Recombinant Human IFN-alpha/beta R1 Fc Avi-tag Protein, CF
Recombinant Human IFN-alpha/beta R1 Fc Avi-tag Protein, CF Summary
- R&D Systems CHO-derived Recombinant Human IFN-alpha/beta R1 Fc Avi-tag Protein (AVI11574)
- Quality control testing to verify active proteins with lot specific assays by in-house scientists
- All R&D Systems proteins are covered with a 100% guarantee
Product Specifications
| Human IFN-A/B R1 (Gly26-Lys436) Accession # AAA52730.1 | GGIEGRMD | Human IgG1 Fc (Pro100-Lys330) | Avi-tag |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | ||
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
AVI11574
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
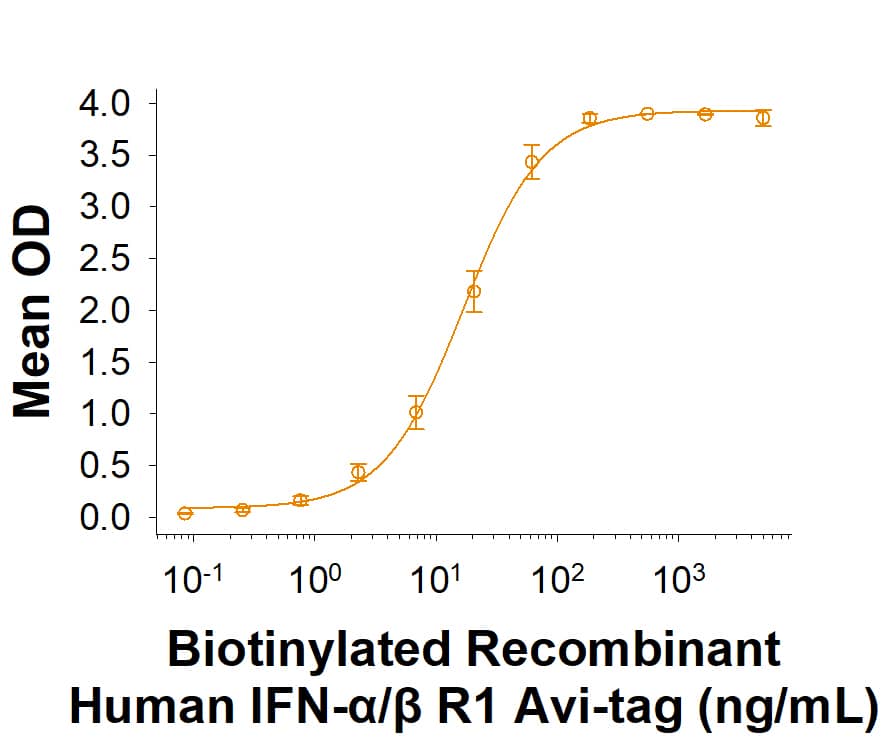 View Larger
View Larger
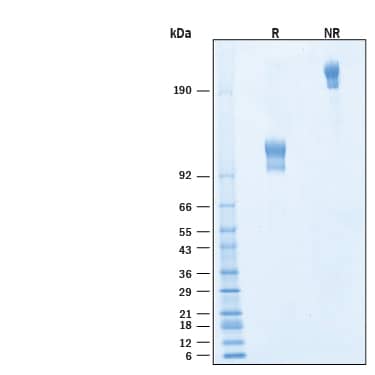 View Larger
View Larger
2 μg/lane of Biotinylated Recombinant Human IFN‑ alpha / beta R1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein (Catalog # AVI11574) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 95-125 kDa and 190-250 kDa, respectively.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: IFN-alpha/beta R1
Interferon‑alpha/beta receptor 1 (IFN‑ alpha / beta R1), also known as IFNAR1, is a 100‑130 kDa member of the class II cytokine receptor family of proteins. These proteins form heterodimeric receptor complexes that mediate class II cytokine signals. Subunits of the different receptor complexes are shared and serve multiple functions (1). IFN‑ alpha / beta R1, in association with IFN‑ alpha / beta R2, is required for propagating anti‑microbial signal transduction triggered by the type 1 interferons such as IFN‑ alpha and IFN‑ beta (2, 3). Mature human IFN‑ alpha / beta R1 consists of a 409 aa extracellular domain (ECD), a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 100 aa cytoplasmic domain (4). The ECD contains three tandem fibronectin type III repeats and is extensively glycosylated. Within the ECD, human IFN‑ alpha / beta R1 shares 47% and 50% aa identity with mouse and rat IFN‑ alpha / beta R1, respectively. Alternative splicing generates two additional isoforms that lack the transmembrane segment and either all or a portion of the cytoplasmic domain. IFN‑ alpha / beta R1 interacts very weakly or not at all with type 1 interferons and does not stably interact with IFN‑ alpha / beta R2. Ligands preferentially associate with IFN‑ alpha / beta R2, and this complex subsequently forms a stable ternary assembly with IFN‑ alpha / beta R1 (5‑7). IFN‑ alpha / beta R1 also associates with IFN‑ gamma R2 even in the absence of IFN‑ gamma stimulation (3). IFN‑ alpha / beta R1 activation depends on tyrosine phoshorylation as well as palmitoylation of its cytoplasmic domain (8, 9). Rapid down‑regulation of the receptor is accomplished by ligand‑dependent or ‑independent pathways (e.g. VEGF R signaling, TLR signaling, or cellular stress) which induce its serine phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and degradation (10‑13). Our Avi-tag Biotinylated human IFN‑ alpha / beta R1 features biotinylation at a single site contained within the Avi-tag, a unique 15 amino acid peptide. Protein orientation will be uniform when bound to streptavidin-coated surface due to the precise control of biotinylation and the rest of the protein is unchanged so there is no interference in the protein's bioactivity.
- Langer, J.A. et al. (2004) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:33.
- Hwang, S.Y. et al. (1995) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:11284.
- Takaoka, A. et al. (2000) Science 288:2357.
- Uze, G. et al. (1990) Cell 60:225.
- Lamken, P. et al. (2004) J. Mol. Biol. 341:303.
- Arduini, R.M. et al. (1999) Prot. Sci. 8:1867.
- Kalie, E. et al. (2008) J. Biol. Chem. 283:32925.
- Platanias, L.C. (2005) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5:375.
- Claudinon, J. et al. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284:24328.
- Zheng, H. et al. (2011) Blood 118:4003.
- Qian, J. et al. (2011) PLoS Pathogens 7:e1002065.
- Bhattacharya, S. et al. (2010) J. Biol. Chem. 285:2318.
- Bhattacharya, S. et al. (2011) J. Biol. Chem. 286:22069.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human IFN-alpha/beta R1 Fc Avi-tag Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Human IFN-alpha/beta R1 Fc Avi-tag Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Human IFN-alpha/beta R1 Fc Avi-tag Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image

