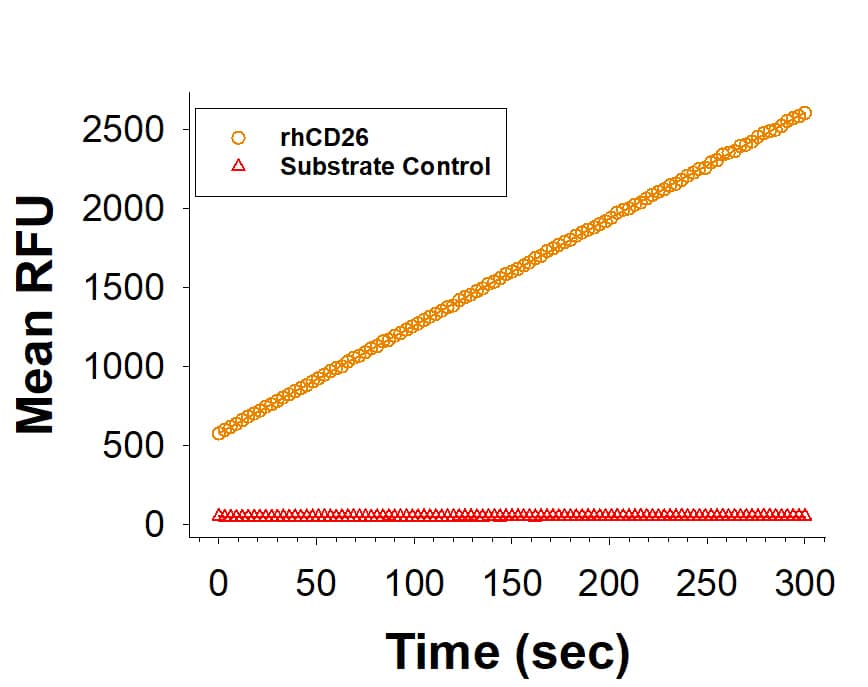 View Larger
View Larger
Recombinant Human DPPIV/CD26 His-tag Protein (Catalog # 11244-SE) is measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate, Gly-Pro-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin (GP-AMC).
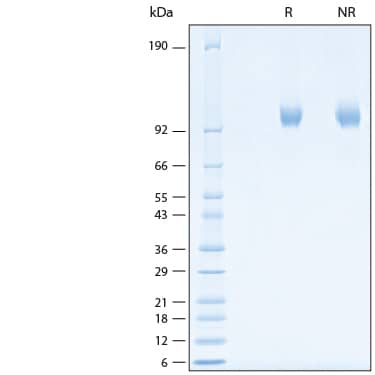 View Larger
View Larger
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human DPPIV/CD26 His-tag Protein (Catalog # 11244-SE) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 96-108 kDa.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: DPPIV/CD26
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPPIV, also known as CD26) is an approximately 110 kDa serine exopeptidase that releases Xaa-Pro or Xaa-Ala dipeptides from the N‑terminus of oligo- and polypeptides. Mature human DPPIV consists of a 6 amino acid (aa) cytoplasmic tail, a 22 aa transmembrane segment, and a 738 aa extracellular domain (ECD) that contains the catalytic active site (1). DPPIV is expressed as a noncovalent homodimer on the surface of epithelial cells, endothelial cells, and activated lymphocytes, and it can be released by MMP mediated shedding (2). It regulates immune and endocrine function through the cleavage of multiple chemokines, growth factors, and peptide hormones (3,4). It cleaves a range of peptide hormones including Glucagon, Glucagon-like Peptides 1 and 2, GIP, GHRH, Procalcitonin, Neuropeptide Y, and Substance P (5). It is released from adipocytes and induces insulin resistance in adipocytes and skeletal muscle (6). DPPIV also cleaves many chemokines, resulting in altered chemotactic activity (7-10) or impacting chemokine blockade of HIV-1 cellular infectivity depending on the chemokine target (7,9,11). It cleaves human GM-CSF and IL-3 and reduces their ability to promote myeloid cell development (12). In addition to enzymatic cleavage functions, DPPIV interacts with adenosine deaminase on T cells and with caveolin-1 on antigen presenting cells (13), provides costimulatory proliferation and activation signals to both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (13,14), and serves as a cell entry coreceptor for HIV and coronavirus MERS-CoV-2 (15,16). DPPIV inhibitors are approved for therapeutic treatment in type 2 diabetes (17) and are being explored for treatment of several additional conditions including autoimmune diseases (18).
- Tanaka, T. et al. (1992) J. Immunol. 149:481.
- Rohrborn, D. et al. (2014) FEBS Lett. 588:3870.
- Klemann, C. et al. (2016) Clin. Exp. Immunol. 185:1.
- Mortier, A. et al. (2016) J. Leukoc. Biol. 99:955.
- Waumans, Y. et al. (2015) Front. Immunol. 6:387.
- Lamers, D. et al. (2011) Diabetes 60:1917.
- Proost, P. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273:7222.
- Proost, P. et al. (2001) Blood 98:3554.
- Ohtsuki, T. et al. (1998) FEBS Lett. 431:236.
- Barreira da Silva, R. et al. (2015) Nat. Immunol. 16:850.
- Guan, E. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:32348.
- Broxmeyer, H.E. et al. (2012) Nat. Med. 18:1786.
- Ohnuma, K. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:10117.
- Hatano, R. et al. (2013) Immunology 138:165.
- Callebaut, C. et al. (1993) Science 262:2045.
- Raj, V.S. et al. (2013) Nature 495:251.
- Makrilakis, K. (2019) Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16:2720.
- Huang, J. et al. (2022) Front. Immunol. 13:830863.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human DPPIV/CD26 His-tag Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Human DPPIV/CD26 His-tag Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Human DPPIV/CD26 His-tag Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
