Type I Interferon Signaling Pathways
Click on the links shown in the Explore Pathways box below to see the signaling pathways that are activated by members of either the type II or type III interferon families.
Protein Synthesis
Protein Synthesis
Processing/Presentation Signals
Processing/Presentation Signals
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Growth
Inhibition
Growth
Inhibition
Heterodimers
Heterodimers
or CrkL-STAT5
or CrkL-STAT5
Inflammatory Response
Inflammatory Response
ISRE
ISRE
GAS
GAS
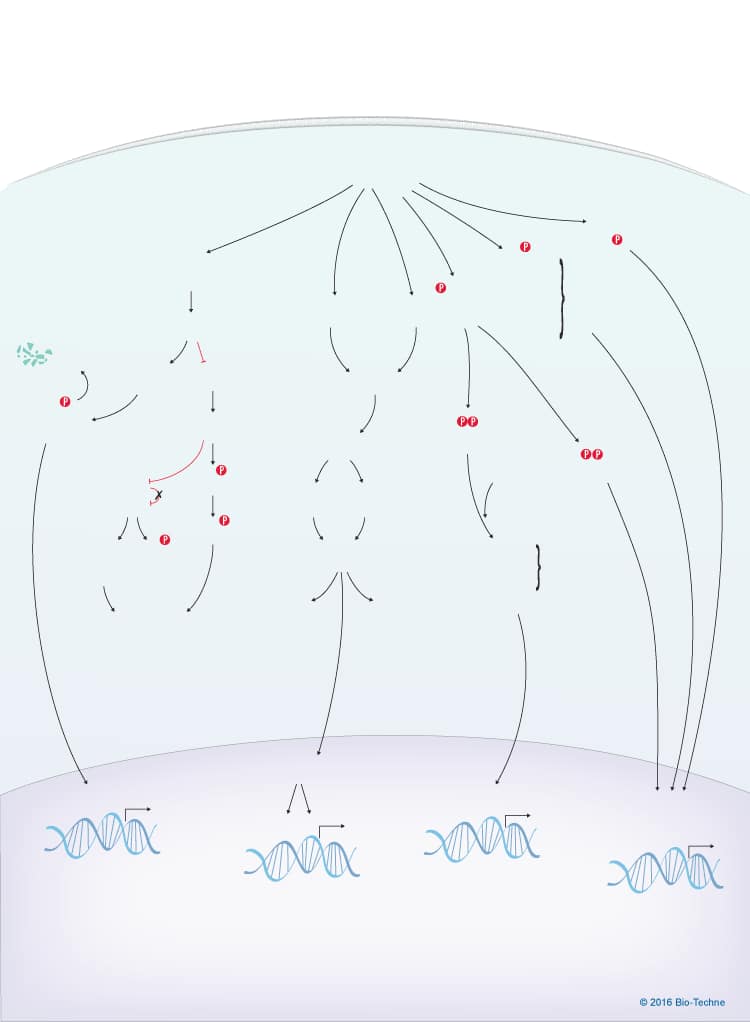
Overview of Type I Interferon Signaling Pathways
Type I IFNs are produced following recognition of microbial products by cell surface and intracellular pattern recognition receptors. The type I interferon (IFN) family consists of multiple IFN-alpha subtypes, IFN-beta, IFN-delta, IFN-epsilon, IFN-kappa, IFN-tau, IFN-omega, and IFN-zeta/Limitin. IFN-alpha, IFN-beta, IFN-epsilon, IFN-kappa, and IFN-omega are all found in humans, while IFN-delta, IFN-tau, and IFN-zeta have only been described in pigs, cattle, and mice, respectively. No human homologues of these three type I interferon subclasses have been identified. All type I interferons have significant structural homology and bind to a common heterodimeric receptor consisting of the IFN-alpha/beta RI and IFN-alpha/beta R2 subunits, which are expressed on most cell types. Receptor engagement activates the IFN-alpha/beta R1-associated Tyk2 protein tyrosine kinase and the IFN-alpha/beta R2-associated Jak1 protein tyrosine kinase. These kinases subsequently regulate the phosphorylation and activation of different STAT proteins. Activated STAT proteins homo- or heterodimerize and translocate to the nucleus, where they promote the expression of numerous target genes. In addition, type I IFNs activate the MAPK, PI 3-K-Akt, and NF-kappa B signaling pathways. One transcriptional complex that is formed following stimulation by type I IFNs is the IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 (ISGF3) complex. This complex consists of phosphorylated STAT1, STAT2, and IRF9 and binds to IFN-stimulated response elements (ISREs) found in the promoters of numerous IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs). Other STAT homo- or heterodimers induced by type I IFNs bind to regulatory sequences in the promoters of target genes known as IFN-gamma-activated sequence (GAS) sites. Binding of STAT proteins to either ISREs or GAS sites regulates the expression of several hundred ISGs, which mediate the anti-viral, anti-proliferative, and apoptotic effects of type I IFNs.
To learn more, please visit our Interferons Research Area page
Immunoassays for Type 1 IFN Research
See how R&D Systems Type 1 IFN ELISA kits compare to the competition. Find out how you can move seamlessly from one immunoassay platform to the next as your needs change.
Get Print Copy of this Pathway



