IL-31 Signaling Pathways
Click on the other IL-6 family cytokines listed below to see the signaling pathways that are activated by each cytokine. Refer to the table below each pathway to see a select list of cytokine-expressing cells or tissues and the primary biological effects induced by the different members of the IL-6 cytokine family.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Cell Proliferation
Cell Proliferation
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
(Unknown)
(Unknown)
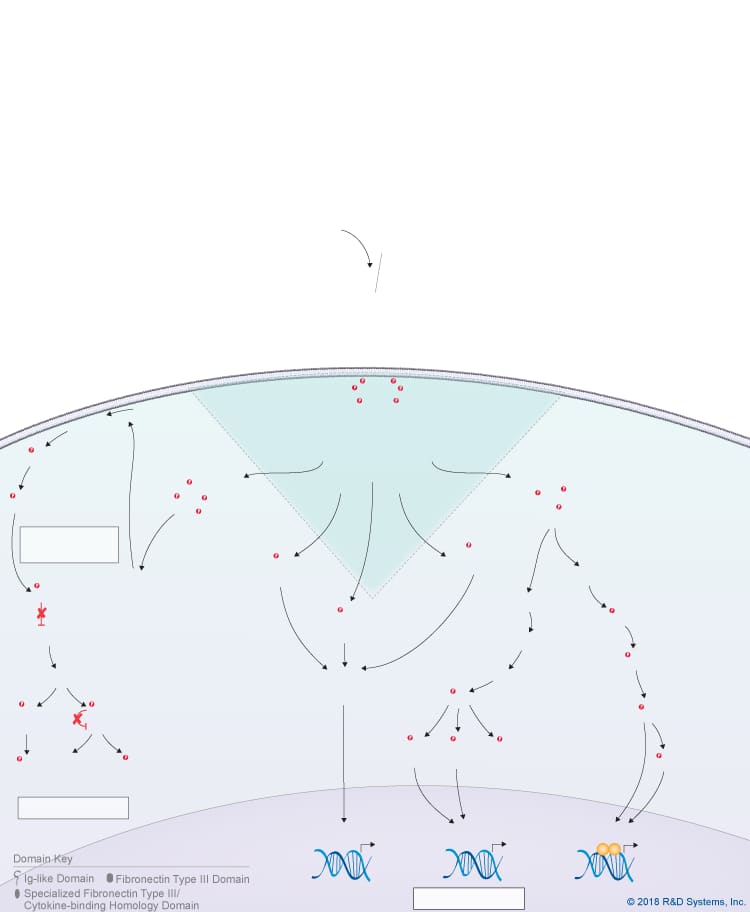
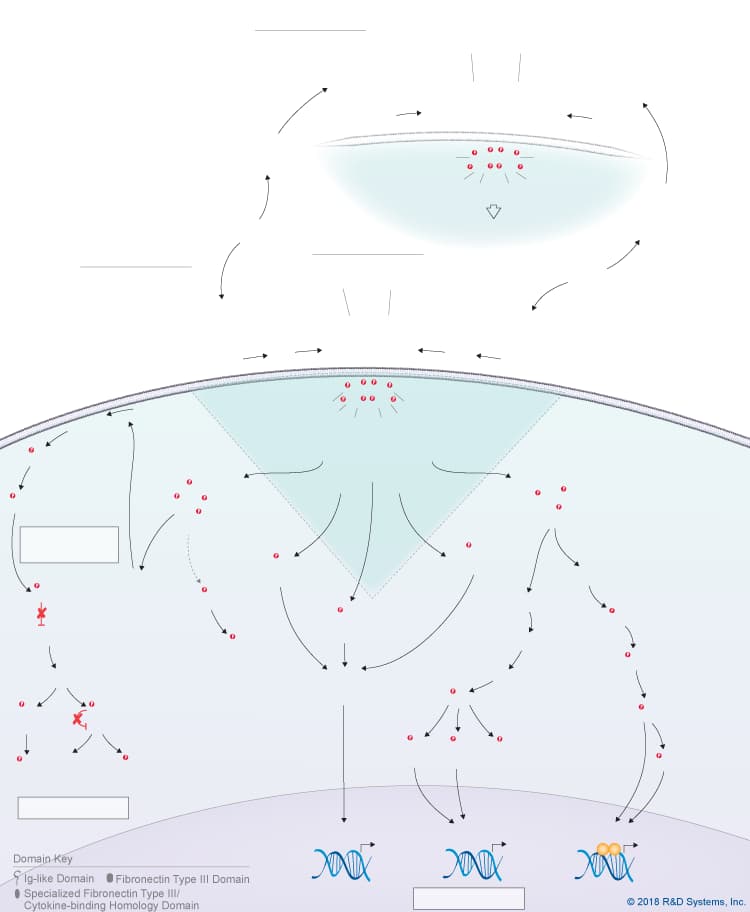
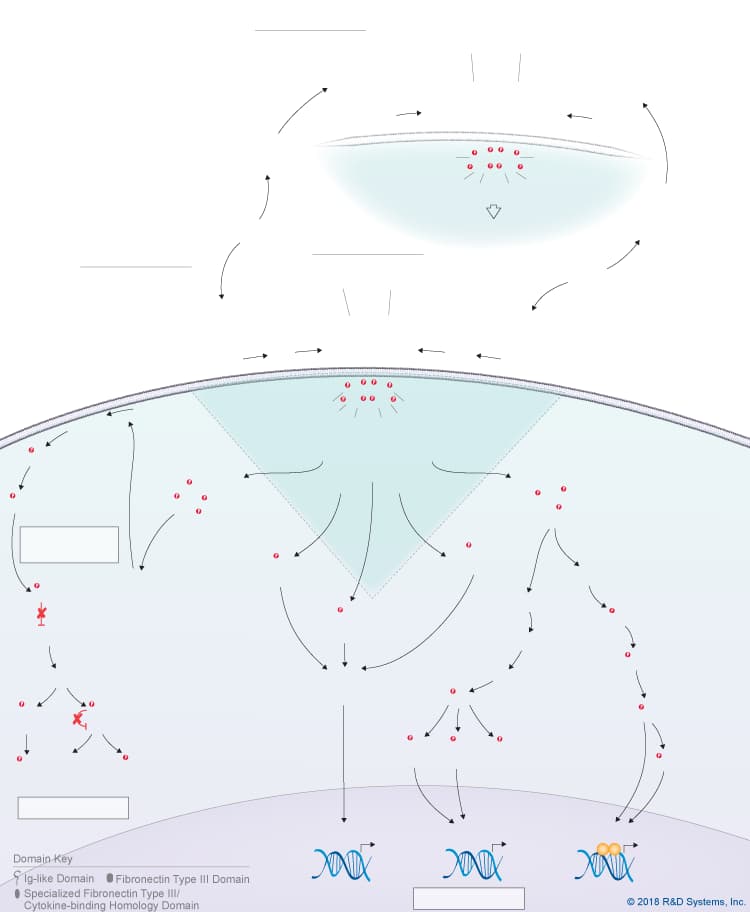
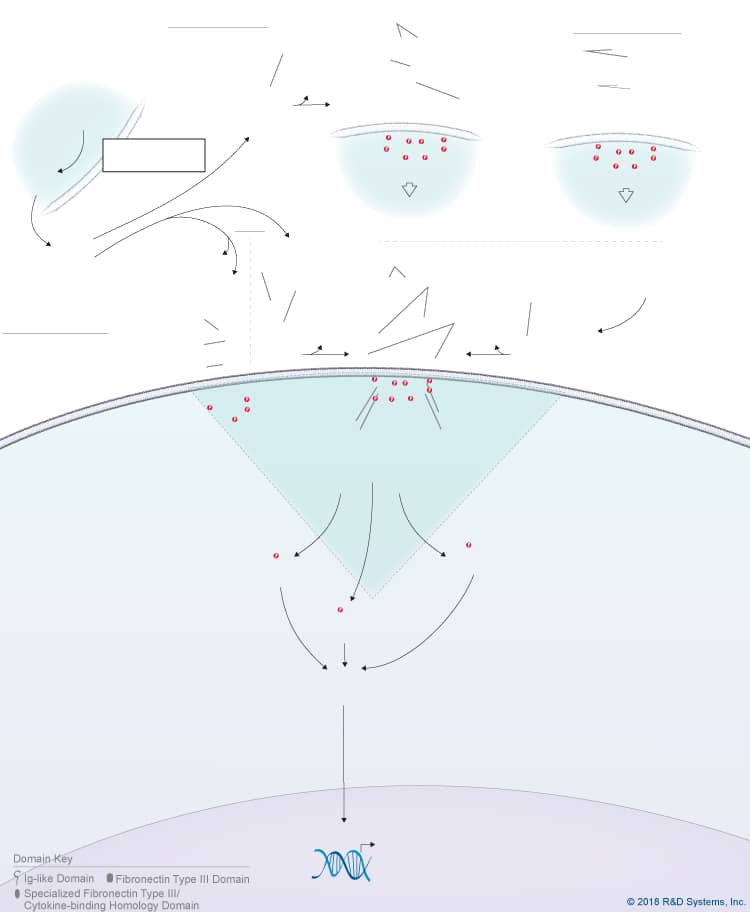
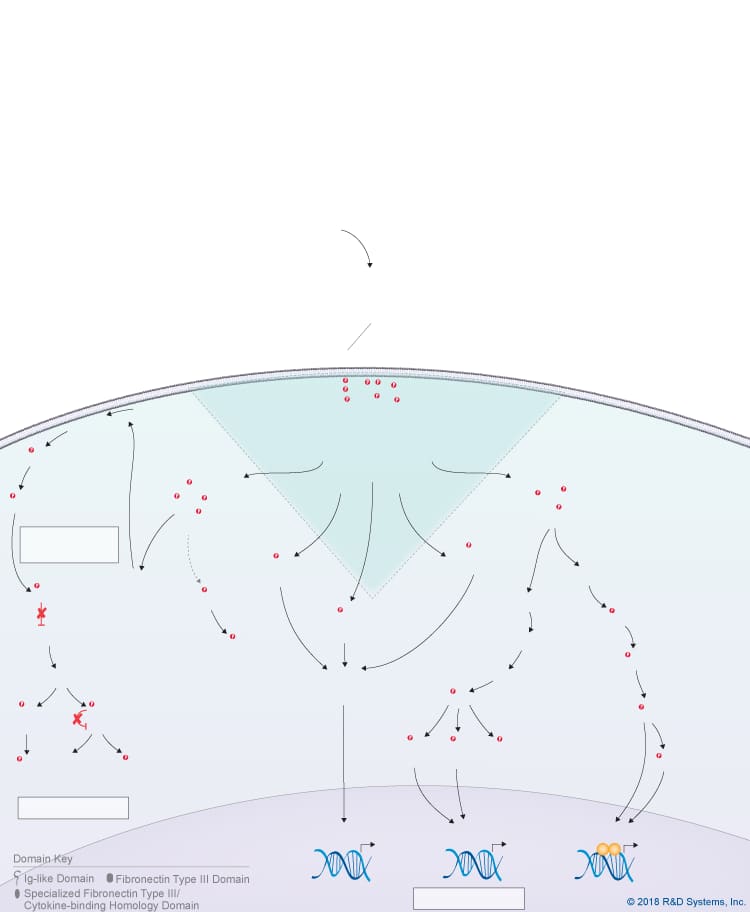
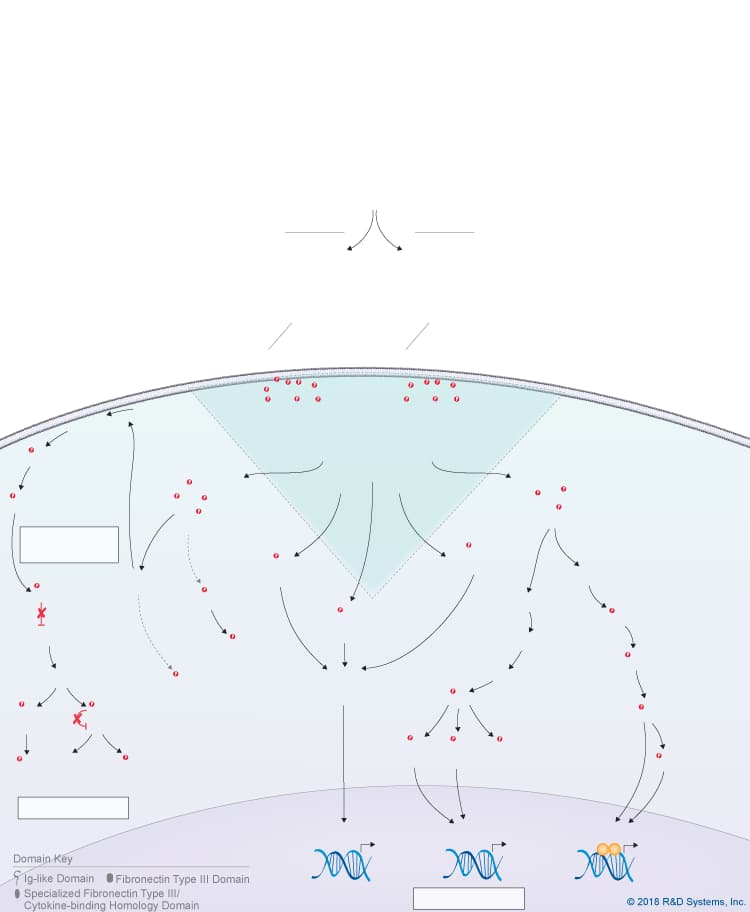
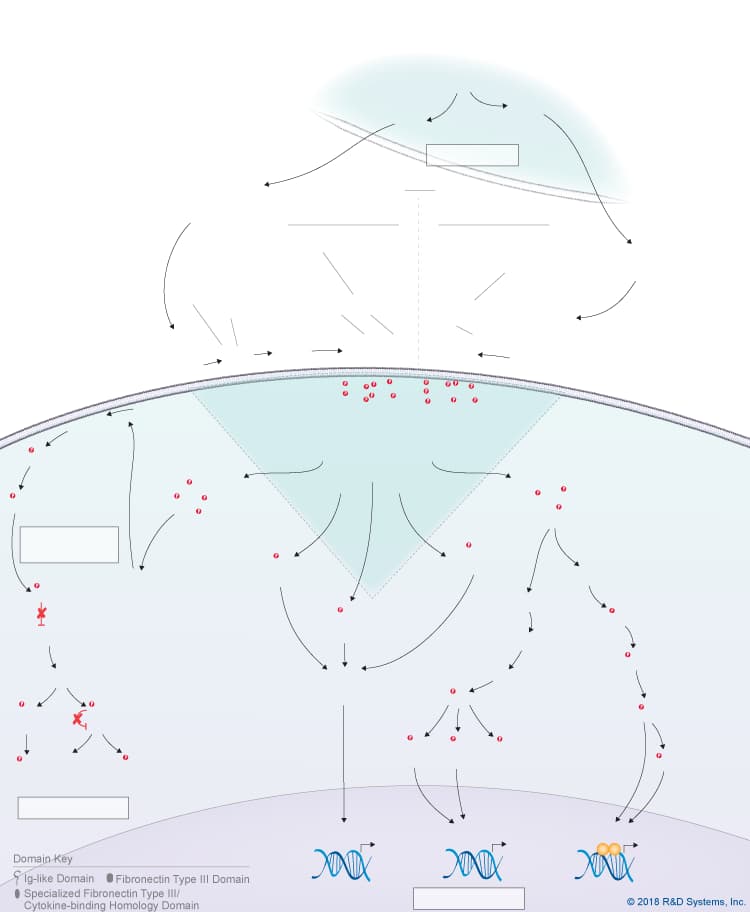
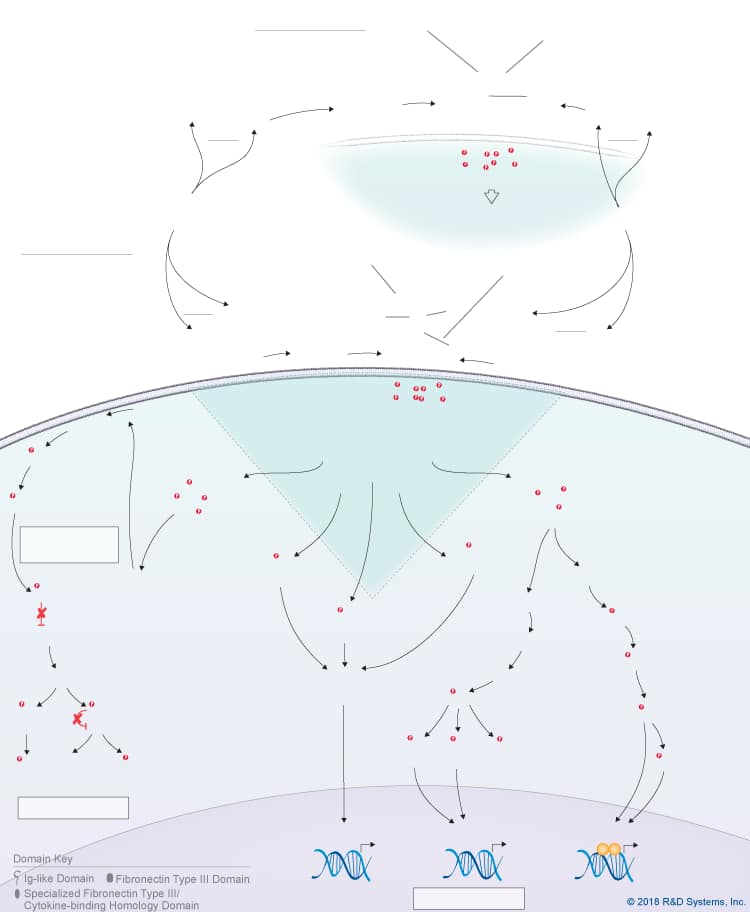
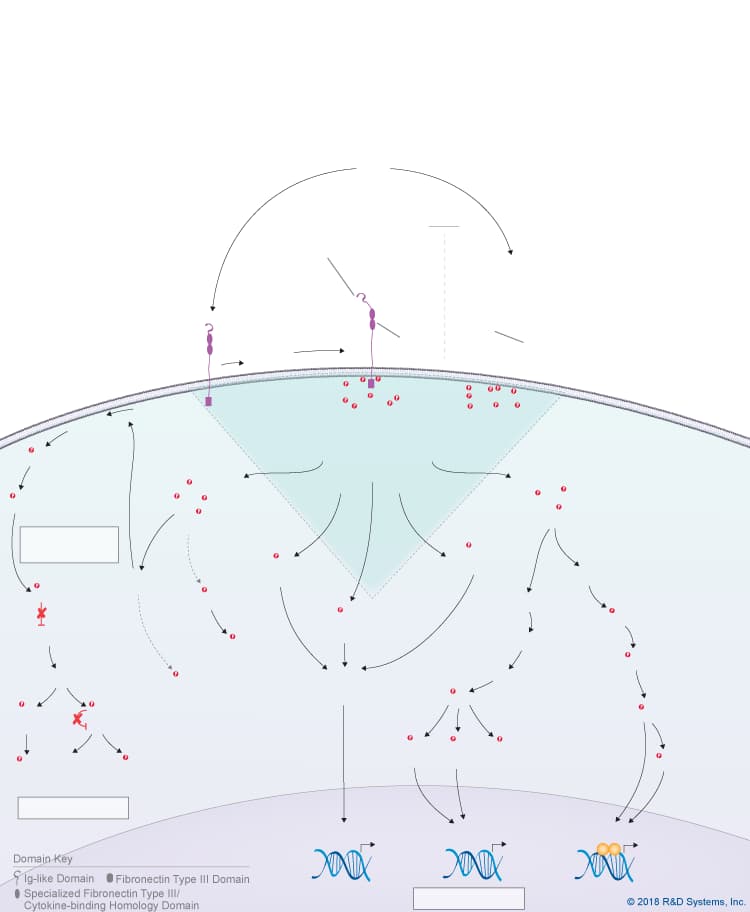
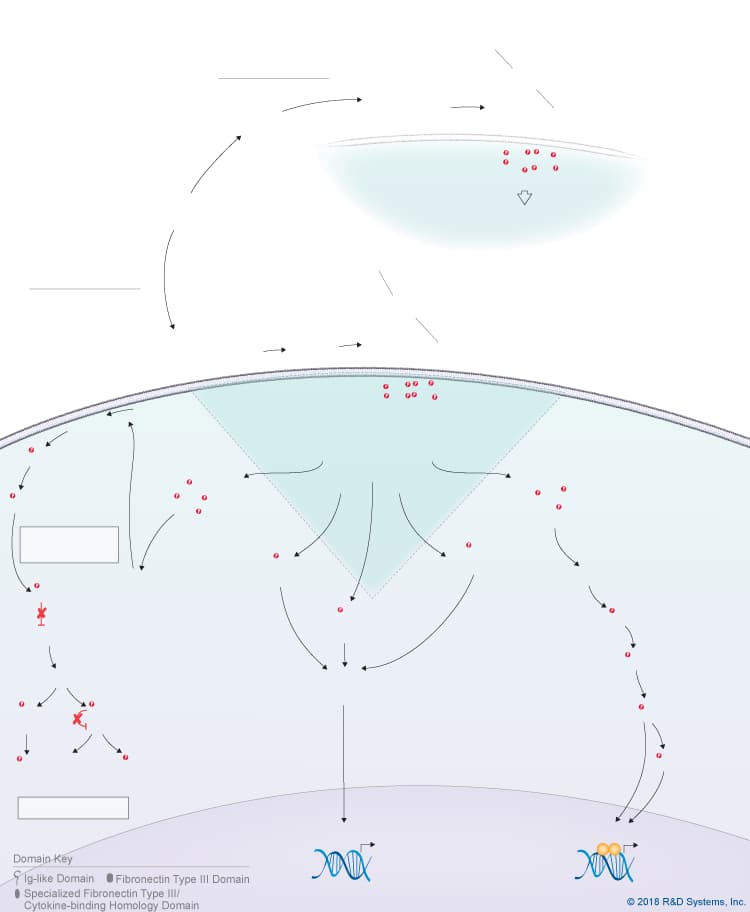
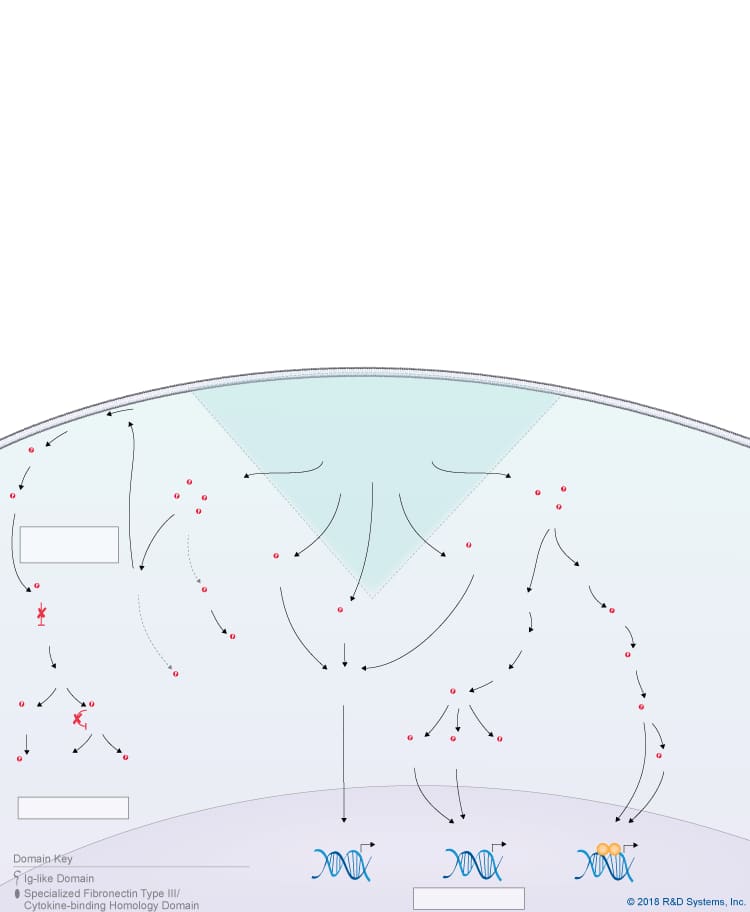
Overview of IL-31 Signaling Pathways
IL-31 is a member of the IL-6 cytokine family, which also includes IL-6, IL-11, IL-27 p28/IL-30, Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), Oncostatin M (OSM), Cardiotrophin-like cytokine (CLC), Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), Cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1), and Neuropoietin. Like other IL-6 family cytokines, IL-31 forms an anti-parallel four-helix bundle structure with up-up-down-down topology, but rather than containing four long chain alpha helices, IL-31 is unique in that it contains two long and two short chain alpha helices. Additionally, IL-31 signals through a heterodimeric receptor complex that does not contain the gp130 signal-transducing subunit, but instead consists of the gp130-like receptor, IL-31 receptor alpha (IL-31 RA), coupled with OSM R beta, which is also part of the type II Oncostatin M (OSM) receptor. Although IL-31 RA and OSM R beta form a complex, IL-31 initially binds to IL-31 RA and then to OSM R beta to form a high affinity receptor complex. Members of the Jak family of tyrosine kinases associate with the cytoplasmic domains of both IL-31 RA and OSM R beta, leading to the phosphorylation of STAT family proteins, predominantly STAT3, STAT5, and to a lesser extent, STAT1. In addition, IL-31 triggers the activation of the Ras-MAPK pathway, the PI 3-K-Akt pathway, and the p38 and JNK MAPK pathways, which are all thought to be activated through the OSM R beta receptor subunit. IL-31 is produced by multiple cell types including activated Th2 cells, CD8+ T cells, skin-homing memory T cells, monocytes, macrophages, monocyte-derived dendritic cells, mast cells, keratinocytes, and dermal fibroblasts. High levels of IL-31 have been found in pruritic skin disorders, allergic asthma, and inflammatory bowel diseases, suggesting that it may be involved in the pathogenesis of these diseases. As a result, IL-31 is being investigated as a potential novel therapeutic target in pruritic skin disorders and may also serve as a target in other chronic inflammatory disorders. IL-31 has been shown to have chemokine-inducing activity and is thought to represent a possible link between the immune and sensory nervous systems. Additionally, it has been suggested to be involved in regulating the homeostasis of hematopoietic progenitor cells, as well as the proliferation and differentiation of non-hematopoietic cells.
To learn more, please visit our IL-6 Family Research Area page.
| Primary IL-31-Expressing Cells/Tissues | Primary Biological Effects of IL-31 |
| Activated Th2 cells | Regulates hematopoietic progenitor cell homeostasis |
| Basophils | Associated with inflammation in the skin, lung, and gut |
| CD8+ T cells | Regulates immune responses in the skin; Involved in the development of inflammatory itch |
| Dendritic cells | Implicated in the pathogenesis of pruritis, alopecia, cutaneous allergic diseases, and atopic dermatitis, and may also contribute to the development of allergic asthma and rhinitis, inflammatory bowel disease, and hematopoietic and lymphoid tissue cancers |
| Eosinophils | Has chemokine-inducing activity |
| Fibroblasts | Suggested to be involved in regulating the proliferation and differentiation of non-hematopoietic cells |
| Keratinocytes | May represent a link between the immune and sensory nervous systems |
| Mast cells | |
| Monocytes/macrophages | |
| Skin-homing memory T cells |
Get Print Copy of this Pathway