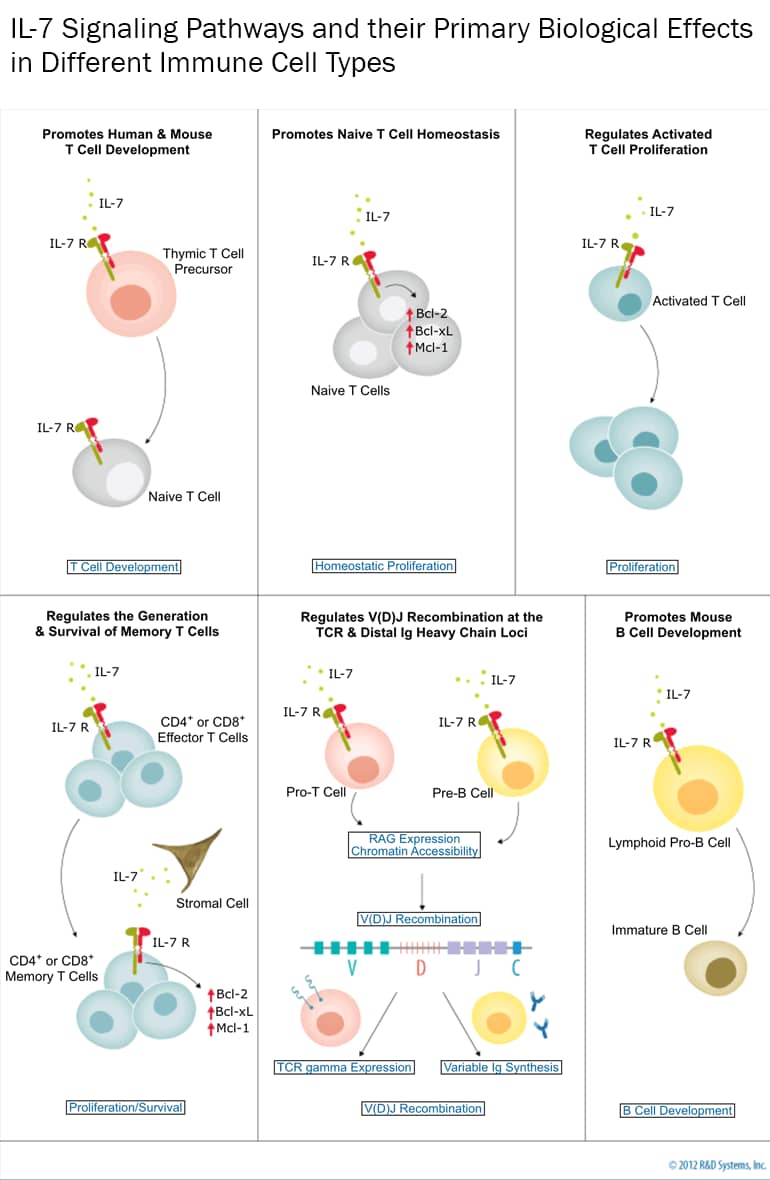
IL-7 Signaling Pathways and their Primary Biological Effects in Different Immune Cell Types
Click on one of the buttons below to see either the IL-7 signaling pathways or information related to one of the other common cytokine receptor gamma-chain family members.
T Cell Development
T Cell Development
Precursor
Precursor
T Cell Development
T Cell Development
Homeostatic Proliferation
Homeostatic Proliferation
T Cell Proliferation
T Cell Proliferation
Proliferation
Proliferation
& Survival of Memory T Cells
& Survival of Memory T Cells
Effector T Cells
Effector T Cells
Memory T Cells
Memory T Cells
Proliferation/Survival
Proliferation/Survival
TCR & Distal Ig Heavy Chain Loci
TCR & Distal Ig Heavy Chain Loci
RAG Expression
Chromatin Accessibility
RAG Expression
Chromatin Accessibility
V(D)J Recombination
V(D)J Recombination
TCR gamma Expression
TCR gamma Expression
Variable Ig Synthesis
Variable Ig Synthesis
V(D)J Recombination
V(D)J Recombination
B Cell Development
B Cell Development
B Cell Development
B Cell Development
Overview of IL-7 Signaling and its Primary Biological Effects in Different Immune Cell Types
Interleukin-7 (IL-7) is a type I glycoprotein that is predicted to form a four alpha-helix structure with a hydrophobic core. It is produced primarily by stromal cells and exerts its effects through a receptor complex consisting of IL-7 R alpha and common gamma-chain/IL-2 R gamma. IL-7 signaling is essential for the establishment and maintenance of normal immune system functions. It is required for mouse and human T cell development and homeostatic proliferation, mouse B cell development, and the generation of CD4+ and CD8+ memory T cells. IL-7 R alpha-deficient mice have reduced numbers of thymocytes, impaired T cell and B cell development, and lack gamma delta T cells, a small subset of T cells found in epithelium-rich tissues. The requirement of IL-7 for T cell survival has been partially attributed to its ability to induce expression of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1 proteins. In addition, IL-7 plays a role in regulating V(D)J recombination at the TCR gamma, TCR beta, and immunoglobulin heavy chain loci.
To learn more, please visit our Common gamma Chain Receptor Family Research Area.
Get Print Copy of this Pathway
View IL-7 Signaling Pathways and their Primary Biological Effects in Different Immune Cell Types Image